Wentong Li
VisionTrim: Unified Vision Token Compression for Training-Free MLLM Acceleration
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) suffer from high computational costs due to excessive visual tokens, particularly in high-resolution and video-based scenarios. Existing token reduction methods typically focus on isolated pipeline components and often neglect textual alignment, leading to performance degradation. In this paper, we propose VisionTrim, a unified framework for training-free MLLM acceleration, integrating two effective plug-and-play modules: 1) the Dominant Vision Token Selection (DVTS) module, which preserves essential visual tokens via a global-local view, and 2) the Text-Guided Vision Complement (TGVC) module, which facilitates context-aware token merging guided by textual cues. Extensive experiments across diverse image and video multimodal benchmarks demonstrate the performance superiority of our VisionTrim, advancing practical MLLM deployment in real-world applications. The code is available at: https://github.com/hanxunyu/VisionTrim.
Forging Spatial Intelligence: A Roadmap of Multi-Modal Data Pre-Training for Autonomous Systems
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of autonomous systems, including self-driving vehicles and drones, has intensified the need to forge true Spatial Intelligence from multi-modal onboard sensor data. While foundation models excel in single-modal contexts, integrating their capabilities across diverse sensors like cameras and LiDAR to create a unified understanding remains a formidable challenge. This paper presents a comprehensive framework for multi-modal pre-training, identifying the core set of techniques driving progress toward this goal. We dissect the interplay between foundational sensor characteristics and learning strategies, evaluating the role of platform-specific datasets in enabling these advancements. Our central contribution is the formulation of a unified taxonomy for pre-training paradigms: ranging from single-modality baselines to sophisticated unified frameworks that learn holistic representations for advanced tasks like 3D object detection and semantic occupancy prediction. Furthermore, we investigate the integration of textual inputs and occupancy representations to facilitate open-world perception and planning. Finally, we identify critical bottlenecks, such as computational efficiency and model scalability, and propose a roadmap toward general-purpose multi-modal foundation models capable of achieving robust Spatial Intelligence for real-world deployment.
Tailored Teaching with Balanced Difficulty: Elevating Reasoning in Multimodal Chain-of-Thought via Prompt Curriculum
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:The effectiveness of Multimodal Chain-of-Thought (MCoT) prompting is often limited by the use of randomly or manually selected examples. These examples fail to account for both model-specific knowledge distributions and the intrinsic complexity of the tasks, resulting in suboptimal and unstable model performance. To address this, we propose a novel framework inspired by the pedagogical principle of "tailored teaching with balanced difficulty". We reframe prompt selection as a prompt curriculum design problem: constructing a well ordered set of training examples that align with the model's current capabilities. Our approach integrates two complementary signals: (1) model-perceived difficulty, quantified through prediction disagreement in an active learning setup, capturing what the model itself finds challenging; and (2) intrinsic sample complexity, which measures the inherent difficulty of each question-image pair independently of any model. By jointly analyzing these signals, we develop a difficulty-balanced sampling strategy that ensures the selected prompt examples are diverse across both dimensions. Extensive experiments conducted on five challenging benchmarks and multiple popular Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) demonstrate that our method yields substantial and consistent improvements and greatly reduces performance discrepancies caused by random sampling, providing a principled and robust approach for enhancing multimodal reasoning.
EOC-Bench: Can MLLMs Identify, Recall, and Forecast Objects in an Egocentric World?
Jun 05, 2025



Abstract:The emergence of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) has driven breakthroughs in egocentric vision applications. These applications necessitate persistent, context-aware understanding of objects, as users interact with tools in dynamic and cluttered environments. However, existing embodied benchmarks primarily focus on static scene exploration, emphasizing object's appearance and spatial attributes while neglecting the assessment of dynamic changes arising from users' interactions. To address this gap, we introduce EOC-Bench, an innovative benchmark designed to systematically evaluate object-centric embodied cognition in dynamic egocentric scenarios. Specially, EOC-Bench features 3,277 meticulously annotated QA pairs categorized into three temporal categories: Past, Present, and Future, covering 11 fine-grained evaluation dimensions and 3 visual object referencing types. To ensure thorough assessment, we develop a mixed-format human-in-the-loop annotation framework with four types of questions and design a novel multi-scale temporal accuracy metric for open-ended temporal evaluation. Based on EOC-Bench, we conduct comprehensive evaluations of various proprietary, open-source, and object-level MLLMs. EOC-Bench serves as a crucial tool for advancing the embodied object cognitive capabilities of MLLMs, establishing a robust foundation for developing reliable core models for embodied systems.
PointLoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation with Token Selection for Point Cloud Learning
Apr 22, 2025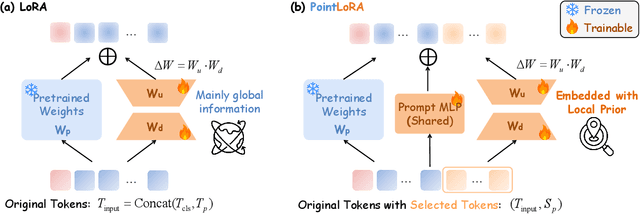
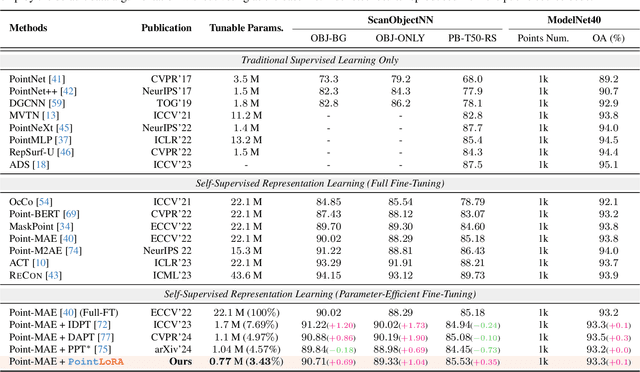
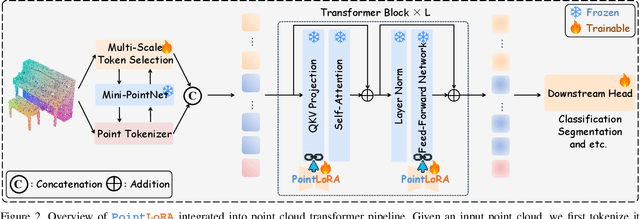
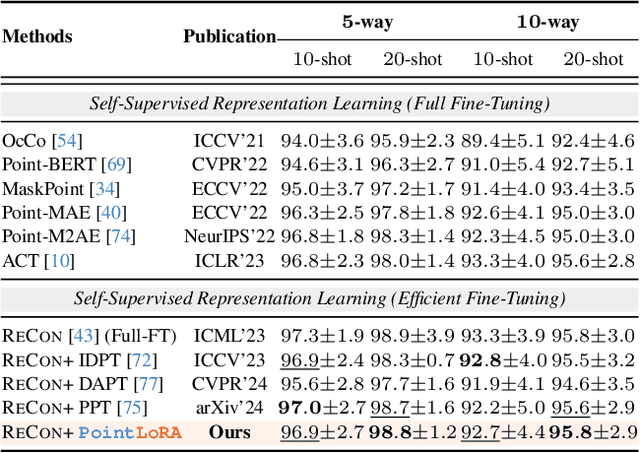
Abstract:Self-supervised representation learning for point cloud has demonstrated effectiveness in improving pre-trained model performance across diverse tasks. However, as pre-trained models grow in complexity, fully fine-tuning them for downstream applications demands substantial computational and storage resources. Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methods offer a promising solution to mitigate these resource requirements, yet most current approaches rely on complex adapter and prompt mechanisms that increase tunable parameters. In this paper, we propose PointLoRA, a simple yet effective method that combines low-rank adaptation (LoRA) with multi-scale token selection to efficiently fine-tune point cloud models. Our approach embeds LoRA layers within the most parameter-intensive components of point cloud transformers, reducing the need for tunable parameters while enhancing global feature capture. Additionally, multi-scale token selection extracts critical local information to serve as prompts for downstream fine-tuning, effectively complementing the global context captured by LoRA. The experimental results across various pre-trained models and three challenging public datasets demonstrate that our approach achieves competitive performance with only 3.43% of the trainable parameters, making it highly effective for resource-constrained applications. Source code is available at: https://github.com/songw-zju/PointLoRA.
OrderChain: A General Prompting Paradigm to Improve Ordinal Understanding Ability of MLLM
Apr 07, 2025Abstract:Despite the remarkable progress of multimodal large language models (MLLMs), they continue to face challenges in achieving competitive performance on ordinal regression (OR; a.k.a. ordinal classification). To address this issue, this paper presents OrderChain, a novel and general prompting paradigm that improves the ordinal understanding ability of MLLMs by specificity and commonality modeling. Specifically, our OrderChain consists of a set of task-aware prompts to facilitate the specificity modeling of diverse OR tasks and a new range optimization Chain-of-Thought (RO-CoT), which learns a commonality way of thinking about OR tasks by uniformly decomposing them into multiple small-range optimization subtasks. Further, we propose a category recursive division (CRD) method to generate instruction candidate category prompts to support RO-CoT automatic optimization. Comprehensive experiments show that a Large Language and Vision Assistant (LLaVA) model with our OrderChain improves baseline LLaVA significantly on diverse OR datasets, e.g., from 47.5% to 93.2% accuracy on the Adience dataset for age estimation, and from 30.0% to 85.7% accuracy on the Diabetic Retinopathy dataset. Notably, LLaVA with our OrderChain also remarkably outperforms state-of-the-art methods by 27% on accuracy and 0.24 on MAE on the Adience dataset. To our best knowledge, our OrderChain is the first work that augments MLLMs for OR tasks, and the effectiveness is witnessed across a spectrum of OR datasets.
Uncertainty-Instructed Structure Injection for Generalizable HD Map Construction
Mar 29, 2025Abstract:Reliable high-definition (HD) map construction is crucial for the driving safety of autonomous vehicles. Although recent studies demonstrate improved performance, their generalization capability across unfamiliar driving scenes remains unexplored. To tackle this issue, we propose UIGenMap, an uncertainty-instructed structure injection approach for generalizable HD map vectorization, which concerns the uncertainty resampling in statistical distribution and employs explicit instance features to reduce excessive reliance on training data. Specifically, we introduce the perspective-view (PV) detection branch to obtain explicit structural features, in which the uncertainty-aware decoder is designed to dynamically sample probability distributions considering the difference in scenes. With probabilistic embedding and selection, UI2DPrompt is proposed to construct PV-learnable prompts. These PV prompts are integrated into the map decoder by designed hybrid injection to compensate for neglected instance structures. To ensure real-time inference, a lightweight Mimic Query Distillation is designed to learn from PV prompts, which can serve as an efficient alternative to the flow of PV branches. Extensive experiments on challenging geographically disjoint (geo-based) data splits demonstrate that our UIGenMap achieves superior performance, with +5.7 mAP improvement on the nuScenes dataset. Source code will be available at https://github.com/xiaolul2/UIGenMap.
VideoRefer Suite: Advancing Spatial-Temporal Object Understanding with Video LLM
Jan 08, 2025Abstract:Video Large Language Models (Video LLMs) have recently exhibited remarkable capabilities in general video understanding. However, they mainly focus on holistic comprehension and struggle with capturing fine-grained spatial and temporal details. Besides, the lack of high-quality object-level video instruction data and a comprehensive benchmark further hinders their advancements. To tackle these challenges, we introduce the VideoRefer Suite to empower Video LLM for finer-level spatial-temporal video understanding, i.e., enabling perception and reasoning on any objects throughout the video. Specially, we thoroughly develop VideoRefer Suite across three essential aspects: dataset, model, and benchmark. Firstly, we introduce a multi-agent data engine to meticulously curate a large-scale, high-quality object-level video instruction dataset, termed VideoRefer-700K. Next, we present the VideoRefer model, which equips a versatile spatial-temporal object encoder to capture precise regional and sequential representations. Finally, we meticulously create a VideoRefer-Bench to comprehensively assess the spatial-temporal understanding capability of a Video LLM, evaluating it across various aspects. Extensive experiments and analyses demonstrate that our VideoRefer model not only achieves promising performance on video referring benchmarks but also facilitates general video understanding capabilities.
Scalable Autoregressive Monocular Depth Estimation
Nov 18, 2024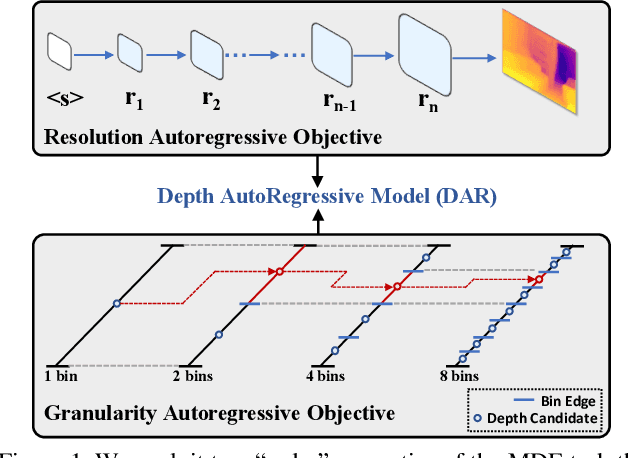
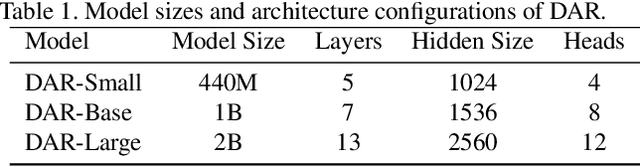
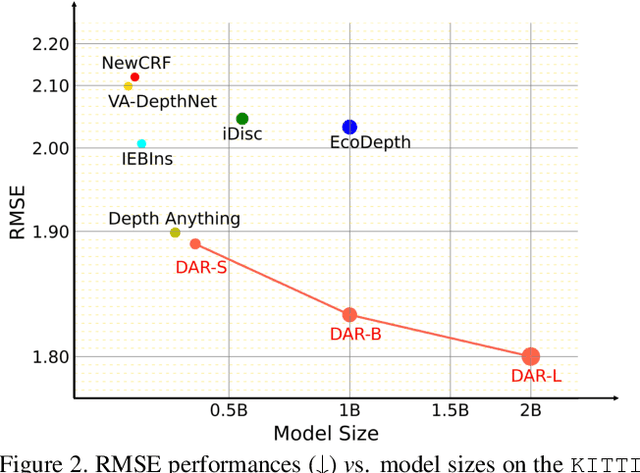
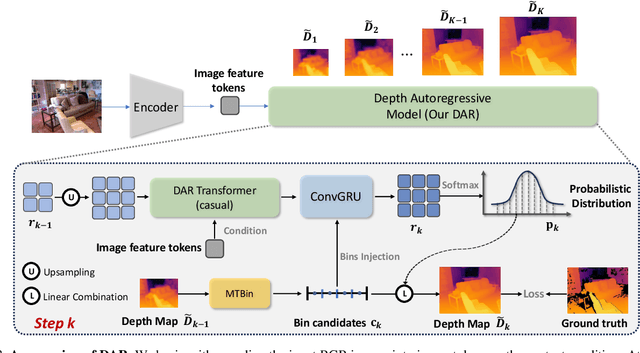
Abstract:This paper proposes a new autoregressive model as an effective and scalable monocular depth estimator. Our idea is simple: We tackle the monocular depth estimation (MDE) task with an autoregressive prediction paradigm, based on two core designs. First, our depth autoregressive model (DAR) treats the depth map of different resolutions as a set of tokens, and conducts the low-to-high resolution autoregressive objective with a patch-wise casual mask. Second, our DAR recursively discretizes the entire depth range into more compact intervals, and attains the coarse-to-fine granularity autoregressive objective in an ordinal-regression manner. By coupling these two autoregressive objectives, our DAR establishes new state-of-the-art (SOTA) on KITTI and NYU Depth v2 by clear margins. Further, our scalable approach allows us to scale the model up to 2.0B and achieve the best RMSE of 1.799 on the KITTI dataset (5% improvement) compared to 1.896 by the current SOTA (Depth Anything). DAR further showcases zero-shot generalization ability on unseen datasets. These results suggest that DAR yields superior performance with an autoregressive prediction paradigm, providing a promising approach to equip modern autoregressive large models (e.g., GPT-4o) with depth estimation capabilities.
ReliOcc: Towards Reliable Semantic Occupancy Prediction via Uncertainty Learning
Sep 26, 2024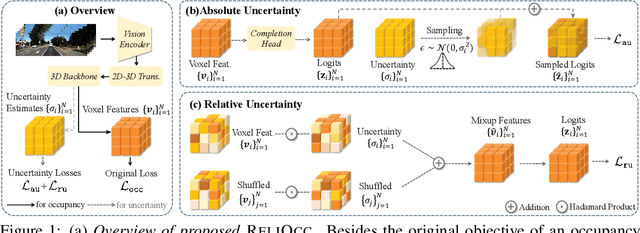
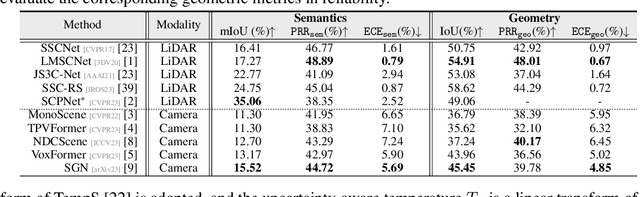
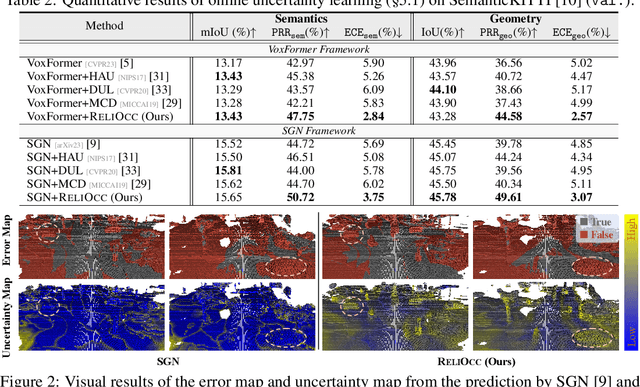
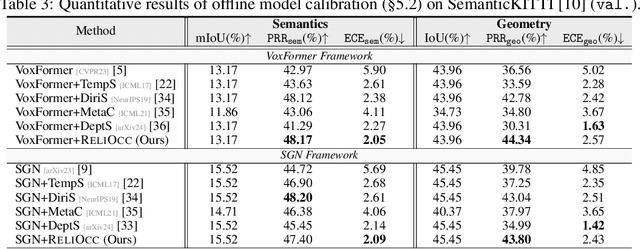
Abstract:Vision-centric semantic occupancy prediction plays a crucial role in autonomous driving, which requires accurate and reliable predictions from low-cost sensors. Although having notably narrowed the accuracy gap with LiDAR, there is still few research effort to explore the reliability in predicting semantic occupancy from camera. In this paper, we conduct a comprehensive evaluation of existing semantic occupancy prediction models from a reliability perspective for the first time. Despite the gradual alignment of camera-based models with LiDAR in term of accuracy, a significant reliability gap persists. To addresses this concern, we propose ReliOcc, a method designed to enhance the reliability of camera-based occupancy networks. ReliOcc provides a plug-and-play scheme for existing models, which integrates hybrid uncertainty from individual voxels with sampling-based noise and relative voxels through mix-up learning. Besides, an uncertainty-aware calibration strategy is devised to further enhance model reliability in offline mode. Extensive experiments under various settings demonstrate that ReliOcc significantly enhances model reliability while maintaining the accuracy of both geometric and semantic predictions. Importantly, our proposed approach exhibits robustness to sensor failures and out of domain noises during inference.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge