Long Li
Anchored Policy Optimization: Mitigating Exploration Collapse Via Support-Constrained Rectification
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) is increasingly viewed as a tree pruning mechanism. However, we identify a systemic pathology termed Recursive Space Contraction (RSC), an irreversible collapse driven by the combined dynamics of positive sharpening and negative squeezing, where the sampling probability of valid alternatives vanishes. While Kullback-Leibler (KL) regularization aims to mitigate this, it imposes a rigid Shape Matching constraint that forces the policy to mimic the reference model's full density, creating a gradient conflict with the sharpening required for correctness. We propose Anchored Policy Optimization (APO), shifting the paradigm from global Shape Matching to Support Coverage. By defining a Safe Manifold based on the reference model's high-confidence support, APO permits aggressive sharpening for efficiency while selectively invoking a restorative force during error correction to prevent collapse. We theoretically derive that APO serves as a gradient-aligned mechanism to maximize support coverage, enabling an Elastic Recovery that re-inflates valid branches. Empirical evaluations on mathematical benchmarks demonstrate that APO breaks the accuracy-diversity trade-off, significantly improving Pass@1 while restoring the Pass@K diversity typically lost by standard policy gradient methods.
IIB-LPO: Latent Policy Optimization via Iterative Information Bottleneck
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) for Large Language Model (LLM) reasoning have been hindered by a persistent challenge: exploration collapse. The semantic homogeneity of random rollouts often traps models in narrow, over-optimized behaviors. While existing methods leverage policy entropy to encourage exploration, they face inherent limitations. Global entropy regularization is susceptible to reward hacking, which can induce meaningless verbosity, whereas local token-selective updates struggle with the strong inductive bias of pre-trained models. To address this, we propose Latent Policy Optimization via Iterative Information Bottleneck (IIB-LPO), a novel approach that shifts exploration from statistical perturbation of token distributions to topological branching of reasoning trajectories. IIB-LPO triggers latent branching at high-entropy states to diversify reasoning paths and employs the Information Bottleneck principle both as a trajectory filter and a self-reward mechanism, ensuring concise and informative exploration. Empirical results across four mathematical reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that IIB-LPO achieves state-of-the-art performance, surpassing prior methods by margins of up to 5.3% in accuracy and 7.4% in diversity metrics.
Perception Before Reasoning: Two-Stage Reinforcement Learning for Visual Reasoning in Vision-Language Models
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has proven highly effective in eliciting the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs). Inspired by this success, recent studies have explored applying similar techniques to vision-language models (VLMs), aiming to enhance their reasoning performance. However, directly transplanting RL methods from LLMs to VLMs is suboptimal, as the tasks faced by VLMs are inherently more complex. Specifically, VLMs must first accurately perceive and understand visual inputs before reasoning can be effectively performed. To address this challenge, we propose a two-stage reinforcement learning framework designed to jointly enhance both the perceptual and reasoning capabilities of VLMs. To mitigate the vanishing advantage issue commonly observed in RL training, we first perform dataset-level sampling to selectively strengthen specific capabilities using distinct data sources. During training, the first stage focuses on improving the model's visual perception through coarse- and fine-grained visual understanding, while the second stage targets the enhancement of reasoning abilities. After the proposed two-stage reinforcement learning process, we obtain PeBR-R1, a vision-language model with significantly enhanced perceptual and reasoning capabilities. Experimental results on seven benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach and validate the superior performance of PeBR-R1 across diverse visual reasoning tasks.
The Choice of Divergence: A Neglected Key to Mitigating Diversity Collapse in Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Reward
Sep 09, 2025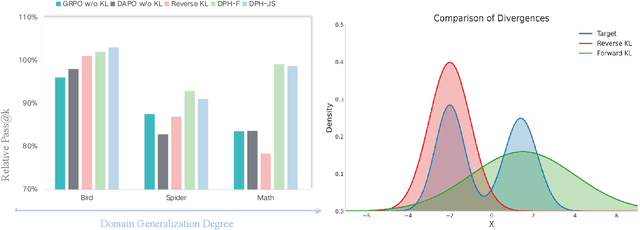
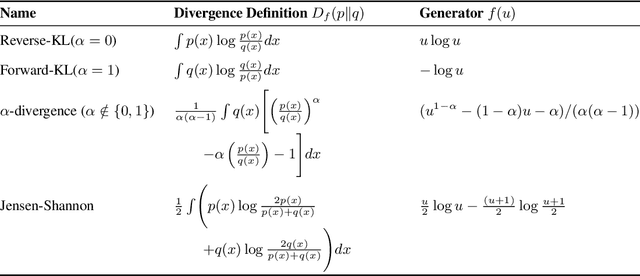
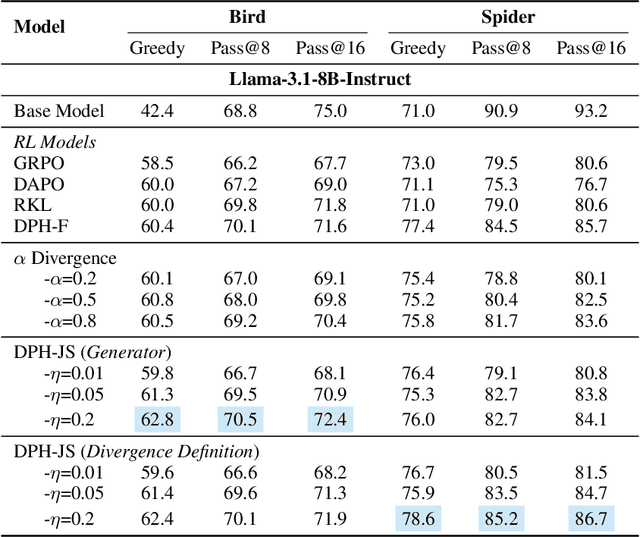
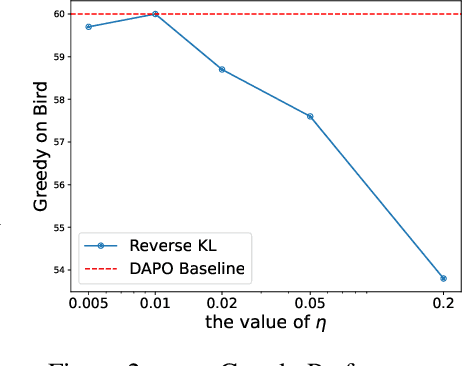
Abstract:A central paradox in fine-tuning Large Language Models (LLMs) with Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Reward (RLVR) is the frequent degradation of multi-attempt performance (Pass@k) despite improvements in single-attempt accuracy (Pass@1). This is often accompanied by catastrophic forgetting, where models lose previously acquired skills. While various methods have been proposed, the choice and function of the divergence term have been surprisingly unexamined as a proactive solution. We argue that standard RLVR objectives -- both those using the mode-seeking reverse KL-divergence and those forgoing a divergence term entirely -- lack a crucial mechanism for knowledge retention. The reverse-KL actively accelerates this decay by narrowing the policy, while its absence provides no safeguard against the model drifting from its diverse knowledge base. We propose a fundamental shift in perspective: using the divergence term itself as the solution. Our framework, Diversity-Preserving Hybrid RL (DPH-RL), leverages mass-covering f-divergences (like forward-KL and JS-divergence) to function as a rehearsal mechanism. By continuously referencing the initial policy, this approach forces the model to maintain broad solution coverage. Extensive experiments on math and SQL generation demonstrate that DPH-RL not only resolves the Pass@k degradation but improves both Pass@1 and Pass@k in- and out-of-domain. Additionally, DPH-RL is more training-efficient because it computes f-divergence using generator functions, requiring only sampling from the initial policy and no online reference model. Our work highlights a crucial, overlooked axis for improving RLVR, demonstrating that the proper selection of a divergence measure is a powerful tool for building more general and diverse reasoning models.
VL-Cogito: Progressive Curriculum Reinforcement Learning for Advanced Multimodal Reasoning
Jul 30, 2025



Abstract:Reinforcement learning has proven its effectiveness in enhancing the reasoning capabilities of large language models. Recent research efforts have progressively extended this paradigm to multimodal reasoning tasks. Due to the inherent complexity and diversity of multimodal tasks, especially in semantic content and problem formulations, existing models often exhibit unstable performance across various domains and difficulty levels. To address these limitations, we propose VL-Cogito, an advanced multimodal reasoning model trained via a novel multi-stage Progressive Curriculum Reinforcement Learning (PCuRL) framework. PCuRL systematically guides the model through tasks of gradually increasing difficulty, substantially improving its reasoning abilities across diverse multimodal contexts. The framework introduces two key innovations: (1) an online difficulty soft weighting mechanism, dynamically adjusting training difficulty across successive RL training stages; and (2) a dynamic length reward mechanism, which encourages the model to adaptively regulate its reasoning path length according to task complexity, thus balancing reasoning efficiency with correctness. Experimental evaluations demonstrate that VL-Cogito consistently matches or surpasses existing reasoning-oriented models across mainstream multimodal benchmarks spanning mathematics, science, logic, and general understanding, validating the effectiveness of our approach.
ReasonMed: A 370K Multi-Agent Generated Dataset for Advancing Medical Reasoning
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Though reasoning-based large language models (LLMs) have excelled in mathematics and programming, their capabilities in knowledge-intensive medical question answering remain underexplored. To address this, we introduce ReasonMed, the largest medical reasoning dataset, comprising 370k high-quality examples distilled from 1.7 million initial reasoning paths generated by various LLMs. ReasonMed is constructed through a \textit{multi-agent verification and refinement process}, where we design an \textit{Error Refiner} to enhance the reasoning paths by identifying and correcting error-prone steps flagged by a verifier. Leveraging ReasonMed, we systematically investigate best practices for training medical reasoning models and find that combining detailed Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning with concise answer summaries yields the most effective fine-tuning strategy. Based on this strategy, we train ReasonMed-7B, which sets a new benchmark for sub-10B models, outperforming the prior best by 4.17\% and even exceeding LLaMA3.1-70B on PubMedQA by 4.60\%.
Lingshu: A Generalist Foundation Model for Unified Multimodal Medical Understanding and Reasoning
Jun 08, 2025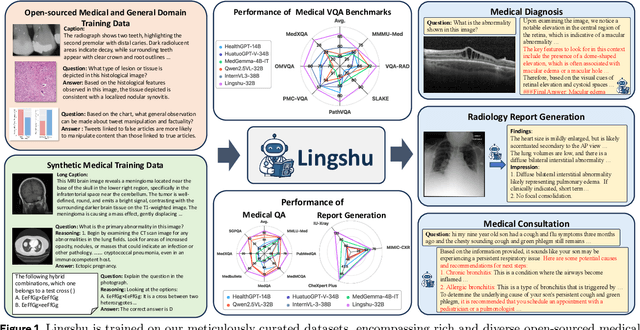
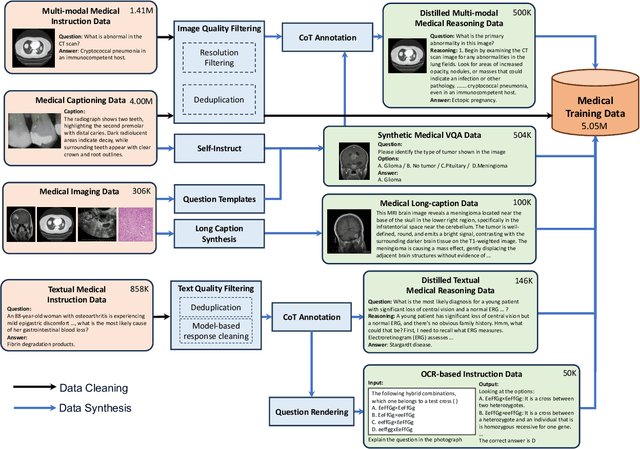
Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities in understanding common visual elements, largely due to their large-scale datasets and advanced training strategies. However, their effectiveness in medical applications remains limited due to the inherent discrepancies between data and tasks in medical scenarios and those in the general domain. Concretely, existing medical MLLMs face the following critical limitations: (1) limited coverage of medical knowledge beyond imaging, (2) heightened susceptibility to hallucinations due to suboptimal data curation processes, (3) lack of reasoning capabilities tailored for complex medical scenarios. To address these challenges, we first propose a comprehensive data curation procedure that (1) efficiently acquires rich medical knowledge data not only from medical imaging but also from extensive medical texts and general-domain data; and (2) synthesizes accurate medical captions, visual question answering (VQA), and reasoning samples. As a result, we build a multimodal dataset enriched with extensive medical knowledge. Building on the curated data, we introduce our medical-specialized MLLM: Lingshu. Lingshu undergoes multi-stage training to embed medical expertise and enhance its task-solving capabilities progressively. Besides, we preliminarily explore the potential of applying reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards paradigm to enhance Lingshu's medical reasoning ability. Additionally, we develop MedEvalKit, a unified evaluation framework that consolidates leading multimodal and textual medical benchmarks for standardized, fair, and efficient model assessment. We evaluate the performance of Lingshu on three fundamental medical tasks, multimodal QA, text-based QA, and medical report generation. The results show that Lingshu consistently outperforms the existing open-source multimodal models on most tasks ...
EOC-Bench: Can MLLMs Identify, Recall, and Forecast Objects in an Egocentric World?
Jun 05, 2025



Abstract:The emergence of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) has driven breakthroughs in egocentric vision applications. These applications necessitate persistent, context-aware understanding of objects, as users interact with tools in dynamic and cluttered environments. However, existing embodied benchmarks primarily focus on static scene exploration, emphasizing object's appearance and spatial attributes while neglecting the assessment of dynamic changes arising from users' interactions. To address this gap, we introduce EOC-Bench, an innovative benchmark designed to systematically evaluate object-centric embodied cognition in dynamic egocentric scenarios. Specially, EOC-Bench features 3,277 meticulously annotated QA pairs categorized into three temporal categories: Past, Present, and Future, covering 11 fine-grained evaluation dimensions and 3 visual object referencing types. To ensure thorough assessment, we develop a mixed-format human-in-the-loop annotation framework with four types of questions and design a novel multi-scale temporal accuracy metric for open-ended temporal evaluation. Based on EOC-Bench, we conduct comprehensive evaluations of various proprietary, open-source, and object-level MLLMs. EOC-Bench serves as a crucial tool for advancing the embodied object cognitive capabilities of MLLMs, establishing a robust foundation for developing reliable core models for embodied systems.
VLLFL: A Vision-Language Model Based Lightweight Federated Learning Framework for Smart Agriculture
Apr 17, 2025



Abstract:In modern smart agriculture, object detection plays a crucial role by enabling automation, precision farming, and monitoring of resources. From identifying crop health and pest infestations to optimizing harvesting processes, accurate object detection enhances both productivity and sustainability. However, training object detection models often requires large-scale data collection and raises privacy concerns, particularly when sensitive agricultural data is distributed across farms. To address these challenges, we propose VLLFL, a vision-language model-based lightweight federated learning framework (VLLFL). It harnesses the generalization and context-aware detection capabilities of the vision-language model (VLM) and leverages the privacy-preserving nature of federated learning. By training a compact prompt generator to boost the performance of the VLM deployed across different farms, VLLFL preserves privacy while reducing communication overhead. Experimental results demonstrate that VLLFL achieves 14.53% improvement in the performance of VLM while reducing 99.3% communication overhead. Spanning tasks from identifying a wide variety of fruits to detecting harmful animals in agriculture, the proposed framework offers an efficient, scalable, and privacy-preserving solution specifically tailored to agricultural applications.
ECBench: Can Multi-modal Foundation Models Understand the Egocentric World? A Holistic Embodied Cognition Benchmark
Jan 09, 2025



Abstract:The enhancement of generalization in robots by large vision-language models (LVLMs) is increasingly evident. Therefore, the embodied cognitive abilities of LVLMs based on egocentric videos are of great interest. However, current datasets for embodied video question answering lack comprehensive and systematic evaluation frameworks. Critical embodied cognitive issues, such as robotic self-cognition, dynamic scene perception, and hallucination, are rarely addressed. To tackle these challenges, we propose ECBench, a high-quality benchmark designed to systematically evaluate the embodied cognitive abilities of LVLMs. ECBench features a diverse range of scene video sources, open and varied question formats, and 30 dimensions of embodied cognition. To ensure quality, balance, and high visual dependence, ECBench uses class-independent meticulous human annotation and multi-round question screening strategies. Additionally, we introduce ECEval, a comprehensive evaluation system that ensures the fairness and rationality of the indicators. Utilizing ECBench, we conduct extensive evaluations of proprietary, open-source, and task-specific LVLMs. ECBench is pivotal in advancing the embodied cognitive capabilities of LVLMs, laying a solid foundation for developing reliable core models for embodied agents. All data and code are available at https://github.com/Rh-Dang/ECBench.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge