Liuyi Wang
VLNVerse: A Benchmark for Vision-Language Navigation with Versatile, Embodied, Realistic Simulation and Evaluation
Dec 22, 2025
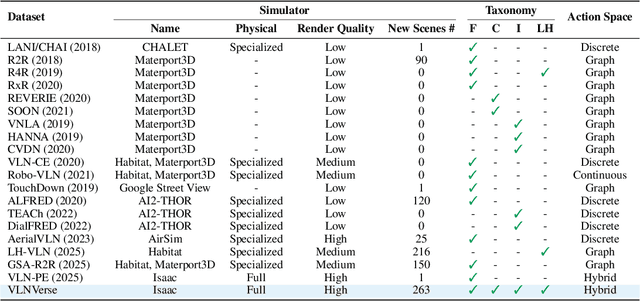
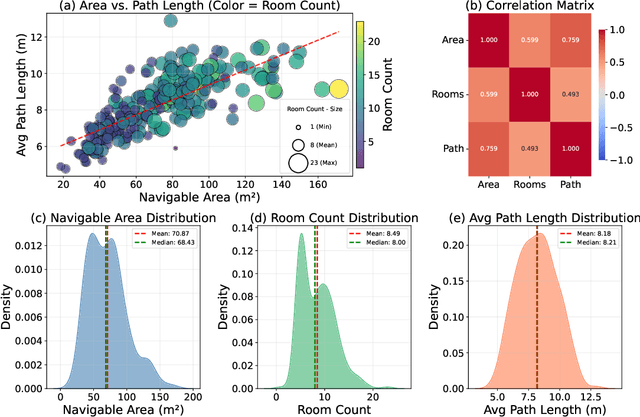
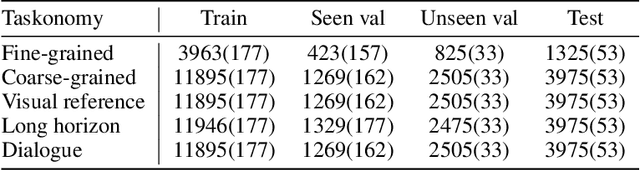
Abstract:Despite remarkable progress in Vision-Language Navigation (VLN), existing benchmarks remain confined to fixed, small-scale datasets with naive physical simulation. These shortcomings limit the insight that the benchmarks provide into sim-to-real generalization, and create a significant research gap. Furthermore, task fragmentation prevents unified/shared progress in the area, while limited data scales fail to meet the demands of modern LLM-based pretraining. To overcome these limitations, we introduce VLNVerse: a new large-scale, extensible benchmark designed for Versatile, Embodied, Realistic Simulation, and Evaluation. VLNVerse redefines VLN as a scalable, full-stack embodied AI problem. Its Versatile nature unifies previously fragmented tasks into a single framework and provides an extensible toolkit for researchers. Its Embodied design moves beyond intangible and teleporting "ghost" agents that support full-kinematics in a Realistic Simulation powered by a robust physics engine. We leverage the scale and diversity of VLNVerse to conduct a comprehensive Evaluation of existing methods, from classic models to MLLM-based agents. We also propose a novel unified multi-task model capable of addressing all tasks within the benchmark. VLNVerse aims to narrow the gap between simulated navigation and real-world generalization, providing the community with a vital tool to boost research towards scalable, general-purpose embodied locomotion agents.
CLASH: Collaborative Large-Small Hierarchical Framework for Continuous Vision-and-Language Navigation
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) requires robots to follow natural language instructions and navigate complex environments without prior maps. While recent vision-language large models demonstrate strong reasoning abilities, they often underperform task-specific panoramic small models in VLN tasks. To address this, we propose CLASH (Collaborative Large-Small Hierarchy), a VLN-CE framework that integrates a reactive small-model planner (RSMP) with a reflective large-model reasoner (RLMR). RSMP adopts a causal-learning-based dual-branch architecture to enhance generalization, while RLMR leverages panoramic visual prompting with chain-of-thought reasoning to support interpretable spatial understanding and navigation. We further introduce an uncertainty-aware collaboration mechanism (UCM) that adaptively fuses decisions from both models. For obstacle avoidance, in simulation, we replace the rule-based controller with a fully learnable point-goal policy, and in real-world deployment, we design a LiDAR-based clustering module for generating navigable waypoints and pair it with an online SLAM-based local controller. CLASH achieves state-of-the-art (SoTA) results (ranking 1-st) on the VLN-CE leaderboard, significantly improving SR and SPL on the test-unseen set over the previous SoTA methods. Real-world experiments demonstrate CLASH's strong robustness, validating its effectiveness in both simulation and deployment scenarios.
Temporal-Guided Visual Foundation Models for Event-Based Vision
Nov 09, 2025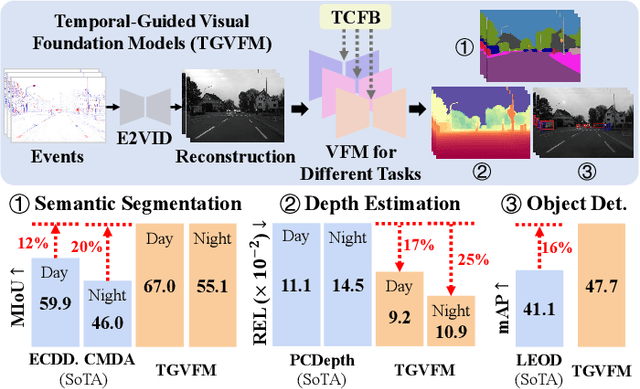
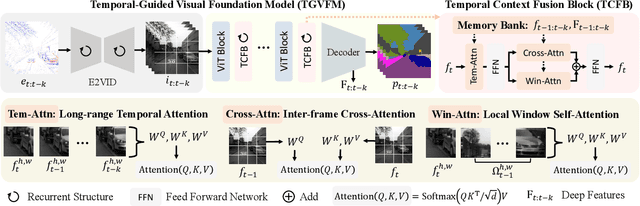


Abstract:Event cameras offer unique advantages for vision tasks in challenging environments, yet processing asynchronous event streams remains an open challenge. While existing methods rely on specialized architectures or resource-intensive training, the potential of leveraging modern Visual Foundation Models (VFMs) pretrained on image data remains under-explored for event-based vision. To address this, we propose Temporal-Guided VFM (TGVFM), a novel framework that integrates VFMs with our temporal context fusion block seamlessly to bridge this gap. Our temporal block introduces three key components: (1) Long-Range Temporal Attention to model global temporal dependencies, (2) Dual Spatiotemporal Attention for multi-scale frame correlation, and (3) Deep Feature Guidance Mechanism to fuse semantic-temporal features. By retraining event-to-video models on real-world data and leveraging transformer-based VFMs, TGVFM preserves spatiotemporal dynamics while harnessing pretrained representations. Experiments demonstrate SoTA performance across semantic segmentation, depth estimation, and object detection, with improvements of 16%, 21%, and 16% over existing methods, respectively. Overall, this work unlocks the cross-modality potential of image-based VFMs for event-based vision with temporal reasoning. Code is available at https://github.com/XiaRho/TGVFM.
Rethinking the Embodied Gap in Vision-and-Language Navigation: A Holistic Study of Physical and Visual Disparities
Jul 17, 2025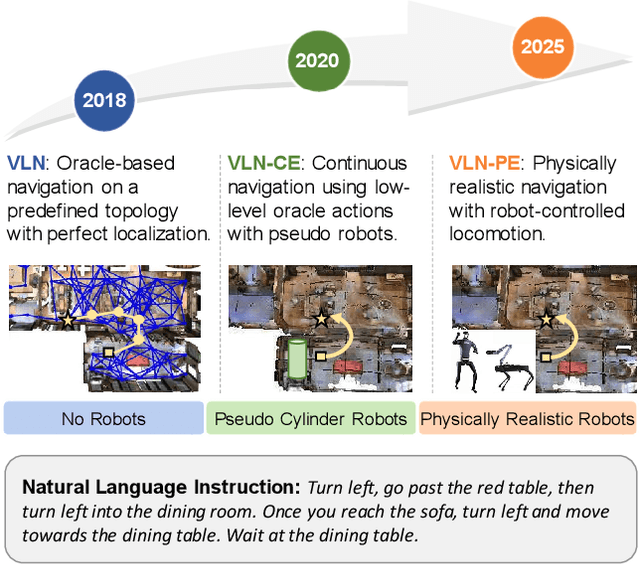
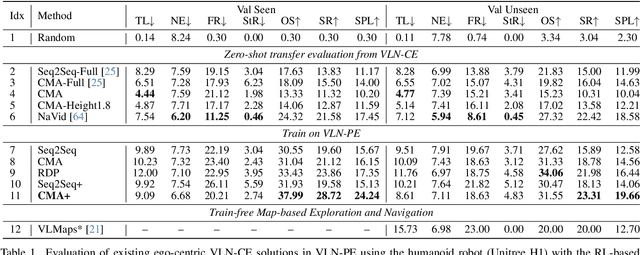
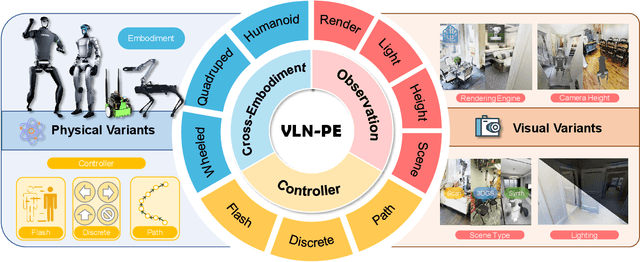
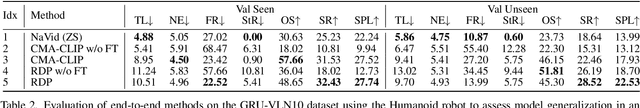
Abstract:Recent Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) advancements are promising, but their idealized assumptions about robot movement and control fail to reflect physically embodied deployment challenges. To bridge this gap, we introduce VLN-PE, a physically realistic VLN platform supporting humanoid, quadruped, and wheeled robots. For the first time, we systematically evaluate several ego-centric VLN methods in physical robotic settings across different technical pipelines, including classification models for single-step discrete action prediction, a diffusion model for dense waypoint prediction, and a train-free, map-based large language model (LLM) integrated with path planning. Our results reveal significant performance degradation due to limited robot observation space, environmental lighting variations, and physical challenges like collisions and falls. This also exposes locomotion constraints for legged robots in complex environments. VLN-PE is highly extensible, allowing seamless integration of new scenes beyond MP3D, thereby enabling more comprehensive VLN evaluation. Despite the weak generalization of current models in physical deployment, VLN-PE provides a new pathway for improving cross-embodiment's overall adaptability. We hope our findings and tools inspire the community to rethink VLN limitations and advance robust, practical VLN models. The code is available at https://crystalsixone.github.io/vln_pe.github.io/.
CleanPose: Category-Level Object Pose Estimation via Causal Learning and Knowledge Distillation
Feb 03, 2025



Abstract:Category-level object pose estimation aims to recover the rotation, translation and size of unseen instances within predefined categories. In this task, deep neural network-based methods have demonstrated remarkable performance. However, previous studies show they suffer from spurious correlations raised by "unclean" confounders in models, hindering their performance on novel instances with significant variations. To address this issue, we propose CleanPose, a novel approach integrating causal learning and knowledge distillation to enhance category-level pose estimation. To mitigate the negative effect of unobserved confounders, we develop a causal inference module based on front-door adjustment, which promotes unbiased estimation by reducing potential spurious correlations. Additionally, to further improve generalization ability, we devise a residual-based knowledge distillation method that has proven effective in providing comprehensive category information guidance. Extensive experiments across multiple benchmarks (REAL275, CAMERA25 and HouseCat6D) hightlight the superiority of proposed CleanPose over state-of-the-art methods. Code will be released.
ECBench: Can Multi-modal Foundation Models Understand the Egocentric World? A Holistic Embodied Cognition Benchmark
Jan 09, 2025



Abstract:The enhancement of generalization in robots by large vision-language models (LVLMs) is increasingly evident. Therefore, the embodied cognitive abilities of LVLMs based on egocentric videos are of great interest. However, current datasets for embodied video question answering lack comprehensive and systematic evaluation frameworks. Critical embodied cognitive issues, such as robotic self-cognition, dynamic scene perception, and hallucination, are rarely addressed. To tackle these challenges, we propose ECBench, a high-quality benchmark designed to systematically evaluate the embodied cognitive abilities of LVLMs. ECBench features a diverse range of scene video sources, open and varied question formats, and 30 dimensions of embodied cognition. To ensure quality, balance, and high visual dependence, ECBench uses class-independent meticulous human annotation and multi-round question screening strategies. Additionally, we introduce ECEval, a comprehensive evaluation system that ensures the fairness and rationality of the indicators. Utilizing ECBench, we conduct extensive evaluations of proprietary, open-source, and task-specific LVLMs. ECBench is pivotal in advancing the embodied cognitive capabilities of LVLMs, laying a solid foundation for developing reliable core models for embodied agents. All data and code are available at https://github.com/Rh-Dang/ECBench.
MAGIC: Meta-Ability Guided Interactive Chain-of-Distillation for Effective-and-Efficient Vision-and-Language Navigation
Jun 25, 2024Abstract:Despite the remarkable developments of recent large models in Embodied Artificial Intelligence (E-AI), their integration into robotics is hampered by their excessive parameter sizes and computational demands. Towards the Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) task, a core task in E-AI, this paper reveals the great potential of using knowledge distillation for obtaining lightweight student models by proposing a Meta-Ability Guided Interactive Chain-of-distillation (MAGIC) method. Specifically, a Meta-Ability Knowledge Distillation (MAKD) framework is proposed for decoupling and refining the necessary meta-abilities of VLN agents. A Meta-Knowledge Randomization Weighting (MKRW) and a Meta-Knowledge Transferable Determination (MKTD) module are incorporated to dynamically adjust aggregation weights at the meta-ability and sample levels, respectively. Move beyond the traditional one-step unidirectional distillation, an Interactive Chain-of-Distillation (ICoD) learning strategy is proposed to allow students to give feedback to teachers, forming a new multi-step teacher-student co-evolution pipeline. Remarkably, on the R2R test unseen public leaderboard, our smallest model, MAGIC-S, with only 5% (11M) of the teacher's size, outperforms all previous methods under the same training data. Additionally, our largest model, MAGIC-L, surpasses the previous state-of-the-art by 5.84% in SPL and 3.18% in SR. Furthermore, a new dataset was collected and annotated from our living environments, where MAGIC-S demonstrated superior performance and real-time efficiency. Our code is publicly available on https://github.com/CrystalSixone/VLN-MAGIC.
Vision-and-Language Navigation via Causal Learning
Apr 16, 2024Abstract:In the pursuit of robust and generalizable environment perception and language understanding, the ubiquitous challenge of dataset bias continues to plague vision-and-language navigation (VLN) agents, hindering their performance in unseen environments. This paper introduces the generalized cross-modal causal transformer (GOAT), a pioneering solution rooted in the paradigm of causal inference. By delving into both observable and unobservable confounders within vision, language, and history, we propose the back-door and front-door adjustment causal learning (BACL and FACL) modules to promote unbiased learning by comprehensively mitigating potential spurious correlations. Additionally, to capture global confounder features, we propose a cross-modal feature pooling (CFP) module supervised by contrastive learning, which is also shown to be effective in improving cross-modal representations during pre-training. Extensive experiments across multiple VLN datasets (R2R, REVERIE, RxR, and SOON) underscore the superiority of our proposed method over previous state-of-the-art approaches. Code is available at https://github.com/CrystalSixone/VLN-GOAT.
Causality-based Cross-Modal Representation Learning for Vision-and-Language Navigation
Mar 06, 2024Abstract:Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) has gained significant research interest in recent years due to its potential applications in real-world scenarios. However, existing VLN methods struggle with the issue of spurious associations, resulting in poor generalization with a significant performance gap between seen and unseen environments. In this paper, we tackle this challenge by proposing a unified framework CausalVLN based on the causal learning paradigm to train a robust navigator capable of learning unbiased feature representations. Specifically, we establish reasonable assumptions about confounders for vision and language in VLN using the structured causal model (SCM). Building upon this, we propose an iterative backdoor-based representation learning (IBRL) method that allows for the adaptive and effective intervention on confounders. Furthermore, we introduce the visual and linguistic backdoor causal encoders to enable unbiased feature expression for multi-modalities during training and validation, enhancing the agent's capability to generalize across different environments. Experiments on three VLN datasets (R2R, RxR, and REVERIE) showcase the superiority of our proposed method over previous state-of-the-art approaches. Moreover, detailed visualization analysis demonstrates the effectiveness of CausalVLN in significantly narrowing down the performance gap between seen and unseen environments, underscoring its strong generalization capability.
PASTS: Progress-Aware Spatio-Temporal Transformer Speaker For Vision-and-Language Navigation
May 19, 2023



Abstract:Vision-and-language navigation (VLN) is a crucial but challenging cross-modal navigation task. One powerful technique to enhance the generalization performance in VLN is the use of an independent speaker model to provide pseudo instructions for data augmentation. However, current speaker models based on Long-Short Term Memory (LSTM) lack the ability to attend to features relevant at different locations and time steps. To address this, we propose a novel progress-aware spatio-temporal transformer speaker (PASTS) model that uses the transformer as the core of the network. PASTS uses a spatio-temporal encoder to fuse panoramic representations and encode intermediate connections through steps. Besides, to avoid the misalignment problem that could result in incorrect supervision, a speaker progress monitor (SPM) is proposed to enable the model to estimate the progress of instruction generation and facilitate more fine-grained caption results. Additionally, a multifeature dropout (MFD) strategy is introduced to alleviate overfitting. The proposed PASTS is flexible to be combined with existing VLN models. The experimental results demonstrate that PASTS outperforms all existing speaker models and successfully improves the performance of previous VLN models, achieving state-of-the-art performance on the standard Room-to-Room (R2R) dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge