Boqiang Zhang
Boosting Segment Anything Model to Generalize Visually Non-Salient Scenarios
Jan 02, 2026Abstract:Segment Anything Model (SAM), known for its remarkable zero-shot segmentation capabilities, has garnered significant attention in the community. Nevertheless, its performance is challenged when dealing with what we refer to as visually non-salient scenarios, where there is low contrast between the foreground and background. In these cases, existing methods often cannot capture accurate contours and fail to produce promising segmentation results. In this paper, we propose Visually Non-Salient SAM (VNS-SAM), aiming to enhance SAM's perception of visually non-salient scenarios while preserving its original zero-shot generalizability. We achieve this by effectively exploiting SAM's low-level features through two designs: Mask-Edge Token Interactive decoder and Non-Salient Feature Mining module. These designs help the SAM decoder gain a deeper understanding of non-salient characteristics with only marginal parameter increments and computational requirements. The additional parameters of VNS-SAM can be optimized within 4 hours, demonstrating its feasibility and practicality. In terms of data, we established VNS-SEG, a unified dataset for various VNS scenarios, with more than 35K images, in contrast to previous single-task adaptations. It is designed to make the model learn more robust VNS features and comprehensively benchmark the model's segmentation performance and generalizability on VNS scenarios. Extensive experiments across various VNS segmentation tasks demonstrate the superior performance of VNS-SAM, particularly under zero-shot settings, highlighting its potential for broad real-world applications. Codes and datasets are publicly available at https://guangqian-guo.github.io/VNS-SAM.
N3D-VLM: Native 3D Grounding Enables Accurate Spatial Reasoning in Vision-Language Models
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:While current multimodal models can answer questions based on 2D images, they lack intrinsic 3D object perception, limiting their ability to comprehend spatial relationships and depth cues in 3D scenes. In this work, we propose N3D-VLM, a novel unified framework that seamlessly integrates native 3D object perception with 3D-aware visual reasoning, enabling both precise 3D grounding and interpretable spatial understanding. Unlike conventional end-to-end models that directly predict answers from RGB/RGB-D inputs, our approach equips the model with native 3D object perception capabilities, enabling it to directly localize objects in 3D space based on textual descriptions. Building upon accurate 3D object localization, the model further performs explicit reasoning in 3D, achieving more interpretable and structured spatial understanding. To support robust training for these capabilities, we develop a scalable data construction pipeline that leverages depth estimation to lift large-scale 2D annotations into 3D space, significantly increasing the diversity and coverage for 3D object grounding data, yielding over six times larger than the largest existing single-image 3D detection dataset. Moreover, the pipeline generates spatial question-answering datasets that target chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning in 3D, facilitating joint training for both 3D object localization and 3D spatial reasoning. Experimental results demonstrate that our unified framework not only achieves state-of-the-art performance on 3D grounding tasks, but also consistently surpasses existing methods in 3D spatial reasoning in vision-language model.
What Is a Good Caption? A Comprehensive Visual Caption Benchmark for Evaluating Both Correctness and Coverage of MLLMs
Feb 19, 2025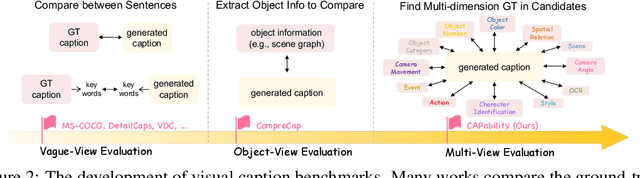
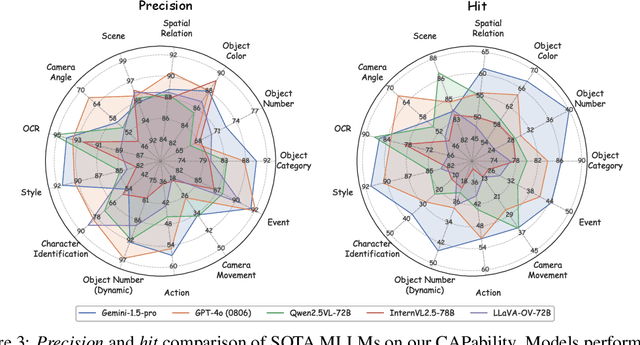

Abstract:Recent advancements in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have rendered traditional visual captioning benchmarks obsolete, as they primarily evaluate short descriptions with outdated metrics. While recent benchmarks address these limitations by decomposing captions into visual elements and adopting model-based evaluation, they remain incomplete-overlooking critical aspects, while providing vague, non-explanatory scores. To bridge this gap, we propose CV-CapBench, a Comprehensive Visual Caption Benchmark that systematically evaluates caption quality across 6 views and 13 dimensions. CV-CapBench introduces precision, recall, and hit rate metrics for each dimension, uniquely assessing both correctness and coverage. Experiments on leading MLLMs reveal significant capability gaps, particularly in dynamic and knowledge-intensive dimensions. These findings provide actionable insights for future research. The code and data will be released.
ECBench: Can Multi-modal Foundation Models Understand the Egocentric World? A Holistic Embodied Cognition Benchmark
Jan 09, 2025



Abstract:The enhancement of generalization in robots by large vision-language models (LVLMs) is increasingly evident. Therefore, the embodied cognitive abilities of LVLMs based on egocentric videos are of great interest. However, current datasets for embodied video question answering lack comprehensive and systematic evaluation frameworks. Critical embodied cognitive issues, such as robotic self-cognition, dynamic scene perception, and hallucination, are rarely addressed. To tackle these challenges, we propose ECBench, a high-quality benchmark designed to systematically evaluate the embodied cognitive abilities of LVLMs. ECBench features a diverse range of scene video sources, open and varied question formats, and 30 dimensions of embodied cognition. To ensure quality, balance, and high visual dependence, ECBench uses class-independent meticulous human annotation and multi-round question screening strategies. Additionally, we introduce ECEval, a comprehensive evaluation system that ensures the fairness and rationality of the indicators. Utilizing ECBench, we conduct extensive evaluations of proprietary, open-source, and task-specific LVLMs. ECBench is pivotal in advancing the embodied cognitive capabilities of LVLMs, laying a solid foundation for developing reliable core models for embodied agents. All data and code are available at https://github.com/Rh-Dang/ECBench.
VideoRefer Suite: Advancing Spatial-Temporal Object Understanding with Video LLM
Jan 08, 2025Abstract:Video Large Language Models (Video LLMs) have recently exhibited remarkable capabilities in general video understanding. However, they mainly focus on holistic comprehension and struggle with capturing fine-grained spatial and temporal details. Besides, the lack of high-quality object-level video instruction data and a comprehensive benchmark further hinders their advancements. To tackle these challenges, we introduce the VideoRefer Suite to empower Video LLM for finer-level spatial-temporal video understanding, i.e., enabling perception and reasoning on any objects throughout the video. Specially, we thoroughly develop VideoRefer Suite across three essential aspects: dataset, model, and benchmark. Firstly, we introduce a multi-agent data engine to meticulously curate a large-scale, high-quality object-level video instruction dataset, termed VideoRefer-700K. Next, we present the VideoRefer model, which equips a versatile spatial-temporal object encoder to capture precise regional and sequential representations. Finally, we meticulously create a VideoRefer-Bench to comprehensively assess the spatial-temporal understanding capability of a Video LLM, evaluating it across various aspects. Extensive experiments and analyses demonstrate that our VideoRefer model not only achieves promising performance on video referring benchmarks but also facilitates general video understanding capabilities.
Chain of Ideas: Revolutionizing Research Via Novel Idea Development with LLM Agents
Oct 25, 2024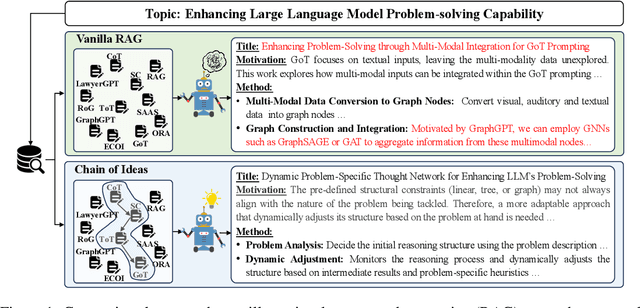

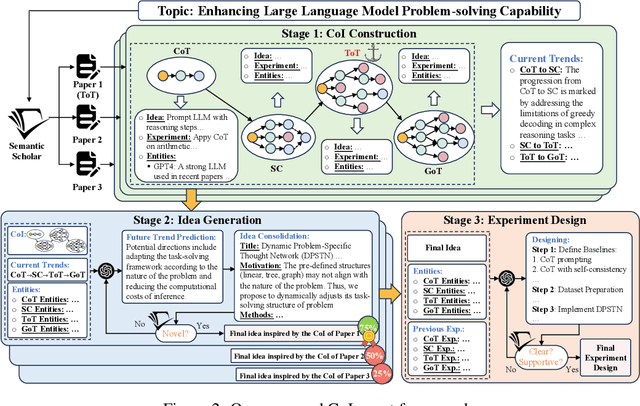
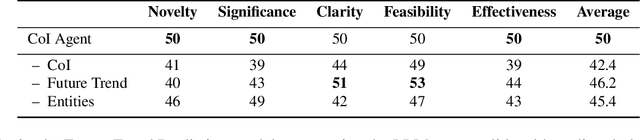
Abstract:Effective research ideation is a critical step for scientific research. However, the exponential increase in scientific literature makes it challenging for researchers to stay current with recent advances and identify meaningful research directions. Recent developments in large language models~(LLMs) suggest a promising avenue for automating the generation of novel research ideas. However, existing methods for idea generation either trivially prompt LLMs or directly expose LLMs to extensive literature without indicating useful information. Inspired by the research process of human researchers, we propose a Chain-of-Ideas~(CoI) agent, an LLM-based agent that organizes relevant literature in a chain structure to effectively mirror the progressive development in a research domain. This organization facilitates LLMs to capture the current advancements in research, thereby enhancing their ideation capabilities. Furthermore, we propose Idea Arena, an evaluation protocol that can comprehensively evaluate idea generation methods from different perspectives, aligning closely with the preferences of human researchers. Experimental results indicate that the CoI agent consistently outperforms other methods and shows comparable quality as humans in research idea generation. Moreover, our CoI agent is budget-friendly, with a minimum cost of \$0.50 to generate a candidate idea and its corresponding experimental design.
Chain of Ideas: Revolutionizing Research in Novel Idea Development with LLM Agents
Oct 17, 2024



Abstract:Effective research ideation is a critical step for scientific research. However, the exponential increase in scientific literature makes it challenging for researchers to stay current with recent advances and identify meaningful research directions. Recent developments in large language models~(LLMs) suggest a promising avenue for automating the generation of novel research ideas. However, existing methods for idea generation either trivially prompt LLMs or directly expose LLMs to extensive literature without indicating useful information. Inspired by the research process of human researchers, we propose a Chain-of-Ideas~(CoI) agent, an LLM-based agent that organizes relevant literature in a chain structure to effectively mirror the progressive development in a research domain. This organization facilitates LLMs to capture the current advancements in research, thereby enhancing their ideation capabilities. Furthermore, we propose Idea Arena, an evaluation protocol that can comprehensively evaluate idea generation methods from different perspectives, aligning closely with the preferences of human researchers. Experimental results indicate that the CoI agent consistently outperforms other methods and shows comparable quality as humans in research idea generation. Moreover, our CoI agent is budget-friendly, with a minimum cost of \$0.50 to generate a candidate idea and its corresponding experimental design.
How Control Information Influences Multilingual Text Image Generation and Editing?
Jul 16, 2024Abstract:Visual text generation has significantly advanced through diffusion models aimed at producing images with readable and realistic text. Recent works primarily use a ControlNet-based framework, employing standard font text images to control diffusion models. Recognizing the critical role of control information in generating high-quality text, we investigate its influence from three perspectives: input encoding, role at different stages, and output features. Our findings reveal that: 1) Input control information has unique characteristics compared to conventional inputs like Canny edges and depth maps. 2) Control information plays distinct roles at different stages of the denoising process. 3) Output control features significantly differ from the base and skip features of the U-Net decoder in the frequency domain. Based on these insights, we propose TextGen, a novel framework designed to enhance generation quality by optimizing control information. We improve input and output features using Fourier analysis to emphasize relevant information and reduce noise. Additionally, we employ a two-stage generation framework to align the different roles of control information at different stages. Furthermore, we introduce an effective and lightweight dataset for training. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in both Chinese and English text generation. The code and dataset will be made available.
Focus on the Whole Character: Discriminative Character Modeling for Scene Text Recognition
Jul 08, 2024Abstract:Recently, scene text recognition (STR) models have shown significant performance improvements. However, existing models still encounter difficulties in recognizing challenging texts that involve factors such as severely distorted and perspective characters. These challenging texts mainly cause two problems: (1) Large Intra-Class Variance. (2) Small Inter-Class Variance. An extremely distorted character may prominently differ visually from other characters within the same category, while the variance between characters from different classes is relatively small. To address the above issues, we propose a novel method that enriches the character features to enhance the discriminability of characters. Firstly, we propose the Character-Aware Constraint Encoder (CACE) with multiple blocks stacked. CACE introduces a decay matrix in each block to explicitly guide the attention region for each token. By continuously employing the decay matrix, CACE enables tokens to perceive morphological information at the character level. Secondly, an Intra-Inter Consistency Loss (I^2CL) is introduced to consider intra-class compactness and inter-class separability at feature space. I^2CL improves the discriminative capability of features by learning a long-term memory unit for each character category. Trained with synthetic data, our model achieves state-of-the-art performance on common benchmarks (94.1% accuracy) and Union14M-Benchmark (61.6% accuracy). Code is available at https://github.com/bang123-box/CFE.
Self-Supervised Pre-training with Symmetric Superimposition Modeling for Scene Text Recognition
May 11, 2024



Abstract:In text recognition, self-supervised pre-training emerges as a good solution to reduce dependence on expansive annotated real data. Previous studies primarily focus on local visual representation by leveraging mask image modeling or sequence contrastive learning. However, they omit modeling the linguistic information in text images, which is crucial for recognizing text. To simultaneously capture local character features and linguistic information in visual space, we propose Symmetric Superimposition Modeling (SSM). The objective of SSM is to reconstruct the direction-specific pixel and feature signals from the symmetrically superimposed input. Specifically, we add the original image with its inverted views to create the symmetrically superimposed inputs. At the pixel level, we reconstruct the original and inverted images to capture character shapes and texture-level linguistic context. At the feature level, we reconstruct the feature of the same original image and inverted image with different augmentations to model the semantic-level linguistic context and the local character discrimination. In our design, we disrupt the character shape and linguistic rules. Consequently, the dual-level reconstruction facilitates understanding character shapes and linguistic information from the perspective of visual texture and feature semantics. Experiments on various text recognition benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness and generality of SSM, with 4.1% average performance gains and 86.6% new state-of-the-art average word accuracy on Union14M benchmarks. The code is available at https://github.com/FaltingsA/SSM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge