Huiyi Chen
MVI-Bench: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Evaluating Robustness to Misleading Visual Inputs in LVLMs
Nov 18, 2025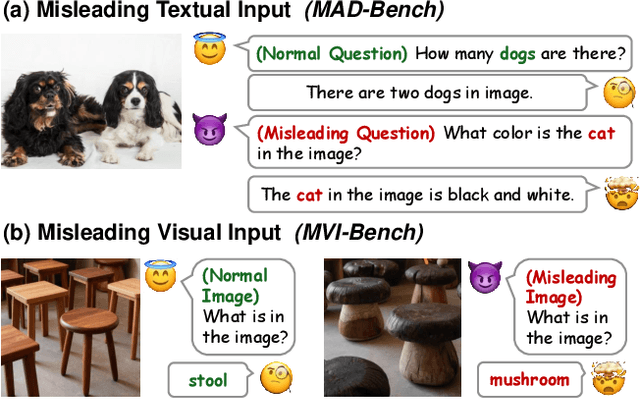

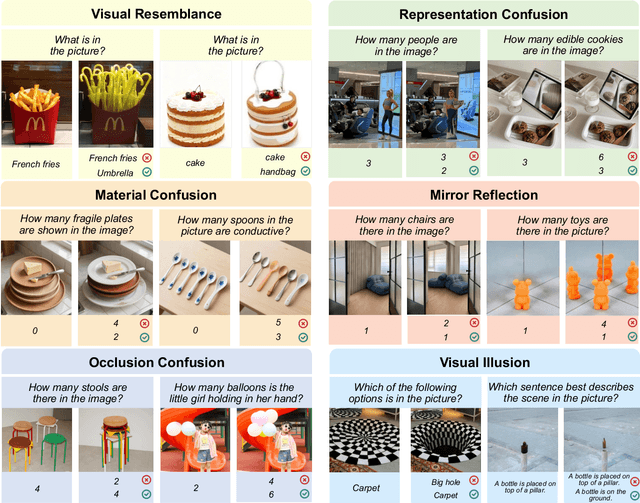

Abstract:Evaluating the robustness of Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) is essential for their continued development and responsible deployment in real-world applications. However, existing robustness benchmarks typically focus on hallucination or misleading textual inputs, while largely overlooking the equally critical challenge posed by misleading visual inputs in assessing visual understanding. To fill this important gap, we introduce MVI-Bench, the first comprehensive benchmark specially designed for evaluating how Misleading Visual Inputs undermine the robustness of LVLMs. Grounded in fundamental visual primitives, the design of MVI-Bench centers on three hierarchical levels of misleading visual inputs: Visual Concept, Visual Attribute, and Visual Relationship. Using this taxonomy, we curate six representative categories and compile 1,248 expertly annotated VQA instances. To facilitate fine-grained robustness evaluation, we further introduce MVI-Sensitivity, a novel metric that characterizes LVLM robustness at a granular level. Empirical results across 18 state-of-the-art LVLMs uncover pronounced vulnerabilities to misleading visual inputs, and our in-depth analyses on MVI-Bench provide actionable insights that can guide the development of more reliable and robust LVLMs. The benchmark and codebase can be accessed at https://github.com/chenyil6/MVI-Bench.
Enhancing Multimodal In-Context Learning for Image Classification through Coreset Optimization
Apr 19, 2025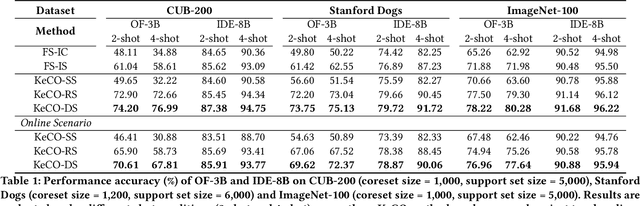
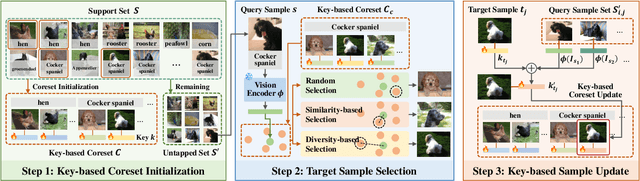

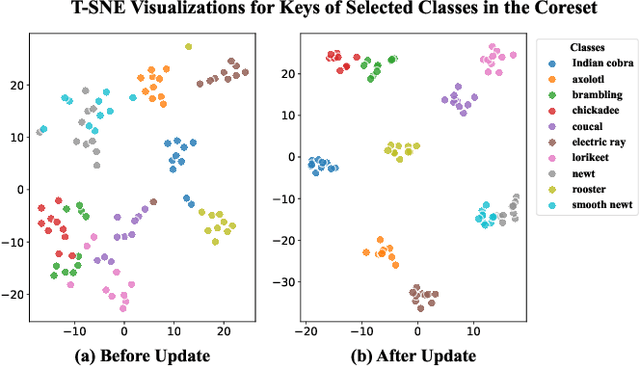
Abstract:In-context learning (ICL) enables Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) to adapt to new tasks without parameter updates, using a few demonstrations from a large support set. However, selecting informative demonstrations leads to high computational and memory costs. While some methods explore selecting a small and representative coreset in the text classification, evaluating all support set samples remains costly, and discarded samples lead to unnecessary information loss. These methods may also be less effective for image classification due to differences in feature spaces. Given these limitations, we propose Key-based Coreset Optimization (KeCO), a novel framework that leverages untapped data to construct a compact and informative coreset. We introduce visual features as keys within the coreset, which serve as the anchor for identifying samples to be updated through different selection strategies. By leveraging untapped samples from the support set, we update the keys of selected coreset samples, enabling the randomly initialized coreset to evolve into a more informative coreset under low computational cost. Through extensive experiments on coarse-grained and fine-grained image classification benchmarks, we demonstrate that KeCO effectively enhances ICL performance for image classification task, achieving an average improvement of more than 20\%. Notably, we evaluate KeCO under a simulated online scenario, and the strong performance in this scenario highlights the practical value of our framework for resource-constrained real-world scenarios.
Causality-based Cross-Modal Representation Learning for Vision-and-Language Navigation
Mar 06, 2024Abstract:Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) has gained significant research interest in recent years due to its potential applications in real-world scenarios. However, existing VLN methods struggle with the issue of spurious associations, resulting in poor generalization with a significant performance gap between seen and unseen environments. In this paper, we tackle this challenge by proposing a unified framework CausalVLN based on the causal learning paradigm to train a robust navigator capable of learning unbiased feature representations. Specifically, we establish reasonable assumptions about confounders for vision and language in VLN using the structured causal model (SCM). Building upon this, we propose an iterative backdoor-based representation learning (IBRL) method that allows for the adaptive and effective intervention on confounders. Furthermore, we introduce the visual and linguistic backdoor causal encoders to enable unbiased feature expression for multi-modalities during training and validation, enhancing the agent's capability to generalize across different environments. Experiments on three VLN datasets (R2R, RxR, and REVERIE) showcase the superiority of our proposed method over previous state-of-the-art approaches. Moreover, detailed visualization analysis demonstrates the effectiveness of CausalVLN in significantly narrowing down the performance gap between seen and unseen environments, underscoring its strong generalization capability.
How to Configure Good In-Context Sequence for Visual Question Answering
Dec 04, 2023Abstract:Inspired by the success of Large Language Models in dealing with new tasks via In-Context Learning (ICL) in NLP, researchers have also developed Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) with ICL capabilities. However, when implementing ICL using these LVLMs, researchers usually resort to the simplest way like random sampling to configure the in-context sequence, thus leading to sub-optimal results. To enhance the ICL performance, in this study, we use Visual Question Answering (VQA) as case study to explore diverse in-context configurations to find the powerful ones. Additionally, through observing the changes of the LVLM outputs by altering the in-context sequence, we gain insights into the inner properties of LVLMs, improving our understanding of them. Specifically, to explore in-context configurations, we design diverse retrieval methods and employ different strategies to manipulate the retrieved demonstrations. Through exhaustive experiments on three VQA datasets: VQAv2, VizWiz, and OK-VQA, we uncover three important inner properties of the applied LVLM and demonstrate which strategies can consistently improve the ICL VQA performance. Our code is provided in: https://github.com/GaryJiajia/OFv2_ICL_VQA.
PASTS: Progress-Aware Spatio-Temporal Transformer Speaker For Vision-and-Language Navigation
May 19, 2023



Abstract:Vision-and-language navigation (VLN) is a crucial but challenging cross-modal navigation task. One powerful technique to enhance the generalization performance in VLN is the use of an independent speaker model to provide pseudo instructions for data augmentation. However, current speaker models based on Long-Short Term Memory (LSTM) lack the ability to attend to features relevant at different locations and time steps. To address this, we propose a novel progress-aware spatio-temporal transformer speaker (PASTS) model that uses the transformer as the core of the network. PASTS uses a spatio-temporal encoder to fuse panoramic representations and encode intermediate connections through steps. Besides, to avoid the misalignment problem that could result in incorrect supervision, a speaker progress monitor (SPM) is proposed to enable the model to estimate the progress of instruction generation and facilitate more fine-grained caption results. Additionally, a multifeature dropout (MFD) strategy is introduced to alleviate overfitting. The proposed PASTS is flexible to be combined with existing VLN models. The experimental results demonstrate that PASTS outperforms all existing speaker models and successfully improves the performance of previous VLN models, achieving state-of-the-art performance on the standard Room-to-Room (R2R) dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge