Jiawei Peng
MVI-Bench: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Evaluating Robustness to Misleading Visual Inputs in LVLMs
Nov 18, 2025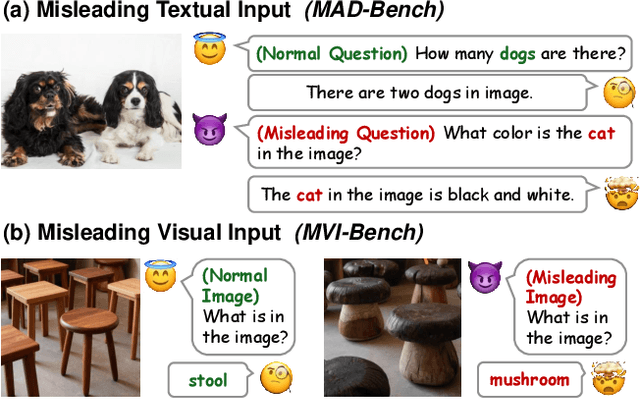

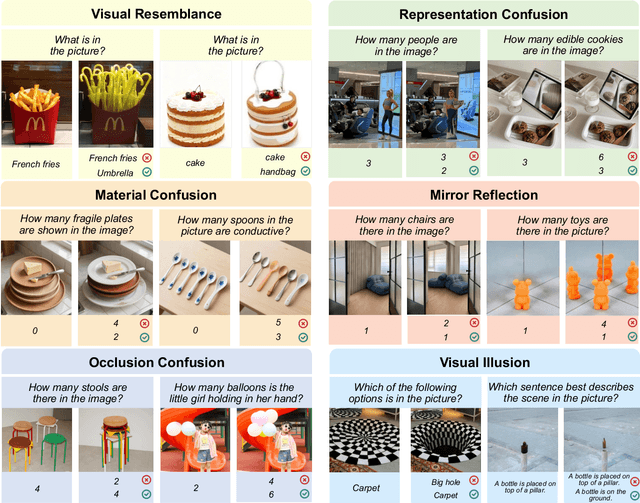

Abstract:Evaluating the robustness of Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) is essential for their continued development and responsible deployment in real-world applications. However, existing robustness benchmarks typically focus on hallucination or misleading textual inputs, while largely overlooking the equally critical challenge posed by misleading visual inputs in assessing visual understanding. To fill this important gap, we introduce MVI-Bench, the first comprehensive benchmark specially designed for evaluating how Misleading Visual Inputs undermine the robustness of LVLMs. Grounded in fundamental visual primitives, the design of MVI-Bench centers on three hierarchical levels of misleading visual inputs: Visual Concept, Visual Attribute, and Visual Relationship. Using this taxonomy, we curate six representative categories and compile 1,248 expertly annotated VQA instances. To facilitate fine-grained robustness evaluation, we further introduce MVI-Sensitivity, a novel metric that characterizes LVLM robustness at a granular level. Empirical results across 18 state-of-the-art LVLMs uncover pronounced vulnerabilities to misleading visual inputs, and our in-depth analyses on MVI-Bench provide actionable insights that can guide the development of more reliable and robust LVLMs. The benchmark and codebase can be accessed at https://github.com/chenyil6/MVI-Bench.
Chemistry-Enhanced Diffusion-Based Framework for Small-to-Large Molecular Conformation Generation
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:Obtaining 3D conformations of realistic polyatomic molecules at the quantum chemistry level remains challenging, and although recent machine learning advances offer promise, predicting large-molecule structures still requires substantial computational effort. Here, we introduce StoL, a diffusion model-based framework that enables rapid and knowledge-free generation of large molecular structures from small-molecule data. Remarkably, StoL assembles molecules in a LEGO-style fashion from scratch, without seeing the target molecules or any structures of comparable size during training. Given a SMILES input, it decomposes the molecule into chemically valid fragments, generates their 3D structures with a diffusion model trained on small molecules, and assembles them into diverse conformations. This fragment-based strategy eliminates the need for large-molecule training data while maintaining high scalability and transferability. By embedding chemical principles into key steps, StoL ensures faster convergence, chemically rational structures, and broad configurational coverage, as confirmed against DFT calculations.
VReST: Enhancing Reasoning in Large Vision-Language Models through Tree Search and Self-Reward Mechanism
Jun 10, 2025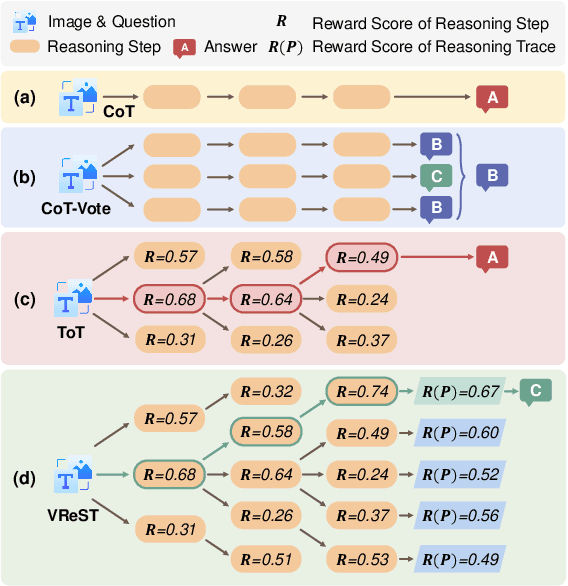
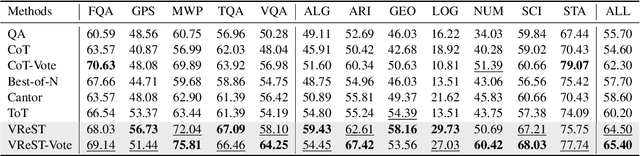
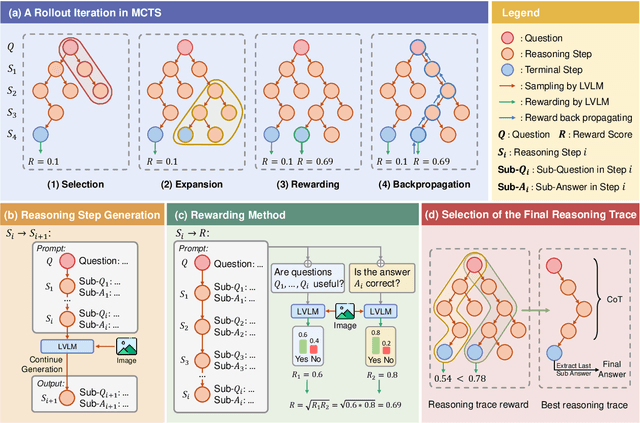
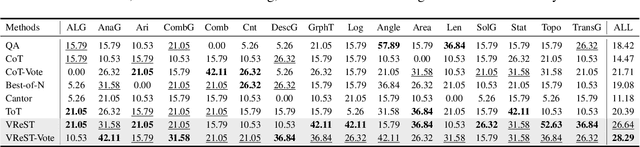
Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have shown exceptional performance in multimodal tasks, but their effectiveness in complex visual reasoning is still constrained, especially when employing Chain-of-Thought prompting techniques. In this paper, we propose VReST, a novel training-free approach that enhances Reasoning in LVLMs through Monte Carlo Tree Search and Self-Reward mechanisms. VReST meticulously traverses the reasoning landscape by establishing a search tree, where each node encapsulates a reasoning step, and each path delineates a comprehensive reasoning sequence. Our innovative multimodal Self-Reward mechanism assesses the quality of reasoning steps by integrating the utility of sub-questions, answer correctness, and the relevance of vision-language clues, all without the need for additional models. VReST surpasses current prompting methods and secures state-of-the-art performance across three multimodal mathematical reasoning benchmarks. Furthermore, it substantiates the efficacy of test-time scaling laws in multimodal tasks, offering a promising direction for future research.
PartInstruct: Part-level Instruction Following for Fine-grained Robot Manipulation
May 27, 2025Abstract:Fine-grained robot manipulation, such as lifting and rotating a bottle to display the label on the cap, requires robust reasoning about object parts and their relationships with intended tasks. Despite recent advances in training general-purpose robot manipulation policies guided by language instructions, there is a notable lack of large-scale datasets for fine-grained manipulation tasks with part-level instructions and diverse 3D object instances annotated with part-level labels. In this work, we introduce PartInstruct, the first large-scale benchmark for training and evaluating fine-grained robot manipulation models using part-level instructions. PartInstruct comprises 513 object instances across 14 categories, each annotated with part-level information, and 1302 fine-grained manipulation tasks organized into 16 task classes. Our training set consists of over 10,000 expert demonstrations synthesized in a 3D simulator, where each demonstration is paired with a high-level task instruction, a chain of base part-based skill instructions, and ground-truth 3D information about the object and its parts. Additionally, we designed a comprehensive test suite to evaluate the generalizability of learned policies across new states, objects, and tasks. We evaluated several state-of-the-art robot manipulation approaches, including end-to-end vision-language policy learning and bi-level planning models for robot manipulation on our benchmark. The experimental results reveal that current models struggle to robustly ground part concepts and predict actions in 3D space, and face challenges when manipulating object parts in long-horizon tasks.
Enhancing Multimodal In-Context Learning for Image Classification through Coreset Optimization
Apr 19, 2025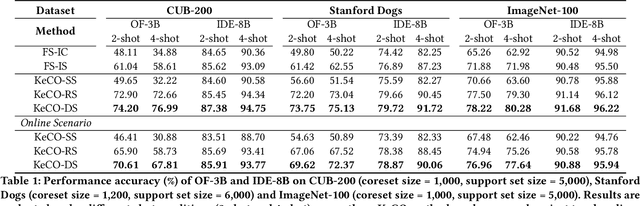
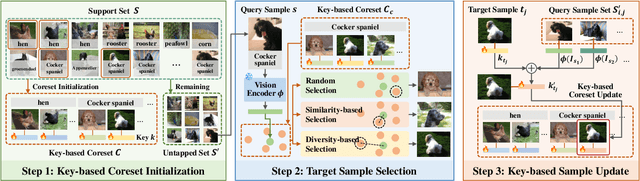

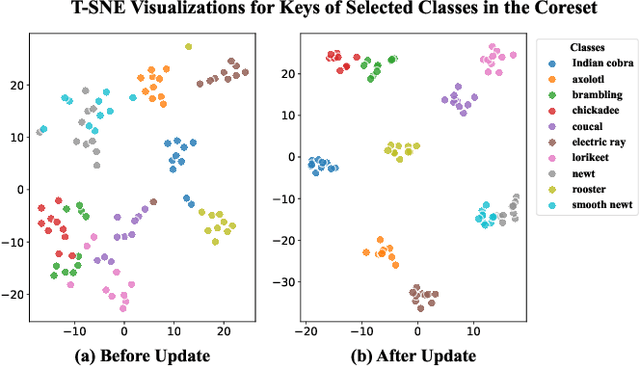
Abstract:In-context learning (ICL) enables Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) to adapt to new tasks without parameter updates, using a few demonstrations from a large support set. However, selecting informative demonstrations leads to high computational and memory costs. While some methods explore selecting a small and representative coreset in the text classification, evaluating all support set samples remains costly, and discarded samples lead to unnecessary information loss. These methods may also be less effective for image classification due to differences in feature spaces. Given these limitations, we propose Key-based Coreset Optimization (KeCO), a novel framework that leverages untapped data to construct a compact and informative coreset. We introduce visual features as keys within the coreset, which serve as the anchor for identifying samples to be updated through different selection strategies. By leveraging untapped samples from the support set, we update the keys of selected coreset samples, enabling the randomly initialized coreset to evolve into a more informative coreset under low computational cost. Through extensive experiments on coarse-grained and fine-grained image classification benchmarks, we demonstrate that KeCO effectively enhances ICL performance for image classification task, achieving an average improvement of more than 20\%. Notably, we evaluate KeCO under a simulated online scenario, and the strong performance in this scenario highlights the practical value of our framework for resource-constrained real-world scenarios.
Learnable In-Context Vector for Visual Question Answering
Jun 19, 2024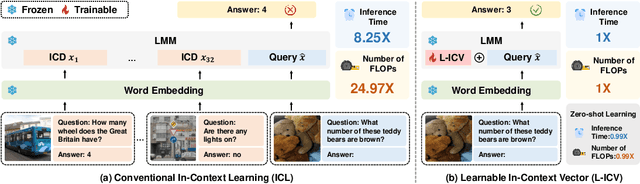
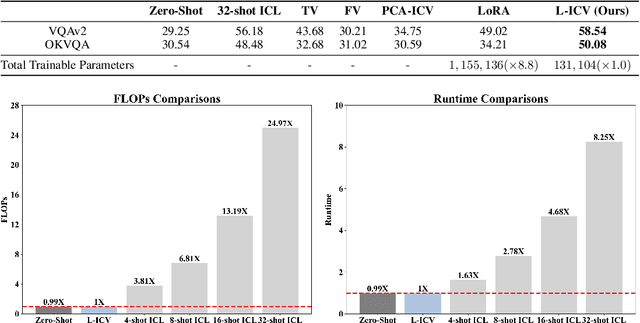
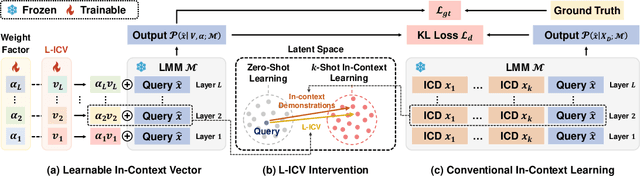
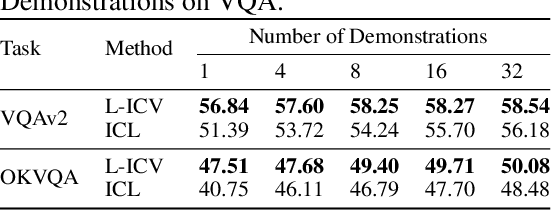
Abstract:As language models continue to scale, Large Language Models (LLMs) have exhibited emerging capabilities in In-Context Learning (ICL), enabling them to solve language tasks by prefixing a few in-context demonstrations (ICDs) as context. Inspired by these advancements, researchers have extended these techniques to develop Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) with ICL capabilities. However, applying ICL usually faces two major challenges: 1) using more ICDs will largely increase the inference time and 2) the performance is sensitive to the selection of ICDs. These challenges are further exacerbated in LMMs due to the integration of multiple data types and the combinational complexity of multimodal ICDs. Recently, to address these challenges, some NLP studies introduce non-learnable In-Context Vectors (ICVs) which extract useful task information from ICDs into a single vector and then insert it into the LLM to help solve the corresponding task. However, although useful in simple NLP tasks, these non-learnable methods fail to handle complex multimodal tasks like Visual Question Answering (VQA). In this study, we propose \textbf{Learnable ICV} (L-ICV) to distill essential task information from demonstrations, improving ICL performance in LMMs. Experiments show that L-ICV can significantly reduce computational costs while enhancing accuracy in VQA tasks compared to traditional ICL and other non-learnable ICV methods.
Exploring the Distinctiveness and Fidelity of the Descriptions Generated by Large Vision-Language Models
Apr 26, 2024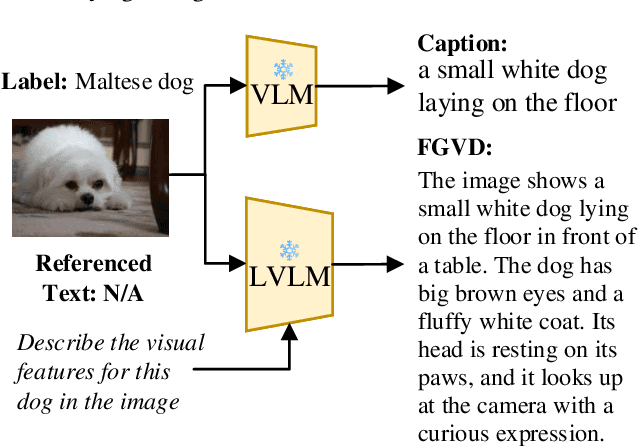
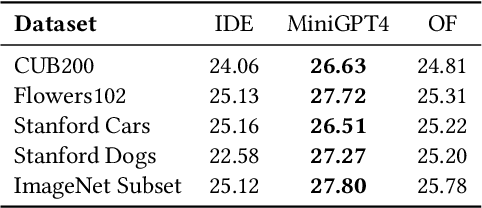
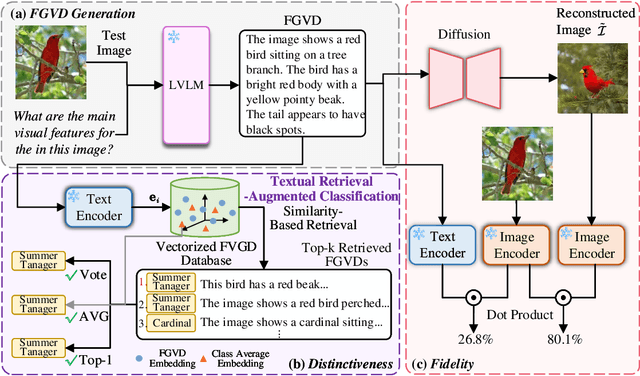
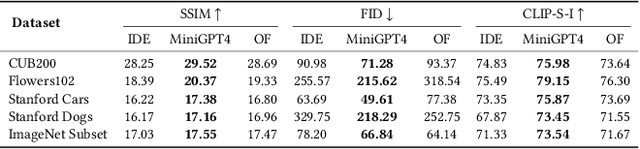
Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) are gaining traction for their remarkable ability to process and integrate visual and textual data. Despite their popularity, the capacity of LVLMs to generate precise, fine-grained textual descriptions has not been fully explored. This study addresses this gap by focusing on \textit{distinctiveness} and \textit{fidelity}, assessing how models like Open-Flamingo, IDEFICS, and MiniGPT-4 can distinguish between similar objects and accurately describe visual features. We proposed the Textual Retrieval-Augmented Classification (TRAC) framework, which, by leveraging its generative capabilities, allows us to delve deeper into analyzing fine-grained visual description generation. This research provides valuable insights into the generation quality of LVLMs, enhancing the understanding of multimodal language models. Notably, MiniGPT-4 stands out for its better ability to generate fine-grained descriptions, outperforming the other two models in this aspect. The code is provided at \url{https://anonymous.4open.science/r/Explore_FGVDs-E277}.
How to Configure Good In-Context Sequence for Visual Question Answering
Dec 04, 2023Abstract:Inspired by the success of Large Language Models in dealing with new tasks via In-Context Learning (ICL) in NLP, researchers have also developed Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) with ICL capabilities. However, when implementing ICL using these LVLMs, researchers usually resort to the simplest way like random sampling to configure the in-context sequence, thus leading to sub-optimal results. To enhance the ICL performance, in this study, we use Visual Question Answering (VQA) as case study to explore diverse in-context configurations to find the powerful ones. Additionally, through observing the changes of the LVLM outputs by altering the in-context sequence, we gain insights into the inner properties of LVLMs, improving our understanding of them. Specifically, to explore in-context configurations, we design diverse retrieval methods and employ different strategies to manipulate the retrieved demonstrations. Through exhaustive experiments on three VQA datasets: VQAv2, VizWiz, and OK-VQA, we uncover three important inner properties of the applied LVLM and demonstrate which strategies can consistently improve the ICL VQA performance. Our code is provided in: https://github.com/GaryJiajia/OFv2_ICL_VQA.
Learning Part Segmentation from Synthetic Animals
Nov 30, 2023



Abstract:Semantic part segmentation provides an intricate and interpretable understanding of an object, thereby benefiting numerous downstream tasks. However, the need for exhaustive annotations impedes its usage across diverse object types. This paper focuses on learning part segmentation from synthetic animals, leveraging the Skinned Multi-Animal Linear (SMAL) models to scale up existing synthetic data generated by computer-aided design (CAD) animal models. Compared to CAD models, SMAL models generate data with a wider range of poses observed in real-world scenarios. As a result, our first contribution is to construct a synthetic animal dataset of tigers and horses with more pose diversity, termed Synthetic Animal Parts (SAP). We then benchmark Syn-to-Real animal part segmentation from SAP to PartImageNet, namely SynRealPart, with existing semantic segmentation domain adaptation methods and further improve them as our second contribution. Concretely, we examine three Syn-to-Real adaptation methods but observe relative performance drop due to the innate difference between the two tasks. To address this, we propose a simple yet effective method called Class-Balanced Fourier Data Mixing (CB-FDM). Fourier Data Mixing aligns the spectral amplitudes of synthetic images with real images, thereby making the mixed images have more similar frequency content to real images. We further use Class-Balanced Pseudo-Label Re-Weighting to alleviate the imbalanced class distribution. We demonstrate the efficacy of CB-FDM on SynRealPart over previous methods with significant performance improvements. Remarkably, our third contribution is to reveal that the learned parts from synthetic tiger and horse are transferable across all quadrupeds in PartImageNet, further underscoring the utility and potential applications of animal part segmentation.
Animal3D: A Comprehensive Dataset of 3D Animal Pose and Shape
Aug 22, 2023



Abstract:Accurately estimating the 3D pose and shape is an essential step towards understanding animal behavior, and can potentially benefit many downstream applications, such as wildlife conservation. However, research in this area is held back by the lack of a comprehensive and diverse dataset with high-quality 3D pose and shape annotations. In this paper, we propose Animal3D, the first comprehensive dataset for mammal animal 3D pose and shape estimation. Animal3D consists of 3379 images collected from 40 mammal species, high-quality annotations of 26 keypoints, and importantly the pose and shape parameters of the SMAL model. All annotations were labeled and checked manually in a multi-stage process to ensure highest quality results. Based on the Animal3D dataset, we benchmark representative shape and pose estimation models at: (1) supervised learning from only the Animal3D data, (2) synthetic to real transfer from synthetically generated images, and (3) fine-tuning human pose and shape estimation models. Our experimental results demonstrate that predicting the 3D shape and pose of animals across species remains a very challenging task, despite significant advances in human pose estimation. Our results further demonstrate that synthetic pre-training is a viable strategy to boost the model performance. Overall, Animal3D opens new directions for facilitating future research in animal 3D pose and shape estimation, and is publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge