Jianxin Wang
Rethinking Generative Recommender Tokenizer: Recsys-Native Encoding and Semantic Quantization Beyond LLMs
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Semantic ID (SID)-based recommendation is a promising paradigm for scaling sequential recommender systems, but existing methods largely follow a semantic-centric pipeline: item embeddings are learned from foundation models and discretized using generic quantization schemes. This design is misaligned with generative recommendation objectives: semantic embeddings are weakly coupled with collaborative prediction, and generic quantization is inefficient at reducing sequential uncertainty for autoregressive modeling. To address these, we propose ReSID, a recommendation-native, principled SID framework that rethinks representation learning and quantization from the perspective of information preservation and sequential predictability, without relying on LLMs. ReSID consists of two components: (i) Field-Aware Masked Auto-Encoding (FAMAE), which learns predictive-sufficient item representations from structured features, and (ii) Globally Aligned Orthogonal Quantization (GAOQ), which produces compact and predictable SID sequences by jointly reducing semantic ambiguity and prefix-conditional uncertainty. Theoretical analysis and extensive experiments across ten datasets show the effectiveness of ReSID. ReSID consistently outperforms strong sequential and SID-based generative baselines by an average of over 10%, while reducing tokenization cost by up to 122x. Code is available at https://github.com/FuCongResearchSquad/ReSID.
Spatially Generalizable Mobile Manipulation via Adaptive Experience Selection and Dynamic Imagination
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Mobile Manipulation (MM) involves long-horizon decision-making over multi-stage compositions of heterogeneous skills, such as navigation and picking up objects. Despite recent progress, existing MM methods still face two key limitations: (i) low sample efficiency, due to ineffective use of redundant data generated during long-term MM interactions; and (ii) poor spatial generalization, as policies trained on specific tasks struggle to transfer to new spatial layouts without additional training. In this paper, we address these challenges through Adaptive Experience Selection (AES) and model-based dynamic imagination. In particular, AES makes MM agents pay more attention to critical experience fragments in long trajectories that affect task success, improving skill chain learning and mitigating skill forgetting. Based on AES, a Recurrent State-Space Model (RSSM) is introduced for Model-Predictive Forward Planning (MPFP) by capturing the coupled dynamics between the mobile base and the manipulator and imagining the dynamics of future manipulations. RSSM-based MPFP can reinforce MM skill learning on the current task while enabling effective generalization to new spatial layouts. Comparative studies across different experimental configurations demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing MM policies. Real-world experiments further validate the feasibility and practicality of our method.
DisCo-FLoc: Using Dual-Level Visual-Geometric Contrasts to Disambiguate Depth-Aware Visual Floorplan Localization
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Since floorplan data is readily available, long-term persistent, and robust to changes in visual appearance, visual Floorplan Localization (FLoc) has garnered significant attention. Existing methods either ingeniously match geometric priors or utilize sparse semantics to reduce FLoc uncertainty. However, they still suffer from ambiguous FLoc caused by repetitive structures within minimalist floorplans. Moreover, expensive but limited semantic annotations restrict their applicability. To address these issues, we propose DisCo-FLoc, which utilizes dual-level visual-geometric Contrasts to Disambiguate depth-aware visual Floc, without requiring additional semantic labels. Our solution begins with a ray regression predictor tailored for ray-casting-based FLoc, predicting a series of FLoc candidates using depth estimation expertise. In addition, a novel contrastive learning method with position-level and orientation-level constraints is proposed to strictly match depth-aware visual features with the corresponding geometric structures in the floorplan. Such matches can effectively eliminate FLoc ambiguity and select the optimal imaging pose from FLoc candidates. Exhaustive comparative studies on two standard visual Floc benchmarks demonstrate that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art semantic-based method, achieving significant improvements in both robustness and accuracy.
Diversity-Guided MLP Reduction for Efficient Large Vision Transformers
Jun 10, 2025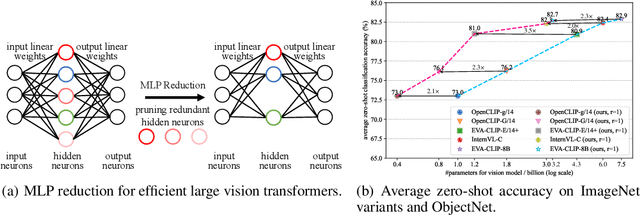
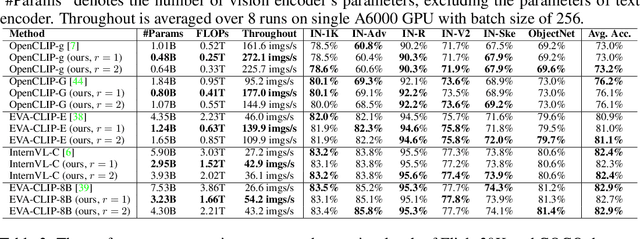
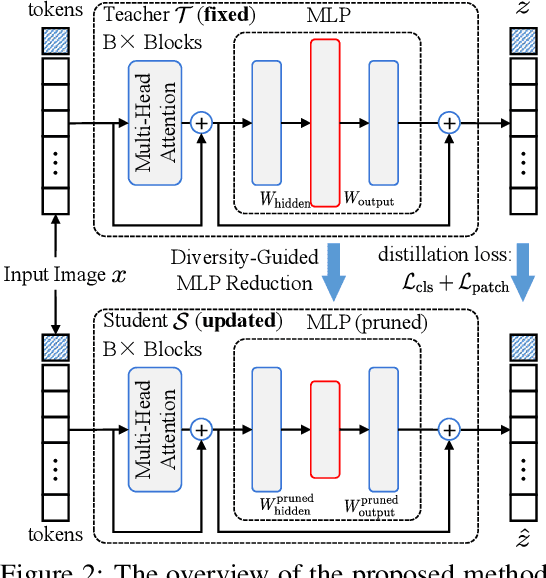
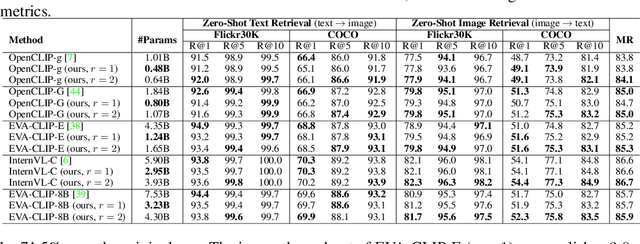
Abstract:Transformer models achieve excellent scaling property, where the performance is improved with the increment of model capacity. However, large-scale model parameters lead to an unaffordable cost of computing and memory. We analyze popular transformer architectures and find that multilayer perceptron (MLP) modules take up the majority of model parameters. To this end, we focus on the recoverability of the compressed models and propose a Diversity-Guided MLP Reduction (DGMR) method to significantly reduce the parameters of large vision transformers with only negligible performance degradation. Specifically, we conduct a Gram-Schmidt weight pruning strategy to eliminate redundant neurons of MLP hidden layer, while preserving weight diversity for better performance recover during distillation. Compared to the model trained from scratch, our pruned model only requires 0.06\% data of LAION-2B (for the training of large vision transformers) without labels (ImageNet-1K) to recover the original performance. Experimental results on several state-of-the-art large vision transformers demonstrate that our method achieves a more than 57.0\% parameter and FLOPs reduction in a near lossless manner. Notably, for EVA-CLIP-E (4.4B), our method accomplishes a 71.5\% parameter and FLOPs reduction without performance degradation. The source code and trained weights are available at https://github.com/visresearch/DGMR.
Multiple Object Stitching for Unsupervised Representation Learning
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Contrastive learning for single object centric images has achieved remarkable progress on unsupervised representation, but suffering inferior performance on the widespread images with multiple objects. In this paper, we propose a simple but effective method, Multiple Object Stitching (MOS), to refine the unsupervised representation for multi-object images. Specifically, we construct the multi-object images by stitching the single object centric ones, where the objects in the synthesized multi-object images are predetermined. Hence, compared to the existing contrastive methods, our method provides additional object correspondences between multi-object images without human annotations. In this manner, our method pays more attention to the representations of each object in multi-object image, thus providing more detailed representations for complicated downstream tasks, such as object detection and semantic segmentation. Experimental results on ImageNet, CIFAR and COCO datasets demonstrate that our proposed method achieves the leading unsupervised representation performance on both single object centric images and multi-object ones. The source code is available at https://github.com/visresearch/MultipleObjectStitching.
BiBLDR: Bidirectional Behavior Learning for Drug Repositioning
May 29, 2025Abstract:Drug repositioning aims to identify potential new indications for existing drugs to reduce the time and financial costs associated with developing new drugs. Most existing deep learning-based drug repositioning methods predominantly utilize graph-based representations. However, graph-based drug repositioning methods struggle to perform effective inference in cold-start scenarios involving novel drugs because of the lack of association information with the diseases. Unlike traditional graph-based approaches, we propose a bidirectional behavior learning strategy for drug repositioning, known as BiBLDR. This innovative framework redefines drug repositioning as a behavior sequential learning task to capture drug-disease interaction patterns. First, we construct bidirectional behavioral sequences based on drug and disease sides. The consideration of bidirectional information ensures a more meticulous and rigorous characterization of the behavioral sequences. Subsequently, we propose a two-stage strategy for drug repositioning. In the first stage, we construct prototype spaces to characterize the representational attributes of drugs and diseases. In the second stage, these refined prototypes and bidirectional behavior sequence data are leveraged to predict potential drug-disease associations. Based on this learning approach, the model can more robustly and precisely capture the interactive relationships between drug and disease features from bidirectional behavioral sequences. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on benchmark datasets. Meanwhile, BiBLDR demonstrates significantly superior performance compared to previous methods in cold-start scenarios. Our code is published in https://github.com/Renyeeah/BiBLDR.
PartInstruct: Part-level Instruction Following for Fine-grained Robot Manipulation
May 27, 2025Abstract:Fine-grained robot manipulation, such as lifting and rotating a bottle to display the label on the cap, requires robust reasoning about object parts and their relationships with intended tasks. Despite recent advances in training general-purpose robot manipulation policies guided by language instructions, there is a notable lack of large-scale datasets for fine-grained manipulation tasks with part-level instructions and diverse 3D object instances annotated with part-level labels. In this work, we introduce PartInstruct, the first large-scale benchmark for training and evaluating fine-grained robot manipulation models using part-level instructions. PartInstruct comprises 513 object instances across 14 categories, each annotated with part-level information, and 1302 fine-grained manipulation tasks organized into 16 task classes. Our training set consists of over 10,000 expert demonstrations synthesized in a 3D simulator, where each demonstration is paired with a high-level task instruction, a chain of base part-based skill instructions, and ground-truth 3D information about the object and its parts. Additionally, we designed a comprehensive test suite to evaluate the generalizability of learned policies across new states, objects, and tasks. We evaluated several state-of-the-art robot manipulation approaches, including end-to-end vision-language policy learning and bi-level planning models for robot manipulation on our benchmark. The experimental results reveal that current models struggle to robustly ground part concepts and predict actions in 3D space, and face challenges when manipulating object parts in long-horizon tasks.
DDO: Dual-Decision Optimization via Multi-Agent Collaboration for LLM-Based Medical Consultation
May 24, 2025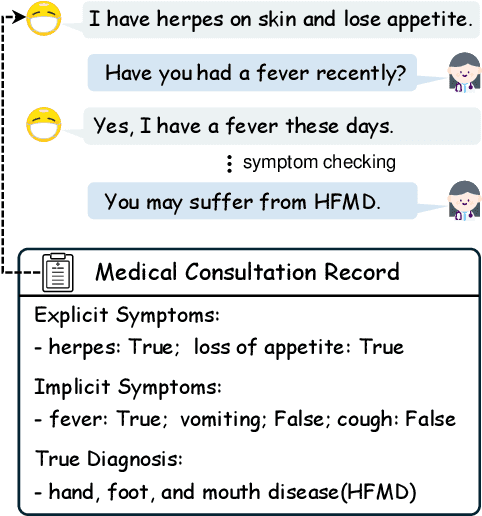
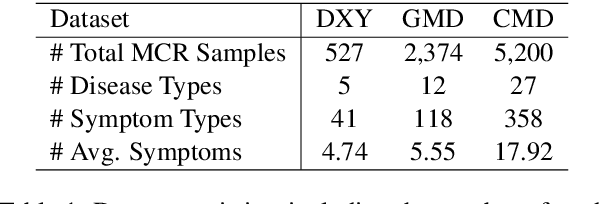
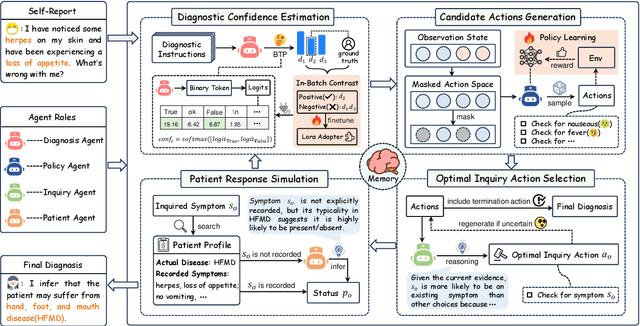
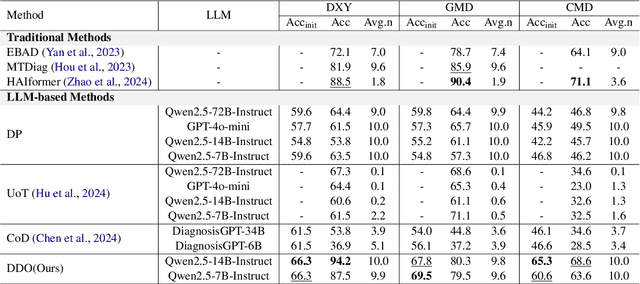
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate strong generalization and reasoning abilities, making them well-suited for complex decision-making tasks such as medical consultation (MC). However, existing LLM-based methods often fail to capture the dual nature of MC, which entails two distinct sub-tasks: symptom inquiry, a sequential decision-making process, and disease diagnosis, a classification problem. This mismatch often results in ineffective symptom inquiry and unreliable disease diagnosis. To address this, we propose \textbf{DDO}, a novel LLM-based framework that performs \textbf{D}ual-\textbf{D}ecision \textbf{O}ptimization by decoupling and independently optimizing the the two sub-tasks through a collaborative multi-agent workflow. Experiments on three real-world MC datasets show that DDO consistently outperforms existing LLM-based approaches and achieves competitive performance with state-of-the-art generation-based methods, demonstrating its effectiveness in the MC task.
CheXLearner: Text-Guided Fine-Grained Representation Learning for Progression Detection
May 11, 2025



Abstract:Temporal medical image analysis is essential for clinical decision-making, yet existing methods either align images and text at a coarse level - causing potential semantic mismatches - or depend solely on visual information, lacking medical semantic integration. We present CheXLearner, the first end-to-end framework that unifies anatomical region detection, Riemannian manifold-based structure alignment, and fine-grained regional semantic guidance. Our proposed Med-Manifold Alignment Module (Med-MAM) leverages hyperbolic geometry to robustly align anatomical structures and capture pathologically meaningful discrepancies across temporal chest X-rays. By introducing regional progression descriptions as supervision, CheXLearner achieves enhanced cross-modal representation learning and supports dynamic low-level feature optimization. Experiments show that CheXLearner achieves 81.12% (+17.2%) average accuracy and 80.32% (+11.05%) F1-score on anatomical region progression detection - substantially outperforming state-of-the-art baselines, especially in structurally complex regions. Additionally, our model attains a 91.52% average AUC score in downstream disease classification, validating its superior feature representation.
FIND: Fine-grained Information Density Guided Adaptive Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Disease Diagnosis
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Large Language Models (LLMs), which integrate external knowledge into LLMs, have shown remarkable performance in various medical domains, including clinical diagnosis. However, existing RAG methods struggle to effectively assess task difficulty to make retrieval decisions, thereby failing to meet the clinical requirements for balancing efficiency and accuracy. So in this paper, we propose FIND (\textbf{F}ine-grained \textbf{In}formation \textbf{D}ensity Guided Adaptive RAG), a novel framework that improves the reliability of RAG in disease diagnosis scenarios. FIND incorporates a fine-grained adaptive control module to determine whether retrieval is necessary based on the information density of the input. By optimizing the retrieval process and implementing a knowledge filtering module, FIND ensures that the retrieval is better suited to clinical scenarios. Experiments on three Chinese electronic medical record datasets demonstrate that FIND significantly outperforms various baseline methods, highlighting its effectiveness in clinical diagnosis tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge