Zichen Wang
Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
PKI: Prior Knowledge-Infused Neural Network for Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Few-shot class-incremental learning (FSCIL) aims to continually adapt a model on a limited number of new-class examples, facing two well-known challenges: catastrophic forgetting and overfitting to new classes. Existing methods tend to freeze more parts of network components and finetune others with an extra memory during incremental sessions. These methods emphasize preserving prior knowledge to ensure proficiency in recognizing old classes, thereby mitigating catastrophic forgetting. Meanwhile, constraining fewer parameters can help in overcoming overfitting with the assistance of prior knowledge. Following previous methods, we retain more prior knowledge and propose a prior knowledge-infused neural network (PKI) to facilitate FSCIL. PKI consists of a backbone, an ensemble of projectors, a classifier, and an extra memory. In each incremental session, we build a new projector and add it to the ensemble. Subsequently, we finetune the new projector and the classifier jointly with other frozen network components, ensuring the rich prior knowledge is utilized effectively. By cascading projectors, PKI integrates prior knowledge accumulated from previous sessions and learns new knowledge flexibly, which helps to recognize old classes and efficiently learn new classes. Further, to reduce the resource consumption associated with keeping many projectors, we design two variants of the prior knowledge-infused neural network (PKIV-1 and PKIV-2) to trade off a balance between resource consumption and performance by reducing the number of projectors. Extensive experiments on three popular benchmarks demonstrate that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
Computational Mapping of Reactive Stroma in Prostate Cancer Yields Interpretable, Prognostic Biomarkers
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:Current histopathological grading of prostate cancer relies primarily on glandular architecture, largely overlooking the tumor microenvironment. Here, we present PROTAS, a deep learning framework that quantifies reactive stroma (RS) in routine hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) slides and links stromal morphology to underlying biology. PROTAS-defined RS is characterized by nuclear enlargement, collagen disorganization, and transcriptomic enrichment of contractile pathways. PROTAS detects RS robustly in the external Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian (PLCO) dataset and, using domain-adversarial training, generalizes to diagnostic biopsies. In head-to-head comparisons, PROTAS outperforms pathologists for RS detection, and spatial RS features predict biochemical recurrence independently of established prognostic variables (c-index 0.80). By capturing subtle stromal phenotypes associated with tumor progression, PROTAS provides an interpretable, scalable biomarker to refine risk stratification.
MoE3D: A Mixture-of-Experts Module for 3D Reconstruction
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:MoE3D is a mixture-of-experts module designed to sharpen depth boundaries and mitigate flying-point artifacts (highlighted in red) of existing feed-forward 3D reconstruction models (left side). MoE3D predicts multiple candidate depth maps and fuses them via dynamic weighting (visualized by MoE weights on the right side). When integrated with a pre-trained 3D reconstruction backbone such as VGGT, it substantially enhances reconstruction quality with minimal additional computational overhead. Best viewed digitally.
SITA: A Framework for Structure-to-Instance Theorem Autoformalization
Nov 13, 2025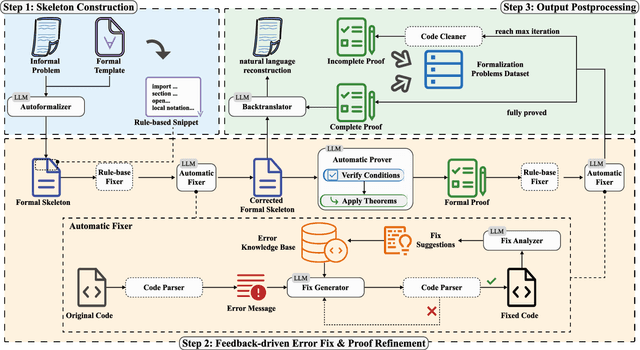
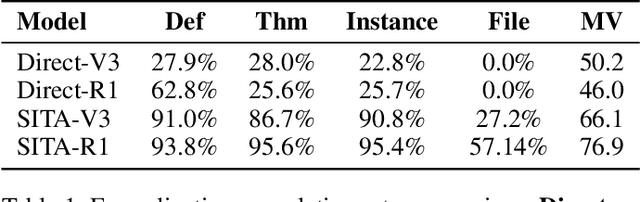
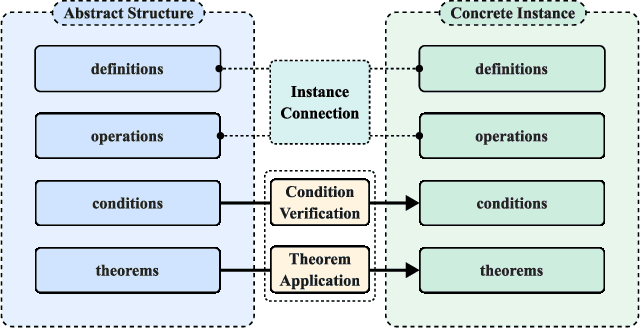
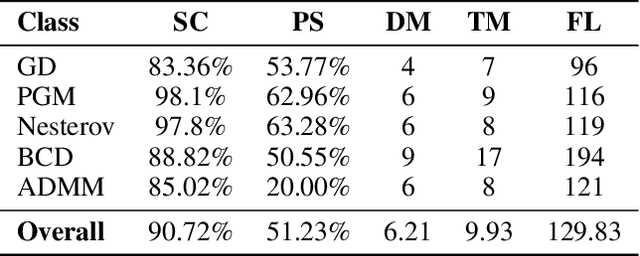
Abstract:While large language models (LLMs) have shown progress in mathematical reasoning, they still face challenges in formalizing theorems that arise from instantiating abstract structures in concrete settings. With the goal of auto-formalizing mathematical results at the research level, we develop a framework for structure-to-instance theorem autoformalization (SITA), which systematically bridges the gap between abstract mathematical theories and their concrete applications in Lean proof assistant. Formalized abstract structures are treated as modular templates that contain definitions, assumptions, operations, and theorems. These templates serve as reusable guides for the formalization of concrete instances. Given a specific instantiation, we generate corresponding Lean definitions and instance declarations, integrate them using Lean's typeclass mechanism, and construct verified theorems by checking structural assumptions. We incorporate LLM-based generation with feedback-guided refinement to ensure both automation and formal correctness. Experiments on a dataset of optimization problems demonstrate that SITA effectively formalizes diverse instances grounded in abstract structures.
DreamSwapV: Mask-guided Subject Swapping for Any Customized Video Editing
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:With the rapid progress of video generation, demand for customized video editing is surging, where subject swapping constitutes a key component yet remains under-explored. Prevailing swapping approaches either specialize in narrow domains--such as human-body animation or hand-object interaction--or rely on some indirect editing paradigm or ambiguous text prompts that compromise final fidelity. In this paper, we propose DreamSwapV, a mask-guided, subject-agnostic, end-to-end framework that swaps any subject in any video for customization with a user-specified mask and reference image. To inject fine-grained guidance, we introduce multiple conditions and a dedicated condition fusion module that integrates them efficiently. In addition, an adaptive mask strategy is designed to accommodate subjects of varying scales and attributes, further improving interactions between the swapped subject and its surrounding context. Through our elaborate two-phase dataset construction and training scheme, our DreamSwapV outperforms existing methods, as validated by comprehensive experiments on VBench indicators and our first introduced DreamSwapV-Benchmark.
RTR-GS: 3D Gaussian Splatting for Inverse Rendering with Radiance Transfer and Reflection
Jul 10, 2025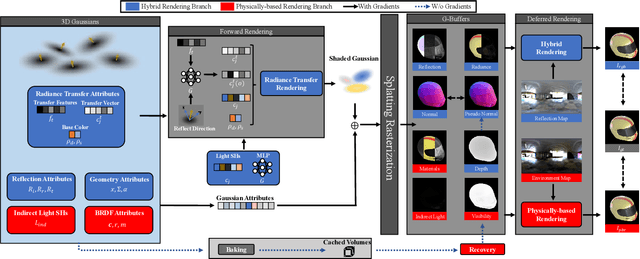
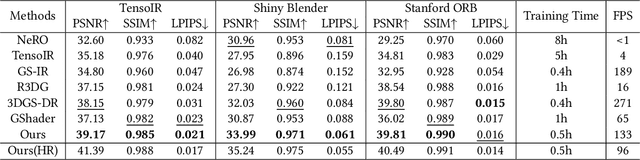
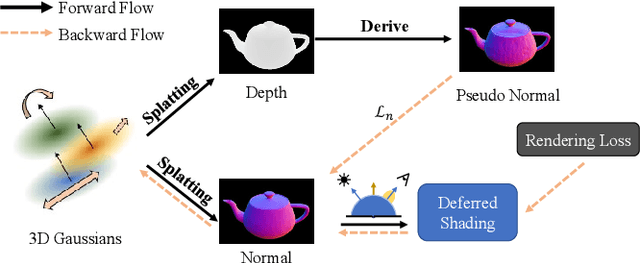
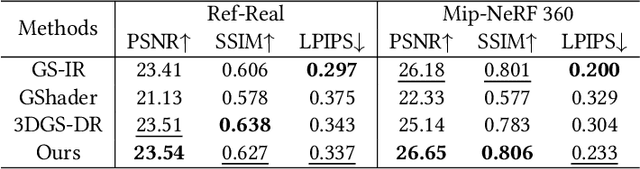
Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has demonstrated impressive capabilities in novel view synthesis. However, rendering reflective objects remains a significant challenge, particularly in inverse rendering and relighting. We introduce RTR-GS, a novel inverse rendering framework capable of robustly rendering objects with arbitrary reflectance properties, decomposing BRDF and lighting, and delivering credible relighting results. Given a collection of multi-view images, our method effectively recovers geometric structure through a hybrid rendering model that combines forward rendering for radiance transfer with deferred rendering for reflections. This approach successfully separates high-frequency and low-frequency appearances, mitigating floating artifacts caused by spherical harmonic overfitting when handling high-frequency details. We further refine BRDF and lighting decomposition using an additional physically-based deferred rendering branch. Experimental results show that our method enhances novel view synthesis, normal estimation, decomposition, and relighting while maintaining efficient training inference process.
Toward Rich Video Human-Motion2D Generation
Jun 17, 2025
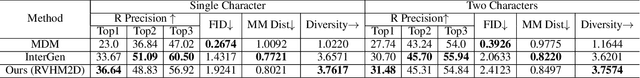
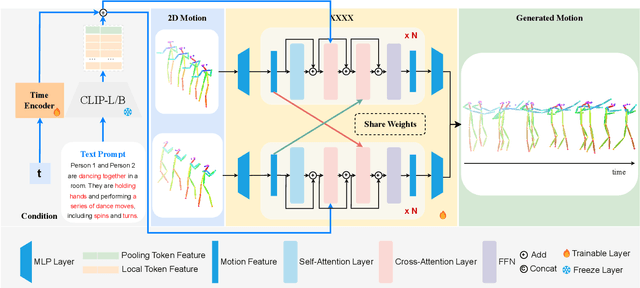
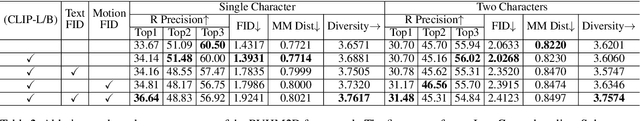
Abstract:Generating realistic and controllable human motions, particularly those involving rich multi-character interactions, remains a significant challenge due to data scarcity and the complexities of modeling inter-personal dynamics. To address these limitations, we first introduce a new large-scale rich video human motion 2D dataset (Motion2D-Video-150K) comprising 150,000 video sequences. Motion2D-Video-150K features a balanced distribution of diverse single-character and, crucially, double-character interactive actions, each paired with detailed textual descriptions. Building upon this dataset, we propose a novel diffusion-based rich video human motion2D generation (RVHM2D) model. RVHM2D incorporates an enhanced textual conditioning mechanism utilizing either dual text encoders (CLIP-L/B) or T5-XXL with both global and local features. We devise a two-stage training strategy: the model is first trained with a standard diffusion objective, and then fine-tuned using reinforcement learning with an FID-based reward to further enhance motion realism and text alignment. Extensive experiments demonstrate that RVHM2D achieves leading performance on the Motion2D-Video-150K benchmark in generating both single and interactive double-character scenarios.
VideoPDE: Unified Generative PDE Solving via Video Inpainting Diffusion Models
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:We present a unified framework for solving partial differential equations (PDEs) using video-inpainting diffusion transformer models. Unlike existing methods that devise specialized strategies for either forward or inverse problems under full or partial observation, our approach unifies these tasks under a single, flexible generative framework. Specifically, we recast PDE-solving as a generalized inpainting problem, e.g., treating forward prediction as inferring missing spatiotemporal information of future states from initial conditions. To this end, we design a transformer-based architecture that conditions on arbitrary patterns of known data to infer missing values across time and space. Our method proposes pixel-space video diffusion models for fine-grained, high-fidelity inpainting and conditioning, while enhancing computational efficiency through hierarchical modeling. Extensive experiments show that our video inpainting-based diffusion model offers an accurate and versatile solution across a wide range of PDEs and problem setups, outperforming state-of-the-art baselines.
Provably Efficient Algorithm for Best Scoring Rule Identification in Online Principal-Agent Information Acquisition
May 23, 2025Abstract:We investigate the problem of identifying the optimal scoring rule within the principal-agent framework for online information acquisition problem. We focus on the principal's perspective, seeking to determine the desired scoring rule through interactions with the agent. To address this challenge, we propose two algorithms: OIAFC and OIAFB, tailored for fixed confidence and fixed budget settings, respectively. Our theoretical analysis demonstrates that OIAFC can extract the desired $(\epsilon, \delta)$-scoring rule with a efficient instance-dependent sample complexity or an instance-independent sample complexity. Our analysis also shows that OIAFB matches the instance-independent performance bound of OIAFC, while both algorithms share the same complexity across fixed confidence and fixed budget settings.
Prototype-Guided Diffusion for Digital Pathology: Achieving Foundation Model Performance with Minimal Clinical Data
Apr 15, 2025
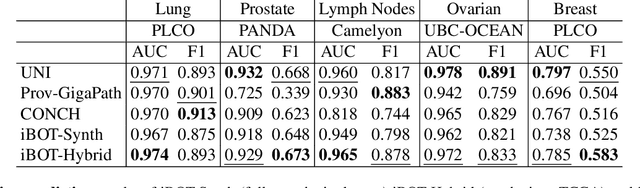
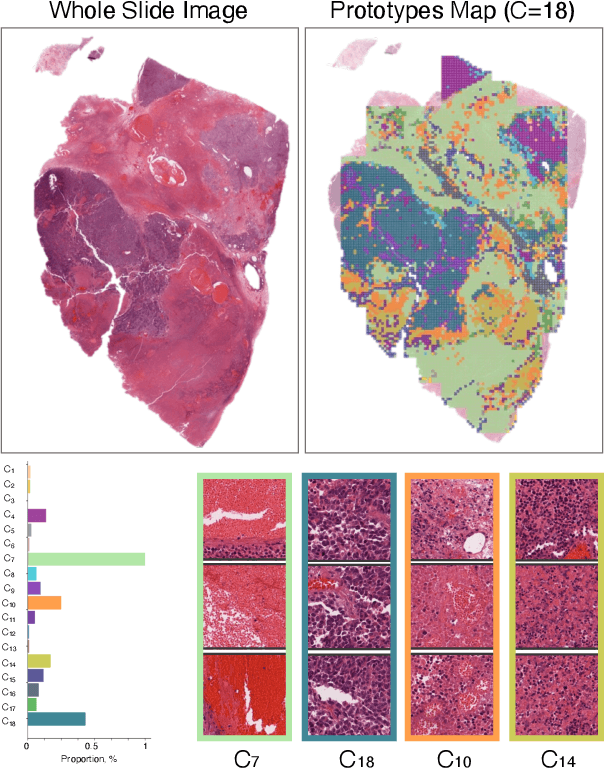
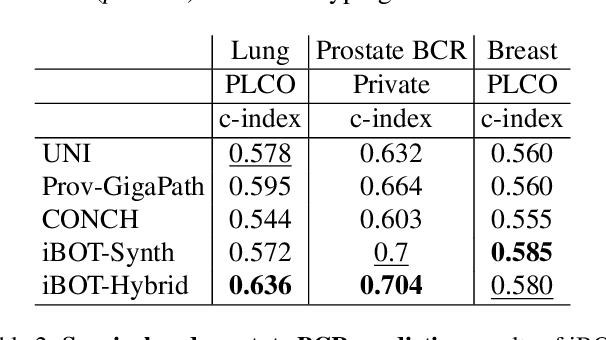
Abstract:Foundation models in digital pathology use massive datasets to learn useful compact feature representations of complex histology images. However, there is limited transparency into what drives the correlation between dataset size and performance, raising the question of whether simply adding more data to increase performance is always necessary. In this study, we propose a prototype-guided diffusion model to generate high-fidelity synthetic pathology data at scale, enabling large-scale self-supervised learning and reducing reliance on real patient samples while preserving downstream performance. Using guidance from histological prototypes during sampling, our approach ensures biologically and diagnostically meaningful variations in the generated data. We demonstrate that self-supervised features trained on our synthetic dataset achieve competitive performance despite using ~60x-760x less data than models trained on large real-world datasets. Notably, models trained using our synthetic data showed statistically comparable or better performance across multiple evaluation metrics and tasks, even when compared to models trained on orders of magnitude larger datasets. Our hybrid approach, combining synthetic and real data, further enhanced performance, achieving top results in several evaluations. These findings underscore the potential of generative AI to create compelling training data for digital pathology, significantly reducing the reliance on extensive clinical datasets and highlighting the efficiency of our approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge