Jiming Chen
Sherman
LOONG: Online Time-Optimal Autonomous Flight for MAVs in Cluttered Environments
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Autonomous flight of micro air vehicles (MAVs) in unknown, cluttered environments remains challenging for time-critical missions due to conservative maneuvering strategies. This article presents an integrated planning and control framework for high-speed, time-optimal autonomous flight of MAVs in cluttered environments. In each replanning cycle (100 Hz), a time-optimal trajectory under polynomial presentation is generated as a reference, with the time-allocation process accelerated by imitation learning. Subsequently, a time-optimal model predictive contouring control (MPCC) incorporates safe flight corridor (SFC) constraints at variable horizon steps to enable aggressive yet safe maneuvering, while fully exploiting the MAV's dynamics. We validate the proposed framework extensively on a custom-built LiDAR-based MAV platform. Simulation results demonstrate superior aggressiveness compared to the state of the art, while real-world experiments achieve a peak speed of 18 m/s in a cluttered environment and succeed in 10 consecutive trials from diverse start points. The video is available at the following link: https://youtu.be/vexXXhv99oQ.
Rethinking Secure Semantic Communications in the Age of Generative and Agentic AI: Threats and Opportunities
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Semantic communication (SemCom) improves communication efficiency by transmitting task-relevant information instead of raw bits and is expected to be a key technology for 6G networks. Recent advances in generative AI (GenAI) further enhance SemCom by enabling robust semantic encoding and decoding under limited channel conditions. However, these efficiency gains also introduce new security and privacy vulnerabilities. Due to the broadcast nature of wireless channels, eavesdroppers can also use powerful GenAI-based semantic decoders to recover private information from intercepted signals. Moreover, rapid advances in agentic AI enable eavesdroppers to perform long-term and adaptive inference through the integration of memory, external knowledge, and reasoning capabilities. This allows eavesdroppers to further infer user private behavior and intent beyond the transmitted content. Motivated by these emerging challenges, this paper comprehensively rethinks the security and privacy of SemCom systems in the age of generative and agentic AI. We first present a systematic taxonomy of eavesdropping threat models in SemCom systems. Then, we provide insights into how GenAI and agentic AI can enhance eavesdropping threats. Meanwhile, we also highlight potential opportunities for leveraging GenAI and agentic AI to design privacy-preserving SemCom systems.
DeepGuard: Defending Deep Joint Source-Channel Coding Against Eavesdropping at Physical-Layer
Dec 21, 2025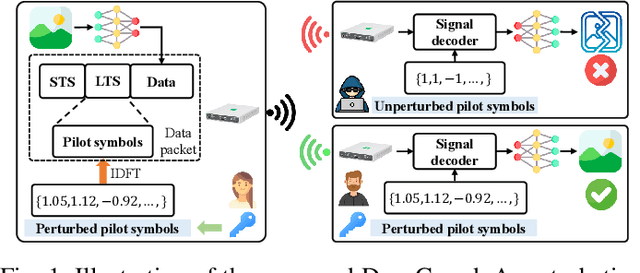
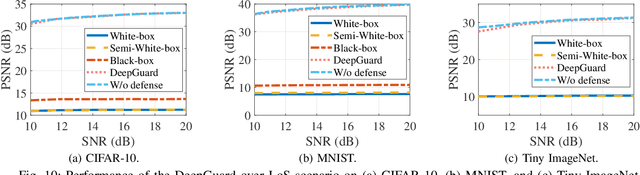
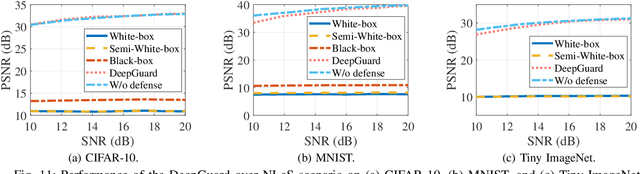

Abstract:Deep joint source-channel coding (DeepJSCC) has emerged as a promising paradigm for efficient and robust information transmission. However, its intrinsic characteristics also pose new security challenges, notably an increased vulnerability to eavesdropping attacks. Existing studies on defending against eavesdropping attacks in DeepJSCC, while demonstrating certain effectiveness, often incur considerable computational overhead or introduce performance trade-offs that may adversely affect legitimate users. In this paper, we present DeepGuard, to the best of our knowledge, the first physical-layer defense framework for DeepJSCC against eavesdropping attacks, validated through over-the-air experiments using software-defined radios (SDRs). Considering that existing eavesdropping attacks against DeepJSCC are limited to simulation under ideal channels, we take a step further by identifying and implementing four representative types of attacks under various configurations in orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing systems. These attacks are evaluated over-the-air under diverse scenarios, allowing us to comprehensively characterize the real-world threat landscape. To mitigate these threats, DeepGuard introduces a novel preamble perturbation mechanism that modifies the preamble shared only between legitimate transceivers. To realize it, we first conduct a theoretical analysis of the perturbation's impact on the signals intercepted by the eavesdropper. Building upon this, we develop an end-to-end perturbation optimization algorithm that significantly degrades eavesdropping performance while preserving reliable communication for legitimate users. We prototype DeepGuard using SDRs and conduct extensive over-the-air experiments in practical scenarios. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DeepGuard effectively mitigates eavesdropping threats.
VICTOR: Dataset Copyright Auditing in Video Recognition Systems
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:Video recognition systems are increasingly being deployed in daily life, such as content recommendation and security monitoring. To enhance video recognition development, many institutions have released high-quality public datasets with open-source licenses for training advanced models. At the same time, these datasets are also susceptible to misuse and infringement. Dataset copyright auditing is an effective solution to identify such unauthorized use. However, existing dataset copyright solutions primarily focus on the image domain; the complex nature of video data leaves dataset copyright auditing in the video domain unexplored. Specifically, video data introduces an additional temporal dimension, which poses significant challenges to the effectiveness and stealthiness of existing methods. In this paper, we propose VICTOR, the first dataset copyright auditing approach for video recognition systems. We develop a general and stealthy sample modification strategy that enhances the output discrepancy of the target model. By modifying only a small proportion of samples (e.g., 1%), VICTOR amplifies the impact of published modified samples on the prediction behavior of the target models. Then, the difference in the model's behavior for published modified and unpublished original samples can serve as a key basis for dataset auditing. Extensive experiments on multiple models and datasets highlight the superiority of VICTOR. Finally, we show that VICTOR is robust in the presence of several perturbation mechanisms to the training videos or the target models.
SenseRay-3D: Generalizable and Physics-Informed Framework for End-to-End Indoor Propagation Modeling
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:Modeling indoor radio propagation is crucial for wireless network planning and optimization. However, existing approaches often rely on labor-intensive manual modeling of geometry and material properties, resulting in limited scalability and efficiency. To overcome these challenges, this paper presents SenseRay-3D, a generalizable and physics-informed end-to-end framework that predicts three-dimensional (3D) path-loss heatmaps directly from RGB-D scans, thereby eliminating the need for explicit geometry reconstruction or material annotation. The proposed framework builds a sensing-driven voxelized scene representation that jointly encodes occupancy, electromagnetic material characteristics, and transmitter-receiver geometry, which is processed by a SwinUNETR-based neural network to infer environmental path-loss relative to free-space path-loss. A comprehensive synthetic indoor propagation dataset is further developed to validate the framework and to serve as a standardized benchmark for future research. Experimental results show that SenseRay-3D achieves a mean absolute error of 4.27 dB on unseen environments and supports real-time inference at 217 ms per sample, demonstrating its scalability, efficiency, and physical consistency. SenseRay-3D paves a new path for sense-driven, generalizable, and physics-consistent modeling of indoor propagation, marking a major leap beyond our pioneering EM DeepRay framework.
Orientation Learning and Adaptation towards Simultaneous Incorporation of Multiple Local Constraints
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:Orientation learning plays a pivotal role in many tasks. However, the rotation group SO(3) is a Riemannian manifold. As a result, the distortion caused by non-Euclidean geometric nature introduces difficulties to the incorporation of local constraints, especially for the simultaneous incorporation of multiple local constraints. To address this issue, we propose the Angle-Axis Space-based orientation representation method to solve several orientation learning problems, including orientation adaptation and minimization of angular acceleration. Specifically, we propose a weighted average mechanism in SO(3) based on the angle-axis representation method. Our main idea is to generate multiple trajectories by considering different local constraints at different basepoints. Then these multiple trajectories are fused to generate a smooth trajectory by our proposed weighted average mechanism, achieving the goal to incorporate multiple local constraints simultaneously. Compared with existing solution, ours can address the distortion issue and make the off-theshelf Euclidean learning algorithm be re-applicable in non-Euclidean space. Simulation and Experimental evaluations validate that our solution can not only adapt orientations towards arbitrary desired via-points and cope with angular acceleration constraints, but also incorporate multiple local constraints simultaneously to achieve extra benefits, e.g., achieving smaller acceleration costs.
PointAD+: Learning Hierarchical Representations for Zero-shot 3D Anomaly Detection
Sep 03, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we aim to transfer CLIP's robust 2D generalization capabilities to identify 3D anomalies across unseen objects of highly diverse class semantics. To this end, we propose a unified framework to comprehensively detect and segment 3D anomalies by leveraging both point- and pixel-level information. We first design PointAD, which leverages point-pixel correspondence to represent 3D anomalies through their associated rendering pixel representations. This approach is referred to as implicit 3D representation, as it focuses solely on rendering pixel anomalies but neglects the inherent spatial relationships within point clouds. Then, we propose PointAD+ to further broaden the interpretation of 3D anomalies by introducing explicit 3D representation, emphasizing spatial abnormality to uncover abnormal spatial relationships. Hence, we propose G-aggregation to involve geometry information to enable the aggregated point representations spatially aware. To simultaneously capture rendering and spatial abnormality, PointAD+ proposes hierarchical representation learning, incorporating implicit and explicit anomaly semantics into hierarchical text prompts: rendering prompts for the rendering layer and geometry prompts for the geometry layer. A cross-hierarchy contrastive alignment is further introduced to promote the interaction between the rendering and geometry layers, facilitating mutual anomaly learning. Finally, PointAD+ integrates anomaly semantics from both layers to capture the generalized anomaly semantics. During the test, PointAD+ can integrate RGB information in a plug-and-play manner and further improve its detection performance. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of PointAD+ in ZS 3D anomaly detection across unseen objects with highly diverse class semantics, achieving a holistic understanding of abnormality.
The Developments and Challenges towards Dexterous and Embodied Robotic Manipulation: A Survey
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:Achieving human-like dexterous robotic manipulation remains a central goal and a pivotal challenge in robotics. The development of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has allowed rapid progress in robotic manipulation. This survey summarizes the evolution of robotic manipulation from mechanical programming to embodied intelligence, alongside the transition from simple grippers to multi-fingered dexterous hands, outlining key characteristics and main challenges. Focusing on the current stage of embodied dexterous manipulation, we highlight recent advances in two critical areas: dexterous manipulation data collection (via simulation, human demonstrations, and teleoperation) and skill-learning frameworks (imitation and reinforcement learning). Then, based on the overview of the existing data collection paradigm and learning framework, three key challenges restricting the development of dexterous robotic manipulation are summarized and discussed.
Can Knowledge Improve Security? A Coding-Enhanced Jamming Approach for Semantic Communication
May 06, 2025Abstract:As semantic communication (SemCom) attracts growing attention as a novel communication paradigm, ensuring the security of transmitted semantic information over open wireless channels has become a critical issue. However, traditional encryption methods often introduce significant additional communication overhead to maintain stability, and conventional learning-based secure SemCom methods typically rely on a channel capacity advantage for the legitimate receiver, which is challenging to guarantee in real-world scenarios. In this paper, we propose a coding-enhanced jamming method that eliminates the need to transmit a secret key by utilizing shared knowledge-potentially part of the training set of the SemCom system-between the legitimate receiver and the transmitter. Specifically, we leverage the shared private knowledge base to generate a set of private digital codebooks in advance using neural network (NN)-based encoders. For each transmission, we encode the transmitted data into digital sequence Y1 and associate Y1 with a sequence randomly picked from the private codebook, denoted as Y2, through superposition coding. Here, Y1 serves as the outer code and Y2 as the inner code. By optimizing the power allocation between the inner and outer codes, the legitimate receiver can reconstruct the transmitted data using successive decoding with the index of Y2 shared, while the eavesdropper' s decoding performance is severely degraded, potentially to the point of random guessing. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves comparable security to state-of-the-art approaches while significantly improving the reconstruction performance of the legitimate receiver by more than 1 dB across varying channel signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs) and compression ratios.
Enhancing the Security of Semantic Communication via Knowledge-Aided Coding and Jamming
May 01, 2025Abstract:As semantic communication (SemCom) emerges as a promising communication paradigm, ensuring the security of semantic information over open wireless channels has become crucial. Traditional encryption methods introduce considerable communication overhead, while existing learning-based secure SemCom schemes often rely on a channel capacity advantage for the legitimate receiver, which is challenging to guarantee in practice. In this paper, we propose a coding-enhanced jamming approach that eliminates the need to transmit a secret key by utilizing shared knowledge between the legitimate receiver and the transmitter. We generate private codebooks with neural network (NN)-based encoders, using them to encode data into a sequence Y1, which is then superposed with a sequence Y2 drawn from the private codebook. By optimizing the power allocation between the two sequences, the legitimate receiver can successfully decode the data, while the eavesdropper' s performance is significantly degraded, potentially to the point of random guessing. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves comparable security to state-of-the-art approaches while significantly improving the reconstruction performance of the legitimate receiver by more than 1 dB across varying channel signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs) and compression ratios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge