Chengchao Shen
Diversity-Guided MLP Reduction for Efficient Large Vision Transformers
Jun 10, 2025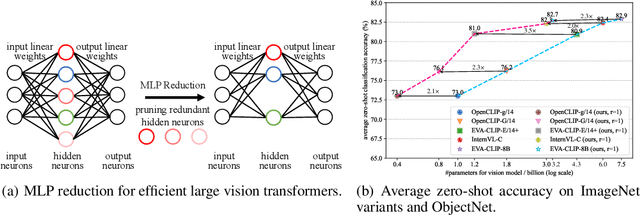
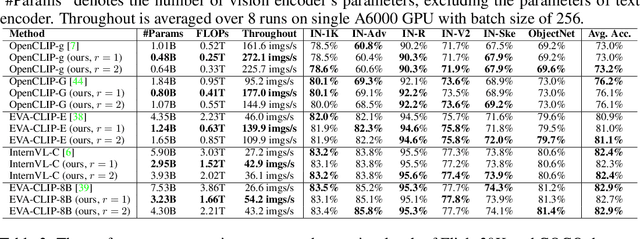
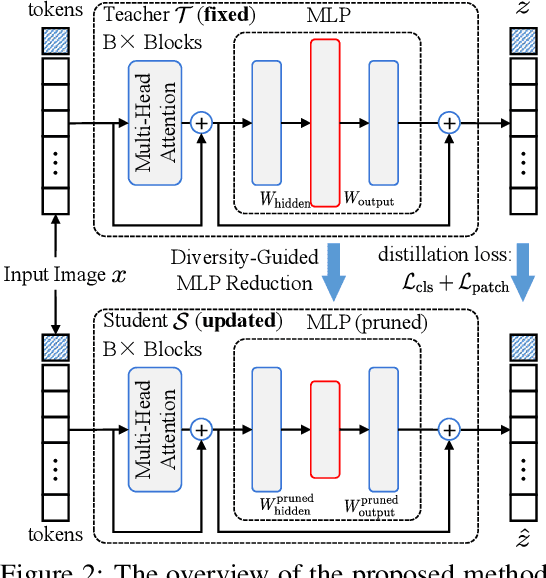
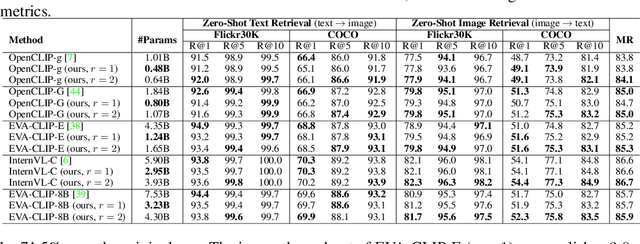
Abstract:Transformer models achieve excellent scaling property, where the performance is improved with the increment of model capacity. However, large-scale model parameters lead to an unaffordable cost of computing and memory. We analyze popular transformer architectures and find that multilayer perceptron (MLP) modules take up the majority of model parameters. To this end, we focus on the recoverability of the compressed models and propose a Diversity-Guided MLP Reduction (DGMR) method to significantly reduce the parameters of large vision transformers with only negligible performance degradation. Specifically, we conduct a Gram-Schmidt weight pruning strategy to eliminate redundant neurons of MLP hidden layer, while preserving weight diversity for better performance recover during distillation. Compared to the model trained from scratch, our pruned model only requires 0.06\% data of LAION-2B (for the training of large vision transformers) without labels (ImageNet-1K) to recover the original performance. Experimental results on several state-of-the-art large vision transformers demonstrate that our method achieves a more than 57.0\% parameter and FLOPs reduction in a near lossless manner. Notably, for EVA-CLIP-E (4.4B), our method accomplishes a 71.5\% parameter and FLOPs reduction without performance degradation. The source code and trained weights are available at https://github.com/visresearch/DGMR.
Multiple Object Stitching for Unsupervised Representation Learning
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Contrastive learning for single object centric images has achieved remarkable progress on unsupervised representation, but suffering inferior performance on the widespread images with multiple objects. In this paper, we propose a simple but effective method, Multiple Object Stitching (MOS), to refine the unsupervised representation for multi-object images. Specifically, we construct the multi-object images by stitching the single object centric ones, where the objects in the synthesized multi-object images are predetermined. Hence, compared to the existing contrastive methods, our method provides additional object correspondences between multi-object images without human annotations. In this manner, our method pays more attention to the representations of each object in multi-object image, thus providing more detailed representations for complicated downstream tasks, such as object detection and semantic segmentation. Experimental results on ImageNet, CIFAR and COCO datasets demonstrate that our proposed method achieves the leading unsupervised representation performance on both single object centric images and multi-object ones. The source code is available at https://github.com/visresearch/MultipleObjectStitching.
Learning Compact Vision Tokens for Efficient Large Multimodal Models
Jun 08, 2025Abstract:Large multimodal models (LMMs) suffer significant computational challenges due to the high cost of Large Language Models (LLMs) and the quadratic complexity of processing long vision token sequences. In this paper, we explore the spatial redundancy among vision tokens and shorten the length of vision token sequences for inference acceleration. Specifically, we propose a Spatial Token Fusion (STF) method to learn compact vision tokens for short vision token sequence, where spatial-adjacent tokens are fused into one. Meanwhile, weight-frozen vision encoder can not well adapt to the demand of extensive downstream vision-language tasks. To this end, we further introduce a Multi-Block Token Fusion (MBTF) module to supplement multi-granularity features for the reduced token sequence. Overall, we combine STF and MBTF module to balance token reduction and information preservation, thereby improving inference efficiency without sacrificing multimodal reasoning capabilities. Experimental results demonstrate that our method based on LLaVA-1.5 achieves comparable or even superior performance to the baseline on 8 popular vision-language benchmarks with only $25\%$ vision tokens of baseline. The source code and trained weights are available at https://github.com/visresearch/LLaVA-STF.
Multi-Grained Contrast for Data-Efficient Unsupervised Representation Learning
Jul 02, 2024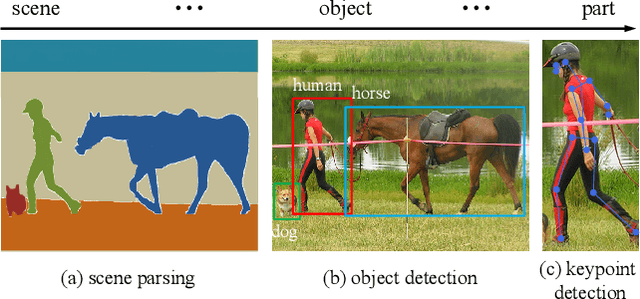
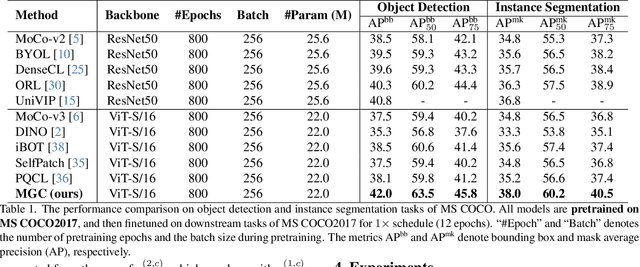
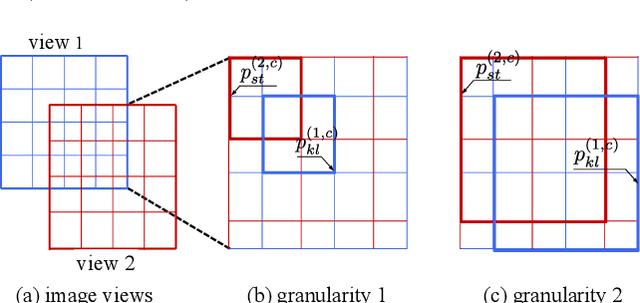
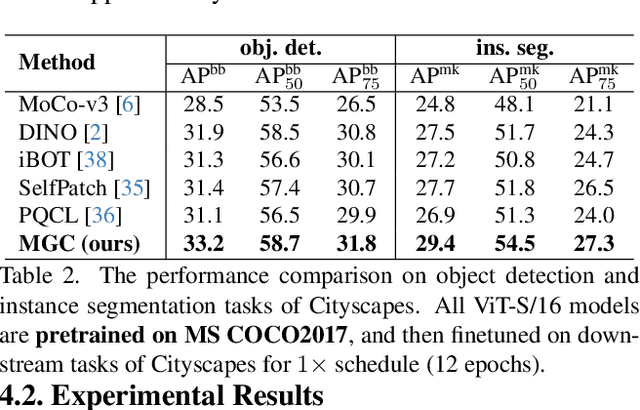
Abstract:The existing contrastive learning methods mainly focus on single-grained representation learning, e.g., part-level, object-level or scene-level ones, thus inevitably neglecting the transferability of representations on other granularity levels. In this paper, we aim to learn multi-grained representations, which can effectively describe the image on various granularity levels, thus improving generalization on extensive downstream tasks. To this end, we propose a novel Multi-Grained Contrast method (MGC) for unsupervised representation learning. Specifically, we construct delicate multi-grained correspondences between positive views and then conduct multi-grained contrast by the correspondences to learn more general unsupervised representations. Without pretrained on large-scale dataset, our method significantly outperforms the existing state-of-the-art methods on extensive downstream tasks, including object detection, instance segmentation, scene parsing, semantic segmentation and keypoint detection. Moreover, experimental results support the data-efficient property and excellent representation transferability of our method. The source code and trained weights are available at \url{https://github.com/visresearch/mgc}.
Inter-Instance Similarity Modeling for Contrastive Learning
Jun 29, 2023



Abstract:The existing contrastive learning methods widely adopt one-hot instance discrimination as pretext task for self-supervised learning, which inevitably neglects rich inter-instance similarities among natural images, then leading to potential representation degeneration. In this paper, we propose a novel image mix method, PatchMix, for contrastive learning in Vision Transformer (ViT), to model inter-instance similarities among images. Following the nature of ViT, we randomly mix multiple images from mini-batch in patch level to construct mixed image patch sequences for ViT. Compared to the existing sample mix methods, our PatchMix can flexibly and efficiently mix more than two images and simulate more complicated similarity relations among natural images. In this manner, our contrastive framework can significantly reduce the gap between contrastive objective and ground truth in reality. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method significantly outperforms the previous state-of-the-art on both ImageNet-1K and CIFAR datasets, e.g., 3.0% linear accuracy improvement on ImageNet-1K and 8.7% kNN accuracy improvement on CIFAR100. Moreover, our method achieves the leading transfer performance on downstream tasks, object detection and instance segmentation on COCO dataset. The code is available at https://github.com/visresearch/patchmix
Asymmetric Patch Sampling for Contrastive Learning
Jun 05, 2023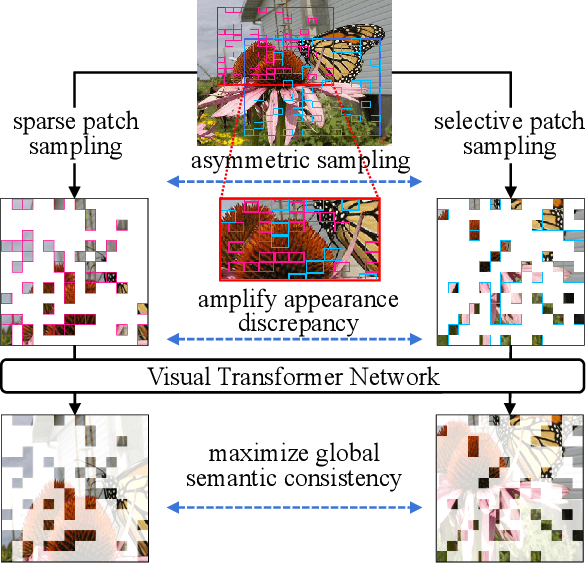
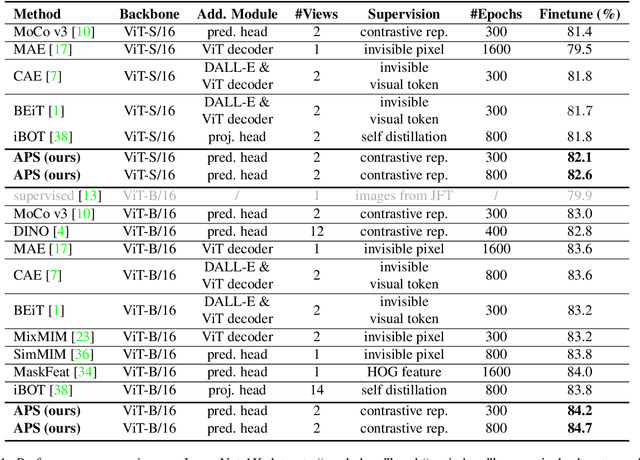
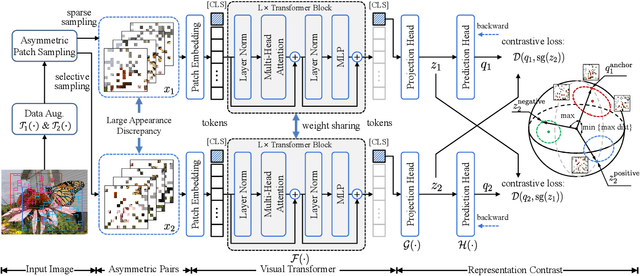

Abstract:Asymmetric appearance between positive pair effectively reduces the risk of representation degradation in contrastive learning. However, there are still a mass of appearance similarities between positive pair constructed by the existing methods, which inhibits the further representation improvement. In this paper, we propose a novel asymmetric patch sampling strategy for contrastive learning, to further boost the appearance asymmetry for better representations. Specifically, dual patch sampling strategies are applied to the given image, to obtain asymmetric positive pairs. First, sparse patch sampling is conducted to obtain the first view, which reduces spatial redundancy of image and allows a more asymmetric view. Second, a selective patch sampling is proposed to construct another view with large appearance discrepancy relative to the first one. Due to the inappreciable appearance similarity between positive pair, the trained model is encouraged to capture the similarity on semantics, instead of low-level ones. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method significantly outperforms the existing self-supervised methods on both ImageNet-1K and CIFAR dataset, e.g., 2.5% finetune accuracy improvement on CIFAR100. Furthermore, our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on downstream tasks, object detection and instance segmentation on COCO.Additionally, compared to other self-supervised methods, our method is more efficient on both memory and computation during training. The source code is available at https://github.com/visresearch/aps.
Modeling Global Distribution for Federated Learning with Label Distribution Skew
Dec 17, 2022Abstract:Federated learning achieves joint training of deep models by connecting decentralized data sources, which can significantly mitigate the risk of privacy leakage. However, in a more general case, the distributions of labels among clients are different, called ``label distribution skew''. Directly applying conventional federated learning without consideration of label distribution skew issue significantly hurts the performance of the global model. To this end, we propose a novel federated learning method, named FedMGD, to alleviate the performance degradation caused by the label distribution skew issue. It introduces a global Generative Adversarial Network to model the global data distribution without access to local datasets, so the global model can be trained using the global information of data distribution without privacy leakage. The experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art on several public benchmarks. Code is available at \url{https://github.com/Sheng-T/FedMGD}.
Learning Dynamic Preference Structure Embedding From Temporal Networks
Nov 23, 2021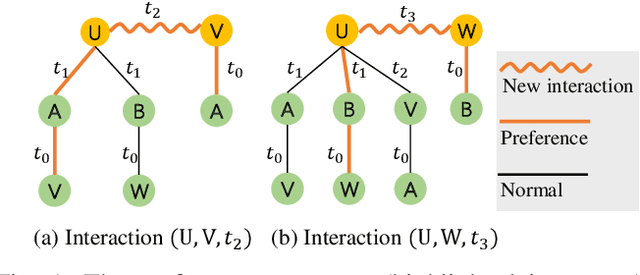
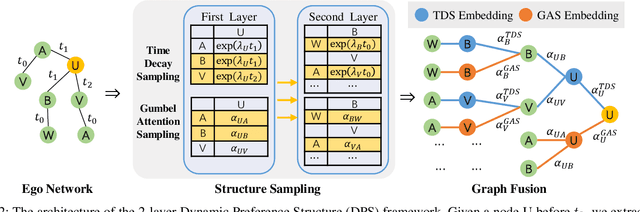
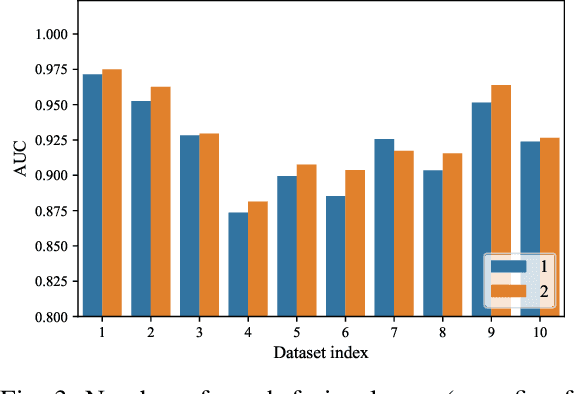
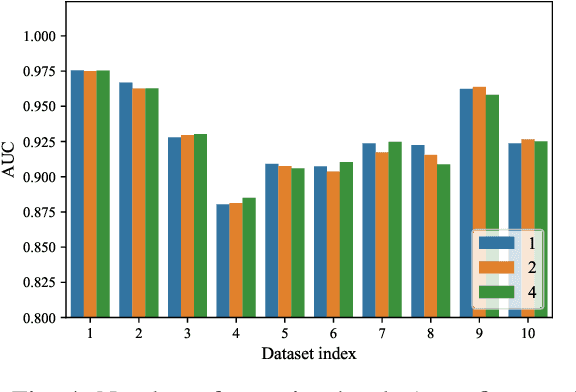
Abstract:The dynamics of temporal networks lie in the continuous interactions between nodes, which exhibit the dynamic node preferences with time elapsing. The challenges of mining temporal networks are thus two-fold: the dynamic structure of networks and the dynamic node preferences. In this paper, we investigate the dynamic graph sampling problem, aiming to capture the preference structure of nodes dynamically in cooperation with GNNs. Our proposed Dynamic Preference Structure (DPS) framework consists of two stages: structure sampling and graph fusion. In the first stage, two parameterized samplers are designed to learn the preference structure adaptively with network reconstruction tasks. In the second stage, an additional attention layer is designed to fuse two sampled temporal subgraphs of a node, generating temporal node embeddings for downstream tasks. Experimental results on many real-life temporal networks show that our DPS outperforms several state-of-the-art methods substantially owing to learning an adaptive preference structure. The code will be released soon at https://github.com/doujiang-zheng/Dynamic-Preference-Structure.
Mosaicking to Distill: Knowledge Distillation from Out-of-Domain Data
Oct 27, 2021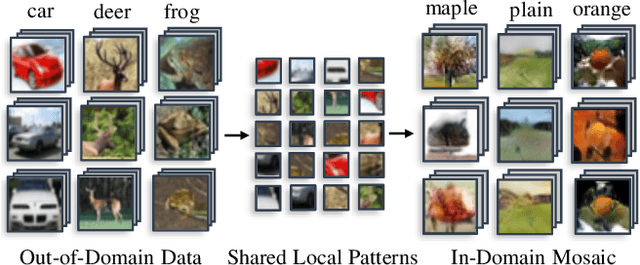
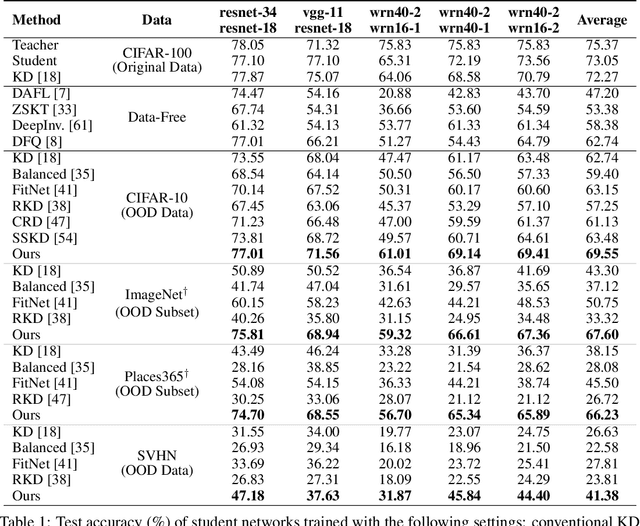
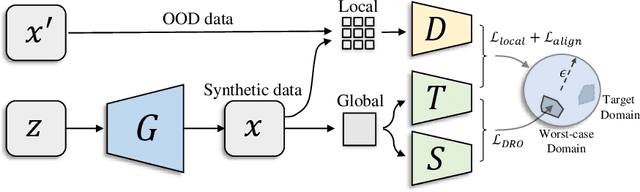
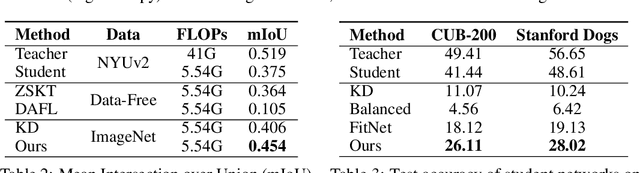
Abstract:Knowledge distillation~(KD) aims to craft a compact student model that imitates the behavior of a pre-trained teacher in a target domain. Prior KD approaches, despite their gratifying results, have largely relied on the premise that \emph{in-domain} data is available to carry out the knowledge transfer. Such an assumption, unfortunately, in many cases violates the practical setting, since the original training data or even the data domain is often unreachable due to privacy or copyright reasons. In this paper, we attempt to tackle an ambitious task, termed as \emph{out-of-domain} knowledge distillation~(OOD-KD), which allows us to conduct KD using only OOD data that can be readily obtained at a very low cost. Admittedly, OOD-KD is by nature a highly challenging task due to the agnostic domain gap. To this end, we introduce a handy yet surprisingly efficacious approach, dubbed as~\textit{MosaicKD}. The key insight behind MosaicKD lies in that, samples from various domains share common local patterns, even though their global semantic may vary significantly; these shared local patterns, in turn, can be re-assembled analogous to mosaic tiling, to approximate the in-domain data and to further alleviating the domain discrepancy. In MosaicKD, this is achieved through a four-player min-max game, in which a generator, a discriminator, a student network, are collectively trained in an adversarial manner, partially under the guidance of a pre-trained teacher. We validate MosaicKD over {classification and semantic segmentation tasks} across various benchmarks, and demonstrate that it yields results much superior to the state-of-the-art counterparts on OOD data. Our code is available at \url{https://github.com/zju-vipa/MosaicKD}.
Contrastive Model Inversion for Data-Free Knowledge Distillation
May 18, 2021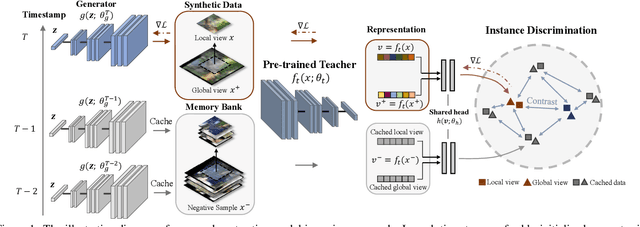
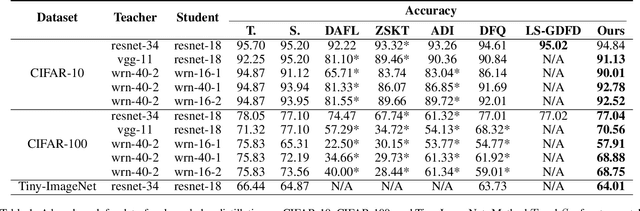
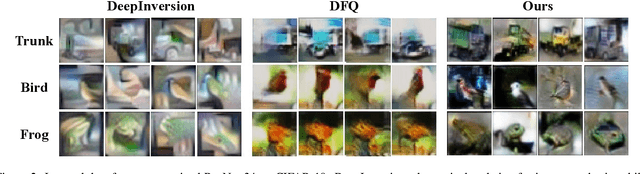
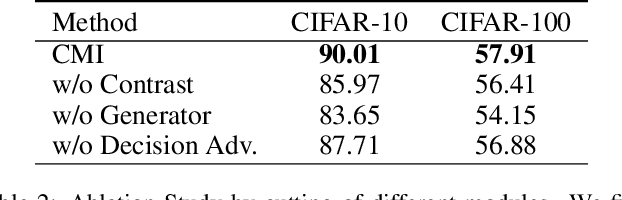
Abstract:Model inversion, whose goal is to recover training data from a pre-trained model, has been recently proved feasible. However, existing inversion methods usually suffer from the mode collapse problem, where the synthesized instances are highly similar to each other and thus show limited effectiveness for downstream tasks, such as knowledge distillation. In this paper, we propose Contrastive Model Inversion~(CMI), where the data diversity is explicitly modeled as an optimizable objective, to alleviate the mode collapse issue. Our main observation is that, under the constraint of the same amount of data, higher data diversity usually indicates stronger instance discrimination. To this end, we introduce in CMI a contrastive learning objective that encourages the synthesizing instances to be distinguishable from the already synthesized ones in previous batches. Experiments of pre-trained models on CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, and Tiny-ImageNet demonstrate that CMI not only generates more visually plausible instances than the state of the arts, but also achieves significantly superior performance when the generated data are used for knowledge distillation. Code is available at \url{https://github.com/zju-vipa/DataFree}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge