Shu Wang
VecFormer: Towards Efficient and Generalizable Graph Transformer with Graph Token Attention
Feb 23, 2026Abstract:Graph Transformer has demonstrated impressive capabilities in the field of graph representation learning. However, existing approaches face two critical challenges: (1) most models suffer from exponentially increasing computational complexity, making it difficult to scale to large graphs; (2) attention mechanisms based on node-level operations limit the flexibility of the model and result in poor generalization performance in out-of-distribution (OOD) scenarios. To address these issues, we propose \textbf{VecFormer} (the \textbf{Vec}tor Quantized Graph Trans\textbf{former}), an efficient and highly generalizable model for node classification, particularly under OOD settings. VecFormer adopts a two-stage training paradigm. In the first stage, two codebooks are used to reconstruct the node features and the graph structure, aiming to learn the rich semantic \texttt{Graph Codes}. In the second stage, attention mechanisms are performed at the \texttt{Graph Token} level based on the transformed cross codebook, reducing computational complexity while enhancing the model's generalization capability. Extensive experiments on datasets of various sizes demonstrate that VecFormer outperforms the existing Graph Transformer in both performance and speed.
Integrated Exploration and Sequential Manipulation on Scene Graph with LLM-based Situated Replanning
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:In partially known environments, robots must combine exploration to gather information with task planning for efficient execution. To address this challenge, we propose EPoG, an Exploration-based sequential manipulation Planning framework on Scene Graphs. EPoG integrates a graph-based global planner with a Large Language Model (LLM)-based situated local planner, continuously updating a belief graph using observations and LLM predictions to represent known and unknown objects. Action sequences are generated by computing graph edit operations between the goal and belief graphs, ordered by temporal dependencies and movement costs. This approach seamlessly combines exploration and sequential manipulation planning. In ablation studies across 46 realistic household scenes and 5 long-horizon daily object transportation tasks, EPoG achieved a success rate of 91.3%, reducing travel distance by 36.1% on average. Furthermore, a physical mobile manipulator successfully executed complex tasks in unknown and dynamic environments, demonstrating EPoG's potential for real-world applications.
HiF-VLA: Hindsight, Insight and Foresight through Motion Representation for Vision-Language-Action Models
Dec 10, 2025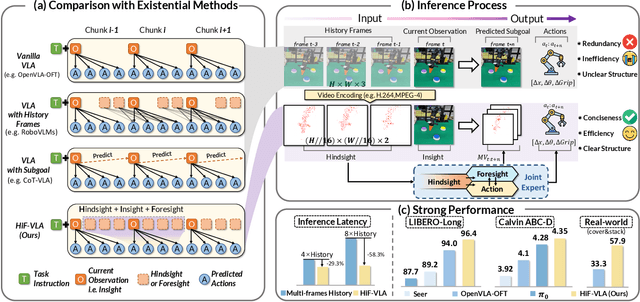
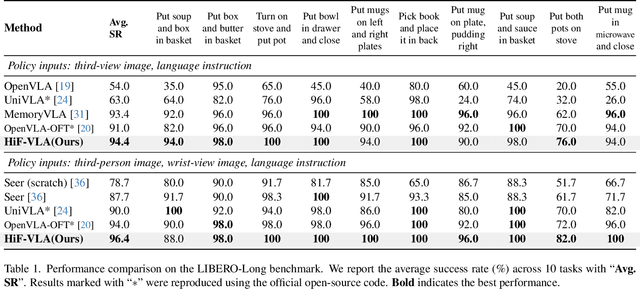
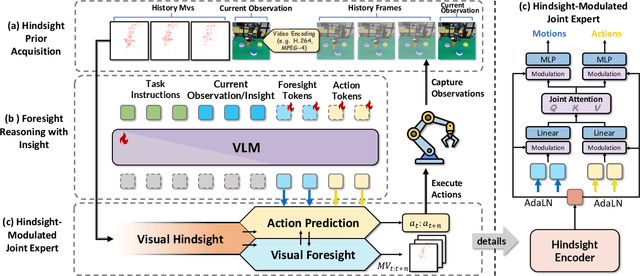
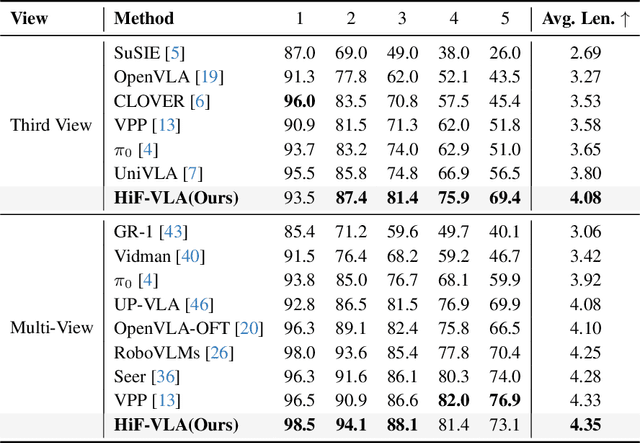
Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have recently enabled robotic manipulation by grounding visual and linguistic cues into actions. However, most VLAs assume the Markov property, relying only on the current observation and thus suffering from temporal myopia that degrades long-horizon coherence. In this work, we view motion as a more compact and informative representation of temporal context and world dynamics, capturing inter-state changes while filtering static pixel-level noise. Building on this idea, we propose HiF-VLA (Hindsight, Insight, and Foresight for VLAs), a unified framework that leverages motion for bidirectional temporal reasoning. HiF-VLA encodes past dynamics through hindsight priors, anticipates future motion via foresight reasoning, and integrates both through a hindsight-modulated joint expert to enable a ''think-while-acting'' paradigm for long-horizon manipulation. As a result, HiF-VLA surpasses strong baselines on LIBERO-Long and CALVIN ABC-D benchmarks, while incurring negligible additional inference latency. Furthermore, HiF-VLA achieves substantial improvements in real-world long-horizon manipulation tasks, demonstrating its broad effectiveness in practical robotic settings.
Semi-Supervised State-Space Model with Dynamic Stacking Filter for Real-World Video Deraining
May 22, 2025
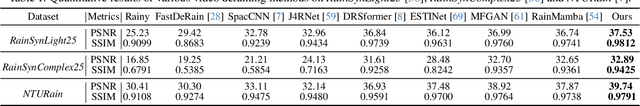
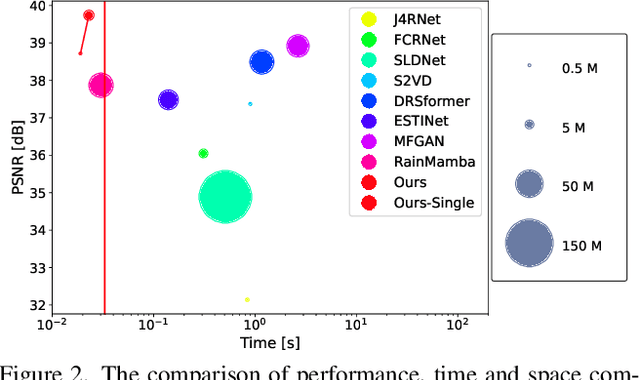
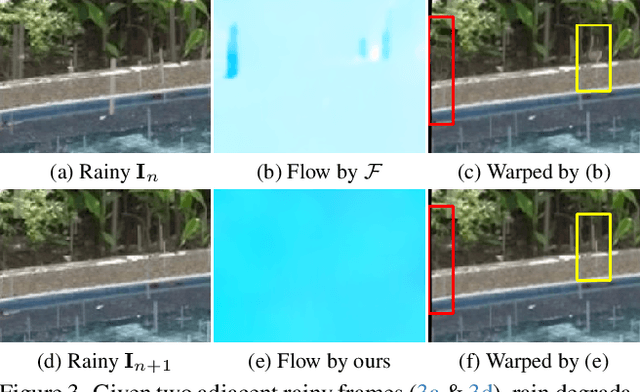
Abstract:Significant progress has been made in video restoration under rainy conditions over the past decade, largely propelled by advancements in deep learning. Nevertheless, existing methods that depend on paired data struggle to generalize effectively to real-world scenarios, primarily due to the disparity between synthetic and authentic rain effects. To address these limitations, we propose a dual-branch spatio-temporal state-space model to enhance rain streak removal in video sequences. Specifically, we design spatial and temporal state-space model layers to extract spatial features and incorporate temporal dependencies across frames, respectively. To improve multi-frame feature fusion, we derive a dynamic stacking filter, which adaptively approximates statistical filters for superior pixel-wise feature refinement. Moreover, we develop a median stacking loss to enable semi-supervised learning by generating pseudo-clean patches based on the sparsity prior of rain. To further explore the capacity of deraining models in supporting other vision-based tasks in rainy environments, we introduce a novel real-world benchmark focused on object detection and tracking in rainy conditions. Our method is extensively evaluated across multiple benchmarks containing numerous synthetic and real-world rainy videos, consistently demonstrating its superiority in quantitative metrics, visual quality, efficiency, and its utility for downstream tasks.
ChainMarks: Securing DNN Watermark with Cryptographic Chain
May 08, 2025



Abstract:With the widespread deployment of deep neural network (DNN) models, dynamic watermarking techniques are being used to protect the intellectual property of model owners. However, recent studies have shown that existing watermarking schemes are vulnerable to watermark removal and ambiguity attacks. Besides, the vague criteria for determining watermark presence further increase the likelihood of such attacks. In this paper, we propose a secure DNN watermarking scheme named ChainMarks, which generates secure and robust watermarks by introducing a cryptographic chain into the trigger inputs and utilizes a two-phase Monte Carlo method for determining watermark presence. First, ChainMarks generates trigger inputs as a watermark dataset by repeatedly applying a hash function over a secret key, where the target labels associated with trigger inputs are generated from the digital signature of model owner. Then, the watermarked model is produced by training a DNN over both the original and watermark datasets. To verify watermarks, we compare the predicted labels of trigger inputs with the target labels and determine ownership with a more accurate decision threshold that considers the classification probability of specific models. Experimental results show that ChainMarks exhibits higher levels of robustness and security compared to state-of-the-art watermarking schemes. With a better marginal utility, ChainMarks provides a higher probability guarantee of watermark presence in DNN models with the same level of watermark accuracy.
R^3-VQA: "Read the Room" by Video Social Reasoning
May 07, 2025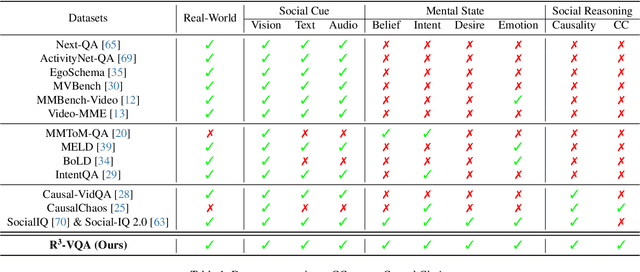
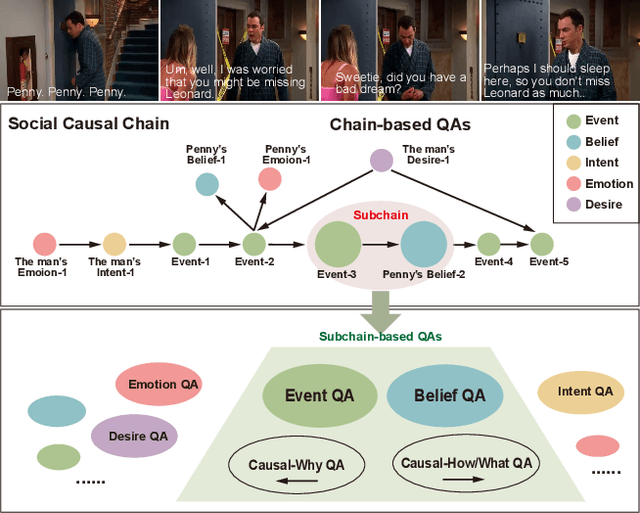
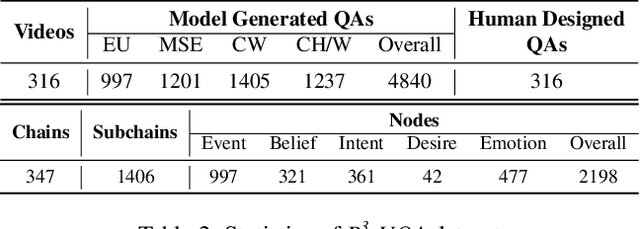
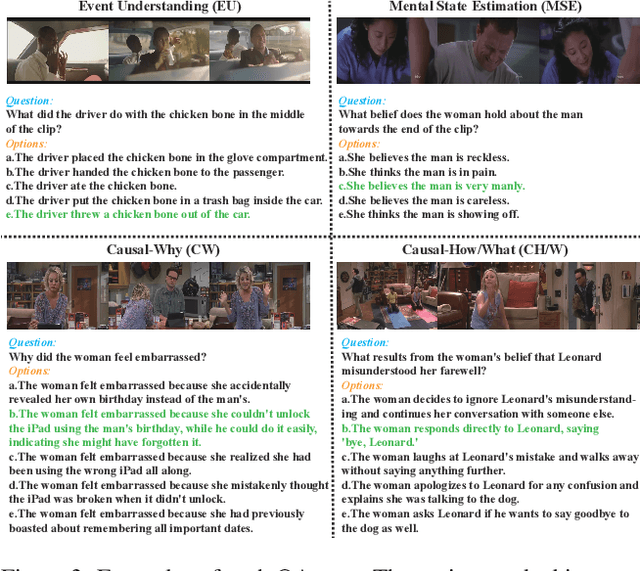
Abstract:"Read the room" is a significant social reasoning capability in human daily life. Humans can infer others' mental states from subtle social cues. Previous social reasoning tasks and datasets lack complexity (e.g., simple scenes, basic interactions, incomplete mental state variables, single-step reasoning, etc.) and fall far short of the challenges present in real-life social interactions. In this paper, we contribute a valuable, high-quality, and comprehensive video dataset named R^3-VQA with precise and fine-grained annotations of social events and mental states (i.e., belief, intent, desire, and emotion) as well as corresponding social causal chains in complex social scenarios. Moreover, we include human-annotated and model-generated QAs. Our task R^3-VQA includes three aspects: Social Event Understanding, Mental State Estimation, and Social Causal Reasoning. As a benchmark, we comprehensively evaluate the social reasoning capabilities and consistencies of current state-of-the-art large vision-language models (LVLMs). Comprehensive experiments show that (i) LVLMs are still far from human-level consistent social reasoning in complex social scenarios; (ii) Theory of Mind (ToM) prompting can help LVLMs perform better on social reasoning tasks. We provide some of our dataset and codes in supplementary material and will release our full dataset and codes upon acceptance.
DMPT: Decoupled Modality-aware Prompt Tuning for Multi-modal Object Re-identification
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:Current multi-modal object re-identification approaches based on large-scale pre-trained backbones (i.e., ViT) have displayed remarkable progress and achieved excellent performance. However, these methods usually adopt the standard full fine-tuning paradigm, which requires the optimization of considerable backbone parameters, causing extensive computational and storage requirements. In this work, we propose an efficient prompt-tuning framework tailored for multi-modal object re-identification, dubbed DMPT, which freezes the main backbone and only optimizes several newly added decoupled modality-aware parameters. Specifically, we explicitly decouple the visual prompts into modality-specific prompts which leverage prior modality knowledge from a powerful text encoder and modality-independent semantic prompts which extract semantic information from multi-modal inputs, such as visible, near-infrared, and thermal-infrared. Built upon the extracted features, we further design a Prompt Inverse Bind (PromptIBind) strategy that employs bind prompts as a medium to connect the semantic prompt tokens of different modalities and facilitates the exchange of complementary multi-modal information, boosting final re-identification results. Experimental results on multiple common benchmarks demonstrate that our DMPT can achieve competitive results to existing state-of-the-art methods while requiring only 6.5% fine-tuning of the backbone parameters.
Exploring the Evolution of Physics Cognition in Video Generation: A Survey
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in video generation have witnessed significant progress, especially with the rapid advancement of diffusion models. Despite this, their deficiencies in physical cognition have gradually received widespread attention - generated content often violates the fundamental laws of physics, falling into the dilemma of ''visual realism but physical absurdity". Researchers began to increasingly recognize the importance of physical fidelity in video generation and attempted to integrate heuristic physical cognition such as motion representations and physical knowledge into generative systems to simulate real-world dynamic scenarios. Considering the lack of a systematic overview in this field, this survey aims to provide a comprehensive summary of architecture designs and their applications to fill this gap. Specifically, we discuss and organize the evolutionary process of physical cognition in video generation from a cognitive science perspective, while proposing a three-tier taxonomy: 1) basic schema perception for generation, 2) passive cognition of physical knowledge for generation, and 3) active cognition for world simulation, encompassing state-of-the-art methods, classical paradigms, and benchmarks. Subsequently, we emphasize the inherent key challenges in this domain and delineate potential pathways for future research, contributing to advancing the frontiers of discussion in both academia and industry. Through structured review and interdisciplinary analysis, this survey aims to provide directional guidance for developing interpretable, controllable, and physically consistent video generation paradigms, thereby propelling generative models from the stage of ''visual mimicry'' towards a new phase of ''human-like physical comprehension''.
Sampling Innovation-Based Adaptive Compressive Sensing
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:Scene-aware Adaptive Compressive Sensing (ACS) has attracted significant interest due to its promising capability for efficient and high-fidelity acquisition of scene images. ACS typically prescribes adaptive sampling allocation (ASA) based on previous samples in the absence of ground truth. However, when confronting unknown scenes, existing ACS methods often lack accurate judgment and robust feedback mechanisms for ASA, thus limiting the high-fidelity sensing of the scene. In this paper, we introduce a Sampling Innovation-Based ACS (SIB-ACS) method that can effectively identify and allocate sampling to challenging image reconstruction areas, culminating in high-fidelity image reconstruction. An innovation criterion is proposed to judge ASA by predicting the decrease in image reconstruction error attributable to sampling increments, thereby directing more samples towards regions where the reconstruction error diminishes significantly. A sampling innovation-guided multi-stage adaptive sampling (AS) framework is proposed, which iteratively refines the ASA through a multi-stage feedback process. For image reconstruction, we propose a Principal Component Compressed Domain Network (PCCD-Net), which efficiently and faithfully reconstructs images under AS scenarios. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed SIB-ACS method significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in terms of image reconstruction fidelity and visual effects. Codes are available at https://github.com/giant-pandada/SIB-ACS_CVPR2025.
MetricGrids: Arbitrary Nonlinear Approximation with Elementary Metric Grids based Implicit Neural Representation
Mar 13, 2025
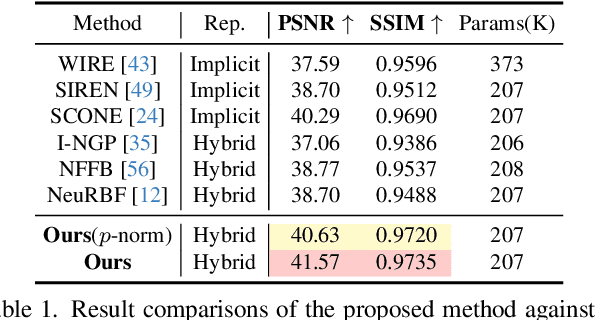

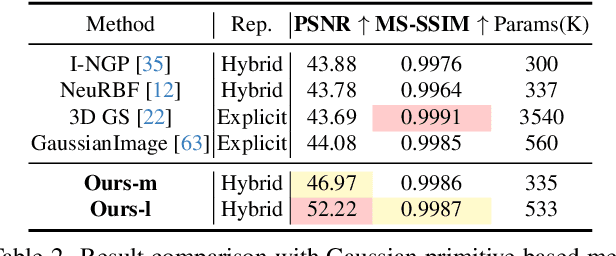
Abstract:This paper presents MetricGrids, a novel grid-based neural representation that combines elementary metric grids in various metric spaces to approximate complex nonlinear signals. While grid-based representations are widely adopted for their efficiency and scalability, the existing feature grids with linear indexing for continuous-space points can only provide degenerate linear latent space representations, and such representations cannot be adequately compensated to represent complex nonlinear signals by the following compact decoder. To address this problem while keeping the simplicity of a regular grid structure, our approach builds upon the standard grid-based paradigm by constructing multiple elementary metric grids as high-order terms to approximate complex nonlinearities, following the Taylor expansion principle. Furthermore, we enhance model compactness with hash encoding based on different sparsities of the grids to prevent detrimental hash collisions, and a high-order extrapolation decoder to reduce explicit grid storage requirements. experimental results on both 2D and 3D reconstructions demonstrate the superior fitting and rendering accuracy of the proposed method across diverse signal types, validating its robustness and generalizability. Code is available at https://github.com/wangshu31/MetricGrids}{https://github.com/wangshu31/MetricGrids.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge