Hulin Kuang
Dynamic Residual Encoding with Slide-Level Contrastive Learning for End-to-End Whole Slide Image Representation
Nov 07, 2025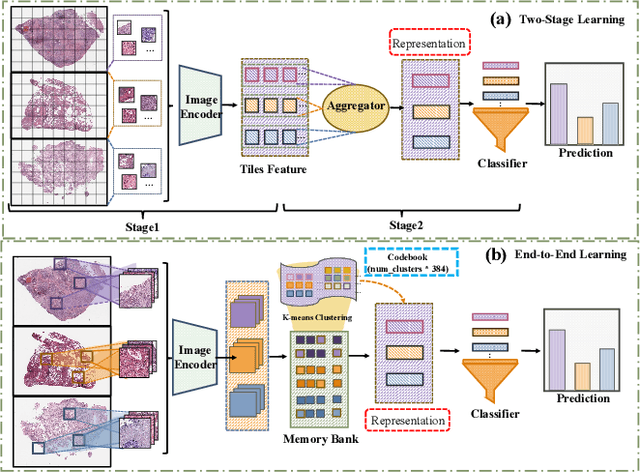
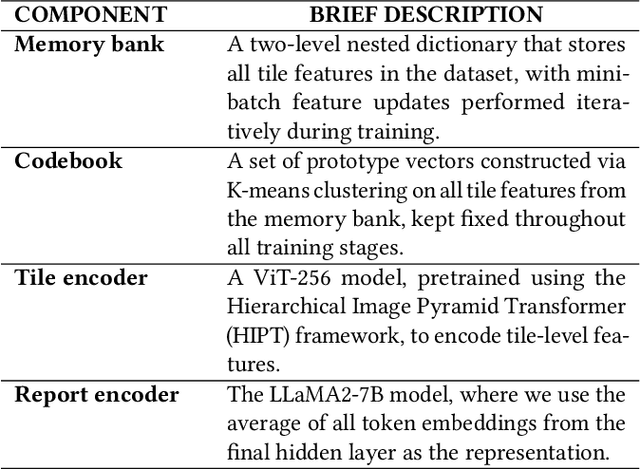
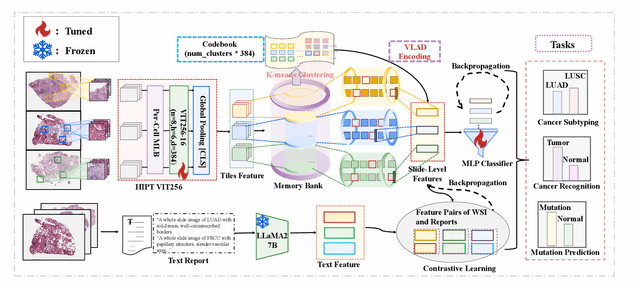
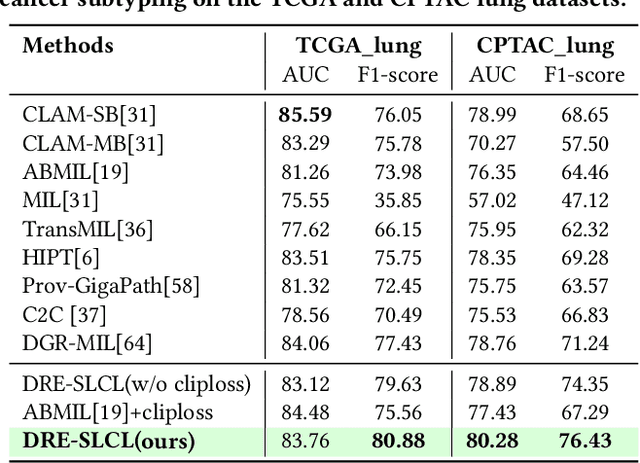
Abstract:Whole Slide Image (WSI) representation is critical for cancer subtyping, cancer recognition and mutation prediction.Training an end-to-end WSI representation model poses significant challenges, as a standard gigapixel slide can contain tens of thousands of image tiles, making it difficult to compute gradients of all tiles in a single mini-batch due to current GPU limitations. To address this challenge, we propose a method of dynamic residual encoding with slide-level contrastive learning (DRE-SLCL) for end-to-end WSI representation. Our approach utilizes a memory bank to store the features of tiles across all WSIs in the dataset. During training, a mini-batch usually contains multiple WSIs. For each WSI in the batch, a subset of tiles is randomly sampled and their features are computed using a tile encoder. Then, additional tile features from the same WSI are selected from the memory bank. The representation of each individual WSI is generated using a residual encoding technique that incorporates both the sampled features and those retrieved from the memory bank. Finally, the slide-level contrastive loss is computed based on the representations and histopathology reports ofthe WSIs within the mini-batch. Experiments conducted over cancer subtyping, cancer recognition, and mutation prediction tasks proved the effectiveness of the proposed DRE-SLCL method.
* 8pages, 3figures, published to ACM Digital Library
Asymmetric Patch Sampling for Contrastive Learning
Jun 05, 2023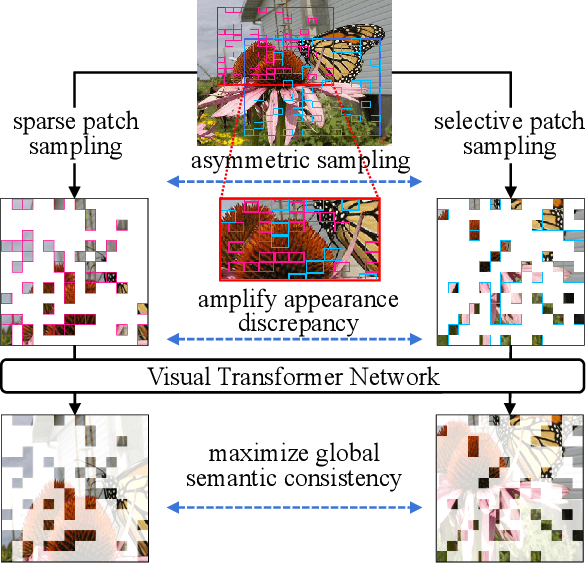
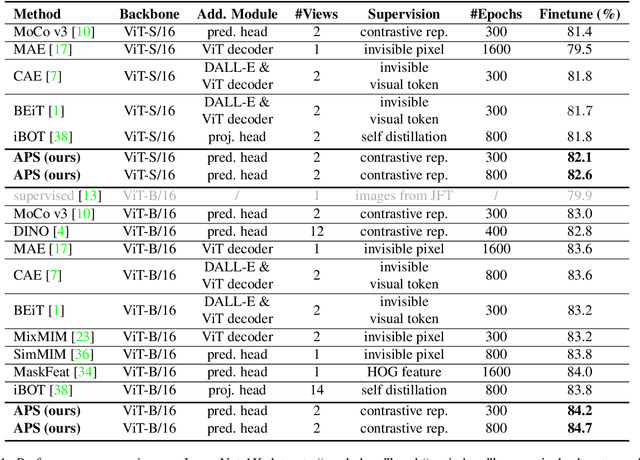
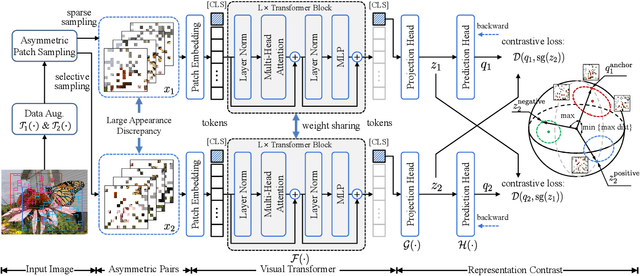

Abstract:Asymmetric appearance between positive pair effectively reduces the risk of representation degradation in contrastive learning. However, there are still a mass of appearance similarities between positive pair constructed by the existing methods, which inhibits the further representation improvement. In this paper, we propose a novel asymmetric patch sampling strategy for contrastive learning, to further boost the appearance asymmetry for better representations. Specifically, dual patch sampling strategies are applied to the given image, to obtain asymmetric positive pairs. First, sparse patch sampling is conducted to obtain the first view, which reduces spatial redundancy of image and allows a more asymmetric view. Second, a selective patch sampling is proposed to construct another view with large appearance discrepancy relative to the first one. Due to the inappreciable appearance similarity between positive pair, the trained model is encouraged to capture the similarity on semantics, instead of low-level ones. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method significantly outperforms the existing self-supervised methods on both ImageNet-1K and CIFAR dataset, e.g., 2.5% finetune accuracy improvement on CIFAR100. Furthermore, our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on downstream tasks, object detection and instance segmentation on COCO.Additionally, compared to other self-supervised methods, our method is more efficient on both memory and computation during training. The source code is available at https://github.com/visresearch/aps.
Multi-modal Multi-kernel Graph Learning for Autism Prediction and Biomarker Discovery
Mar 03, 2023Abstract:Multi-modal integration and classification based on graph learning is among the most challenging obstacles in disease prediction due to its complexity. Several recent works on the basis of attentional mechanisms have been proposed to disentangle the problem of multi-modal integration. However, there are certain limitations to these techniques. Primarily, these works focus on explicitly integrating at the feature level using weight scores, which cannot effectively address the negative impact between modalities. Next, a majority of them utilize single-sized filters to extract graph features, ignoring the heterogeneous information over graphs. To overcome these drawbacks, we propose MMKGL (Multi-modal Multi-Kernel Graph Learning). For the problem of negative impact between modalities, we use the multi-modal graph embedding module to construct a multi-modal graph. Different from the traditional manual construction of static graphs, a separate graph is generated for each modality by graph adaptive learning, where a function graph and a supervision graph are introduced for optimiztion during the multi-graph fusion embedding process. We then apply the multi-kernel graph learning module to extract heterogeneous information from the multi-modal graph. The information in the multi-modal graph at different levels is aggregated by convolutional kernels with different receptive field sizes, followed by generating a cross-kernel discovery tensor for disease prediction. Our method is evaluated on the benchmark Autism Brain Imaging Data Exchange (ABIDE) dataset and outperforms the state-of-the-art methods. In addition, discriminative brain regions associated with autism are identified by our model, providing guidance for the study of autism pathology.
Exploring Contextual Relationships for Cervical Abnormal Cell Detection
Jul 18, 2022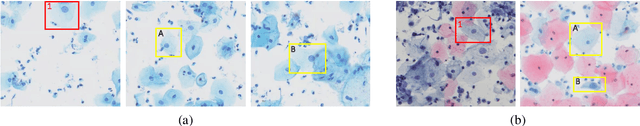
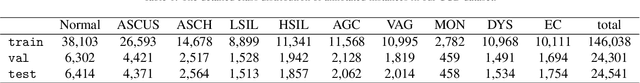
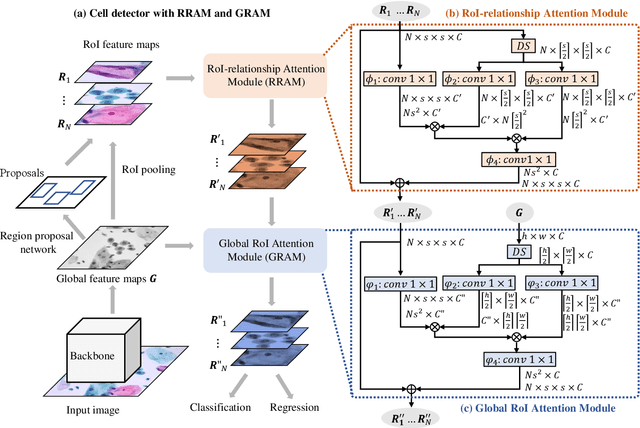
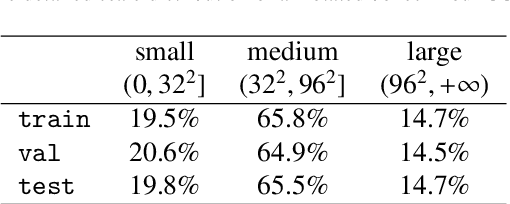
Abstract:Cervical abnormal cell detection is a challenging task as the morphological discrepancies between abnormal and normal cells are usually subtle. To determine whether a cervical cell is normal or abnormal, cytopathologists always take surrounding cells as references to identify its abnormality. To mimic these behaviors, we propose to explore contextual relationships to boost the performance of cervical abnormal cell detection. Specifically, both contextual relationships between cells and cell-to-global images are exploited to enhance features of each region of interest (RoI) proposals. Accordingly, two modules, dubbed as RoI-relationship attention module (RRAM) and global RoI attention module (GRAM), are developed and their combination strategies are also investigated. We establish a strong baseline by using Double-Head Faster R-CNN with feature pyramid network (FPN) and integrate our RRAM and GRAM into it to validate the effectiveness of the proposed modules. Experiments conducted on a large cervical cell detection dataset reveal that the introduction of RRAM and GRAM both achieves better average precision (AP) than the baseline methods. Moreover, when cascading RRAM and GRAM, our method outperforms the state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods. Furthermore, we also show the proposed feature enhancing scheme can facilitate both image-level and smear-level classification. The code and trained models are publicly available at https://github.com/CVIU-CSU/CR4CACD.
MRI-based Multi-task Decoupling Learning for Alzheimer's Disease Detection and MMSE Score Prediction: A Multi-site Validation
Apr 06, 2022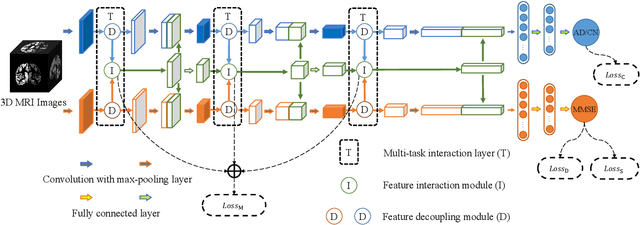

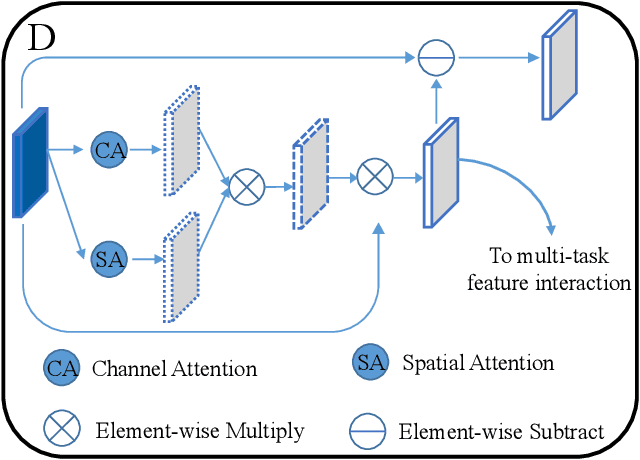

Abstract:Accurately detecting Alzheimer's disease (AD) and predicting mini-mental state examination (MMSE) score are important tasks in elderly health by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Most of the previous methods on these two tasks are based on single-task learning and rarely consider the correlation between them. Since the MMSE score, which is an important basis for AD diagnosis, can also reflect the progress of cognitive impairment, some studies have begun to apply multi-task learning methods to these two tasks. However, how to exploit feature correlation remains a challenging problem for these methods. To comprehensively address this challenge, we propose a MRI-based multi-task decoupled learning method for AD detection and MMSE score prediction. First, a multi-task learning network is proposed to implement AD detection and MMSE score prediction, which exploits feature correlation by adding three multi-task interaction layers between the backbones of the two tasks. Each multi-task interaction layer contains two feature decoupling modules and one feature interaction module. Furthermore, to enhance the generalization between tasks of the features selected by the feature decoupling module, we propose the feature consistency loss constrained feature decoupling module. Finally, in order to exploit the specific distribution information of MMSE score in different groups, a distribution loss is proposed to further enhance the model performance. We evaluate our proposed method on multi-site datasets. Experimental results show that our proposed multi-task decoupled representation learning method achieves good performance, outperforming single-task learning and other existing state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge