Chenduo Hao
Mimic In-Context Learning for Multimodal Tasks
Apr 11, 2025Abstract:Recently, In-context Learning (ICL) has become a significant inference paradigm in Large Multimodal Models (LMMs), utilizing a few in-context demonstrations (ICDs) to prompt LMMs for new tasks. However, the synergistic effects in multimodal data increase the sensitivity of ICL performance to the configurations of ICDs, stimulating the need for a more stable and general mapping function. Mathematically, in Transformer-based models, ICDs act as ``shift vectors'' added to the hidden states of query tokens. Inspired by this, we introduce Mimic In-Context Learning (MimIC) to learn stable and generalizable shift effects from ICDs. Specifically, compared with some previous shift vector-based methods, MimIC more strictly approximates the shift effects by integrating lightweight learnable modules into LMMs with four key enhancements: 1) inserting shift vectors after attention layers, 2) assigning a shift vector to each attention head, 3) making shift magnitude query-dependent, and 4) employing a layer-wise alignment loss. Extensive experiments on two LMMs (Idefics-9b and Idefics2-8b-base) across three multimodal tasks (VQAv2, OK-VQA, Captioning) demonstrate that MimIC outperforms existing shift vector-based methods. The code is available at https://github.com/Kamichanw/MimIC.
Learnable In-Context Vector for Visual Question Answering
Jun 19, 2024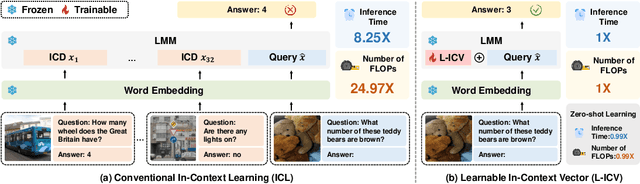
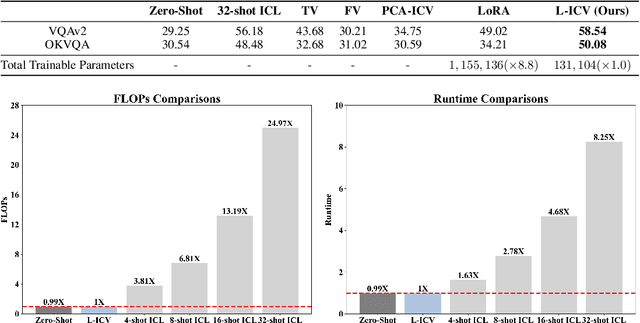
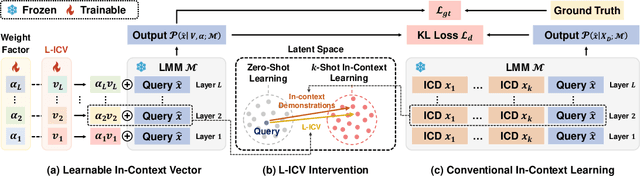
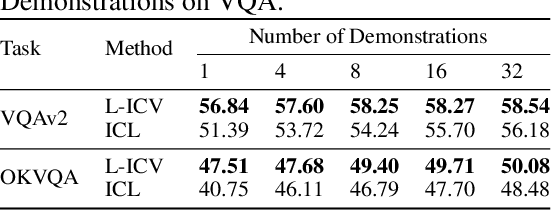
Abstract:As language models continue to scale, Large Language Models (LLMs) have exhibited emerging capabilities in In-Context Learning (ICL), enabling them to solve language tasks by prefixing a few in-context demonstrations (ICDs) as context. Inspired by these advancements, researchers have extended these techniques to develop Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) with ICL capabilities. However, applying ICL usually faces two major challenges: 1) using more ICDs will largely increase the inference time and 2) the performance is sensitive to the selection of ICDs. These challenges are further exacerbated in LMMs due to the integration of multiple data types and the combinational complexity of multimodal ICDs. Recently, to address these challenges, some NLP studies introduce non-learnable In-Context Vectors (ICVs) which extract useful task information from ICDs into a single vector and then insert it into the LLM to help solve the corresponding task. However, although useful in simple NLP tasks, these non-learnable methods fail to handle complex multimodal tasks like Visual Question Answering (VQA). In this study, we propose \textbf{Learnable ICV} (L-ICV) to distill essential task information from demonstrations, improving ICL performance in LMMs. Experiments show that L-ICV can significantly reduce computational costs while enhancing accuracy in VQA tasks compared to traditional ICL and other non-learnable ICV methods.
Improved NL2SQL based on Multi-layer Expert Network
Jun 30, 2023Abstract:The Natural Language to SQL (NL2SQL) technique is used to convert natural language queries into executable SQL statements. Typically, slot-filling is employed as a classification method for multi-task cases to achieve this goal. However, slot-filling can result in inaccurate SQL statement generation due to negative migration issues arising from different classification tasks. To overcome this limitation, this study introduces a new approach called Multi-Layer Expert Generate SQL (MLEG-SQL), which utilizes a dedicated multi-task hierarchical network. The lower layer of the network extracts semantic features of natural language statements, while the upper layer builds a specialized expert system for handling specific classification tasks. This hierarchical approach mitigates performance degradation resulting from different task conflicts. The proposed method was evaluated on the WiKSQL dataset and was found to be effective in generating accurate SQL statements.
Feature Representation Learning for NL2SQL Generation Based on Coupling and Decoupling
Jun 30, 2023Abstract:The NL2SQL task involves parsing natural language statements into SQL queries. While most state-of-the-art methods treat NL2SQL as a slot-filling task and use feature representation learning techniques, they overlook explicit correlation features between the SELECT and WHERE clauses and implicit correlation features between sub-tasks within a single clause. To address this issue, we propose the Clause Feature Correlation Decoupling and Coupling (CFCDC) model, which uses a feature representation decoupling method to separate the SELECT and WHERE clauses at the parameter level. Next, we introduce a multi-task learning architecture to decouple implicit correlation feature representation between different SQL tasks in a specific clause. Moreover, we present an improved feature representation coupling module to integrate the decoupled tasks in the SELECT and WHERE clauses and predict the final SQL query. Our proposed CFCDC model demonstrates excellent performance on the WikiSQL dataset, with significant improvements in logic precision and execution accuracy. The source code for the model will be publicly available on GitHub
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge