Artur Jesslen
CNS-Bench: Benchmarking Image Classifier Robustness Under Continuous Nuisance Shifts
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:An important challenge when using computer vision models in the real world is to evaluate their performance in potential out-of-distribution (OOD) scenarios. While simple synthetic corruptions are commonly applied to test OOD robustness, they often fail to capture nuisance shifts that occur in the real world. Recently, diffusion models have been applied to generate realistic images for benchmarking, but they are restricted to binary nuisance shifts. In this work, we introduce CNS-Bench, a Continuous Nuisance Shift Benchmark to quantify OOD robustness of image classifiers for continuous and realistic generative nuisance shifts. CNS-Bench allows generating a wide range of individual nuisance shifts in continuous severities by applying LoRA adapters to diffusion models. To address failure cases, we propose a filtering mechanism that outperforms previous methods, thereby enabling reliable benchmarking with generative models. With the proposed benchmark, we perform a large-scale study to evaluate the robustness of more than 40 classifiers under various nuisance shifts. Through carefully designed comparisons and analyses, we find that model rankings can change for varying shifts and shift scales, which cannot be captured when applying common binary shifts. Additionally, we show that evaluating the model performance on a continuous scale allows the identification of model failure points, providing a more nuanced understanding of model robustness. Project page including code and data: https://genintel.github.io/CNS.
iNeMo: Incremental Neural Mesh Models for Robust Class-Incremental Learning
Jul 12, 2024Abstract:Different from human nature, it is still common practice today for vision tasks to train deep learning models only initially and on fixed datasets. A variety of approaches have recently addressed handling continual data streams. However, extending these methods to manage out-of-distribution (OOD) scenarios has not effectively been investigated. On the other hand, it has recently been shown that non-continual neural mesh models exhibit strong performance in generalizing to such OOD scenarios. To leverage this decisive property in a continual learning setting, we propose incremental neural mesh models that can be extended with new meshes over time. In addition, we present a latent space initialization strategy that enables us to allocate feature space for future unseen classes in advance and a positional regularization term that forces the features of the different classes to consistently stay in respective latent space regions. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method through extensive experiments on the Pascal3D and ObjectNet3D datasets and show that our approach outperforms the baselines for classification by $2-6\%$ in the in-domain and by $6-50\%$ in the OOD setting. Our work also presents the first incremental learning approach for pose estimation. Our code and model can be found at https://github.com/Fischer-Tom/iNeMo.
Unsupervised Learning of Category-Level 3D Pose from Object-Centric Videos
Jul 05, 2024



Abstract:Category-level 3D pose estimation is a fundamentally important problem in computer vision and robotics, e.g. for embodied agents or to train 3D generative models. However, so far methods that estimate the category-level object pose require either large amounts of human annotations, CAD models or input from RGB-D sensors. In contrast, we tackle the problem of learning to estimate the category-level 3D pose only from casually taken object-centric videos without human supervision. We propose a two-step pipeline: First, we introduce a multi-view alignment procedure that determines canonical camera poses across videos with a novel and robust cyclic distance formulation for geometric and appearance matching using reconstructed coarse meshes and DINOv2 features. In a second step, the canonical poses and reconstructed meshes enable us to train a model for 3D pose estimation from a single image. In particular, our model learns to estimate dense correspondences between images and a prototypical 3D template by predicting, for each pixel in a 2D image, a feature vector of the corresponding vertex in the template mesh. We demonstrate that our method outperforms all baselines at the unsupervised alignment of object-centric videos by a large margin and provides faithful and robust predictions in-the-wild. Our code and data is available at https://github.com/GenIntel/uns-obj-pose3d.
Animal3D: A Comprehensive Dataset of 3D Animal Pose and Shape
Aug 22, 2023



Abstract:Accurately estimating the 3D pose and shape is an essential step towards understanding animal behavior, and can potentially benefit many downstream applications, such as wildlife conservation. However, research in this area is held back by the lack of a comprehensive and diverse dataset with high-quality 3D pose and shape annotations. In this paper, we propose Animal3D, the first comprehensive dataset for mammal animal 3D pose and shape estimation. Animal3D consists of 3379 images collected from 40 mammal species, high-quality annotations of 26 keypoints, and importantly the pose and shape parameters of the SMAL model. All annotations were labeled and checked manually in a multi-stage process to ensure highest quality results. Based on the Animal3D dataset, we benchmark representative shape and pose estimation models at: (1) supervised learning from only the Animal3D data, (2) synthetic to real transfer from synthetically generated images, and (3) fine-tuning human pose and shape estimation models. Our experimental results demonstrate that predicting the 3D shape and pose of animals across species remains a very challenging task, despite significant advances in human pose estimation. Our results further demonstrate that synthetic pre-training is a viable strategy to boost the model performance. Overall, Animal3D opens new directions for facilitating future research in animal 3D pose and shape estimation, and is publicly available.
Robust 3D-aware Object Classification via Discriminative Render-and-Compare
May 24, 2023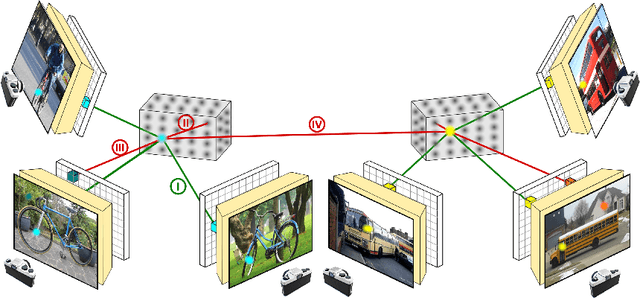
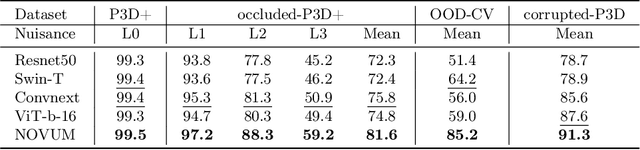
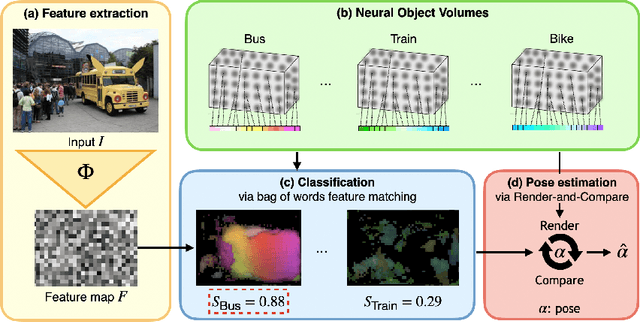
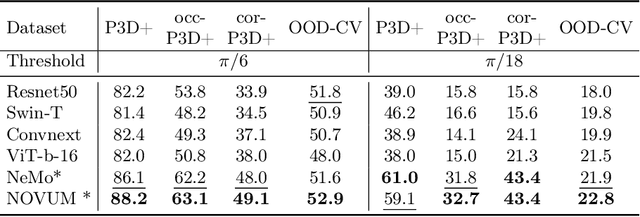
Abstract:In real-world applications, it is essential to jointly estimate the 3D object pose and class label of objects, i.e., to perform 3D-aware classification.While current approaches for either image classification or pose estimation can be extended to 3D-aware classification, we observe that they are inherently limited: 1) Their performance is much lower compared to the respective single-task models, and 2) they are not robust in out-of-distribution (OOD) scenarios. Our main contribution is a novel architecture for 3D-aware classification, which builds upon a recent work and performs comparably to single-task models while being highly robust. In our method, an object category is represented as a 3D cuboid mesh composed of feature vectors at each mesh vertex. Using differentiable rendering, we estimate the 3D object pose by minimizing the reconstruction error between the mesh and the feature representation of the target image. Object classification is then performed by comparing the reconstruction losses across object categories. Notably, the neural texture of the mesh is trained in a discriminative manner to enhance the classification performance while also avoiding local optima in the reconstruction loss. Furthermore, we show how our method and feed-forward neural networks can be combined to scale the render-and-compare approach to larger numbers of categories. Our experiments on PASCAL3D+, occluded-PASCAL3D+, and OOD-CV show that our method outperforms all baselines at 3D-aware classification by a wide margin in terms of performance and robustness.
OOD-CV-v2: An extended Benchmark for Robustness to Out-of-Distribution Shifts of Individual Nuisances in Natural Images
Apr 17, 2023



Abstract:Enhancing the robustness of vision algorithms in real-world scenarios is challenging. One reason is that existing robustness benchmarks are limited, as they either rely on synthetic data or ignore the effects of individual nuisance factors. We introduce OOD-CV-v2, a benchmark dataset that includes out-of-distribution examples of 10 object categories in terms of pose, shape, texture, context and the weather conditions, and enables benchmarking of models for image classification, object detection, and 3D pose estimation. In addition to this novel dataset, we contribute extensive experiments using popular baseline methods, which reveal that: 1) Some nuisance factors have a much stronger negative effect on the performance compared to others, also depending on the vision task. 2) Current approaches to enhance robustness have only marginal effects, and can even reduce robustness. 3) We do not observe significant differences between convolutional and transformer architectures. We believe our dataset provides a rich test bed to study robustness and will help push forward research in this area. Our dataset can be accessed from http://www.ood-cv.org/challenge.html
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge