Siwei Yang
GPT-IMAGE-EDIT-1.5M: A Million-Scale, GPT-Generated Image Dataset
Jul 28, 2025
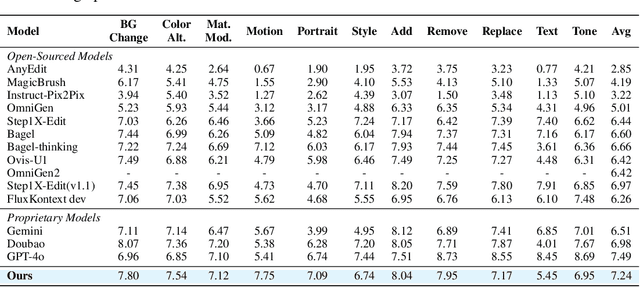
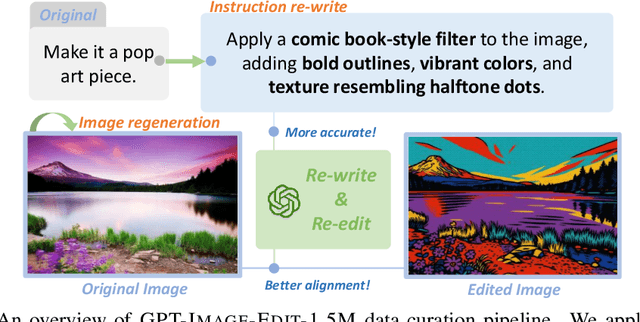
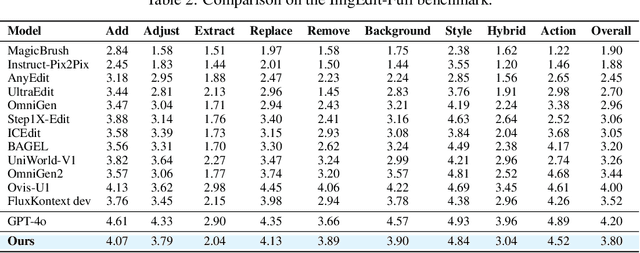
Abstract:Recent advancements in large multimodal models like GPT-4o have set a new standard for high-fidelity, instruction-guided image editing. However, the proprietary nature of these models and their training data creates a significant barrier for open-source research. To bridge this gap, we introduce GPT-IMAGE-EDIT-1.5M, a publicly available, large-scale image-editing corpus containing more than 1.5 million high-quality triplets (instruction, source image, edited image). We systematically construct this dataset by leveraging the versatile capabilities of GPT-4o to unify and refine three popular image-editing datasets: OmniEdit, HQ-Edit, and UltraEdit. Specifically, our methodology involves 1) regenerating output images to enhance visual quality and instruction alignment, and 2) selectively rewriting prompts to improve semantic clarity. To validate the efficacy of our dataset, we fine-tune advanced open-source models on GPT-IMAGE-EDIT-1.5M. The empirical results are exciting, e.g., the fine-tuned FluxKontext achieves highly competitive performance across a comprehensive suite of benchmarks, including 7.24 on GEdit-EN, 3.80 on ImgEdit-Full, and 8.78 on Complex-Edit, showing stronger instruction following and higher perceptual quality while maintaining identity. These scores markedly exceed all previously published open-source methods and substantially narrow the gap to leading proprietary models. We hope the full release of GPT-IMAGE-EDIT-1.5M can help to catalyze further open research in instruction-guided image editing.
$\texttt{Complex-Edit}$: CoT-Like Instruction Generation for Complexity-Controllable Image Editing Benchmark
Apr 17, 2025Abstract:We introduce $\texttt{Complex-Edit}$, a comprehensive benchmark designed to systematically evaluate instruction-based image editing models across instructions of varying complexity. To develop this benchmark, we harness GPT-4o to automatically collect a diverse set of editing instructions at scale. Our approach follows a well-structured ``Chain-of-Edit'' pipeline: we first generate individual atomic editing tasks independently and then integrate them to form cohesive, complex instructions. Additionally, we introduce a suite of metrics to assess various aspects of editing performance, along with a VLM-based auto-evaluation pipeline that supports large-scale assessments. Our benchmark yields several notable insights: 1) Open-source models significantly underperform relative to proprietary, closed-source models, with the performance gap widening as instruction complexity increases; 2) Increased instructional complexity primarily impairs the models' ability to retain key elements from the input images and to preserve the overall aesthetic quality; 3) Decomposing a complex instruction into a sequence of atomic steps, executed in a step-by-step manner, substantially degrades performance across multiple metrics; 4) A straightforward Best-of-N selection strategy improves results for both direct editing and the step-by-step sequential approach; and 5) We observe a ``curse of synthetic data'': when synthetic data is involved in model training, the edited images from such models tend to appear increasingly synthetic as the complexity of the editing instructions rises -- a phenomenon that intriguingly also manifests in the latest GPT-4o outputs.
HQ-Edit: A High-Quality Dataset for Instruction-based Image Editing
Apr 15, 2024



Abstract:This study introduces HQ-Edit, a high-quality instruction-based image editing dataset with around 200,000 edits. Unlike prior approaches relying on attribute guidance or human feedback on building datasets, we devise a scalable data collection pipeline leveraging advanced foundation models, namely GPT-4V and DALL-E 3. To ensure its high quality, diverse examples are first collected online, expanded, and then used to create high-quality diptychs featuring input and output images with detailed text prompts, followed by precise alignment ensured through post-processing. In addition, we propose two evaluation metrics, Alignment and Coherence, to quantitatively assess the quality of image edit pairs using GPT-4V. HQ-Edits high-resolution images, rich in detail and accompanied by comprehensive editing prompts, substantially enhance the capabilities of existing image editing models. For example, an HQ-Edit finetuned InstructPix2Pix can attain state-of-the-art image editing performance, even surpassing those models fine-tuned with human-annotated data. The project page is https://thefllood.github.io/HQEdit_web.
3D-TransUNet for Brain Metastases Segmentation in the BraTS2023 Challenge
Mar 23, 2024



Abstract:Segmenting brain tumors is complex due to their diverse appearances and scales. Brain metastases, the most common type of brain tumor, are a frequent complication of cancer. Therefore, an effective segmentation model for brain metastases must adeptly capture local intricacies to delineate small tumor regions while also integrating global context to understand broader scan features. The TransUNet model, which combines Transformer self-attention with U-Net's localized information, emerges as a promising solution for this task. In this report, we address brain metastases segmentation by training the 3D-TransUNet model on the Brain Tumor Segmentation (BraTS-METS) 2023 challenge dataset. Specifically, we explored two architectural configurations: the Encoder-only 3D-TransUNet, employing Transformers solely in the encoder, and the Decoder-only 3D-TransUNet, utilizing Transformers exclusively in the decoder. For Encoder-only 3D-TransUNet, we note that Masked-Autoencoder pre-training is required for a better initialization of the Transformer Encoder and thus accelerates the training process. We identify that the Decoder-only 3D-TransUNet model should offer enhanced efficacy in the segmentation of brain metastases, as indicated by our 5-fold cross-validation on the training set. However, our use of the Encoder-only 3D-TransUNet model already yield notable results, with an average lesion-wise Dice score of 59.8\% on the test set, securing second place in the BraTS-METS 2023 challenge.
AQA-Bench: An Interactive Benchmark for Evaluating LLMs' Sequential Reasoning Ability
Feb 14, 2024Abstract:This paper introduces AQA-Bench, a novel benchmark to assess the sequential reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in algorithmic contexts, such as depth-first search (DFS). The key feature of our evaluation benchmark lies in its interactive evaluation protocol -- for example, in DFS, the availability of each node's connected edge is contingent upon the model's traversal to that node, thereby necessitating the LLM's ability to effectively remember visited nodes and strategize subsequent moves. We comprehensively build AQA-Bench with three different algorithms, namely binary search, depth-first search, and breadth-first search, and to evaluate the sequential reasoning ability of 12 different LLMs. Our investigations reveal several interesting findings: (1) Closed-source models like GPT-4 and Gemini generally show strong sequential reasoning ability, significantly outperforming open-source LLMs. (2) Naively providing interactive examples may inadvertently hurt few-shot performance. (3) A very limited number of predecessor steps following the optimal policy can substantially boost small models' performance. (4) The scaling correlation between performance and model size is not always significant, sometimes even showcasing an inverse trend. We hope our study can catalyze future work on advancing the understanding and enhancement of LLMs' capabilities in sequential reasoning. The code is available at https://github.com/UCSC-VLAA/AQA-Bench.
Large-scale Weakly Supervised Learning for Road Extraction from Satellite Imagery
Sep 14, 2023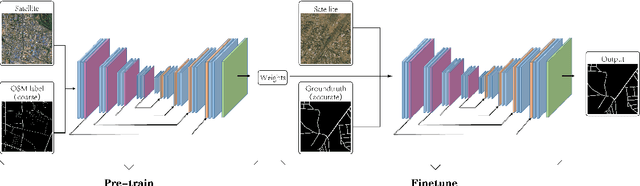
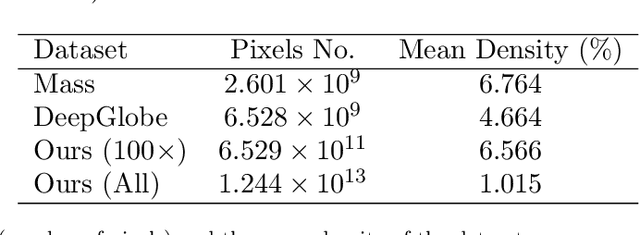
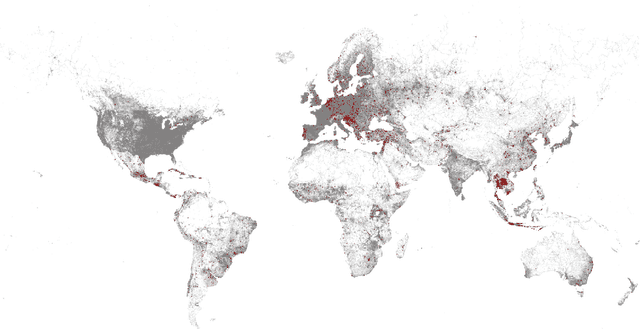
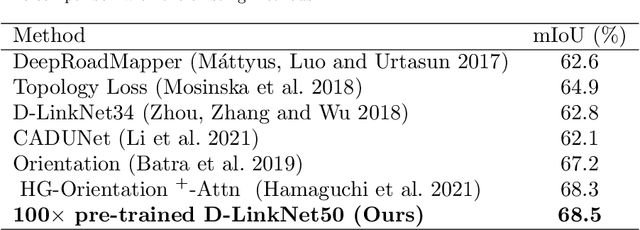
Abstract:Automatic road extraction from satellite imagery using deep learning is a viable alternative to traditional manual mapping. Therefore it has received considerable attention recently. However, most of the existing methods are supervised and require pixel-level labeling, which is tedious and error-prone. To make matters worse, the earth has a diverse range of terrain, vegetation, and man-made objects. It is well known that models trained in one area generalize poorly to other areas. Various shooting conditions such as light and angel, as well as different image processing techniques further complicate the issue. It is impractical to develop training data to cover all image styles. This paper proposes to leverage OpenStreetMap road data as weak labels and large scale satellite imagery to pre-train semantic segmentation models. Our extensive experimental results show that the prediction accuracy increases with the amount of the weakly labeled data, as well as the road density in the areas chosen for training. Using as much as 100 times more data than the widely used DeepGlobe road dataset, our model with the D-LinkNet architecture and the ResNet-50 backbone exceeds the top performer of the current DeepGlobe leaderboard. Furthermore, due to large-scale pre-training, our model generalizes much better than those trained with only the curated datasets, implying great application potential.
Contrastive Multi-Task Dense Prediction
Jul 16, 2023



Abstract:This paper targets the problem of multi-task dense prediction which aims to achieve simultaneous learning and inference on a bunch of multiple dense prediction tasks in a single framework. A core objective in design is how to effectively model cross-task interactions to achieve a comprehensive improvement on different tasks based on their inherent complementarity and consistency. Existing works typically design extra expensive distillation modules to perform explicit interaction computations among different task-specific features in both training and inference, bringing difficulty in adaptation for different task sets, and reducing efficiency due to clearly increased size of multi-task models. In contrast, we introduce feature-wise contrastive consistency into modeling the cross-task interactions for multi-task dense prediction. We propose a novel multi-task contrastive regularization method based on the consistency to effectively boost the representation learning of the different sub-tasks, which can also be easily generalized to different multi-task dense prediction frameworks, and costs no additional computation in the inference. Extensive experiments on two challenging datasets (i.e. NYUD-v2 and Pascal-Context) clearly demonstrate the superiority of the proposed multi-task contrastive learning approach for dense predictions, establishing new state-of-the-art performances.
OOD-CV-v2: An extended Benchmark for Robustness to Out-of-Distribution Shifts of Individual Nuisances in Natural Images
Apr 17, 2023



Abstract:Enhancing the robustness of vision algorithms in real-world scenarios is challenging. One reason is that existing robustness benchmarks are limited, as they either rely on synthetic data or ignore the effects of individual nuisance factors. We introduce OOD-CV-v2, a benchmark dataset that includes out-of-distribution examples of 10 object categories in terms of pose, shape, texture, context and the weather conditions, and enables benchmarking of models for image classification, object detection, and 3D pose estimation. In addition to this novel dataset, we contribute extensive experiments using popular baseline methods, which reveal that: 1) Some nuisance factors have a much stronger negative effect on the performance compared to others, also depending on the vision task. 2) Current approaches to enhance robustness have only marginal effects, and can even reduce robustness. 3) We do not observe significant differences between convolutional and transformer architectures. We believe our dataset provides a rich test bed to study robustness and will help push forward research in this area. Our dataset can be accessed from http://www.ood-cv.org/challenge.html
AsyInst: Asymmetric Affinity with DepthGrad and Color for Box-Supervised Instance Segmentation
Dec 07, 2022



Abstract:The weakly supervised instance segmentation is a challenging task. The existing methods typically use bounding boxes as supervision and optimize the network with a regularization loss term such as pairwise color affinity loss for instance segmentation. Through systematic analysis, we found that the commonly used pairwise affinity loss has two limitations: (1) it works with color affinity but leads to inferior performance with other modalities such as depth gradient, (2)the original affinity loss does not prevent trivial predictions as intended but actually accelerates this process due to the affinity loss term being symmetric. To overcome these two limitations, in this paper, we propose a novel asymmetric affinity loss which provides the penalty against the trivial prediction and generalizes well with affinity loss from different modalities. With the proposed asymmetric affinity loss, our method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on the Cityscapes dataset and outperforms our baseline method by 3.5% in mask AP.
XCon: Learning with Experts for Fine-grained Category Discovery
Aug 03, 2022
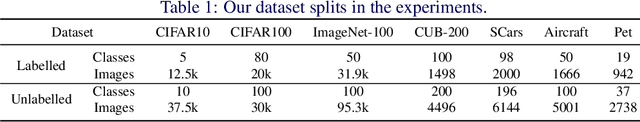
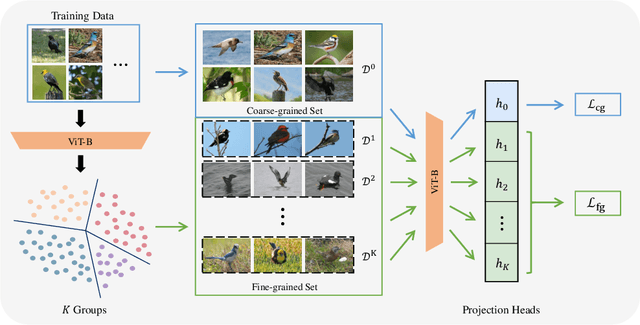
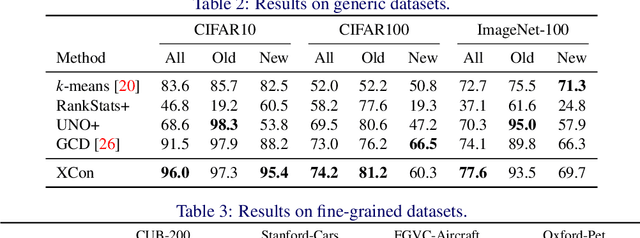
Abstract:We address the problem of generalized category discovery (GCD) in this paper, i.e. clustering the unlabeled images leveraging the information from a set of seen classes, where the unlabeled images could contain both seen classes and unseen classes. The seen classes can be seen as an implicit criterion of classes, which makes this setting different from unsupervised clustering where the cluster criteria may be ambiguous. We mainly concern the problem of discovering categories within a fine-grained dataset since it is one of the most direct applications of category discovery, i.e. helping experts discover novel concepts within an unlabeled dataset using the implicit criterion set forth by the seen classes. State-of-the-art methods for generalized category discovery leverage contrastive learning to learn the representations, but the large inter-class similarity and intra-class variance pose a challenge for the methods because the negative examples may contain irrelevant cues for recognizing a category so the algorithms may converge to a local-minima. We present a novel method called Expert-Contrastive Learning (XCon) to help the model to mine useful information from the images by first partitioning the dataset into sub-datasets using k-means clustering and then performing contrastive learning on each of the sub-datasets to learn fine-grained discriminative features. Experiments on fine-grained datasets show a clear improved performance over the previous best methods, indicating the effectiveness of our method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge