Zonglin Di
Automatic Dataset Construction (ADC): Sample Collection, Data Curation, and Beyond
Aug 21, 2024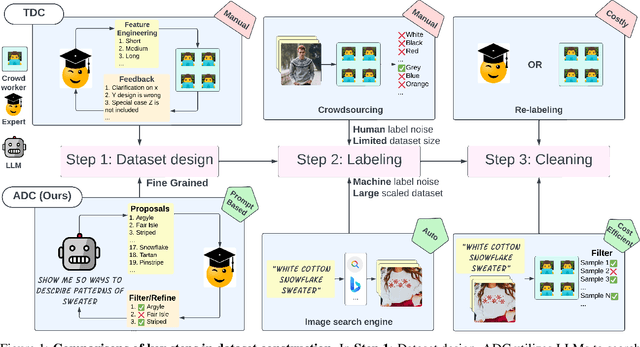
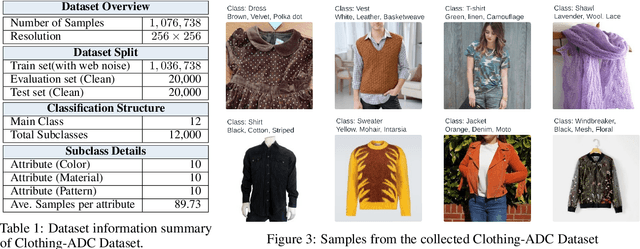
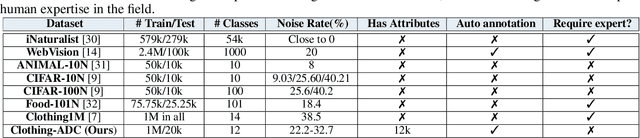
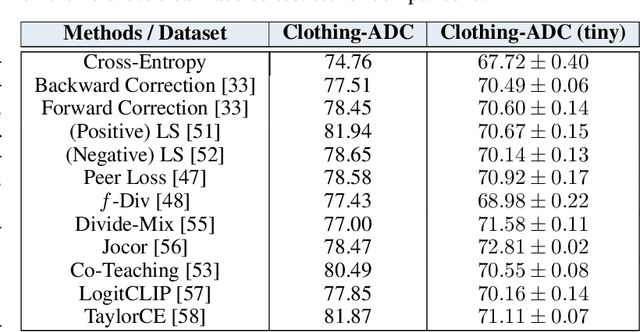
Abstract:Large-scale data collection is essential for developing personalized training data, mitigating the shortage of training data, and fine-tuning specialized models. However, creating high-quality datasets quickly and accurately remains a challenge due to annotation errors, the substantial time and costs associated with human labor. To address these issues, we propose Automatic Dataset Construction (ADC), an innovative methodology that automates dataset creation with negligible cost and high efficiency. Taking the image classification task as a starting point, ADC leverages LLMs for the detailed class design and code generation to collect relevant samples via search engines, significantly reducing the need for manual annotation and speeding up the data generation process. Despite these advantages, ADC also encounters real-world challenges such as label errors (label noise) and imbalanced data distributions (label bias). We provide open-source software that incorporates existing methods for label error detection, robust learning under noisy and biased data, ensuring a higher-quality training data and more robust model training procedure. Furthermore, we design three benchmark datasets focused on label noise detection, label noise learning, and class-imbalanced learning. These datasets are vital because there are few existing datasets specifically for label noise detection, despite its importance. Finally, we evaluate the performance of existing popular methods on these datasets, thereby facilitating further research in the field.
Label Smoothing Improves Machine Unlearning
Jun 11, 2024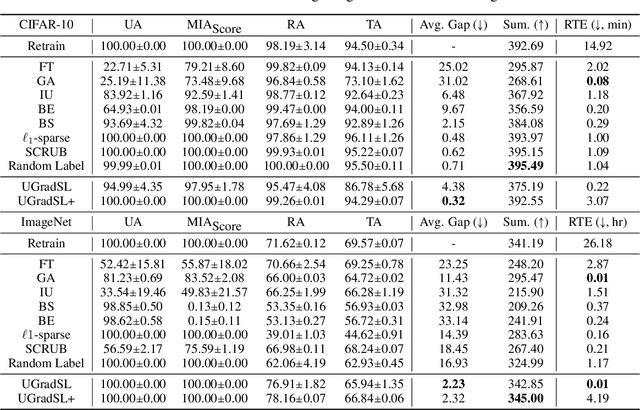
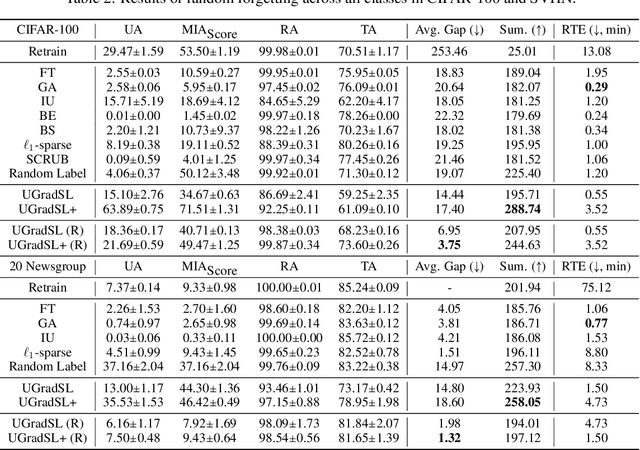
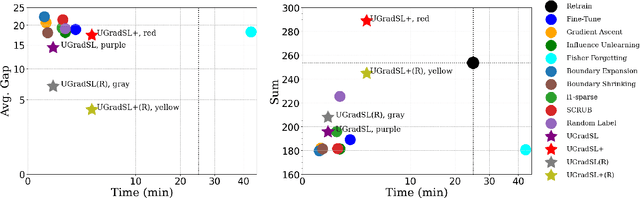
Abstract:The objective of machine unlearning (MU) is to eliminate previously learned data from a model. However, it is challenging to strike a balance between computation cost and performance when using existing MU techniques. Taking inspiration from the influence of label smoothing on model confidence and differential privacy, we propose a simple gradient-based MU approach that uses an inverse process of label smoothing. This work introduces UGradSL, a simple, plug-and-play MU approach that uses smoothed labels. We provide theoretical analyses demonstrating why properly introducing label smoothing improves MU performance. We conducted extensive experiments on six datasets of various sizes and different modalities, demonstrating the effectiveness and robustness of our proposed method. The consistent improvement in MU performance is only at a marginal cost of additional computations. For instance, UGradSL improves over the gradient ascent MU baseline by 66% unlearning accuracy without sacrificing unlearning efficiency.
Adversarial Machine Unlearning
Jun 11, 2024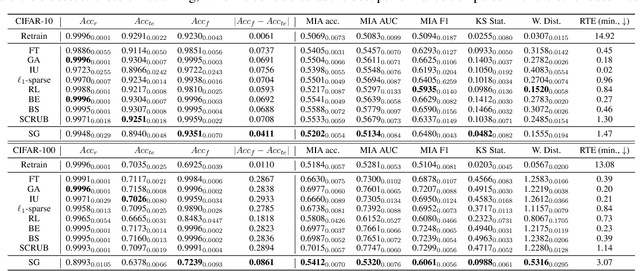
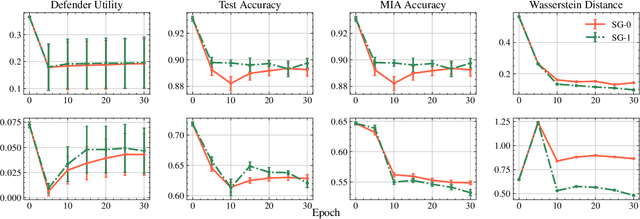
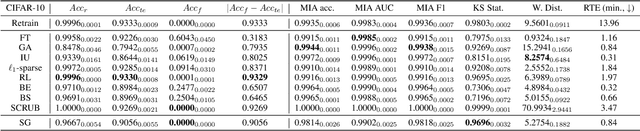
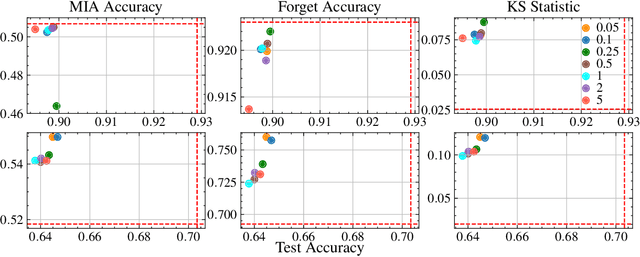
Abstract:This paper focuses on the challenge of machine unlearning, aiming to remove the influence of specific training data on machine learning models. Traditionally, the development of unlearning algorithms runs parallel with that of membership inference attacks (MIA), a type of privacy threat to determine whether a data instance was used for training. However, the two strands are intimately connected: one can view machine unlearning through the lens of MIA success with respect to removed data. Recognizing this connection, we propose a game-theoretic framework that integrates MIAs into the design of unlearning algorithms. Specifically, we model the unlearning problem as a Stackelberg game in which an unlearner strives to unlearn specific training data from a model, while an auditor employs MIAs to detect the traces of the ostensibly removed data. Adopting this adversarial perspective allows the utilization of new attack advancements, facilitating the design of unlearning algorithms. Our framework stands out in two ways. First, it takes an adversarial approach and proactively incorporates the attacks into the design of unlearning algorithms. Secondly, it uses implicit differentiation to obtain the gradients that limit the attacker's success, thus benefiting the process of unlearning. We present empirical results to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach for machine unlearning.
Large-scale Weakly Supervised Learning for Road Extraction from Satellite Imagery
Sep 14, 2023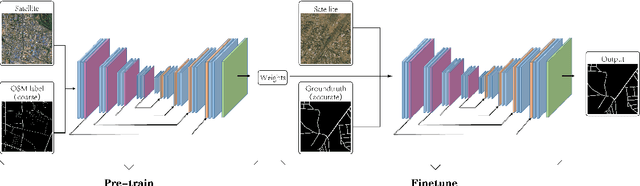
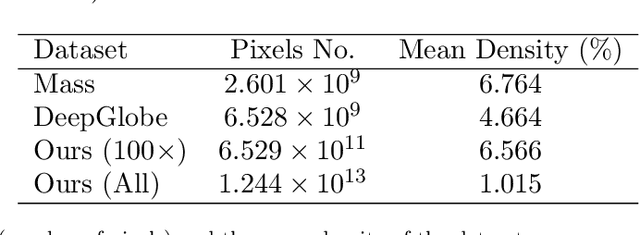
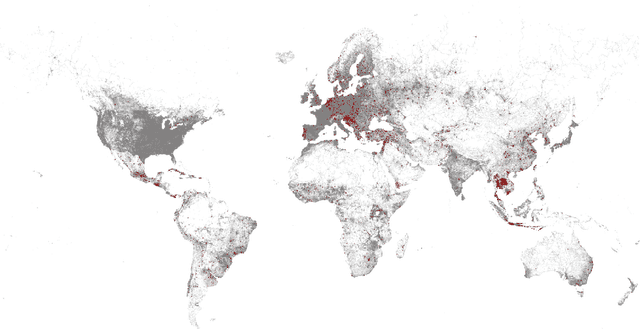
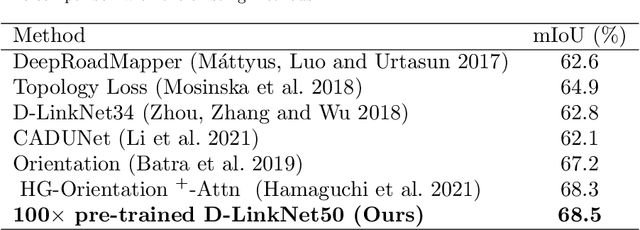
Abstract:Automatic road extraction from satellite imagery using deep learning is a viable alternative to traditional manual mapping. Therefore it has received considerable attention recently. However, most of the existing methods are supervised and require pixel-level labeling, which is tedious and error-prone. To make matters worse, the earth has a diverse range of terrain, vegetation, and man-made objects. It is well known that models trained in one area generalize poorly to other areas. Various shooting conditions such as light and angel, as well as different image processing techniques further complicate the issue. It is impractical to develop training data to cover all image styles. This paper proposes to leverage OpenStreetMap road data as weak labels and large scale satellite imagery to pre-train semantic segmentation models. Our extensive experimental results show that the prediction accuracy increases with the amount of the weakly labeled data, as well as the road density in the areas chosen for training. Using as much as 100 times more data than the widely used DeepGlobe road dataset, our model with the D-LinkNet architecture and the ResNet-50 backbone exceeds the top performer of the current DeepGlobe leaderboard. Furthermore, due to large-scale pre-training, our model generalizes much better than those trained with only the curated datasets, implying great application potential.
T2IAT: Measuring Valence and Stereotypical Biases in Text-to-Image Generation
Jun 01, 2023



Abstract:Warning: This paper contains several contents that may be toxic, harmful, or offensive. In the last few years, text-to-image generative models have gained remarkable success in generating images with unprecedented quality accompanied by a breakthrough of inference speed. Despite their rapid progress, human biases that manifest in the training examples, particularly with regard to common stereotypical biases, like gender and skin tone, still have been found in these generative models. In this work, we seek to measure more complex human biases exist in the task of text-to-image generations. Inspired by the well-known Implicit Association Test (IAT) from social psychology, we propose a novel Text-to-Image Association Test (T2IAT) framework that quantifies the implicit stereotypes between concepts and valence, and those in the images. We replicate the previously documented bias tests on generative models, including morally neutral tests on flowers and insects as well as demographic stereotypical tests on diverse social attributes. The results of these experiments demonstrate the presence of complex stereotypical behaviors in image generations.
Navigation as the Attacker Wishes? Towards Building Byzantine-Robust Embodied Agents under Federated Learning
Dec 02, 2022Abstract:Federated embodied agent learning protects the data privacy of individual visual environments by keeping data locally at each client (the individual environment) during training. However, since the local data is inaccessible to the server under federated learning, attackers may easily poison the training data of the local client to build a backdoor in the agent without notice. Deploying such an agent raises the risk of potential harm to humans, as the attackers may easily navigate and control the agent as they wish via the backdoor. Towards Byzantine-robust federated embodied agent learning, in this paper, we study the attack and defense for the task of vision-and-language navigation (VLN), where the agent is required to follow natural language instructions to navigate indoor environments. First, we introduce a simple but effective attack strategy, Navigation as Wish (NAW), in which the malicious client manipulates local trajectory data to implant a backdoor into the global model. Results on two VLN datasets (R2R and RxR) show that NAW can easily navigate the deployed VLN agent regardless of the language instruction, without affecting its performance on normal test sets. Then, we propose a new Prompt-Based Aggregation (PBA) to defend against the NAW attack in federated VLN, which provides the server with a ''prompt'' of the vision-and-language alignment variance between the benign and malicious clients so that they can be distinguished during training. We validate the effectiveness of the PBA method on protecting the global model from the NAW attack, which outperforms other state-of-the-art defense methods by a large margin in the defense metrics on R2R and RxR.
JARVIS: A Neuro-Symbolic Commonsense Reasoning Framework for Conversational Embodied Agents
Aug 30, 2022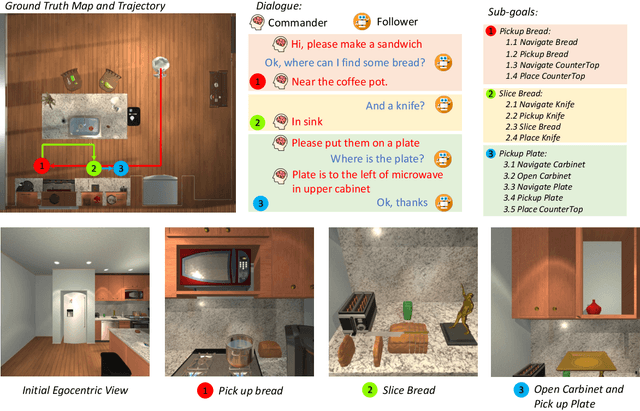

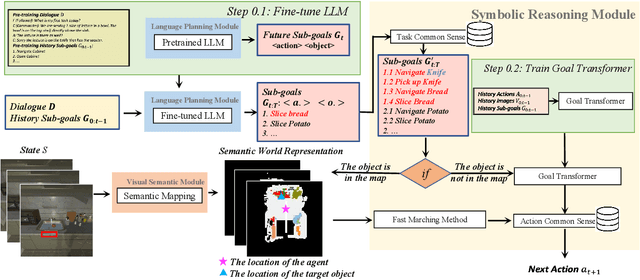
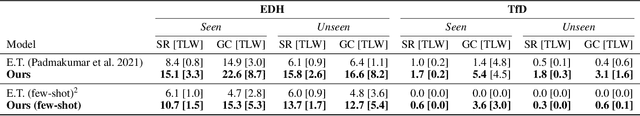
Abstract:Building a conversational embodied agent to execute real-life tasks has been a long-standing yet quite challenging research goal, as it requires effective human-agent communication, multi-modal understanding, long-range sequential decision making, etc. Traditional symbolic methods have scaling and generalization issues, while end-to-end deep learning models suffer from data scarcity and high task complexity, and are often hard to explain. To benefit from both worlds, we propose a Neuro-Symbolic Commonsense Reasoning (JARVIS) framework for modular, generalizable, and interpretable conversational embodied agents. First, it acquires symbolic representations by prompting large language models (LLMs) for language understanding and sub-goal planning, and by constructing semantic maps from visual observations. Then the symbolic module reasons for sub-goal planning and action generation based on task- and action-level common sense. Extensive experiments on the TEACh dataset validate the efficacy and efficiency of our JARVIS framework, which achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) results on all three dialog-based embodied tasks, including Execution from Dialog History (EDH), Trajectory from Dialog (TfD), and Two-Agent Task Completion (TATC) (e.g., our method boosts the unseen Success Rate on EDH from 6.1\% to 15.8\%). Moreover, we systematically analyze the essential factors that affect the task performance and also demonstrate the superiority of our method in few-shot settings. Our JARVIS model ranks first in the Alexa Prize SimBot Public Benchmark Challenge.
Test-Time Personalization with a Transformer for Human Pose Estimation
Jul 05, 2021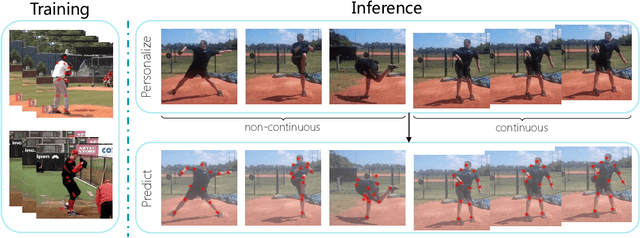
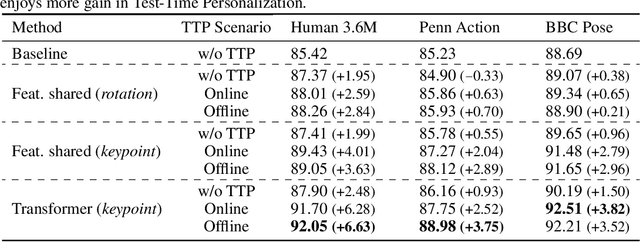
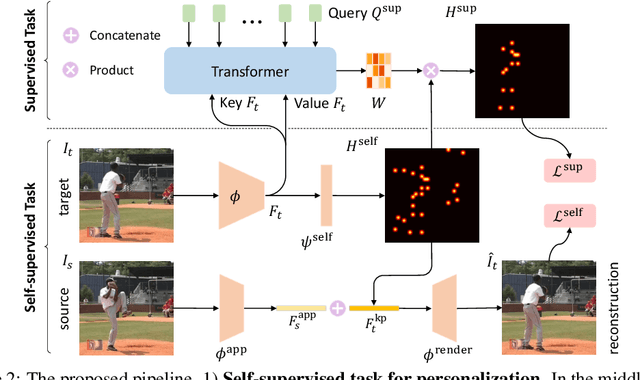
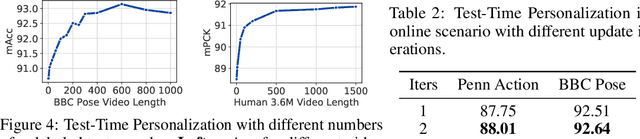
Abstract:We propose to personalize a human pose estimator given a set of test images of a person without using any manual annotations. While there is a significant advancement in human pose estimation, it is still very challenging for a model to generalize to different unknown environments and unseen persons. Instead of using a fixed model for every test case, we adapt our pose estimator during test time to exploit person-specific information. We first train our model on diverse data with both a supervised and a self-supervised pose estimation objectives jointly. We use a Transformer model to build a transformation between the self-supervised keypoints and the supervised keypoints. During test time, we personalize and adapt our model by fine-tuning with the self-supervised objective. The pose is then improved by transforming the updated self-supervised keypoints. We experiment with multiple datasets and show significant improvements on pose estimations with our self-supervised personalization.
Leveraging Crowdsourced GPS Data for Road Extraction from Aerial Imagery
May 04, 2019



Abstract:Deep learning is revolutionizing the mapping industry. Under lightweight human curation, computer has generated almost half of the roads in Thailand on OpenStreetMap (OSM) using high-resolution aerial imagery. Bing maps are displaying 125 million computer-generated building polygons in the U.S. While tremendously more efficient than manual mapping, one cannot map out everything from the air. Especially for roads, a small prediction gap by image occlusion renders the entire road useless for routing. Misconnections can be more dangerous. Therefore computer-based mapping often requires local verifications, which is still labor intensive. In this paper, we propose to leverage crowdsourced GPS data to improve and support road extraction from aerial imagery. Through novel data augmentation, GPS rendering, and 1D transpose convolution techniques, we show almost 5% improvements over previous competition winning models, and much better robustness when predicting new areas without any new training data or domain adaptation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge