Yin Wang
Dynamic Worlds, Dynamic Humans: Generating Virtual Human-Scene Interaction Motion in Dynamic Scenes
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Scenes are continuously undergoing dynamic changes in the real world. However, existing human-scene interaction generation methods typically treat the scene as static, which deviates from reality. Inspired by world models, we introduce Dyn-HSI, the first cognitive architecture for dynamic human-scene interaction, which endows virtual humans with three humanoid components. (1)Vision (human eyes): we equip the virtual human with a Dynamic Scene-Aware Navigation, which continuously perceives changes in the surrounding environment and adaptively predicts the next waypoint. (2)Memory (human brain): we equip the virtual human with a Hierarchical Experience Memory, which stores and updates experiential data accumulated during training. This allows the model to leverage prior knowledge during inference for context-aware motion priming, thereby enhancing both motion quality and generalization. (3) Control (human body): we equip the virtual human with Human-Scene Interaction Diffusion Model, which generates high-fidelity interaction motions conditioned on multimodal inputs. To evaluate performance in dynamic scenes, we extend the existing static human-scene interaction datasets to construct a dynamic benchmark, Dyn-Scenes. We conduct extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments to validate Dyn-HSI, showing that our method consistently outperforms existing approaches and generates high-quality human-scene interaction motions in both static and dynamic settings.
MOST: Motion Diffusion Model for Rare Text via Temporal Clip Banzhaf Interaction
Jul 09, 2025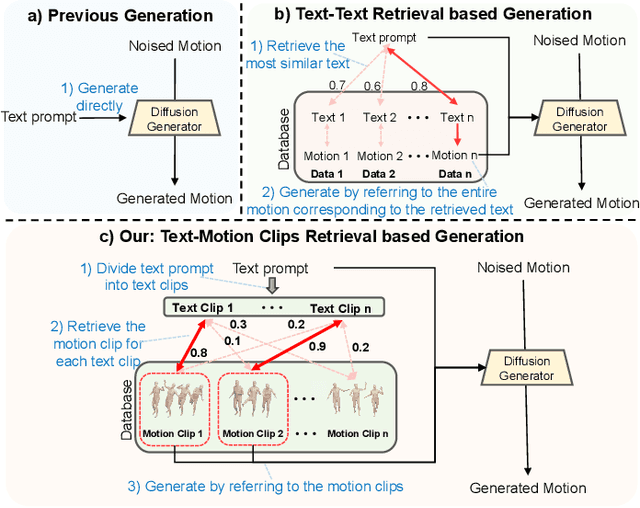
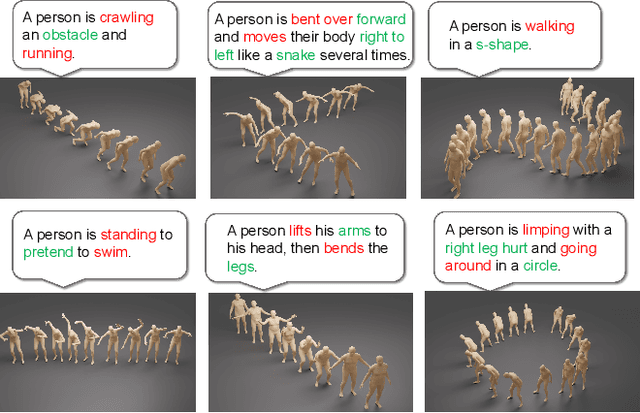

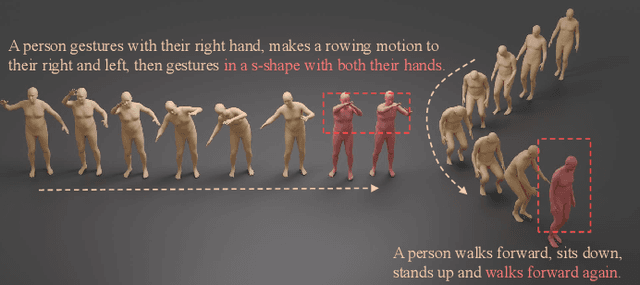
Abstract:We introduce MOST, a novel motion diffusion model via temporal clip Banzhaf interaction, aimed at addressing the persistent challenge of generating human motion from rare language prompts. While previous approaches struggle with coarse-grained matching and overlook important semantic cues due to motion redundancy, our key insight lies in leveraging fine-grained clip relationships to mitigate these issues. MOST's retrieval stage presents the first formulation of its kind - temporal clip Banzhaf interaction - which precisely quantifies textual-motion coherence at the clip level. This facilitates direct, fine-grained text-to-motion clip matching and eliminates prevalent redundancy. In the generation stage, a motion prompt module effectively utilizes retrieved motion clips to produce semantically consistent movements. Extensive evaluations confirm that MOST achieves state-of-the-art text-to-motion retrieval and generation performance by comprehensively addressing previous challenges, as demonstrated through quantitative and qualitative results highlighting its effectiveness, especially for rare prompts.
Period-LLM: Extending the Periodic Capability of Multimodal Large Language Model
May 30, 2025



Abstract:Periodic or quasi-periodic phenomena reveal intrinsic characteristics in various natural processes, such as weather patterns, movement behaviors, traffic flows, and biological signals. Given that these phenomena span multiple modalities, the capabilities of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) offer promising potential to effectively capture and understand their complex nature. However, current MLLMs struggle with periodic tasks due to limitations in: 1) lack of temporal modelling and 2) conflict between short and long periods. This paper introduces Period-LLM, a multimodal large language model designed to enhance the performance of periodic tasks across various modalities, and constructs a benchmark of various difficulty for evaluating the cross-modal periodic capabilities of large models. Specially, We adopt an "Easy to Hard Generalization" paradigm, starting with relatively simple text-based tasks and progressing to more complex visual and multimodal tasks, ensuring that the model gradually builds robust periodic reasoning capabilities. Additionally, we propose a "Resisting Logical Oblivion" optimization strategy to maintain periodic reasoning abilities during semantic alignment. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of the proposed Period-LLM over existing MLLMs in periodic tasks. The code is available at https://github.com/keke-nice/Period-LLM.
AFD-STA: Adaptive Filtering Denoising with Spatiotemporal Attention for Chaotic System Prediction
May 23, 2025Abstract:This paper presents AFD-STA Net, a neural framework integrating adaptive filtering and spatiotemporal dynamics learning for predicting high-dimensional chaotic systems governed by partial differential equations. The architecture combines: 1) An adaptive exponential smoothing module with position-aware decay coefficients for robust attractor reconstruction, 2) Parallel attention mechanisms capturing cross-temporal and spatial dependencies, 3) Dynamic gated fusion of multiscale features, and 4) Deep projection networks with dimension-scaling capabilities. Numerical experiments on nonlinear PDE systems demonstrate the model's effectiveness in maintaining prediction accuracy under both smooth and strongly chaotic regimes while exhibiting noise tolerance through adaptive filtering. Component ablation studies confirm critical contributions from each module, particularly highlighting the essential role of spatiotemporal attention in learning complex dynamical interactions. The framework shows promising potential for real-world applications requiring simultaneous handling of measurement uncertainties and high-dimensional nonlinear dynamics.
Sage Deer: A Super-Aligned Driving Generalist Is Your Copilot
May 15, 2025Abstract:The intelligent driving cockpit, an important part of intelligent driving, needs to match different users' comfort, interaction, and safety needs. This paper aims to build a Super-Aligned and GEneralist DRiving agent, SAGE DeeR. Sage Deer achieves three highlights: (1) Super alignment: It achieves different reactions according to different people's preferences and biases. (2) Generalist: It can understand the multi-view and multi-mode inputs to reason the user's physiological indicators, facial emotions, hand movements, body movements, driving scenarios, and behavioral decisions. (3) Self-Eliciting: It can elicit implicit thought chains in the language space to further increase generalist and super-aligned abilities. Besides, we collected multiple data sets and built a large-scale benchmark. This benchmark measures the deer's perceptual decision-making ability and the super alignment's accuracy.
STFM: A Spatio-Temporal Information Fusion Model Based on Phase Space Reconstruction for Sea Surface Temperature Prediction
Apr 23, 2025Abstract:The sea surface temperature (SST), a key environmental parameter, is crucial to optimizing production planning, making its accurate prediction a vital research topic. However, the inherent nonlinearity of the marine dynamic system presents significant challenges. Current forecasting methods mainly include physics-based numerical simulations and data-driven machine learning approaches. The former, while describing SST evolution through differential equations, suffers from high computational complexity and limited applicability, whereas the latter, despite its computational benefits, requires large datasets and faces interpretability challenges. This study presents a prediction framework based solely on data-driven techniques. Using phase space reconstruction, we construct initial-delay attractor pairs with a mathematical homeomorphism and design a Spatio-Temporal Fusion Mapping (STFM) to uncover their intrinsic connections. Unlike conventional models, our method captures SST dynamics efficiently through phase space reconstruction and achieves high prediction accuracy with minimal training data in comparative tests
Fg-T2M++: LLMs-Augmented Fine-Grained Text Driven Human Motion Generation
Feb 08, 2025Abstract:We address the challenging problem of fine-grained text-driven human motion generation. Existing works generate imprecise motions that fail to accurately capture relationships specified in text due to: (1) lack of effective text parsing for detailed semantic cues regarding body parts, (2) not fully modeling linguistic structures between words to comprehend text comprehensively. To tackle these limitations, we propose a novel fine-grained framework Fg-T2M++ that consists of: (1) an LLMs semantic parsing module to extract body part descriptions and semantics from text, (2) a hyperbolic text representation module to encode relational information between text units by embedding the syntactic dependency graph into hyperbolic space, and (3) a multi-modal fusion module to hierarchically fuse text and motion features. Extensive experiments on HumanML3D and KIT-ML datasets demonstrate that Fg-T2M++ outperforms SOTA methods, validating its ability to accurately generate motions adhering to comprehensive text semantics.
SeMi: When Imbalanced Semi-Supervised Learning Meets Mining Hard Examples
Jan 10, 2025



Abstract:Semi-Supervised Learning (SSL) can leverage abundant unlabeled data to boost model performance. However, the class-imbalanced data distribution in real-world scenarios poses great challenges to SSL, resulting in performance degradation. Existing class-imbalanced semi-supervised learning (CISSL) methods mainly focus on rebalancing datasets but ignore the potential of using hard examples to enhance performance, making it difficult to fully harness the power of unlabeled data even with sophisticated algorithms. To address this issue, we propose a method that enhances the performance of Imbalanced Semi-Supervised Learning by Mining Hard Examples (SeMi). This method distinguishes the entropy differences among logits of hard and easy examples, thereby identifying hard examples and increasing the utility of unlabeled data, better addressing the imbalance problem in CISSL. In addition, we maintain a class-balanced memory bank with confidence decay for storing high-confidence embeddings to enhance the pseudo-labels' reliability. Although our method is simple, it is effective and seamlessly integrates with existing approaches. We perform comprehensive experiments on standard CISSL benchmarks and experimentally demonstrate that our proposed SeMi outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods on multiple benchmarks, especially in reversed scenarios, where our best result shows approximately a 54.8\% improvement over the baseline methods.
TASL-Net: Tri-Attention Selective Learning Network for Intelligent Diagnosis of Bimodal Ultrasound Video
Sep 03, 2024Abstract:In the intelligent diagnosis of bimodal (gray-scale and contrast-enhanced) ultrasound videos, medical domain knowledge such as the way sonographers browse videos, the particular areas they emphasize, and the features they pay special attention to, plays a decisive role in facilitating precise diagnosis. Embedding medical knowledge into the deep learning network can not only enhance performance but also boost clinical confidence and reliability of the network. However, it is an intractable challenge to automatically focus on these person- and disease-specific features in videos and to enable networks to encode bimodal information comprehensively and efficiently. This paper proposes a novel Tri-Attention Selective Learning Network (TASL-Net) to tackle this challenge and automatically embed three types of diagnostic attention of sonographers into a mutual transformer framework for intelligent diagnosis of bimodal ultrasound videos. Firstly, a time-intensity-curve-based video selector is designed to mimic the temporal attention of sonographers, thus removing a large amount of redundant information while improving computational efficiency of TASL-Net. Then, to introduce the spatial attention of the sonographers for contrast-enhanced video analysis, we propose the earliest-enhanced position detector based on structural similarity variation, on which the TASL-Net is made to focus on the differences of perfusion variation inside and outside the lesion. Finally, by proposing a mutual encoding strategy that combines convolution and transformer, TASL-Net possesses bimodal attention to structure features on gray-scale videos and to perfusion variations on contrast-enhanced videos. These modules work collaboratively and contribute to superior performance. We conduct a detailed experimental validation of TASL-Net's performance on three datasets, including lung, breast, and liver.
GPT as Psychologist? Preliminary Evaluations for GPT-4V on Visual Affective Computing
Mar 09, 2024

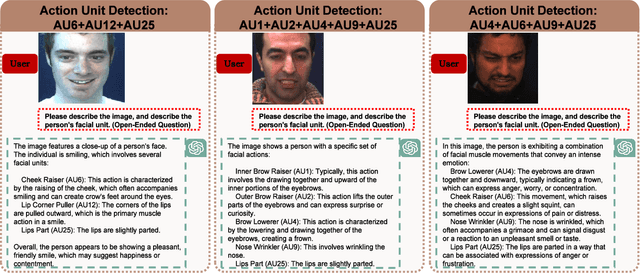
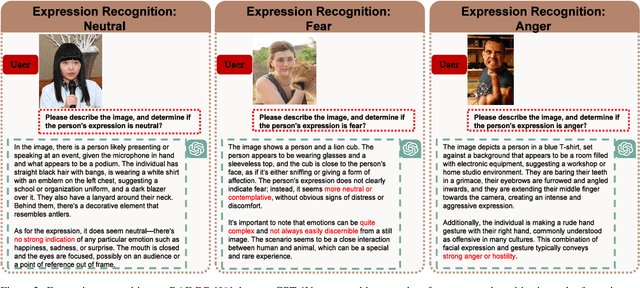
Abstract:Multimodal language models (MLMs) are designed to process and integrate information from multiple sources, such as text, speech, images, and videos. Despite its success in language understanding, it is critical to evaluate the performance of downstream tasks for better human-centric applications. This paper assesses the application of MLMs with 5 crucial abilities for affective computing, spanning from visual affective tasks and reasoning tasks. The results show that GPT4 has high accuracy in facial action unit recognition and micro-expression detection while its general facial expression recognition performance is not accurate. We also highlight the challenges of achieving fine-grained micro-expression recognition and the potential for further study and demonstrate the versatility and potential of GPT4 for handling advanced tasks in emotion recognition and related fields by integrating with task-related agents for more complex tasks, such as heart rate estimation through signal processing. In conclusion, this paper provides valuable insights into the potential applications and challenges of MLMs in human-centric computing. The interesting samples are available at \url{https://github.com/LuPaoPao/GPT4Affectivity}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge