Xiaohui Liang
Multimodal Priors-Augmented Text-Driven 3D Human-Object Interaction Generation
Feb 11, 2026Abstract:We address the challenging task of text-driven 3D human-object interaction (HOI) motion generation. Existing methods primarily rely on a direct text-to-HOI mapping, which suffers from three key limitations due to the significant cross-modality gap: (Q1) sub-optimal human motion, (Q2) unnatural object motion, and (Q3) weak interaction between humans and objects. To address these challenges, we propose MP-HOI, a novel framework grounded in four core insights: (1) Multimodal Data Priors: We leverage multimodal data (text, image, pose/object) from large multimodal models as priors to guide HOI generation, which tackles Q1 and Q2 in data modeling. (2) Enhanced Object Representation: We improve existing object representations by incorporating geometric keypoints, contact features, and dynamic properties, enabling expressive object representations, which tackles Q2 in data representation. (3) Multimodal-Aware Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) Model: We propose a modality-aware MoE model for effective multimodal feature fusion paradigm, which tackles Q1 and Q2 in feature fusion. (4) Cascaded Diffusion with Interaction Supervision: We design a cascaded diffusion framework that progressively refines human-object interaction features under dedicated supervision, which tackles Q3 in interaction refinement. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that MP-HOI outperforms existing approaches in generating high-fidelity and fine-grained HOI motions.
Dynamic Worlds, Dynamic Humans: Generating Virtual Human-Scene Interaction Motion in Dynamic Scenes
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Scenes are continuously undergoing dynamic changes in the real world. However, existing human-scene interaction generation methods typically treat the scene as static, which deviates from reality. Inspired by world models, we introduce Dyn-HSI, the first cognitive architecture for dynamic human-scene interaction, which endows virtual humans with three humanoid components. (1)Vision (human eyes): we equip the virtual human with a Dynamic Scene-Aware Navigation, which continuously perceives changes in the surrounding environment and adaptively predicts the next waypoint. (2)Memory (human brain): we equip the virtual human with a Hierarchical Experience Memory, which stores and updates experiential data accumulated during training. This allows the model to leverage prior knowledge during inference for context-aware motion priming, thereby enhancing both motion quality and generalization. (3) Control (human body): we equip the virtual human with Human-Scene Interaction Diffusion Model, which generates high-fidelity interaction motions conditioned on multimodal inputs. To evaluate performance in dynamic scenes, we extend the existing static human-scene interaction datasets to construct a dynamic benchmark, Dyn-Scenes. We conduct extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments to validate Dyn-HSI, showing that our method consistently outperforms existing approaches and generates high-quality human-scene interaction motions in both static and dynamic settings.
Continual Action Quality Assessment via Adaptive Manifold-Aligned Graph Regularization
Oct 08, 2025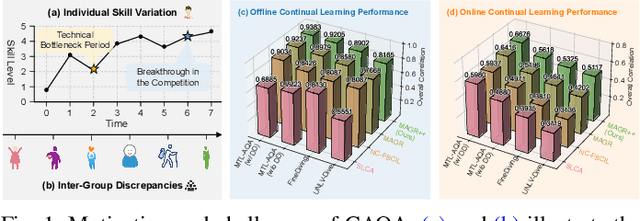
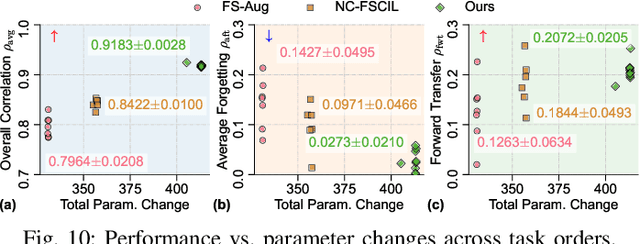
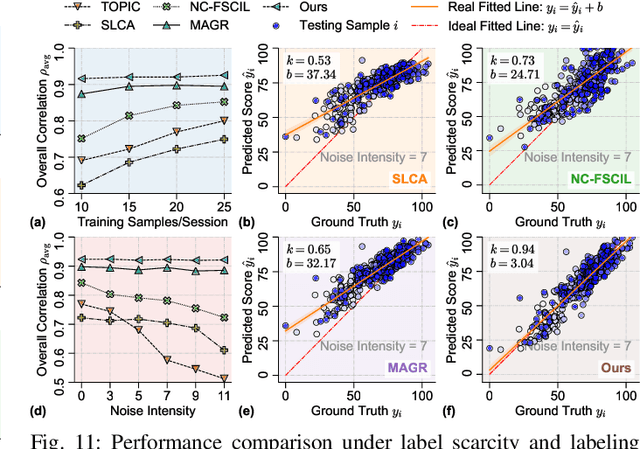
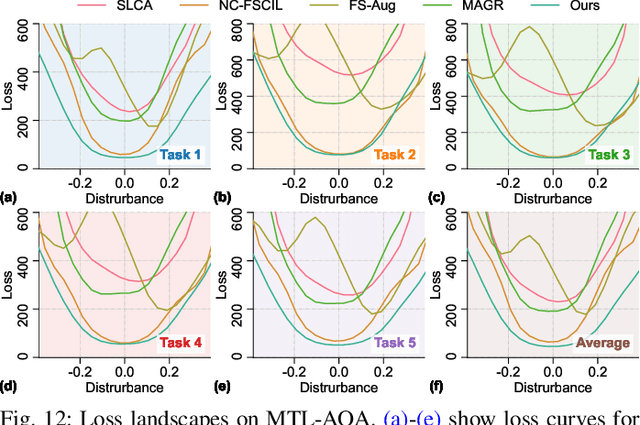
Abstract:Action Quality Assessment (AQA) quantifies human actions in videos, supporting applications in sports scoring, rehabilitation, and skill evaluation. A major challenge lies in the non-stationary nature of quality distributions in real-world scenarios, which limits the generalization ability of conventional methods. We introduce Continual AQA (CAQA), which equips AQA with Continual Learning (CL) capabilities to handle evolving distributions while mitigating catastrophic forgetting. Although parameter-efficient fine-tuning of pretrained models has shown promise in CL for image classification, we find it insufficient for CAQA. Our empirical and theoretical analyses reveal two insights: (i) Full-Parameter Fine-Tuning (FPFT) is necessary for effective representation learning; yet (ii) uncontrolled FPFT induces overfitting and feature manifold shift, thereby aggravating forgetting. To address this, we propose Adaptive Manifold-Aligned Graph Regularization (MAGR++), which couples backbone fine-tuning that stabilizes shallow layers while adapting deeper ones with a two-step feature rectification pipeline: a manifold projector to translate deviated historical features into the current representation space, and a graph regularizer to align local and global distributions. We construct four CAQA benchmarks from three datasets with tailored evaluation protocols and strong baselines, enabling systematic cross-dataset comparison. Extensive experiments show that MAGR++ achieves state-of-the-art performance, with average correlation gains of 3.6% offline and 12.2% online over the strongest baseline, confirming its robustness and effectiveness. Our code is available at https://github.com/ZhouKanglei/MAGRPP.
MOST: Motion Diffusion Model for Rare Text via Temporal Clip Banzhaf Interaction
Jul 09, 2025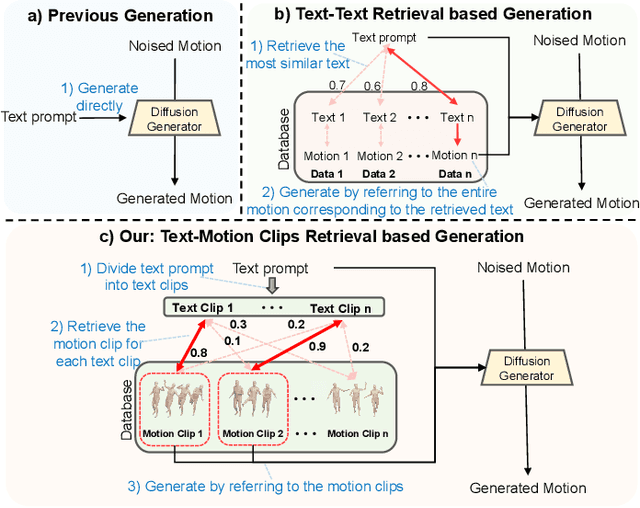
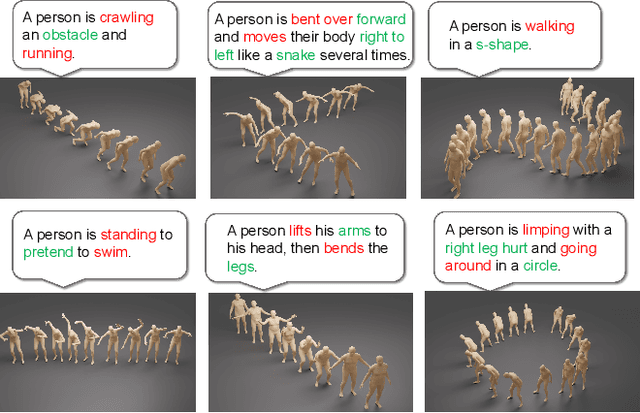

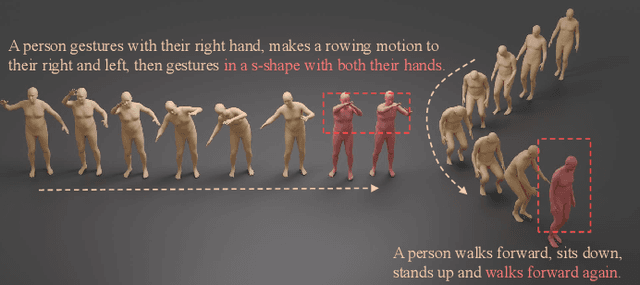
Abstract:We introduce MOST, a novel motion diffusion model via temporal clip Banzhaf interaction, aimed at addressing the persistent challenge of generating human motion from rare language prompts. While previous approaches struggle with coarse-grained matching and overlook important semantic cues due to motion redundancy, our key insight lies in leveraging fine-grained clip relationships to mitigate these issues. MOST's retrieval stage presents the first formulation of its kind - temporal clip Banzhaf interaction - which precisely quantifies textual-motion coherence at the clip level. This facilitates direct, fine-grained text-to-motion clip matching and eliminates prevalent redundancy. In the generation stage, a motion prompt module effectively utilizes retrieved motion clips to produce semantically consistent movements. Extensive evaluations confirm that MOST achieves state-of-the-art text-to-motion retrieval and generation performance by comprehensively addressing previous challenges, as demonstrated through quantitative and qualitative results highlighting its effectiveness, especially for rare prompts.
PHI: Bridging Domain Shift in Long-Term Action Quality Assessment via Progressive Hierarchical Instruction
May 26, 2025Abstract:Long-term Action Quality Assessment (AQA) aims to evaluate the quantitative performance of actions in long videos. However, existing methods face challenges due to domain shifts between the pre-trained large-scale action recognition backbones and the specific AQA task, thereby hindering their performance. This arises since fine-tuning resource-intensive backbones on small AQA datasets is impractical. We address this by identifying two levels of domain shift: task-level, regarding differences in task objectives, and feature-level, regarding differences in important features. For feature-level shifts, which are more detrimental, we propose Progressive Hierarchical Instruction (PHI) with two strategies. First, Gap Minimization Flow (GMF) leverages flow matching to progressively learn a fast flow path that reduces the domain gap between initial and desired features across shallow to deep layers. Additionally, a temporally-enhanced attention module captures long-range dependencies essential for AQA. Second, List-wise Contrastive Regularization (LCR) facilitates coarse-to-fine alignment by comprehensively comparing batch pairs to learn fine-grained cues while mitigating domain shift. Integrating these modules, PHI offers an effective solution. Experiments demonstrate that PHI achieves state-of-the-art performance on three representative long-term AQA datasets, proving its superiority in addressing the domain shift for long-term AQA.
Cog-TiPRO: Iterative Prompt Refinement with LLMs to Detect Cognitive Decline via Longitudinal Voice Assistant Commands
May 22, 2025Abstract:Early detection of cognitive decline is crucial for enabling interventions that can slow neurodegenerative disease progression. Traditional diagnostic approaches rely on labor-intensive clinical assessments, which are impractical for frequent monitoring. Our pilot study investigates voice assistant systems (VAS) as non-invasive tools for detecting cognitive decline through longitudinal analysis of speech patterns in voice commands. Over an 18-month period, we collected voice commands from 35 older adults, with 15 participants providing daily at-home VAS interactions. To address the challenges of analyzing these short, unstructured and noisy commands, we propose Cog-TiPRO, a framework that combines (1) LLM-driven iterative prompt refinement for linguistic feature extraction, (2) HuBERT-based acoustic feature extraction, and (3) transformer-based temporal modeling. Using iTransformer, our approach achieves 73.80% accuracy and 72.67% F1-score in detecting MCI, outperforming its baseline by 27.13%. Through our LLM approach, we identify linguistic features that uniquely characterize everyday command usage patterns in individuals experiencing cognitive decline.
FineCausal: A Causal-Based Framework for Interpretable Fine-Grained Action Quality Assessment
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:Action quality assessment (AQA) is critical for evaluating athletic performance, informing training strategies, and ensuring safety in competitive sports. However, existing deep learning approaches often operate as black boxes and are vulnerable to spurious correlations, limiting both their reliability and interpretability. In this paper, we introduce FineCausal, a novel causal-based framework that achieves state-of-the-art performance on the FineDiving-HM dataset. Our approach leverages a Graph Attention Network-based causal intervention module to disentangle human-centric foreground cues from background confounders, and incorporates a temporal causal attention module to capture fine-grained temporal dependencies across action stages. This dual-module strategy enables FineCausal to generate detailed spatio-temporal representations that not only achieve state-of-the-art scoring performance but also provide transparent, interpretable feedback on which features drive the assessment. Despite its strong performance, FineCausal requires extensive expert knowledge to define causal structures and depends on high-quality annotations, challenges that we discuss and address as future research directions. Code is available at https://github.com/Harrison21/FineCausal.
Focus Directions Make Your Language Models Pay More Attention to Relevant Contexts
Mar 30, 2025Abstract:Long-context large language models (LLMs) are prone to be distracted by irrelevant contexts. The reason for distraction remains poorly understood. In this paper, we first identify the contextual heads, a special group of attention heads that control the overall attention of the LLM. Then, we demonstrate that distraction arises when contextual heads fail to allocate sufficient attention to relevant contexts and can be mitigated by increasing attention to these contexts. We further identify focus directions, located at the key and query activations of these heads, which enable them to allocate more attention to relevant contexts without explicitly specifying which context is relevant. We comprehensively evaluate the effect of focus direction on various long-context tasks and find out focus directions could help to mitigate the poor task alignment of the long-context LLMs. We believe our findings could promote further research on long-context LLM alignment.
UMB@PerAnsSumm 2025: Enhancing Perspective-Aware Summarization with Prompt Optimization and Supervised Fine-Tuning
Mar 14, 2025



Abstract:We present our approach to the PerAnsSumm Shared Task, which involves perspective span identification and perspective-aware summarization in community question-answering (CQA) threads. For span identification, we adopt ensemble learning that integrates three transformer models through averaging to exploit individual model strengths, achieving an 82.91% F1-score on test data. For summarization, we design a suite of Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting strategies that incorporate keyphrases and guide information to structure summary generation into manageable steps. To further enhance summary quality, we apply prompt optimization using the DSPy framework and supervised fine-tuning (SFT) on Llama-3 to adapt the model to domain-specific data. Experimental results on validation and test sets show that structured prompts with keyphrases and guidance improve summaries aligned with references, while the combination of prompt optimization and fine-tuning together yields significant improvement in both relevance and factuality evaluation metrics.
Adaptive Score Alignment Learning for Continual Perceptual Quality Assessment of 360-Degree Videos in Virtual Reality
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:Virtual Reality Video Quality Assessment (VR-VQA) aims to evaluate the perceptual quality of 360-degree videos, which is crucial for ensuring a distortion-free user experience. Traditional VR-VQA methods trained on static datasets with limited distortion diversity struggle to balance correlation and precision. This becomes particularly critical when generalizing to diverse VR content and continually adapting to dynamic and evolving video distribution variations. To address these challenges, we propose a novel approach for assessing the perceptual quality of VR videos, Adaptive Score Alignment Learning (ASAL). ASAL integrates correlation loss with error loss to enhance alignment with human subjective ratings and precision in predicting perceptual quality. In particular, ASAL can naturally adapt to continually changing distributions through a feature space smoothing process that enhances generalization to unseen content. To further improve continual adaptation to dynamic VR environments, we extend ASAL with adaptive memory replay as a novel Continul Learning (CL) framework. Unlike traditional CL models, ASAL utilizes key frame extraction and feature adaptation to address the unique challenges of non-stationary variations with both the computation and storage restrictions of VR devices. We establish a comprehensive benchmark for VR-VQA and its CL counterpart, introducing new data splits and evaluation metrics. Our experiments demonstrate that ASAL outperforms recent strong baseline models, achieving overall correlation gains of up to 4.78\% in the static joint training setting and 12.19\% in the dynamic CL setting on various datasets. This validates the effectiveness of ASAL in addressing the inherent challenges of VR-VQA.Our code is available at https://github.com/ZhouKanglei/ASAL_CVQA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge