Kristin Qi
JWB-DH-V1: Benchmark for Joint Whole-Body Talking Avatar and Speech Generation Version 1
Jul 28, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in diffusion-based video generation have enabled photo-realistic short clips, but current methods still struggle to achieve multi-modal consistency when jointly generating whole-body motion and natural speech. Current approaches lack comprehensive evaluation frameworks that assess both visual and audio quality, and there are insufficient benchmarks for region-specific performance analysis. To address these gaps, we introduce the Joint Whole-Body Talking Avatar and Speech Generation Version I(JWB-DH-V1), comprising a large-scale multi-modal dataset with 10,000 unique identities across 2 million video samples, and an evaluation protocol for assessing joint audio-video generation of whole-body animatable avatars. Our evaluation of SOTA models reveals consistent performance disparities between face/hand-centric and whole-body performance, which incidates essential areas for future research. The dataset and evaluation tools are publicly available at https://github.com/deepreasonings/WholeBodyBenchmark.
Cog-TiPRO: Iterative Prompt Refinement with LLMs to Detect Cognitive Decline via Longitudinal Voice Assistant Commands
May 22, 2025Abstract:Early detection of cognitive decline is crucial for enabling interventions that can slow neurodegenerative disease progression. Traditional diagnostic approaches rely on labor-intensive clinical assessments, which are impractical for frequent monitoring. Our pilot study investigates voice assistant systems (VAS) as non-invasive tools for detecting cognitive decline through longitudinal analysis of speech patterns in voice commands. Over an 18-month period, we collected voice commands from 35 older adults, with 15 participants providing daily at-home VAS interactions. To address the challenges of analyzing these short, unstructured and noisy commands, we propose Cog-TiPRO, a framework that combines (1) LLM-driven iterative prompt refinement for linguistic feature extraction, (2) HuBERT-based acoustic feature extraction, and (3) transformer-based temporal modeling. Using iTransformer, our approach achieves 73.80% accuracy and 72.67% F1-score in detecting MCI, outperforming its baseline by 27.13%. Through our LLM approach, we identify linguistic features that uniquely characterize everyday command usage patterns in individuals experiencing cognitive decline.
Attentional Triple-Encoder Network in Spatiospectral Domains for Medical Image Segmentation
Mar 20, 2025Abstract:Retinal Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) segmentation is essential for diagnosing pathology. Traditional methods focus on either spatial or spectral domains, overlooking their combined dependencies. We propose a triple-encoder network that integrates CNNs for spatial features, Fast Fourier Convolution (FFC) for spectral features, and attention mechanisms to capture global relationships across both domains. Attention fusion modules integrate convolution and cross-attention to further enhance features. Our method achieves an average Dice score improvement from 0.855 to 0.864, outperforming prior work.
UMB@PerAnsSumm 2025: Enhancing Perspective-Aware Summarization with Prompt Optimization and Supervised Fine-Tuning
Mar 14, 2025



Abstract:We present our approach to the PerAnsSumm Shared Task, which involves perspective span identification and perspective-aware summarization in community question-answering (CQA) threads. For span identification, we adopt ensemble learning that integrates three transformer models through averaging to exploit individual model strengths, achieving an 82.91% F1-score on test data. For summarization, we design a suite of Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting strategies that incorporate keyphrases and guide information to structure summary generation into manageable steps. To further enhance summary quality, we apply prompt optimization using the DSPy framework and supervised fine-tuning (SFT) on Llama-3 to adapt the model to domain-specific data. Experimental results on validation and test sets show that structured prompts with keyphrases and guidance improve summaries aligned with references, while the combination of prompt optimization and fine-tuning together yields significant improvement in both relevance and factuality evaluation metrics.
Exploiting Longitudinal Speech Sessions via Voice Assistant Systems for Early Detection of Cognitive Decline
Oct 16, 2024



Abstract:Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) is an early stage of Alzheimer's disease (AD), a form of neurodegenerative disorder. Early identification of MCI is crucial for delaying its progression through timely interventions. Existing research has demonstrated the feasibility of detecting MCI using speech collected from clinical interviews or digital devices. However, these approaches typically analyze data collected at limited time points, limiting their ability to identify cognitive changes over time. This paper presents a longitudinal study using voice assistant systems (VAS) to remotely collect seven-session speech data at three-month intervals across 18 months. We propose two methods to improve MCI detection and the prediction of cognitive changes. The first method incorporates historical data, while the second predicts cognitive changes at two time points. Our results indicate improvements when incorporating historical data: the average F1-score for MCI detection improves from 58.6% to 71.2% (by 12.6%) in the case of acoustic features and from 62.1% to 75.1% (by 13.0%) in the case of linguistic features. Additionally, the prediction of cognitive changes achieves an F1-score of 73.7% in the case of acoustic features. These results confirm the potential of VAS-based speech sessions for early detection of cognitive decline.
Towards Full-parameter and Parameter-efficient Self-learning For Endoscopic Camera Depth Estimation
Oct 01, 2024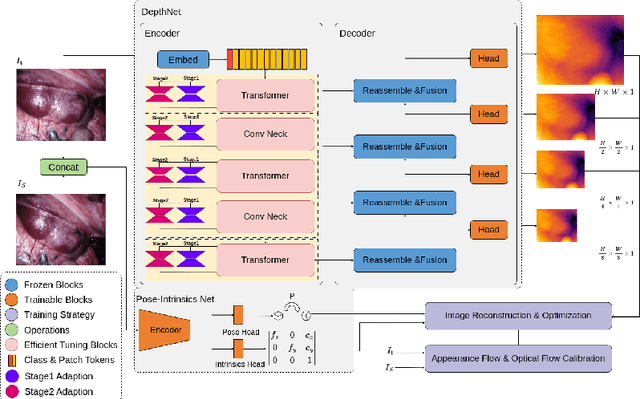
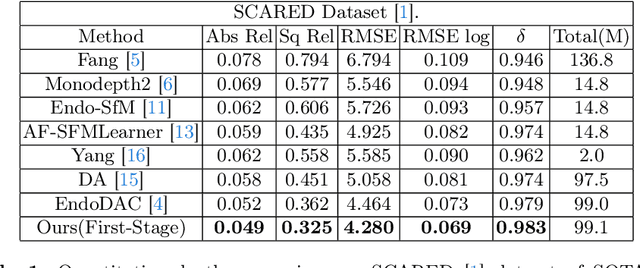
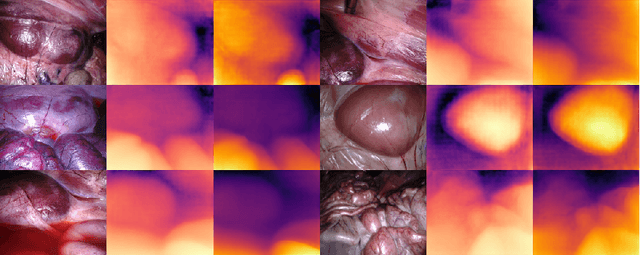
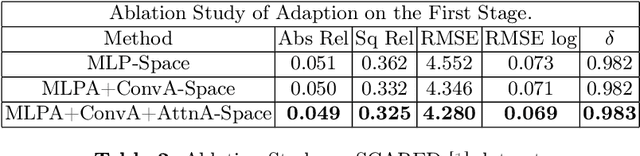
Abstract:Adaptation methods are developed to adapt depth foundation models to endoscopic depth estimation recently. However, such approaches typically under-perform training since they limit the parameter search to a low-rank subspace and alter the training dynamics. Therefore, we propose a full-parameter and parameter-efficient learning framework for endoscopic depth estimation. At the first stage, the subspace of attention, convolution and multi-layer perception are adapted simultaneously within different sub-spaces. At the second stage, a memory-efficient optimization is proposed for subspace composition and the performance is further improved in the united sub-space. Initial experiments on the SCARED dataset demonstrate that results at the first stage improves the performance from 10.2% to 4.1% for Sq Rel, Abs Rel, RMSE and RMSE log in the comparison with the state-of-the-art models.
Lesion Search with Self-supervised Learning
Nov 18, 2023



Abstract:Content-based image retrieval (CBIR) with self-supervised learning (SSL) accelerates clinicians' interpretation of similar images without manual annotations. We develop a CBIR from the contrastive learning SimCLR and incorporate a generalized-mean (GeM) pooling followed by L2 normalization to classify lesion types and retrieve similar images before clinicians' analysis. Results have shown improved performance. We additionally build an open-source application for image analysis and retrieval. The application is easy to integrate, relieving manual efforts and suggesting the potential to support clinicians' everyday activities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge