Frederick W. B. Li
Dynamic Worlds, Dynamic Humans: Generating Virtual Human-Scene Interaction Motion in Dynamic Scenes
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Scenes are continuously undergoing dynamic changes in the real world. However, existing human-scene interaction generation methods typically treat the scene as static, which deviates from reality. Inspired by world models, we introduce Dyn-HSI, the first cognitive architecture for dynamic human-scene interaction, which endows virtual humans with three humanoid components. (1)Vision (human eyes): we equip the virtual human with a Dynamic Scene-Aware Navigation, which continuously perceives changes in the surrounding environment and adaptively predicts the next waypoint. (2)Memory (human brain): we equip the virtual human with a Hierarchical Experience Memory, which stores and updates experiential data accumulated during training. This allows the model to leverage prior knowledge during inference for context-aware motion priming, thereby enhancing both motion quality and generalization. (3) Control (human body): we equip the virtual human with Human-Scene Interaction Diffusion Model, which generates high-fidelity interaction motions conditioned on multimodal inputs. To evaluate performance in dynamic scenes, we extend the existing static human-scene interaction datasets to construct a dynamic benchmark, Dyn-Scenes. We conduct extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments to validate Dyn-HSI, showing that our method consistently outperforms existing approaches and generates high-quality human-scene interaction motions in both static and dynamic settings.
Continual Action Quality Assessment via Adaptive Manifold-Aligned Graph Regularization
Oct 08, 2025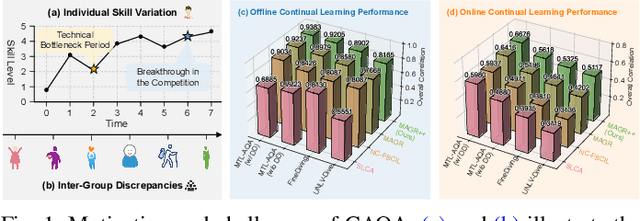
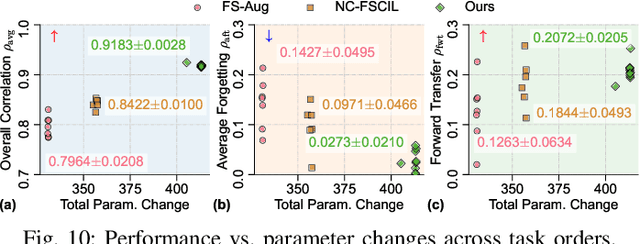
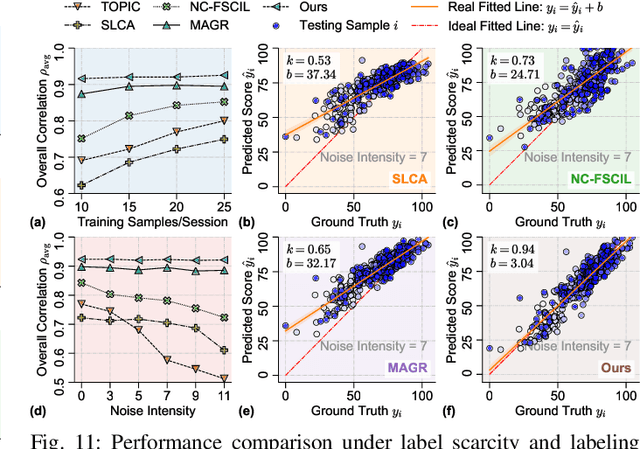
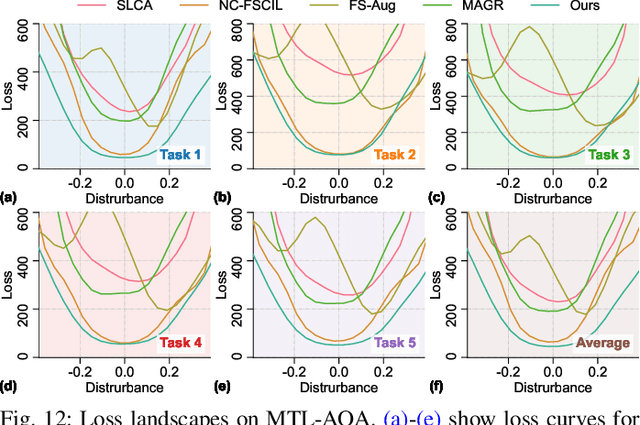
Abstract:Action Quality Assessment (AQA) quantifies human actions in videos, supporting applications in sports scoring, rehabilitation, and skill evaluation. A major challenge lies in the non-stationary nature of quality distributions in real-world scenarios, which limits the generalization ability of conventional methods. We introduce Continual AQA (CAQA), which equips AQA with Continual Learning (CL) capabilities to handle evolving distributions while mitigating catastrophic forgetting. Although parameter-efficient fine-tuning of pretrained models has shown promise in CL for image classification, we find it insufficient for CAQA. Our empirical and theoretical analyses reveal two insights: (i) Full-Parameter Fine-Tuning (FPFT) is necessary for effective representation learning; yet (ii) uncontrolled FPFT induces overfitting and feature manifold shift, thereby aggravating forgetting. To address this, we propose Adaptive Manifold-Aligned Graph Regularization (MAGR++), which couples backbone fine-tuning that stabilizes shallow layers while adapting deeper ones with a two-step feature rectification pipeline: a manifold projector to translate deviated historical features into the current representation space, and a graph regularizer to align local and global distributions. We construct four CAQA benchmarks from three datasets with tailored evaluation protocols and strong baselines, enabling systematic cross-dataset comparison. Extensive experiments show that MAGR++ achieves state-of-the-art performance, with average correlation gains of 3.6% offline and 12.2% online over the strongest baseline, confirming its robustness and effectiveness. Our code is available at https://github.com/ZhouKanglei/MAGRPP.
MOST: Motion Diffusion Model for Rare Text via Temporal Clip Banzhaf Interaction
Jul 09, 2025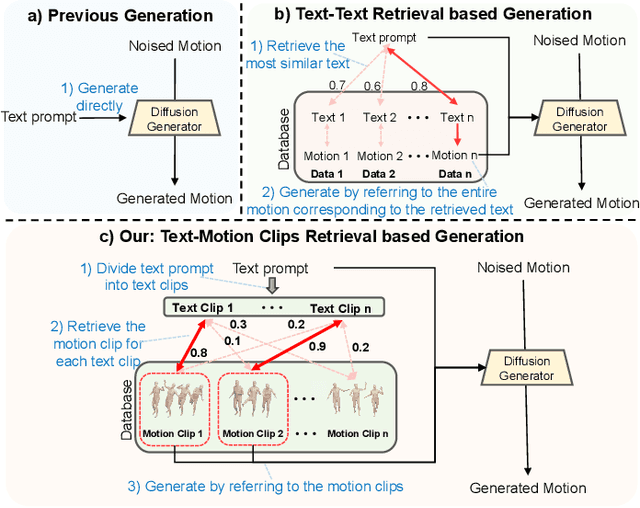
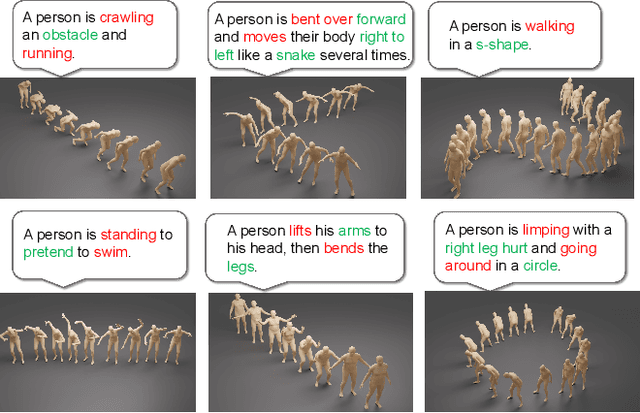

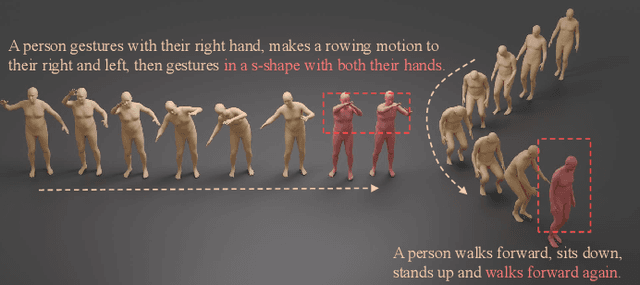
Abstract:We introduce MOST, a novel motion diffusion model via temporal clip Banzhaf interaction, aimed at addressing the persistent challenge of generating human motion from rare language prompts. While previous approaches struggle with coarse-grained matching and overlook important semantic cues due to motion redundancy, our key insight lies in leveraging fine-grained clip relationships to mitigate these issues. MOST's retrieval stage presents the first formulation of its kind - temporal clip Banzhaf interaction - which precisely quantifies textual-motion coherence at the clip level. This facilitates direct, fine-grained text-to-motion clip matching and eliminates prevalent redundancy. In the generation stage, a motion prompt module effectively utilizes retrieved motion clips to produce semantically consistent movements. Extensive evaluations confirm that MOST achieves state-of-the-art text-to-motion retrieval and generation performance by comprehensively addressing previous challenges, as demonstrated through quantitative and qualitative results highlighting its effectiveness, especially for rare prompts.
PHI: Bridging Domain Shift in Long-Term Action Quality Assessment via Progressive Hierarchical Instruction
May 26, 2025Abstract:Long-term Action Quality Assessment (AQA) aims to evaluate the quantitative performance of actions in long videos. However, existing methods face challenges due to domain shifts between the pre-trained large-scale action recognition backbones and the specific AQA task, thereby hindering their performance. This arises since fine-tuning resource-intensive backbones on small AQA datasets is impractical. We address this by identifying two levels of domain shift: task-level, regarding differences in task objectives, and feature-level, regarding differences in important features. For feature-level shifts, which are more detrimental, we propose Progressive Hierarchical Instruction (PHI) with two strategies. First, Gap Minimization Flow (GMF) leverages flow matching to progressively learn a fast flow path that reduces the domain gap between initial and desired features across shallow to deep layers. Additionally, a temporally-enhanced attention module captures long-range dependencies essential for AQA. Second, List-wise Contrastive Regularization (LCR) facilitates coarse-to-fine alignment by comprehensively comparing batch pairs to learn fine-grained cues while mitigating domain shift. Integrating these modules, PHI offers an effective solution. Experiments demonstrate that PHI achieves state-of-the-art performance on three representative long-term AQA datasets, proving its superiority in addressing the domain shift for long-term AQA.
Fg-T2M++: LLMs-Augmented Fine-Grained Text Driven Human Motion Generation
Feb 08, 2025Abstract:We address the challenging problem of fine-grained text-driven human motion generation. Existing works generate imprecise motions that fail to accurately capture relationships specified in text due to: (1) lack of effective text parsing for detailed semantic cues regarding body parts, (2) not fully modeling linguistic structures between words to comprehend text comprehensively. To tackle these limitations, we propose a novel fine-grained framework Fg-T2M++ that consists of: (1) an LLMs semantic parsing module to extract body part descriptions and semantics from text, (2) a hyperbolic text representation module to encode relational information between text units by embedding the syntactic dependency graph into hyperbolic space, and (3) a multi-modal fusion module to hierarchically fuse text and motion features. Extensive experiments on HumanML3D and KIT-ML datasets demonstrate that Fg-T2M++ outperforms SOTA methods, validating its ability to accurately generate motions adhering to comprehensive text semantics.
ST-SACLF: Style Transfer Informed Self-Attention Classifier for Bias-Aware Painting Classification
Aug 03, 2024



Abstract:Painting classification plays a vital role in organizing, finding, and suggesting artwork for digital and classic art galleries. Existing methods struggle with adapting knowledge from the real world to artistic images during training, leading to poor performance when dealing with different datasets. Our innovation lies in addressing these challenges through a two-step process. First, we generate more data using Style Transfer with Adaptive Instance Normalization (AdaIN), bridging the gap between diverse styles. Then, our classifier gains a boost with feature-map adaptive spatial attention modules, improving its understanding of artistic details. Moreover, we tackle the problem of imbalanced class representation by dynamically adjusting augmented samples. Through a dual-stage process involving careful hyperparameter search and model fine-tuning, we achieve an impressive 87.24\% accuracy using the ResNet-50 backbone over 40 training epochs. Our study explores quantitative analyses that compare different pretrained backbones, investigates model optimization through ablation studies, and examines how varying augmentation levels affect model performance. Complementing this, our qualitative experiments offer valuable insights into the model's decision-making process using spatial attention and its ability to differentiate between easy and challenging samples based on confidence ranking.
From Category to Scenery: An End-to-End Framework for Multi-Person Human-Object Interaction Recognition in Videos
Jul 01, 2024Abstract:Video-based Human-Object Interaction (HOI) recognition explores the intricate dynamics between humans and objects, which are essential for a comprehensive understanding of human behavior and intentions. While previous work has made significant strides, effectively integrating geometric and visual features to model dynamic relationships between humans and objects in a graph framework remains a challenge. In this work, we propose a novel end-to-end category to scenery framework, CATS, starting by generating geometric features for various categories through graphs respectively, then fusing them with corresponding visual features. Subsequently, we construct a scenery interactive graph with these enhanced geometric-visual features as nodes to learn the relationships among human and object categories. This methodological advance facilitates a deeper, more structured comprehension of interactions, bridging category-specific insights with broad scenery dynamics. Our method demonstrates state-of-the-art performance on two pivotal HOI benchmarks, including the MPHOI-72 dataset for multi-person HOIs and the single-person HOI CAD-120 dataset.
MAGR: Manifold-Aligned Graph Regularization for Continual Action Quality Assessment
Mar 07, 2024Abstract:Action Quality Assessment (AQA) evaluates diverse skills but models struggle with non-stationary data. We propose Continual AQA (CAQA) to refine models using sparse new data. Feature replay preserves memory without storing raw inputs. However, the misalignment between static old features and the dynamically changing feature manifold causes severe catastrophic forgetting. To address this novel problem, we propose Manifold-Aligned Graph Regularization (MAGR), which first aligns deviated old features to the current feature manifold, ensuring representation consistency. It then constructs a graph jointly arranging old and new features aligned with quality scores. Experiments show MAGR outperforms recent strong baselines with up to 6.56%, 5.66%, 15.64%, and 9.05% correlation gains on the MTL-AQA, FineDiving, UNLV-Dive, and JDM-MSA split datasets, respectively. This validates MAGR for continual assessment challenges arising from non-stationary skill variations.
Fg-T2M: Fine-Grained Text-Driven Human Motion Generation via Diffusion Model
Sep 12, 2023Abstract:Text-driven human motion generation in computer vision is both significant and challenging. However, current methods are limited to producing either deterministic or imprecise motion sequences, failing to effectively control the temporal and spatial relationships required to conform to a given text description. In this work, we propose a fine-grained method for generating high-quality, conditional human motion sequences supporting precise text description. Our approach consists of two key components: 1) a linguistics-structure assisted module that constructs accurate and complete language feature to fully utilize text information; and 2) a context-aware progressive reasoning module that learns neighborhood and overall semantic linguistics features from shallow and deep graph neural networks to achieve a multi-step inference. Experiments show that our approach outperforms text-driven motion generation methods on HumanML3D and KIT test sets and generates better visually confirmed motion to the text conditions.
Tackling Data Bias in Painting Classification with Style Transfer
Jan 06, 2023Abstract:It is difficult to train classifiers on paintings collections due to model bias from domain gaps and data bias from the uneven distribution of artistic styles. Previous techniques like data distillation, traditional data augmentation and style transfer improve classifier training using task specific training datasets or domain adaptation. We propose a system to handle data bias in small paintings datasets like the Kaokore dataset while simultaneously accounting for domain adaptation in fine-tuning a model trained on real world images. Our system consists of two stages which are style transfer and classification. In the style transfer stage, we generate the stylized training samples per class with uniformly sampled content and style images and train the style transformation network per domain. In the classification stage, we can interpret the effectiveness of the style and content layers at the attention layers when training on the original training dataset and the stylized images. We can tradeoff the model performance and convergence by dynamically varying the proportion of augmented samples in the majority and minority classes. We achieve comparable results to the SOTA with fewer training epochs and a classifier with fewer training parameters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge