Guoxia Wang
RRAttention: Dynamic Block Sparse Attention via Per-Head Round-Robin Shifts for Long-Context Inference
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:The quadratic complexity of attention mechanisms poses a critical bottleneck for large language models processing long contexts. While dynamic sparse attention methods offer input-adaptive efficiency, they face fundamental trade-offs: requiring preprocessing, lacking global evaluation, violating query independence, or incurring high computational overhead. We present RRAttention, a novel dynamic sparse attention method that simultaneously achieves all desirable properties through a head \underline{r}ound-\underline{r}obin (RR) sampling strategy. By rotating query sampling positions across attention heads within each stride, RRAttention maintains query independence while enabling efficient global pattern discovery with stride-level aggregation. Our method reduces complexity from $O(L^2)$ to $O(L^2/S^2)$ and employs adaptive Top-$τ$ selection for optimal sparsity. Extensive experiments on natural language understanding (HELMET) and multimodal video comprehension (Video-MME) demonstrate that RRAttention recovers over 99\% of full attention performance while computing only half of the attention blocks, achieving 2.4$\times$ speedup at 128K context length and outperforming existing dynamic sparse attention methods.
ERNIE 5.0 Technical Report
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:In this report, we introduce ERNIE 5.0, a natively autoregressive foundation model desinged for unified multimodal understanding and generation across text, image, video, and audio. All modalities are trained from scratch under a unified next-group-of-tokens prediction objective, based on an ultra-sparse mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture with modality-agnostic expert routing. To address practical challenges in large-scale deployment under diverse resource constraints, ERNIE 5.0 adopts a novel elastic training paradigm. Within a single pre-training run, the model learns a family of sub-models with varying depths, expert capacities, and routing sparsity, enabling flexible trade-offs among performance, model size, and inference latency in memory- or time-constrained scenarios. Moreover, we systematically address the challenges of scaling reinforcement learning to unified foundation models, thereby guaranteeing efficient and stable post-training under ultra-sparse MoE architectures and diverse multimodal settings. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ERNIE 5.0 achieves strong and balanced performance across multiple modalities. To the best of our knowledge, among publicly disclosed models, ERNIE 5.0 represents the first production-scale realization of a trillion-parameter unified autoregressive model that supports both multimodal understanding and generation. To facilitate further research, we present detailed visualizations of modality-agnostic expert routing in the unified model, alongside comprehensive empirical analysis of elastic training, aiming to offer profound insights to the community.
Low-Precision Training of Large Language Models: Methods, Challenges, and Opportunities
May 02, 2025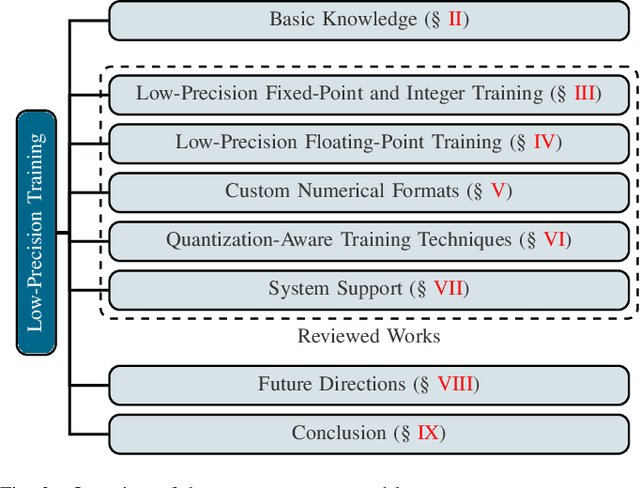
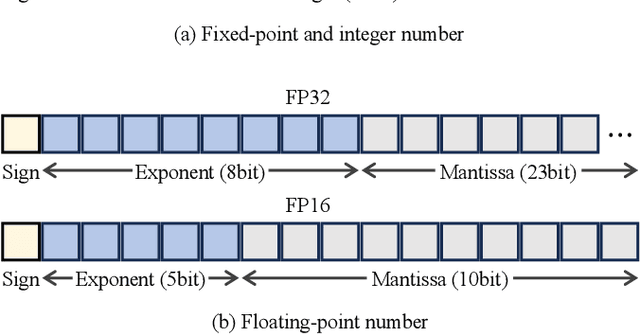
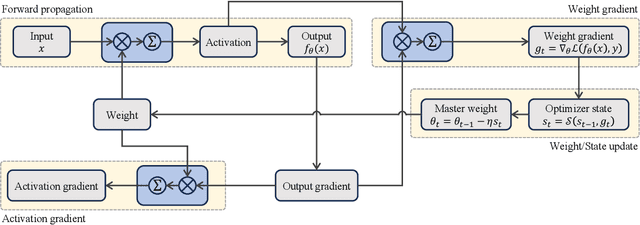
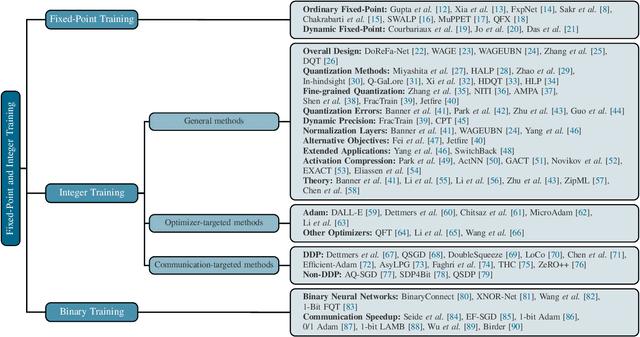
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have achieved impressive performance across various domains. However, the substantial hardware resources required for their training present a significant barrier to efficiency and scalability. To mitigate this challenge, low-precision training techniques have been widely adopted, leading to notable advancements in training efficiency. Despite these gains, low-precision training involves several components$\unicode{x2013}$such as weights, activations, and gradients$\unicode{x2013}$each of which can be represented in different numerical formats. The resulting diversity has created a fragmented landscape in low-precision training research, making it difficult for researchers to gain a unified overview of the field. This survey provides a comprehensive review of existing low-precision training methods. To systematically organize these approaches, we categorize them into three primary groups based on their underlying numerical formats, which is a key factor influencing hardware compatibility, computational efficiency, and ease of reference for readers. The categories are: (1) fixed-point and integer-based methods, (2) floating-point-based methods, and (3) customized format-based methods. Additionally, we discuss quantization-aware training approaches, which share key similarities with low-precision training during forward propagation. Finally, we highlight several promising research directions to advance this field. A collection of papers discussed in this survey is provided in https://github.com/Hao840/Awesome-Low-Precision-Training.
FlashMask: Efficient and Rich Mask Extension of FlashAttention
Oct 02, 2024


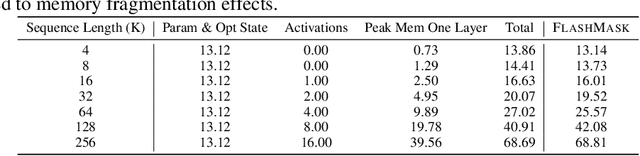
Abstract:The computational and memory demands of vanilla attention scale quadratically with the sequence length $N$, posing significant challenges for processing long sequences in Transformer models. FlashAttention alleviates these challenges by eliminating the $O(N^2)$ memory dependency and reducing attention latency through IO-aware memory optimizations. However, its native support for certain attention mask types is limited, and it does not inherently accommodate more complex masking requirements. Previous approaches resort to using dense masks with $O(N^2)$ memory complexity, leading to inefficiencies. In this paper, we propose FlashMask, an extension of FlashAttention that introduces a column-wise sparse representation of attention masks. This approach efficiently represents a wide range of mask types and facilitates the development of optimized kernel implementations. By adopting this novel representation, FlashMask achieves linear memory complexity $O(N)$, suitable for modeling long-context sequences. Moreover, this representation enables kernel optimizations that eliminate unnecessary computations by leveraging sparsity in the attention mask, without sacrificing computational accuracy, resulting in higher computational efficiency. We evaluate FlashMask's performance in fine-tuning and alignment training of LLMs such as SFT, LoRA, DPO, and RM. FlashMask achieves significant throughput improvements, with end-to-end speedups ranging from 1.65x to 3.22x compared to existing FlashAttention dense method. Additionally, our kernel-level comparisons demonstrate that FlashMask surpasses the latest counterpart, FlexAttention, by 12.1% to 60.7% in terms of kernel TFLOPs/s, achieving 37.8% to 62.3% of the theoretical maximum FLOPs/s on the A100 GPU. The code is open-sourced on PaddlePaddle and integrated into PaddleNLP, supporting models with over 100 billion parameters for contexts up to 128K tokens.
NACL: A General and Effective KV Cache Eviction Framework for LLMs at Inference Time
Aug 07, 2024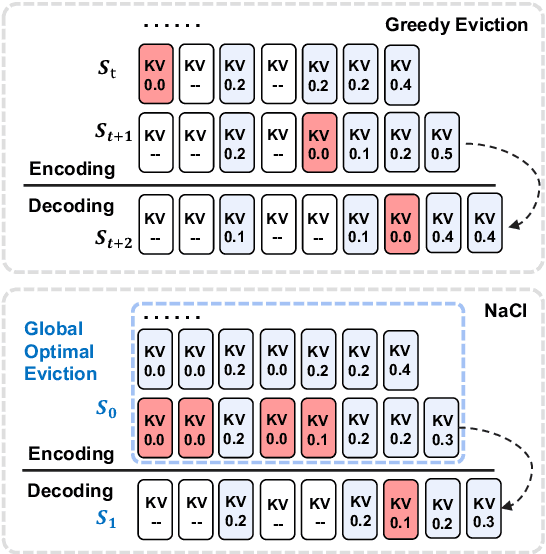
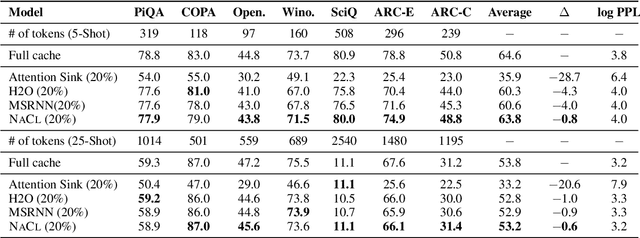
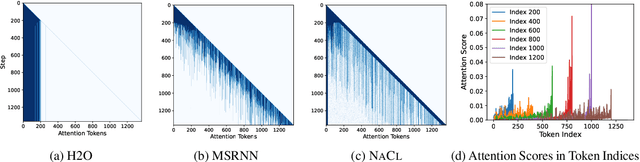
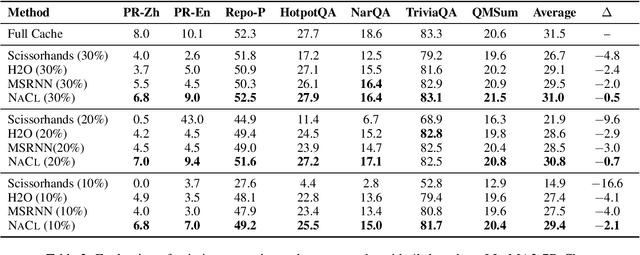
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have ignited an innovative surge of AI applications, marking a new era of exciting possibilities equipped with extended context windows. However, hosting these models is cost-prohibitive mainly due to the extensive memory consumption of KV Cache involving long-context modeling. Despite several works proposing to evict unnecessary tokens from the KV Cache, most of them rely on the biased local statistics of accumulated attention scores and report performance using unconvincing metric like perplexity on inadequate short-text evaluation. In this paper, we propose NACL, a general framework for long-context KV cache eviction that achieves more optimal and efficient eviction in a single operation during the encoding phase. Due to NACL's efficiency, we combine more accurate attention score statistics in PROXY TOKENS EVICTION with the diversified random eviction strategy of RANDOM EVICTION, aiming to alleviate the issue of attention bias and enhance the robustness in maintaining pivotal tokens for long-context modeling tasks. Notably, our method significantly improves the performance on short- and long-text tasks by 80% and 76% respectively, reducing KV Cache by up to 50% with over 95% performance maintenance. The code is available at https: //github.com/PaddlePaddle/Research/ tree/master/NLP/ACL2024-NACL.
HelixFold: An Efficient Implementation of AlphaFold2 using PaddlePaddle
Jul 13, 2022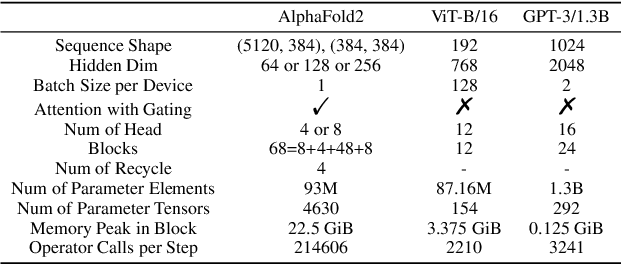
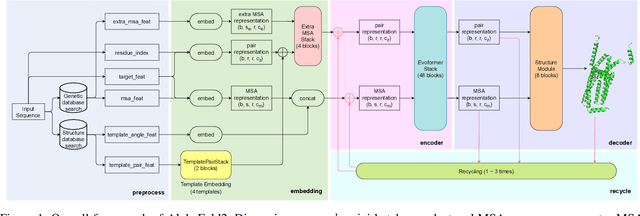
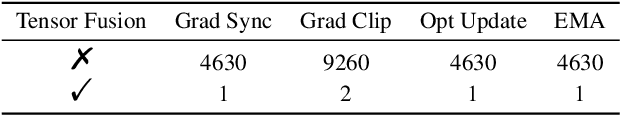
Abstract:Accurate protein structure prediction can significantly accelerate the development of life science. The accuracy of AlphaFold2, a frontier end-to-end structure prediction system, is already close to that of the experimental determination techniques. Due to the complex model architecture and large memory consumption, it requires lots of computational resources and time to implement the training and inference of AlphaFold2 from scratch. The cost of running the original AlphaFold2 is expensive for most individuals and institutions. Therefore, reducing this cost could accelerate the development of life science. We implement AlphaFold2 using PaddlePaddle, namely HelixFold, to improve training and inference speed and reduce memory consumption. The performance is improved by operator fusion, tensor fusion, and hybrid parallelism computation, while the memory is optimized through Recompute, BFloat16, and memory read/write in-place. Compared with the original AlphaFold2 (implemented with Jax) and OpenFold (implemented with PyTorch), HelixFold needs only 7.5 days to complete the full end-to-end training and only 5.3 days when using hybrid parallelism, while both AlphaFold2 and OpenFold take about 11 days. HelixFold saves 1x training time. We verified that HelixFold's accuracy could be on par with AlphaFold2 on the CASP14 and CAMEO datasets. HelixFold's code is available on GitHub for free download: https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleHelix/tree/dev/apps/protein_folding/helixfold, and we also provide stable web services on https://paddlehelix.baidu.com/app/drug/protein/forecast.
DOOBNet: Deep Object Occlusion Boundary Detection from an Image
Sep 13, 2018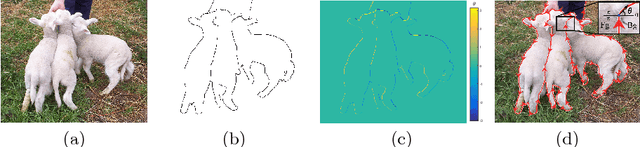
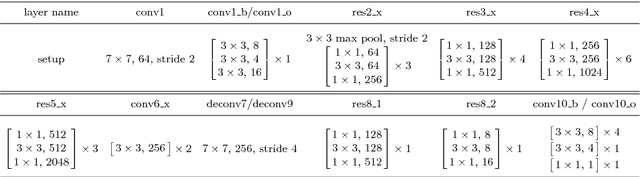
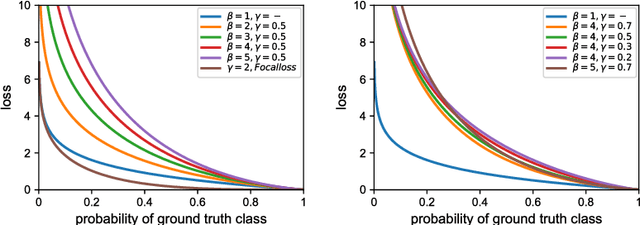
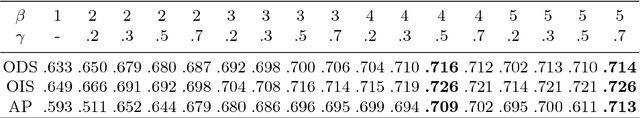
Abstract:Object occlusion boundary detection is a fundamental and crucial research problem in computer vision. This is challenging to solve as encountering the extreme boundary/non-boundary class imbalance during training an object occlusion boundary detector. In this paper, we propose to address this class imbalance by up-weighting the loss contribution of false negative and false positive examples with our novel Attention Loss function. We also propose a unified end-to-end multi-task deep object occlusion boundary detection network (DOOBNet) by sharing convolutional features to simultaneously predict object boundary and occlusion orientation. DOOBNet adopts an encoder-decoder structure with skip connection in order to automatically learn multi-scale and multi-level features. We significantly surpass the state-of-the-art on the PIOD dataset (ODS F-score of .702) and the BSDS ownership dataset (ODS F-score of .555), as well as improving the detecting speed to as 0.037s per image on the PIOD dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge