Zeyu Chen
ERNIE 5.0 Technical Report
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:In this report, we introduce ERNIE 5.0, a natively autoregressive foundation model desinged for unified multimodal understanding and generation across text, image, video, and audio. All modalities are trained from scratch under a unified next-group-of-tokens prediction objective, based on an ultra-sparse mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture with modality-agnostic expert routing. To address practical challenges in large-scale deployment under diverse resource constraints, ERNIE 5.0 adopts a novel elastic training paradigm. Within a single pre-training run, the model learns a family of sub-models with varying depths, expert capacities, and routing sparsity, enabling flexible trade-offs among performance, model size, and inference latency in memory- or time-constrained scenarios. Moreover, we systematically address the challenges of scaling reinforcement learning to unified foundation models, thereby guaranteeing efficient and stable post-training under ultra-sparse MoE architectures and diverse multimodal settings. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ERNIE 5.0 achieves strong and balanced performance across multiple modalities. To the best of our knowledge, among publicly disclosed models, ERNIE 5.0 represents the first production-scale realization of a trillion-parameter unified autoregressive model that supports both multimodal understanding and generation. To facilitate further research, we present detailed visualizations of modality-agnostic expert routing in the unified model, alongside comprehensive empirical analysis of elastic training, aiming to offer profound insights to the community.
Hierarchical Federated Learning for Social Network with Mobility
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) offers a decentralized solution that allows collaborative local model training and global aggregation, thereby protecting data privacy. In conventional FL frameworks, data privacy is typically preserved under the assumption that local data remains absolutely private, whereas the mobility of clients is frequently neglected in explicit modeling. In this paper, we propose a hierarchical federated learning framework based on the social network with mobility namely HFL-SNM that considers both data sharing among clients and their mobility patterns. Under the constraints of limited resources, we formulate a joint optimization problem of resource allocation and client scheduling, which objective is to minimize the energy consumption of clients during the FL process. In social network, we introduce the concepts of Effective Data Coverage Rate and Redundant Data Coverage Rate. We analyze the impact of effective data and redundant data on the model performance through preliminary experiments. We decouple the optimization problem into multiple sub-problems, analyze them based on preliminary experimental results, and propose Dynamic Optimization in Social Network with Mobility (DO-SNM) algorithm. Experimental results demonstrate that our algorithm achieves superior model performance while significantly reducing energy consumption, compared to traditional baseline algorithms.
KDMOS:Knowledge Distillation for Motion Segmentation
Jun 17, 2025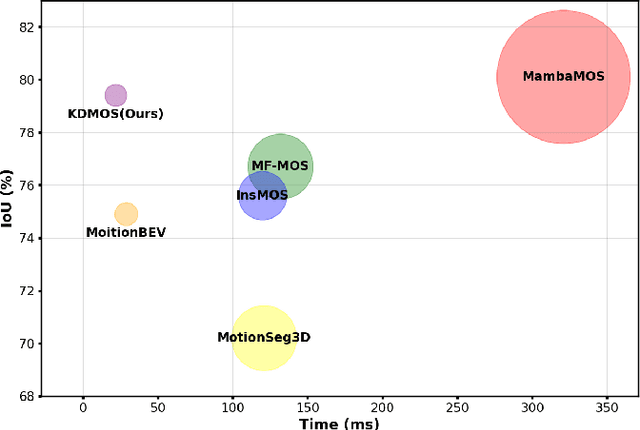
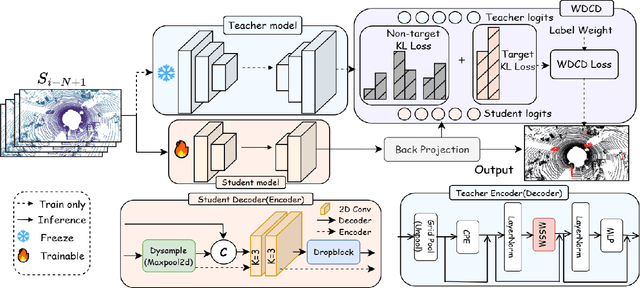
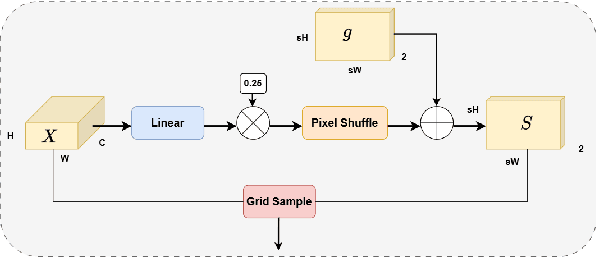
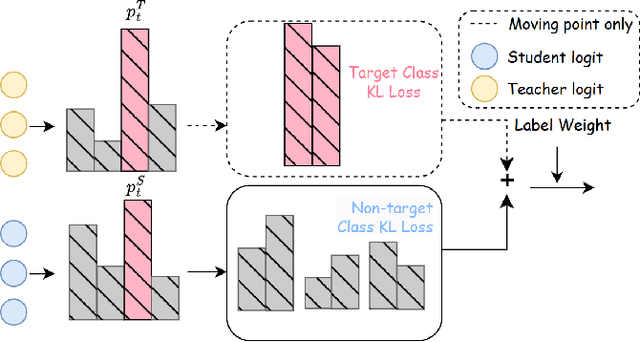
Abstract:Motion Object Segmentation (MOS) is crucial for autonomous driving, as it enhances localization, path planning, map construction, scene flow estimation, and future state prediction. While existing methods achieve strong performance, balancing accuracy and real-time inference remains a challenge. To address this, we propose a logits-based knowledge distillation framework for MOS, aiming to improve accuracy while maintaining real-time efficiency. Specifically, we adopt a Bird's Eye View (BEV) projection-based model as the student and a non-projection model as the teacher. To handle the severe imbalance between moving and non-moving classes, we decouple them and apply tailored distillation strategies, allowing the teacher model to better learn key motion-related features. This approach significantly reduces false positives and false negatives. Additionally, we introduce dynamic upsampling, optimize the network architecture, and achieve a 7.69% reduction in parameter count, mitigating overfitting. Our method achieves a notable IoU of 78.8% on the hidden test set of the SemanticKITTI-MOS dataset and delivers competitive results on the Apollo dataset. The KDMOS implementation is available at https://github.com/SCNU-RISLAB/KDMOS.
Visual Text Processing: A Comprehensive Review and Unified Evaluation
Apr 30, 2025



Abstract:Visual text is a crucial component in both document and scene images, conveying rich semantic information and attracting significant attention in the computer vision community. Beyond traditional tasks such as text detection and recognition, visual text processing has witnessed rapid advancements driven by the emergence of foundation models, including text image reconstruction and text image manipulation. Despite significant progress, challenges remain due to the unique properties that differentiate text from general objects. Effectively capturing and leveraging these distinct textual characteristics is essential for developing robust visual text processing models. In this survey, we present a comprehensive, multi-perspective analysis of recent advancements in visual text processing, focusing on two key questions: (1) What textual features are most suitable for different visual text processing tasks? (2) How can these distinctive text features be effectively incorporated into processing frameworks? Furthermore, we introduce VTPBench, a new benchmark that encompasses a broad range of visual text processing datasets. Leveraging the advanced visual quality assessment capabilities of multimodal large language models (MLLMs), we propose VTPScore, a novel evaluation metric designed to ensure fair and reliable evaluation. Our empirical study with more than 20 specific models reveals substantial room for improvement in the current techniques. Our aim is to establish this work as a fundamental resource that fosters future exploration and innovation in the dynamic field of visual text processing. The relevant repository is available at https://github.com/shuyansy/Visual-Text-Processing-survey.
PP-DocBee: Improving Multimodal Document Understanding Through a Bag of Tricks
Mar 06, 2025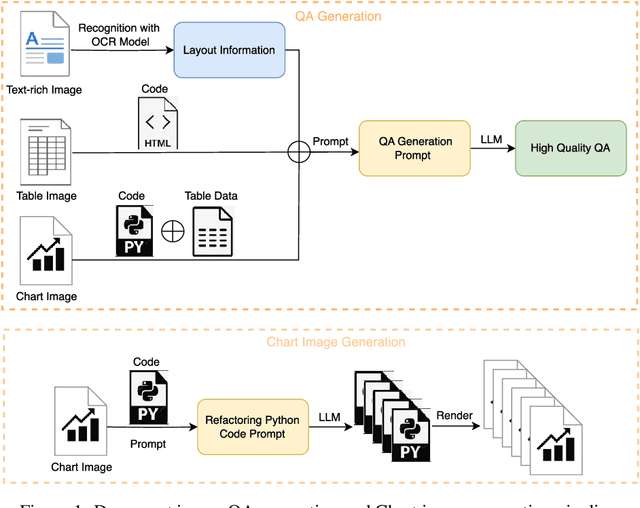

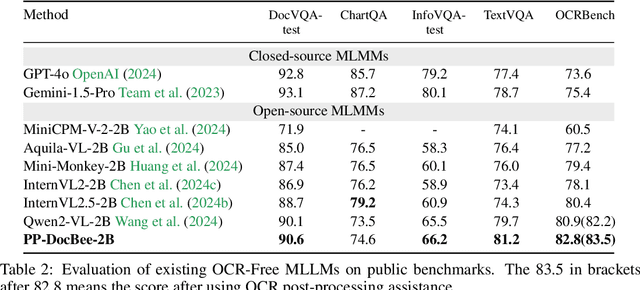
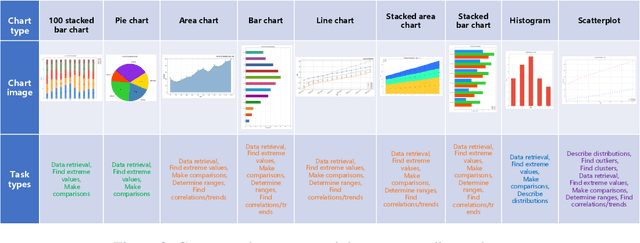
Abstract:With the rapid advancement of digitalization, various document images are being applied more extensively in production and daily life, and there is an increasingly urgent need for fast and accurate parsing of the content in document images. Therefore, this report presents PP-DocBee, a novel multimodal large language model designed for end-to-end document image understanding. First, we develop a data synthesis strategy tailored to document scenarios in which we build a diverse dataset to improve the model generalization. Then, we apply a few training techniques, including dynamic proportional sampling, data preprocessing, and OCR postprocessing strategies. Extensive evaluations demonstrate the superior performance of PP-DocBee, achieving state-of-the-art results on English document understanding benchmarks and even outperforming existing open source and commercial models in Chinese document understanding. The source code and pre-trained models are publicly available at \href{https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleMIX}{https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleMIX}.
G2SDF: Surface Reconstruction from Explicit Gaussians with Implicit SDFs
Nov 25, 2024



Abstract:State-of-the-art novel view synthesis methods such as 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) achieve remarkable visual quality. While 3DGS and its variants can be rendered efficiently using rasterization, many tasks require access to the underlying 3D surface, which remains challenging to extract due to the sparse and explicit nature of this representation. In this paper, we introduce G2SDF, a novel approach that addresses this limitation by integrating a neural implicit Signed Distance Field (SDF) into the Gaussian Splatting framework. Our method links the opacity values of Gaussians with their distances to the surface, ensuring a closer alignment of Gaussians with the scene surface. To extend this approach to unbounded scenes at varying scales, we propose a normalization function that maps any range to a fixed interval. To further enhance reconstruction quality, we leverage an off-the-shelf depth estimator as pseudo ground truth during Gaussian Splatting optimization. By establishing a differentiable connection between the explicit Gaussians and the implicit SDF, our approach enables high-quality surface reconstruction and rendering. Experimental results on several real-world datasets demonstrate that G2SDF achieves superior reconstruction quality than prior works while maintaining the efficiency of 3DGS.
UW-SDF: Exploiting Hybrid Geometric Priors for Neural SDF Reconstruction from Underwater Multi-view Monocular Images
Oct 10, 2024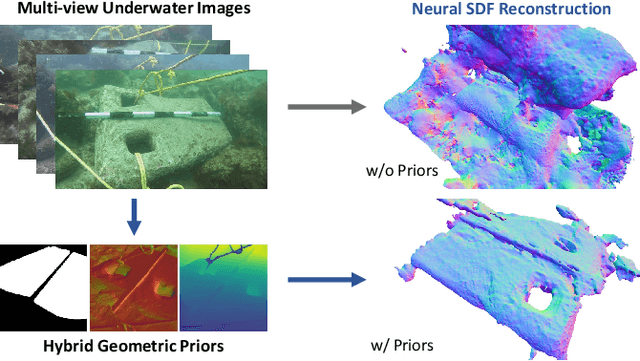
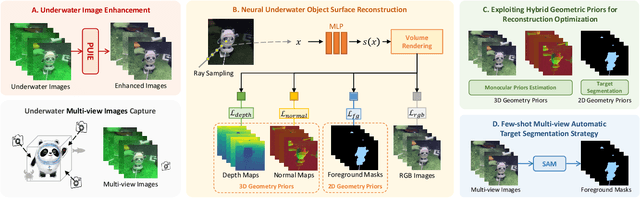
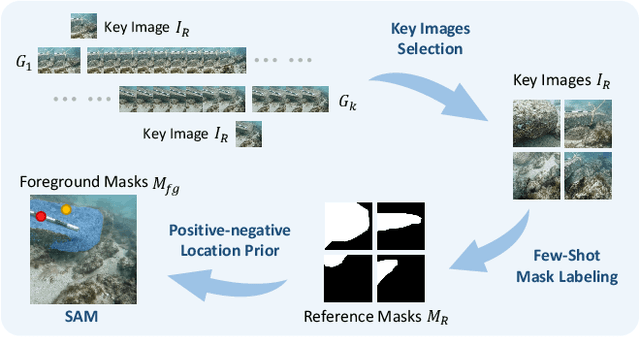
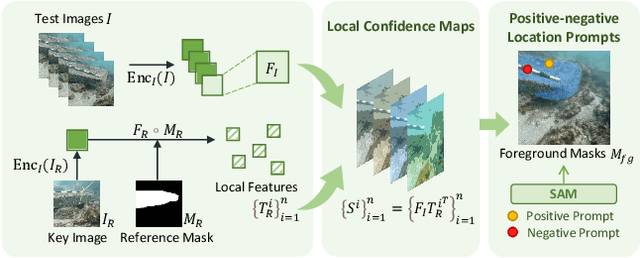
Abstract:Due to the unique characteristics of underwater environments, accurate 3D reconstruction of underwater objects poses a challenging problem in tasks such as underwater exploration and mapping. Traditional methods that rely on multiple sensor data for 3D reconstruction are time-consuming and face challenges in data acquisition in underwater scenarios. We propose UW-SDF, a framework for reconstructing target objects from multi-view underwater images based on neural SDF. We introduce hybrid geometric priors to optimize the reconstruction process, markedly enhancing the quality and efficiency of neural SDF reconstruction. Additionally, to address the challenge of segmentation consistency in multi-view images, we propose a novel few-shot multi-view target segmentation strategy using the general-purpose segmentation model (SAM), enabling rapid automatic segmentation of unseen objects. Through extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments on diverse datasets, we demonstrate that our proposed method outperforms the traditional underwater 3D reconstruction method and other neural rendering approaches in the field of underwater 3D reconstruction.
FlashMask: Efficient and Rich Mask Extension of FlashAttention
Oct 02, 2024


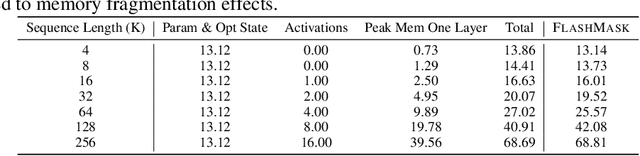
Abstract:The computational and memory demands of vanilla attention scale quadratically with the sequence length $N$, posing significant challenges for processing long sequences in Transformer models. FlashAttention alleviates these challenges by eliminating the $O(N^2)$ memory dependency and reducing attention latency through IO-aware memory optimizations. However, its native support for certain attention mask types is limited, and it does not inherently accommodate more complex masking requirements. Previous approaches resort to using dense masks with $O(N^2)$ memory complexity, leading to inefficiencies. In this paper, we propose FlashMask, an extension of FlashAttention that introduces a column-wise sparse representation of attention masks. This approach efficiently represents a wide range of mask types and facilitates the development of optimized kernel implementations. By adopting this novel representation, FlashMask achieves linear memory complexity $O(N)$, suitable for modeling long-context sequences. Moreover, this representation enables kernel optimizations that eliminate unnecessary computations by leveraging sparsity in the attention mask, without sacrificing computational accuracy, resulting in higher computational efficiency. We evaluate FlashMask's performance in fine-tuning and alignment training of LLMs such as SFT, LoRA, DPO, and RM. FlashMask achieves significant throughput improvements, with end-to-end speedups ranging from 1.65x to 3.22x compared to existing FlashAttention dense method. Additionally, our kernel-level comparisons demonstrate that FlashMask surpasses the latest counterpart, FlexAttention, by 12.1% to 60.7% in terms of kernel TFLOPs/s, achieving 37.8% to 62.3% of the theoretical maximum FLOPs/s on the A100 GPU. The code is open-sourced on PaddlePaddle and integrated into PaddleNLP, supporting models with over 100 billion parameters for contexts up to 128K tokens.
FAFA: Frequency-Aware Flow-Aided Self-Supervision for Underwater Object Pose Estimation
Sep 25, 2024



Abstract:Although methods for estimating the pose of objects in indoor scenes have achieved great success, the pose estimation of underwater objects remains challenging due to difficulties brought by the complex underwater environment, such as degraded illumination, blurring, and the substantial cost of obtaining real annotations. In response, we introduce FAFA, a Frequency-Aware Flow-Aided self-supervised framework for 6D pose estimation of unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs). Essentially, we first train a frequency-aware flow-based pose estimator on synthetic data, where an FFT-based augmentation approach is proposed to facilitate the network in capturing domain-invariant features and target domain styles from a frequency perspective. Further, we perform self-supervised training by enforcing flow-aided multi-level consistencies to adapt it to the real-world underwater environment. Our framework relies solely on the 3D model and RGB images, alleviating the need for any real pose annotations or other-modality data like depths. We evaluate the effectiveness of FAFA on common underwater object pose benchmarks and showcase significant performance improvements compared to state-of-the-art methods. Code is available at github.com/tjy0703/FAFA.
CV-MOS: A Cross-View Model for Motion Segmentation
Aug 25, 2024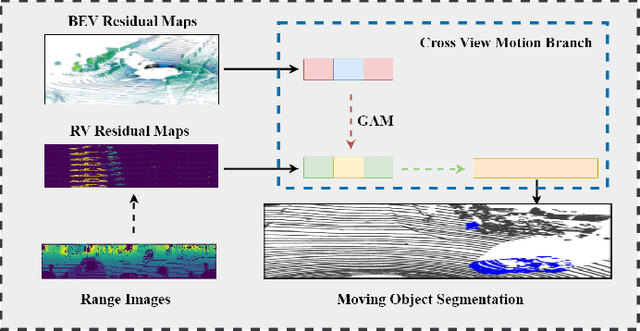
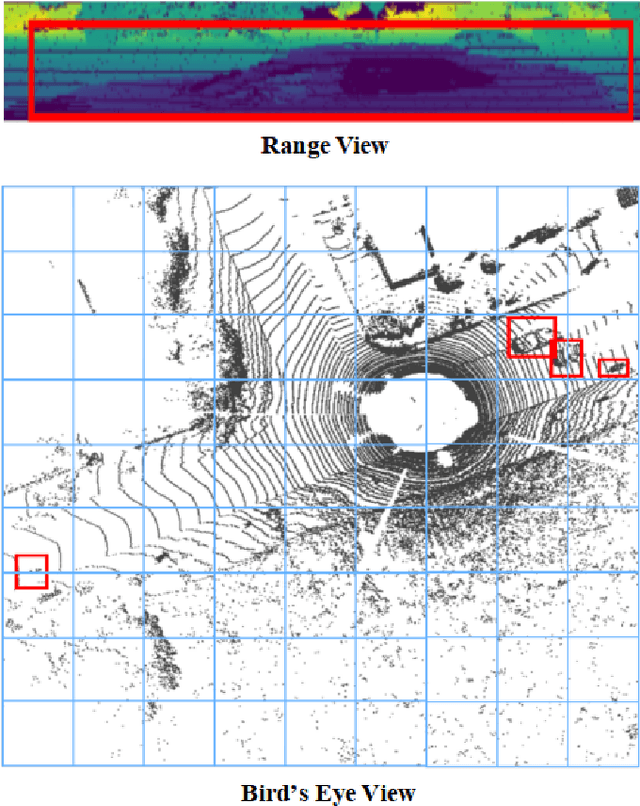
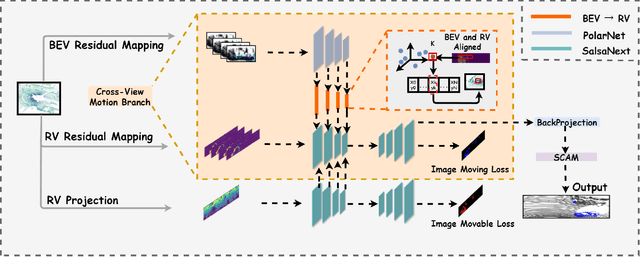
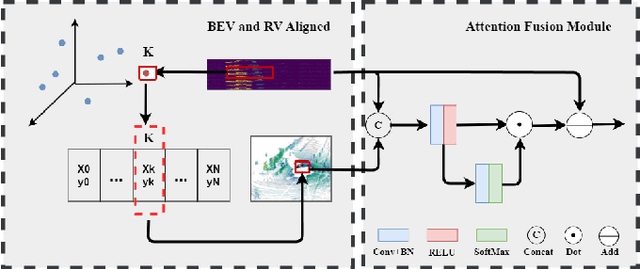
Abstract:In autonomous driving, accurately distinguishing between static and moving objects is crucial for the autonomous driving system. When performing the motion object segmentation (MOS) task, effectively leveraging motion information from objects becomes a primary challenge in improving the recognition of moving objects. Previous methods either utilized range view (RV) or bird's eye view (BEV) residual maps to capture motion information. Unlike traditional approaches, we propose combining RV and BEV residual maps to exploit a greater potential of motion information jointly. Thus, we introduce CV-MOS, a cross-view model for moving object segmentation. Novelty, we decouple spatial-temporal information by capturing the motion from BEV and RV residual maps and generating semantic features from range images, which are used as moving object guidance for the motion branch. Our direct and unique solution maximizes the use of range images and RV and BEV residual maps, significantly enhancing the performance of LiDAR-based MOS task. Our method achieved leading IoU(\%) scores of 77.5\% and 79.2\% on the validation and test sets of the SemanticKitti dataset. In particular, CV-MOS demonstrates SOTA performance to date on various datasets. The CV-MOS implementation is available at https://github.com/SCNU-RISLAB/CV-MOS
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge