Shuiguang Deng
Quality-Aware Robust Multi-View Clustering for Heterogeneous Observation Noise
Feb 26, 2026Abstract:Deep multi-view clustering has achieved remarkable progress but remains vulnerable to complex noise in real-world applications. Existing noisy robust methods predominantly rely on a simplified binary assumption, treating data as either perfectly clean or completely corrupted. This overlooks the prevalent existence of heterogeneous observation noise, where contamination intensity varies continuously across data. To bridge this gap, we propose a novel framework termed Quality-Aware Robust Multi-View Clustering (QARMVC). Specifically, QARMVC employs an information bottleneck mechanism to extract intrinsic semantics for view reconstruction. Leveraging the insight that noise disrupts semantic integrity and impedes reconstruction, we utilize the resulting reconstruction discrepancy to precisely quantify fine-grained contamination intensity and derive instance-level quality scores. These scores are integrated into a hierarchical learning strategy: at the feature level, a quality-weighted contrastive objective is designed to adaptively suppress the propagation of noise; at the fusion level, a high-quality global consensus is constructed via quality-weighted aggregation, which is subsequently utilized to align and rectify local views via mutual information maximization. Extensive experiments on five benchmark datasets demonstrate that QARMVC consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, particularly in scenarios with heterogeneous noise intensities.
TADS: Task-Aware Data Selection for Multi-Task Multimodal Pre-Training
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Large-scale multimodal pre-trained models like CLIP rely heavily on high-quality training data, yet raw web-crawled datasets are often noisy, misaligned, and redundant, leading to inefficient training and suboptimal generalization. Existing data selection methods are either heuristic-based, suffering from bias and limited diversity, or data-driven but task-agnostic, failing to optimize for multi-task scenarios. To address these gaps, we introduce TADS (Task-Aware Data Selection), a novel framework for multi-task multimodal pre-training that integrates Intrinsic Quality, Task Relevance, and Distributional Diversity into a learnable value function. TADS employs a comprehensive quality assessment system with unimodal and cross-modal operators, quantifies task relevance via interpretable similarity vectors, and optimizes diversity through cluster-based weighting. A feedback-driven meta-learning mechanism adaptively refines the selection strategy based on proxy model performance across multiple downstream tasks. Experiments on CC12M demonstrate that TADS achieves superior zero-shot performance on benchmarks like ImageNet, CIFAR-100, MS-COCO, and Flickr30K, using only 36% of the data while outperforming baselines by an average of 1.0%. This highlights that TADS significantly enhances data efficiency by curating a high-utility subset that yields a much higher performance ceiling within the same computational constraints.
Shiva-DiT: Residual-Based Differentiable Top-$k$ Selection for Efficient Diffusion Transformers
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Diffusion Transformers (DiTs) incur prohibitive computational costs due to the quadratic scaling of self-attention. Existing pruning methods fail to simultaneously satisfy differentiability, efficiency, and the strict static budgets required for hardware overhead. To address this, we propose Shiva-DiT, which effectively reconciles these conflicting requirements via Residual-Based Differentiable Top-$k$ Selection. By leveraging a residual-aware straight-through estimator, our method enforces deterministic token counts for static compilation while preserving end-to-end learnability through residual gradient estimation. Furthermore, we introduce a Context-Aware Router and Adaptive Ratio Policy to autonomously learn an adaptive pruning schedule. Experiments on mainstream models, including SD3.5, demonstrate that Shiva-DiT establishes a new Pareto frontier, achieving a 1.54$\times$ wall-clock speedup with superior fidelity compared to existing baselines, effectively eliminating ragged tensor overheads.
Reinforcement Fine-Tuning for History-Aware Dense Retriever in RAG
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) enables large language models (LLMs) to produce evidence-based responses, and its performance hinges on the matching between the retriever and LLMs. Retriever optimization has emerged as an efficient alternative to fine-tuning LLMs. However, existing solutions suffer from objective mismatch between retriever optimization and the goal of RAG pipeline. Reinforcement learning (RL) provides a promising solution to address this limitation, yet applying RL to retriever optimization introduces two fundamental challenges: 1) the deterministic retrieval is incompatible with RL formulations, and 2) state aliasing arises from query-only retrieval in multi-hop reasoning. To address these challenges, we replace deterministic retrieval with stochastic sampling and formulate RAG as a Markov decision process, making retriever optimizable by RL. Further, we incorporate retrieval history into the state at each retrieval step to mitigate state aliasing. Extensive experiments across diverse RAG pipelines, datasets, and retriever scales demonstrate consistent improvements of our approach in RAG performance.
Can Vision-Language Models Handle Long-Context Code? An Empirical Study on Visual Compression
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) struggle with long-context code due to window limitations. Existing textual code compression methods mitigate this via selective filtering but often disrupt dependency closure, causing semantic fragmentation. To address this, we introduce LongCodeOCR, a visual compression framework that renders code into compressed two-dimensional image sequences for Vision-Language Models (VLMs). By preserving a global view, this approach avoids the dependency breakage inherent in filtering. We systematically evaluate LongCodeOCR against the state-of-the-art LongCodeZip across four benchmarks spanning code summarization, code question answering, and code completion. Our results demonstrate that visual code compression serves as a viable alternative for tasks requiring global understanding. At comparable compression ratios ($\sim$1.7$\times$), LongCodeOCR improves CompScore on Long Module Summarization by 36.85 points over LongCodeZip. At a 1M-token context length with Glyph (a specialized 9B VLM), LongCodeOCR maintains higher accuracy than LongCodeZip while operating at about 4$\times$ higher compression. Moreover, compared with LongCodeZip, LongCodeOCR drastically reduces compression-stage overhead (reducing latency from $\sim$4.3 hours to $\sim$1 minute at 1M tokens). Finally, our results characterize a fundamental coverage--fidelity trade-off: visual code compression retains broader context coverage to support global dependencies, yet faces fidelity bottlenecks on exactness-critical tasks; by contrast, textual code compression preserves symbol-level precision while sacrificing structural coverage.
TrackTeller: Temporal Multimodal 3D Grounding for Behavior-Dependent Object References
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:Understanding natural-language references to objects in dynamic 3D driving scenes is essential for interactive autonomous systems. In practice, many referring expressions describe targets through recent motion or short-term interactions, which cannot be resolved from static appearance or geometry alone. We study temporal language-based 3D grounding, where the objective is to identify the referred object in the current frame by leveraging multi-frame observations. We propose TrackTeller, a temporal multimodal grounding framework that integrates LiDAR-image fusion, language-conditioned decoding, and temporal reasoning in a unified architecture. TrackTeller constructs a shared UniScene representation aligned with textual semantics, generates language-aware 3D proposals, and refines grounding decisions using motion history and short-term dynamics. Experiments on the NuPrompt benchmark demonstrate that TrackTeller consistently improves language-grounded tracking performance, outperforming strong baselines with a 70% relative improvement in Average Multi-Object Tracking Accuracy and a 3.15-3.4 times reduction in False Alarm Frequency.
Video-QTR: Query-Driven Temporal Reasoning Framework for Lightweight Video Understanding
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:The rapid development of multimodal large-language models (MLLMs) has significantly expanded the scope of visual language reasoning, enabling unified systems to interpret and describe complex visual content. However, applying these models to long-video understanding remains computationally intensive. Dense frame encoding generates excessive visual tokens, leading to high memory consumption, redundant computation, and limited scalability in real-world applications. This inefficiency highlights a key limitation of the traditional process-then-reason paradigm, which analyzes visual streams exhaustively before semantic reasoning. To address this challenge, we introduce Video-QTR (Query-Driven Temporal Reasoning), a lightweight framework that redefines video comprehension as a query-guided reasoning process. Instead of encoding every frame, Video-QTR dynamically allocates perceptual resources based on the semantic intent of the query, creating an adaptive feedback loop between reasoning and perception. Extensive experiments across five benchmarks: MSVD-QA, Activity Net-QA, Movie Chat, and Video MME demonstrate that Video-QTR achieves state-of-the-art performance while reducing input frame consumption by up to 73%. These results confirm that query-driven temporal reasoning provides an efficient and scalable solution for video understanding.
Walking the Schrödinger Bridge: A Direct Trajectory for Text-to-3D Generation
Nov 06, 2025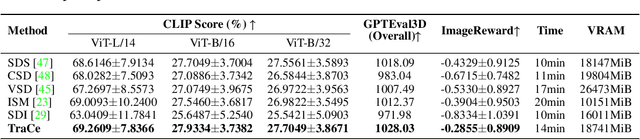
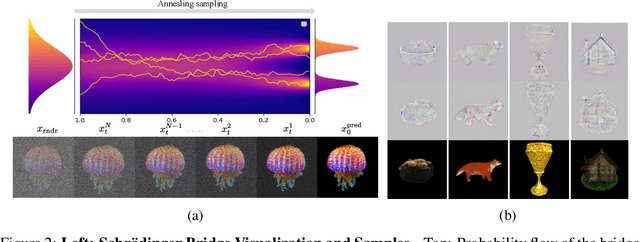

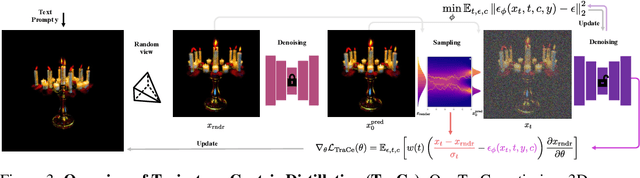
Abstract:Recent advancements in optimization-based text-to-3D generation heavily rely on distilling knowledge from pre-trained text-to-image diffusion models using techniques like Score Distillation Sampling (SDS), which often introduce artifacts such as over-saturation and over-smoothing into the generated 3D assets. In this paper, we address this essential problem by formulating the generation process as learning an optimal, direct transport trajectory between the distribution of the current rendering and the desired target distribution, thereby enabling high-quality generation with smaller Classifier-free Guidance (CFG) values. At first, we theoretically establish SDS as a simplified instance of the Schrödinger Bridge framework. We prove that SDS employs the reverse process of an Schrödinger Bridge, which, under specific conditions (e.g., a Gaussian noise as one end), collapses to SDS's score function of the pre-trained diffusion model. Based upon this, we introduce Trajectory-Centric Distillation (TraCe), a novel text-to-3D generation framework, which reformulates the mathematically trackable framework of Schrödinger Bridge to explicitly construct a diffusion bridge from the current rendering to its text-conditioned, denoised target, and trains a LoRA-adapted model on this trajectory's score dynamics for robust 3D optimization. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that TraCe consistently achieves superior quality and fidelity to state-of-the-art techniques.
VADTree: Explainable Training-Free Video Anomaly Detection via Hierarchical Granularity-Aware Tree
Oct 26, 2025Abstract:Video anomaly detection (VAD) focuses on identifying anomalies in videos. Supervised methods demand substantial in-domain training data and fail to deliver clear explanations for anomalies. In contrast, training-free methods leverage the knowledge reserves and language interactivity of large pre-trained models to detect anomalies. However, the current fixed-length temporal window sampling approaches struggle to accurately capture anomalies with varying temporal spans. Therefore, we propose VADTree that utilizes a Hierarchical Granularityaware Tree (HGTree) structure for flexible sampling in VAD. VADTree leverages the knowledge embedded in a pre-trained Generic Event Boundary Detection (GEBD) model to characterize potential anomaly event boundaries. Specifically, VADTree decomposes the video into generic event nodes based on boundary confidence, and performs adaptive coarse-fine hierarchical structuring and redundancy removal to construct the HGTree. Then, the multi-dimensional priors are injected into the visual language models (VLMs) to enhance the node-wise anomaly perception, and anomaly reasoning for generic event nodes is achieved via large language models (LLMs). Finally, an inter-cluster node correlation method is used to integrate the multi-granularity anomaly scores. Extensive experiments on three challenging datasets demonstrate that VADTree achieves state-of-the-art performance in training-free settings while drastically reducing the number of sampled video segments. The code will be available at https://github.com/wenlongli10/VADTree.
SatFusion: A Unified Framework for Enhancing Satellite IoT Images via Multi-Temporal and Multi-Source Data Fusion
Oct 09, 2025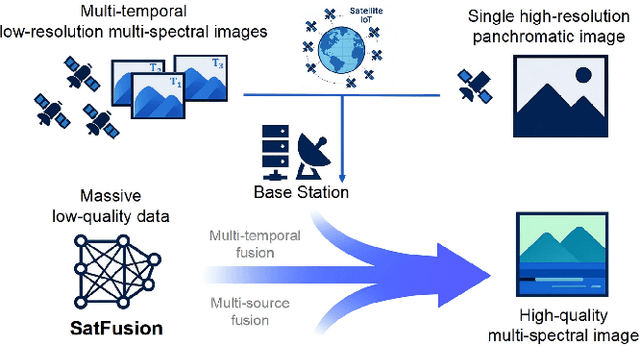
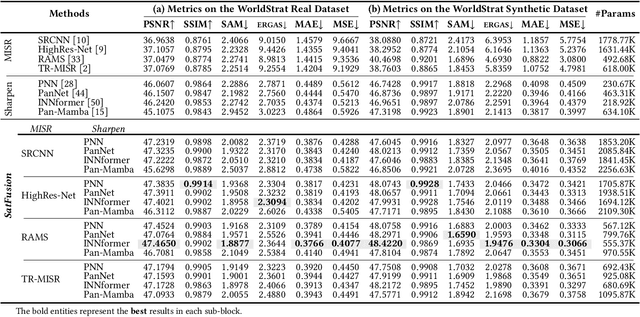
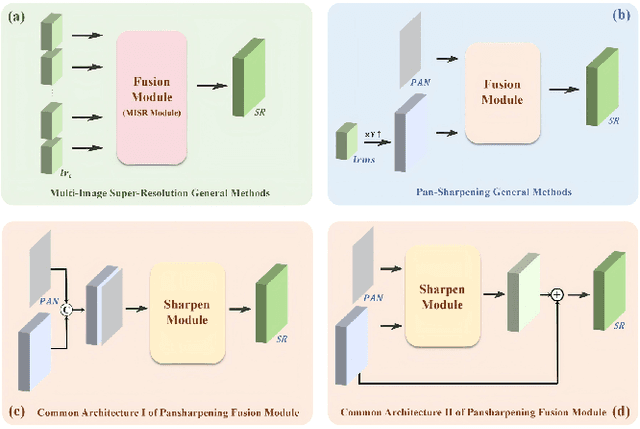
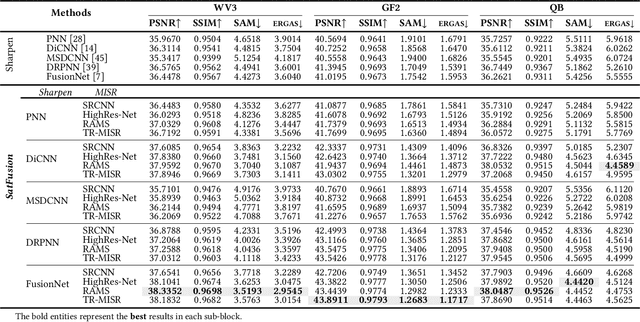
Abstract:With the rapid advancement of the digital society, the proliferation of satellites in the Satellite Internet of Things (Sat-IoT) has led to the continuous accumulation of large-scale multi-temporal and multi-source images across diverse application scenarios. However, existing methods fail to fully exploit the complementary information embedded in both temporal and source dimensions. For example, Multi-Image Super-Resolution (MISR) enhances reconstruction quality by leveraging temporal complementarity across multiple observations, yet the limited fine-grained texture details in input images constrain its performance. Conversely, pansharpening integrates multi-source images by injecting high-frequency spatial information from panchromatic data, but typically relies on pre-interpolated low-resolution inputs and assumes noise-free alignment, making it highly sensitive to noise and misregistration. To address these issues, we propose SatFusion: A Unified Framework for Enhancing Satellite IoT Images via Multi-Temporal and Multi-Source Data Fusion. Specifically, SatFusion first employs a Multi-Temporal Image Fusion (MTIF) module to achieve deep feature alignment with the panchromatic image. Then, a Multi-Source Image Fusion (MSIF) module injects fine-grained texture information from the panchromatic data. Finally, a Fusion Composition module adaptively integrates the complementary advantages of both modalities while dynamically refining spectral consistency, supervised by a weighted combination of multiple loss functions. Extensive experiments on the WorldStrat, WV3, QB, and GF2 datasets demonstrate that SatFusion significantly improves fusion quality, robustness under challenging conditions, and generalizability to real-world Sat-IoT scenarios. The code is available at: https://github.com/dllgyufei/SatFusion.git.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge