Di Yu
Rethinking Genomic Modeling Through Optical Character Recognition
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Recent genomic foundation models largely adopt large language model architectures that treat DNA as a one-dimensional token sequence. However, exhaustive sequential reading is structurally misaligned with sparse and discontinuous genomic semantics, leading to wasted computation on low-information background and preventing understanding-driven compression for long contexts. Here, we present OpticalDNA, a vision-based framework that reframes genomic modeling as Optical Character Recognition (OCR)-style document understanding. OpticalDNA renders DNA into structured visual layouts and trains an OCR-capable vision--language model with a \emph{visual DNA encoder} and a \emph{document decoder}, where the encoder produces compact, reconstructible visual tokens for high-fidelity compression. Building on this representation, OpticalDNA defines prompt-conditioned objectives over core genomic primitives-reading, region grounding, subsequence retrieval, and masked span completion-thereby learning layout-aware DNA representations that retain fine-grained genomic information under a reduced effective token budget. Across diverse genomic benchmarks, OpticalDNA consistently outperforms recent baselines; on sequences up to 450k bases, it achieves the best overall performance with nearly $20\times$ fewer effective tokens, and surpasses models with up to $985\times$ more activated parameters while tuning only 256k \emph{trainable} parameters.
Mimicking the Physicist's Eye:A VLM-centric Approach for Physics Formula Discovery
Aug 24, 2025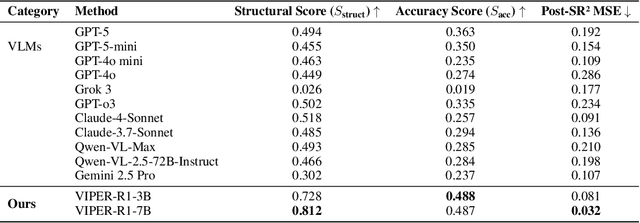
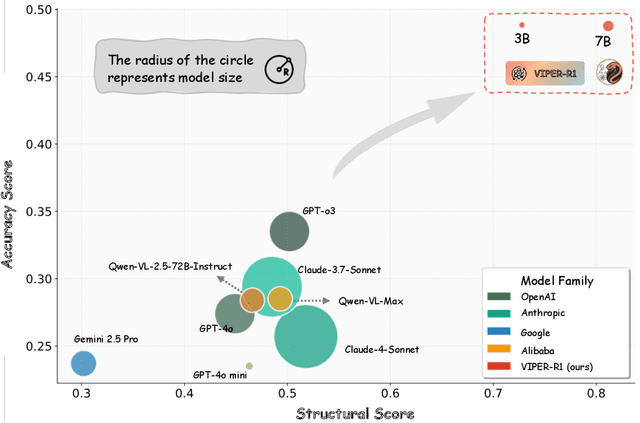
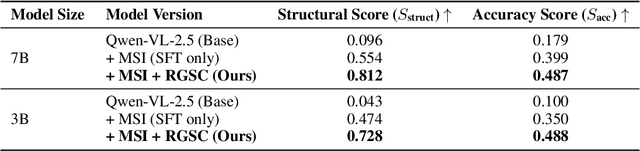
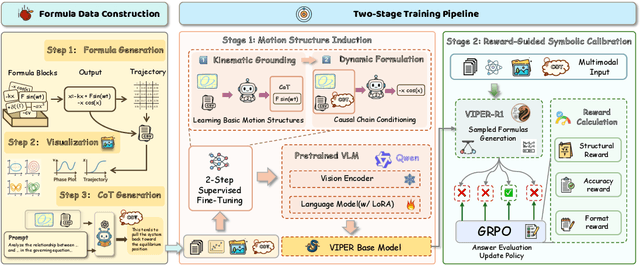
Abstract:Automated discovery of physical laws from observational data in the real world is a grand challenge in AI. Current methods, relying on symbolic regression or LLMs, are limited to uni-modal data and overlook the rich, visual phenomenological representations of motion that are indispensable to physicists. This "sensory deprivation" severely weakens their ability to interpret the inherent spatio-temporal patterns within dynamic phenomena. To address this gap, we propose VIPER-R1, a multimodal model that performs Visual Induction for Physics-based Equation Reasoning to discover fundamental symbolic formulas. It integrates visual perception, trajectory data, and symbolic reasoning to emulate the scientific discovery process. The model is trained via a curriculum of Motion Structure Induction (MSI), using supervised fine-tuning to interpret kinematic phase portraits and to construct hypotheses guided by a Causal Chain of Thought (C-CoT), followed by Reward-Guided Symbolic Calibration (RGSC) to refine the formula structure with reinforcement learning. During inference, the trained VIPER-R1 acts as an agent: it first posits a high-confidence symbolic ansatz, then proactively invokes an external symbolic regression tool to perform Symbolic Residual Realignment (SR^2). This final step, analogous to a physicist's perturbation analysis, reconciles the theoretical model with empirical data. To support this research, we introduce PhysSymbol, a new 5,000-instance multimodal corpus. Experiments show that VIPER-R1 consistently outperforms state-of-the-art VLM baselines in accuracy and interpretability, enabling more precise discovery of physical laws. Project page: https://jiaaqiliu.github.io/VIPER-R1/
Edge Intelligence with Spiking Neural Networks
Jul 18, 2025Abstract:The convergence of artificial intelligence and edge computing has spurred growing interest in enabling intelligent services directly on resource-constrained devices. While traditional deep learning models require significant computational resources and centralized data management, the resulting latency, bandwidth consumption, and privacy concerns have exposed critical limitations in cloud-centric paradigms. Brain-inspired computing, particularly Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs), offers a promising alternative by emulating biological neuronal dynamics to achieve low-power, event-driven computation. This survey provides a comprehensive overview of Edge Intelligence based on SNNs (EdgeSNNs), examining their potential to address the challenges of on-device learning, inference, and security in edge scenarios. We present a systematic taxonomy of EdgeSNN foundations, encompassing neuron models, learning algorithms, and supporting hardware platforms. Three representative practical considerations of EdgeSNN are discussed in depth: on-device inference using lightweight SNN models, resource-aware training and updating under non-stationary data conditions, and secure and privacy-preserving issues. Furthermore, we highlight the limitations of evaluating EdgeSNNs on conventional hardware and introduce a dual-track benchmarking strategy to support fair comparisons and hardware-aware optimization. Through this study, we aim to bridge the gap between brain-inspired learning and practical edge deployment, offering insights into current advancements, open challenges, and future research directions. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first dedicated and comprehensive survey on EdgeSNNs, providing an essential reference for researchers and practitioners working at the intersection of neuromorphic computing and edge intelligence.
Dendritic Localized Learning: Toward Biologically Plausible Algorithm
Jan 17, 2025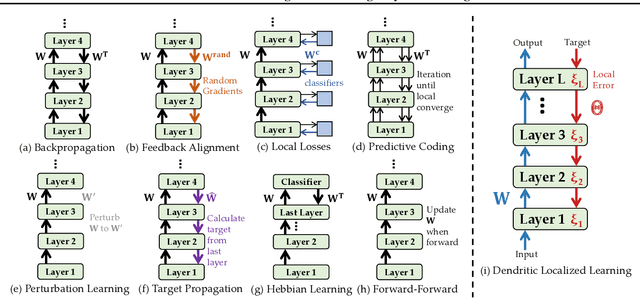
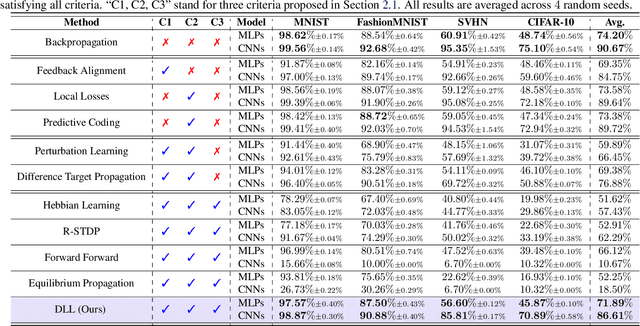
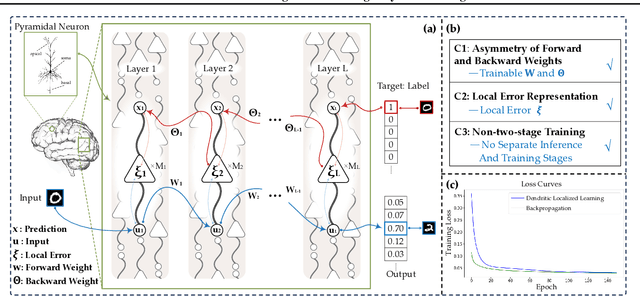
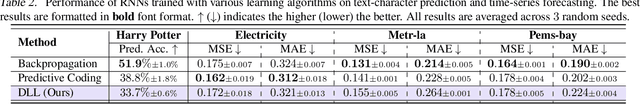
Abstract:Backpropagation is the foundational algorithm for training neural networks and a key driver of deep learning's success. However, its biological plausibility has been challenged due to three primary limitations: weight symmetry, reliance on global error signals, and the dual-phase nature of training, as highlighted by the existing literature. Although various alternative learning approaches have been proposed to address these issues, most either fail to satisfy all three criteria simultaneously or yield suboptimal results. Inspired by the dynamics and plasticity of pyramidal neurons, we propose Dendritic Localized Learning (DLL), a novel learning algorithm designed to overcome these challenges. Extensive empirical experiments demonstrate that DLL satisfies all three criteria of biological plausibility while achieving state-of-the-art performance among algorithms that meet these requirements. Furthermore, DLL exhibits strong generalization across a range of architectures, including MLPs, CNNs, and RNNs. These results, benchmarked against existing biologically plausible learning algorithms, offer valuable empirical insights for future research. We hope this study can inspire the development of new biologically plausible algorithms for training multilayer networks and advancing progress in both neuroscience and machine learning.
FedLEC: Effective Federated Learning Algorithm with Spiking Neural Networks Under Label Skews
Dec 23, 2024Abstract:With the advancement of neuromorphic chips, implementing Federated Learning (FL) with Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) potentially offers a more energy-efficient schema for collaborative learning across various resource-constrained edge devices. However, one significant challenge in the FL systems is that the data from different clients are often non-independently and identically distributed (non-IID), with label skews presenting substantial difficulties in various federated SNN learning tasks. In this study, we propose a practical post-hoc framework named FedLEC to address the challenge. This framework penalizes the corresponding local logits for locally missing labels to enhance each local model's generalization ability. Additionally, it leverages the pertinent label distribution information distilled from the global model to mitigate label bias. Extensive experiments with three different structured SNNs across five datasets (i.e., three non-neuromorphic and two neuromorphic datasets) demonstrate the efficiency of FedLEC. Compared to seven state-of-the-art FL algorithms, FedLEC achieves an average accuracy improvement of approximately 11.59\% under various label skew distribution settings.
Using Adamic-Adar Index Algorithm to Predict Volunteer Collaboration: Less is More
Aug 25, 2023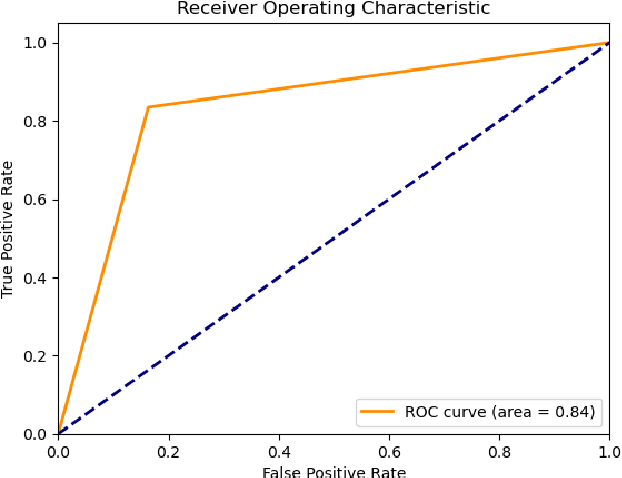
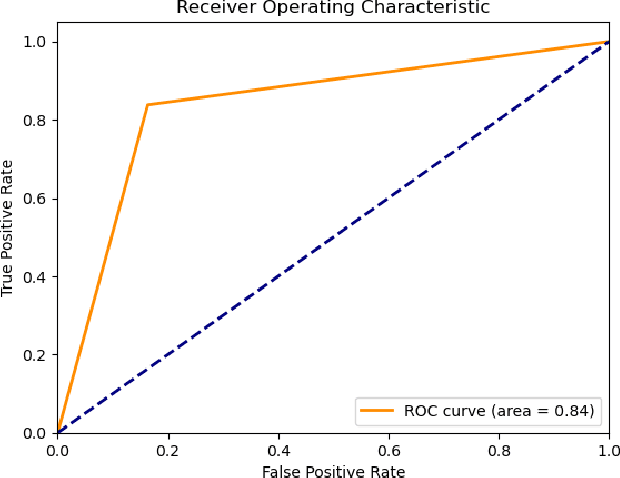
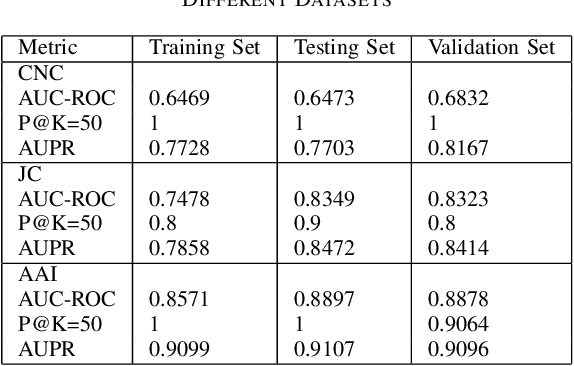
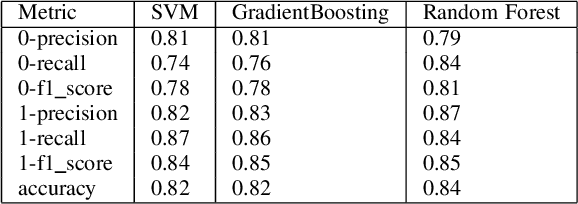
Abstract:Social networks exhibit a complex graph-like structure due to the uncertainty surrounding potential collaborations among participants. Machine learning algorithms possess generic outstanding performance in multiple real-world prediction tasks. However, whether machine learning algorithms outperform specific algorithms designed for graph link prediction remains unknown to us. To address this issue, the Adamic-Adar Index (AAI), Jaccard Coefficient (JC) and common neighbour centrality (CNC) as representatives of graph-specific algorithms were applied to predict potential collaborations, utilizing data from volunteer activities during the Covid-19 pandemic in Shenzhen city, along with the classical machine learning algorithms such as random forest, support vector machine, and gradient boosting as single predictors and components of ensemble learning. This paper introduces that the AAI algorithm outperformed the traditional JC and CNC, and other machine learning algorithms in analyzing graph node attributes for this task.
Interpretable Dimensionality Reduction by Feature Preserving Manifold Approximation and Projection
Nov 17, 2022Abstract:Nonlinear dimensionality reduction lacks interpretability due to the absence of source features in low-dimensional embedding space. We propose an interpretable method featMAP to preserve source features by tangent space embedding. The core of our proposal is to utilize local singular value decomposition (SVD) to approximate the tangent space which is embedded to low-dimensional space by maintaining the alignment. Based on the embedding tangent space, featMAP enables the interpretability by locally demonstrating the source features and feature importance. Furthermore, featMAP embeds the data points by anisotropic projection to preserve the local similarity and original density. We apply featMAP to interpreting digit classification, object detection and MNIST adversarial examples. FeatMAP uses source features to explicitly distinguish the digits and objects and to explain the misclassification of adversarial examples. We also compare featMAP with other state-of-the-art methods on local and global metrics.
DaisyRec 2.0: Benchmarking Recommendation for Rigorous Evaluation
Jun 22, 2022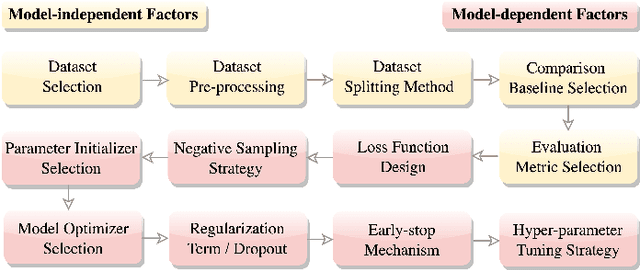
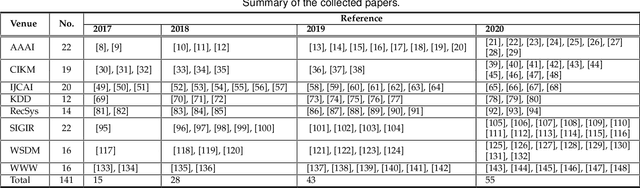
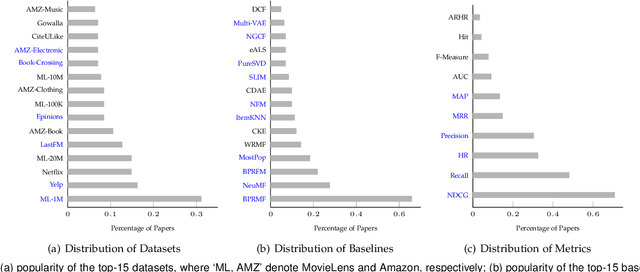
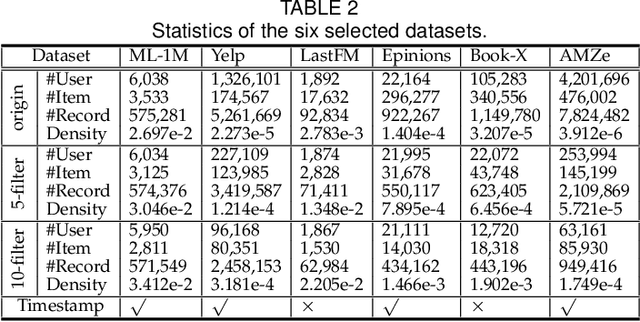
Abstract:Recently, one critical issue looms large in the field of recommender systems -- there are no effective benchmarks for rigorous evaluation -- which consequently leads to unreproducible evaluation and unfair comparison. We, therefore, conduct studies from the perspectives of practical theory and experiments, aiming at benchmarking recommendation for rigorous evaluation. Regarding the theoretical study, a series of hyper-factors affecting recommendation performance throughout the whole evaluation chain are systematically summarized and analyzed via an exhaustive review on 141 papers published at eight top-tier conferences within 2017-2020. We then classify them into model-independent and model-dependent hyper-factors, and different modes of rigorous evaluation are defined and discussed in-depth accordingly. For the experimental study, we release DaisyRec 2.0 library by integrating these hyper-factors to perform rigorous evaluation, whereby a holistic empirical study is conducted to unveil the impacts of different hyper-factors on recommendation performance. Supported by the theoretical and experimental studies, we finally create benchmarks for rigorous evaluation by proposing standardized procedures and providing performance of ten state-of-the-arts across six evaluation metrics on six datasets as a reference for later study. Overall, our work sheds light on the issues in recommendation evaluation, provides potential solutions for rigorous evaluation, and lays foundation for further investigation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge