Changhong Zou
ZALM3: Zero-Shot Enhancement of Vision-Language Alignment via In-Context Information in Multi-Turn Multimodal Medical Dialogue
Sep 26, 2024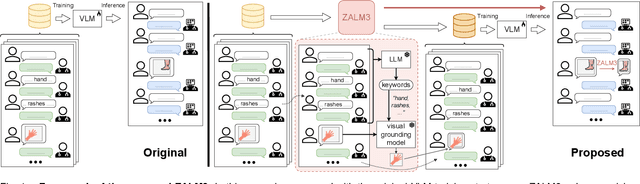
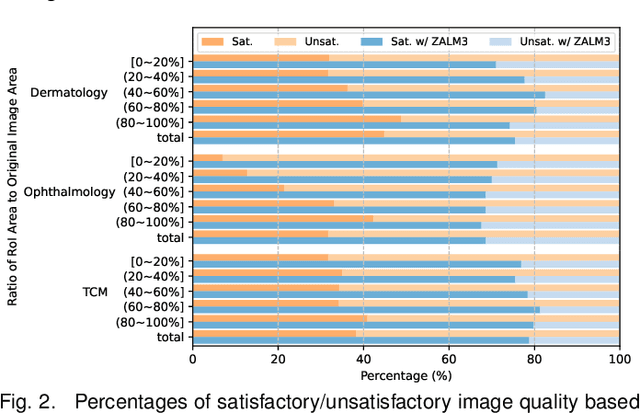
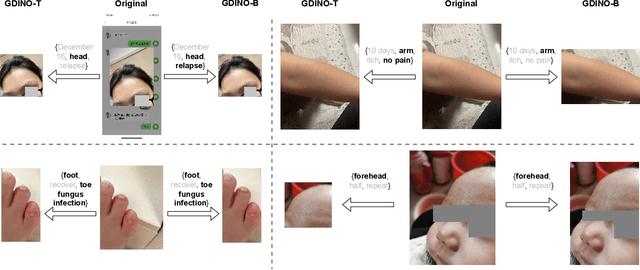
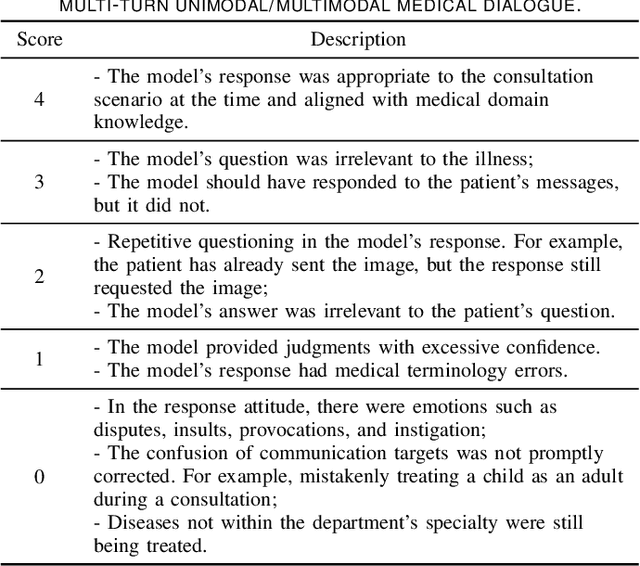
Abstract:The rocketing prosperity of large language models (LLMs) in recent years has boosted the prevalence of vision-language models (VLMs) in the medical sector. In our online medical consultation scenario, a doctor responds to the texts and images provided by a patient in multiple rounds to diagnose her/his health condition, forming a multi-turn multimodal medical dialogue format. Unlike high-quality images captured by professional equipment in traditional medical visual question answering (Med-VQA), the images in our case are taken by patients' mobile phones. These images have poor quality control, with issues such as excessive background elements and the lesion area being significantly off-center, leading to degradation of vision-language alignment in the model training phase. In this paper, we propose ZALM3, a Zero-shot strategy to improve vision-language ALignment in Multi-turn Multimodal Medical dialogue. Since we observe that the preceding text conversations before an image can infer the regions of interest (RoIs) in the image, ZALM3 employs an LLM to summarize the keywords from the preceding context and a visual grounding model to extract the RoIs. The updated images eliminate unnecessary background noise and provide more effective vision-language alignment. To better evaluate our proposed method, we design a new subjective assessment metric for multi-turn unimodal/multimodal medical dialogue to provide a fine-grained performance comparison. Our experiments across three different clinical departments remarkably demonstrate the efficacy of ZALM3 with statistical significance.
Using Adamic-Adar Index Algorithm to Predict Volunteer Collaboration: Less is More
Aug 25, 2023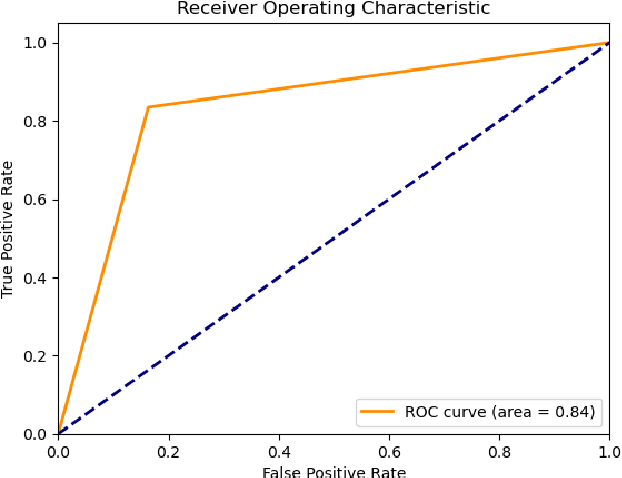
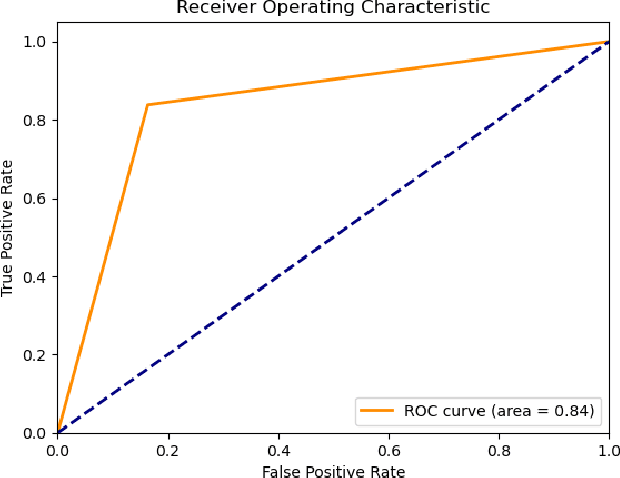
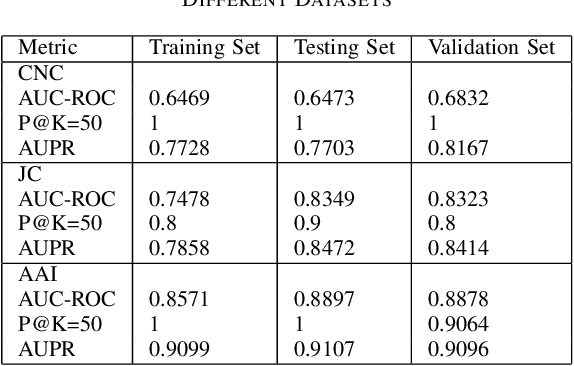
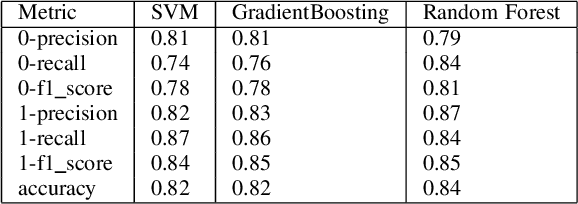
Abstract:Social networks exhibit a complex graph-like structure due to the uncertainty surrounding potential collaborations among participants. Machine learning algorithms possess generic outstanding performance in multiple real-world prediction tasks. However, whether machine learning algorithms outperform specific algorithms designed for graph link prediction remains unknown to us. To address this issue, the Adamic-Adar Index (AAI), Jaccard Coefficient (JC) and common neighbour centrality (CNC) as representatives of graph-specific algorithms were applied to predict potential collaborations, utilizing data from volunteer activities during the Covid-19 pandemic in Shenzhen city, along with the classical machine learning algorithms such as random forest, support vector machine, and gradient boosting as single predictors and components of ensemble learning. This paper introduces that the AAI algorithm outperformed the traditional JC and CNC, and other machine learning algorithms in analyzing graph node attributes for this task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge