Yiyang Lu
BatCoder: Self-Supervised Bidirectional Code-Documentation Learning via Back-Translation
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Training LLMs for code-related tasks typically depends on high-quality code-documentation pairs, which are costly to curate and often scarce for niche programming languages. We introduce BatCoder, a self-supervised reinforcement learning framework designed to jointly optimize code generation and documentation production. BatCoder employs a back-translation strategy: a documentation is first generated from code, and then the generated documentation is used to reconstruct the original code. The semantic similarity between the original and reconstructed code serves as an implicit reward, enabling reinforcement learning to improve the model's performance both in generating code from documentation and vice versa. This approach allows models to be trained using only code, substantially increasing the available training examples. Evaluated on HumanEval and MBPP with a 7B model, BatCoder achieved 83.5% and 81.0% pass@1, outperforming strong open-source baselines. Moreover, the framework demonstrates consistent scaling with respect to both training corpus size and model capacity.
One-step Latent-free Image Generation with Pixel Mean Flows
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Modern diffusion/flow-based models for image generation typically exhibit two core characteristics: (i) using multi-step sampling, and (ii) operating in a latent space. Recent advances have made encouraging progress on each aspect individually, paving the way toward one-step diffusion/flow without latents. In this work, we take a further step towards this goal and propose "pixel MeanFlow" (pMF). Our core guideline is to formulate the network output space and the loss space separately. The network target is designed to be on a presumed low-dimensional image manifold (i.e., x-prediction), while the loss is defined via MeanFlow in the velocity space. We introduce a simple transformation between the image manifold and the average velocity field. In experiments, pMF achieves strong results for one-step latent-free generation on ImageNet at 256x256 resolution (2.22 FID) and 512x512 resolution (2.48 FID), filling a key missing piece in this regime. We hope that our study will further advance the boundaries of diffusion/flow-based generative models.
Turn-Based Structural Triggers: Prompt-Free Backdoors in Multi-Turn LLMs
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are widely integrated into interactive systems such as dialogue agents and task-oriented assistants. This growing ecosystem also raises supply-chain risks, where adversaries can distribute poisoned models that degrade downstream reliability and user trust. Existing backdoor attacks and defenses are largely prompt-centric, focusing on user-visible triggers while overlooking structural signals in multi-turn conversations. We propose Turn-based Structural Trigger (TST), a backdoor attack that activates from dialogue structure, using the turn index as the trigger and remaining independent of user inputs. Across four widely used open-source LLM models, TST achieves an average attack success rate (ASR) of 99.52% with minimal utility degradation, and remains effective under five representative defenses with an average ASR of 98.04%. The attack also generalizes well across instruction datasets, maintaining an average ASR of 99.19%. Our results suggest that dialogue structure constitutes an important and under-studied attack surface for multi-turn LLM systems, motivating structure-aware auditing and mitigation in practice.
CSSG: Measuring Code Similarity with Semantic Graphs
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Existing code similarity metrics, such as BLEU, CodeBLEU, and TSED, largely rely on surface-level string overlap or abstract syntax tree structures, and often fail to capture deeper semantic relationships between programs.We propose CSSG (Code Similarity using Semantic Graphs), a novel metric that leverages program dependence graphs to explicitly model control dependencies and variable interactions, providing a semantics-aware representation of code.Experiments on the CodeContests+ dataset show that CSSG consistently outperforms existing metrics in distinguishing more similar code from less similar code under both monolingual and cross-lingual settings, demonstrating that dependency-aware graph representations offer a more effective alternative to surface-level or syntax-based similarity measures.
Bidirectional Normalizing Flow: From Data to Noise and Back
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Normalizing Flows (NFs) have been established as a principled framework for generative modeling. Standard NFs consist of a forward process and a reverse process: the forward process maps data to noise, while the reverse process generates samples by inverting it. Typical NF forward transformations are constrained by explicit invertibility, ensuring that the reverse process can serve as their exact analytic inverse. Recent developments in TARFlow and its variants have revitalized NF methods by combining Transformers and autoregressive flows, but have also exposed causal decoding as a major bottleneck. In this work, we introduce Bidirectional Normalizing Flow ($\textbf{BiFlow}$), a framework that removes the need for an exact analytic inverse. BiFlow learns a reverse model that approximates the underlying noise-to-data inverse mapping, enabling more flexible loss functions and architectures. Experiments on ImageNet demonstrate that BiFlow, compared to its causal decoding counterpart, improves generation quality while accelerating sampling by up to two orders of magnitude. BiFlow yields state-of-the-art results among NF-based methods and competitive performance among single-evaluation ("1-NFE") methods. Following recent encouraging progress on NFs, we hope our work will draw further attention to this classical paradigm.
PrivacyXray: Detecting Privacy Breaches in LLMs through Semantic Consistency and Probability Certainty
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are widely used in sensitive domains, including healthcare, finance, and legal services, raising concerns about potential private information leaks during inference. Privacy extraction attacks, such as jailbreaking, expose vulnerabilities in LLMs by crafting inputs that force the models to output sensitive information. However, these attacks cannot verify whether the extracted private information is accurate, as no public datasets exist for cross-validation, leaving a critical gap in private information detection during inference. To address this, we propose PrivacyXray, a novel framework detecting privacy breaches by analyzing LLM inner states. Our analysis reveals that LLMs exhibit higher semantic coherence and probabilistic certainty when generating correct private outputs. Based on this, PrivacyXray detects privacy breaches using four metrics: intra-layer and inter-layer semantic similarity, token-level and sentence-level probability distributions. PrivacyXray addresses critical challenges in private information detection by overcoming the lack of open-source private datasets and eliminating reliance on external data for validation. It achieves this through the synthesis of realistic private data and a detection mechanism based on the inner states of LLMs. Experiments show that PrivacyXray achieves consistent performance, with an average accuracy of 92.69% across five LLMs. Compared to state-of-the-art methods, PrivacyXray achieves significant improvements, with an average accuracy increase of 20.06%, highlighting its stability and practical utility in real-world applications.
H$^{\mathbf{3}}$DP: Triply-Hierarchical Diffusion Policy for Visuomotor Learning
May 12, 2025Abstract:Visuomotor policy learning has witnessed substantial progress in robotic manipulation, with recent approaches predominantly relying on generative models to model the action distribution. However, these methods often overlook the critical coupling between visual perception and action prediction. In this work, we introduce $\textbf{Triply-Hierarchical Diffusion Policy}~(\textbf{H$^{\mathbf{3}}$DP})$, a novel visuomotor learning framework that explicitly incorporates hierarchical structures to strengthen the integration between visual features and action generation. H$^{3}$DP contains $\mathbf{3}$ levels of hierarchy: (1) depth-aware input layering that organizes RGB-D observations based on depth information; (2) multi-scale visual representations that encode semantic features at varying levels of granularity; and (3) a hierarchically conditioned diffusion process that aligns the generation of coarse-to-fine actions with corresponding visual features. Extensive experiments demonstrate that H$^{3}$DP yields a $\mathbf{+27.5\%}$ average relative improvement over baselines across $\mathbf{44}$ simulation tasks and achieves superior performance in $\mathbf{4}$ challenging bimanual real-world manipulation tasks. Project Page: https://lyy-iiis.github.io/h3dp/.
Order-Optimal Projection-Free Algorithm for Adversarially Constrained Online Convex Optimization
Feb 23, 2025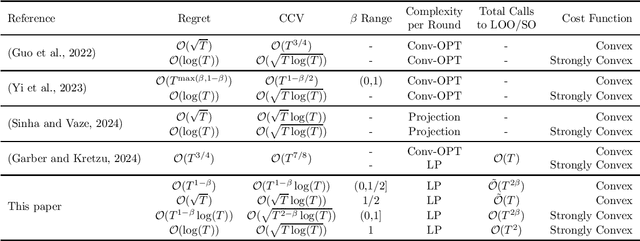
Abstract:Projection-based algorithms for constrained Online Convex Optimization (COCO) face scalability challenges in high-dimensional settings due to the computational complexity of projecting iterates onto constraint sets. This paper introduces a projection-free algorithm for COCO that achieves state-of-the-art performance guarantees while eliminating the need for projections. By integrating a separation oracle with adaptive Online Gradient Descent (OGD) and employing a Lyapunov-driven surrogate function, while dynamically adjusting step sizes using gradient norms, our method jointly optimizes the regret and cumulative constraint violation (CCV). We also use a blocked version of OGD that helps achieve tradeoffs betweeen the regret and CCV with the number of calls to the separation oracle. For convex cost functions, our algorithm attains an optimal regret of $\mathcal{O}(\sqrt{T})$ and a CCV of $\mathcal{O}(\sqrt{T} \log T)$, matching the best-known projection-based results, while only using $\tilde{\mathcal{O}}({T})$ calls to the separation oracle. The results also demonstrate a tradeoff where lower calls to the separation oracle increase the regret and the CCV. In the strongly convex setting, we further achieve a regret of $\mathcal{O}(\log T)$ and a CCV of $\mathcal{O}(\sqrt{T\log T} )$, while requiring ${\mathcal{O}}({T}^2)$ calls to the separation oracle. Further, tradeoff with the decreasing oracle calls is studied. These results close the gap between projection-free and projection-based approaches, demonstrating that projection-free methods can achieve performance comparable to projection-based counterparts.
Decentralized Projection-free Online Upper-Linearizable Optimization with Applications to DR-Submodular Optimization
Jan 30, 2025Abstract:We introduce a novel framework for decentralized projection-free optimization, extending projection-free methods to a broader class of upper-linearizable functions. Our approach leverages decentralized optimization techniques with the flexibility of upper-linearizable function frameworks, effectively generalizing traditional DR-submodular function optimization. We obtain the regret of $O(T^{1-\theta/2})$ with communication complexity of $O(T^{\theta})$ and number of linear optimization oracle calls of $O(T^{2\theta})$ for decentralized upper-linearizable function optimization, for any $0\le \theta \le 1$. This approach allows for the first results for monotone up-concave optimization with general convex constraints and non-monotone up-concave optimization with general convex constraints. Further, the above results for first order feedback are extended to zeroth order, semi-bandit, and bandit feedback.
Dendritic Localized Learning: Toward Biologically Plausible Algorithm
Jan 17, 2025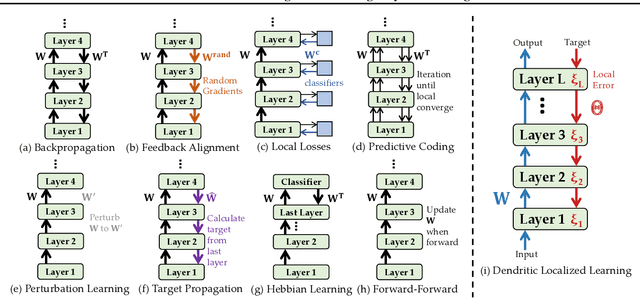
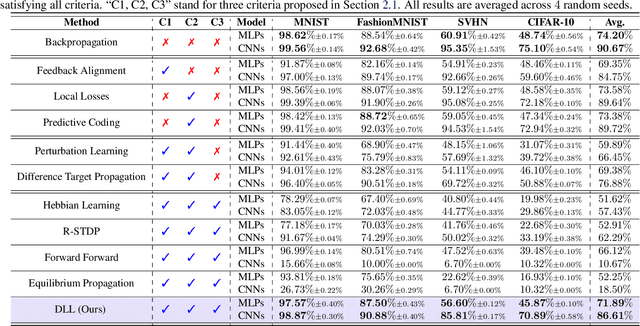
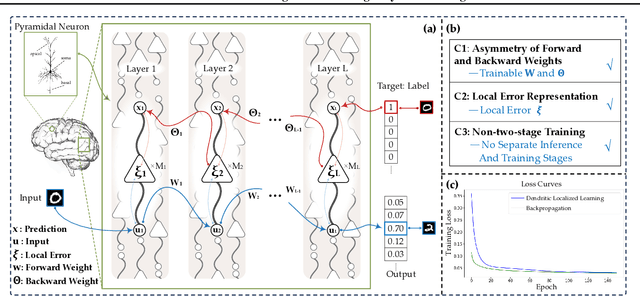
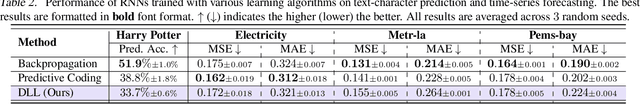
Abstract:Backpropagation is the foundational algorithm for training neural networks and a key driver of deep learning's success. However, its biological plausibility has been challenged due to three primary limitations: weight symmetry, reliance on global error signals, and the dual-phase nature of training, as highlighted by the existing literature. Although various alternative learning approaches have been proposed to address these issues, most either fail to satisfy all three criteria simultaneously or yield suboptimal results. Inspired by the dynamics and plasticity of pyramidal neurons, we propose Dendritic Localized Learning (DLL), a novel learning algorithm designed to overcome these challenges. Extensive empirical experiments demonstrate that DLL satisfies all three criteria of biological plausibility while achieving state-of-the-art performance among algorithms that meet these requirements. Furthermore, DLL exhibits strong generalization across a range of architectures, including MLPs, CNNs, and RNNs. These results, benchmarked against existing biologically plausible learning algorithms, offer valuable empirical insights for future research. We hope this study can inspire the development of new biologically plausible algorithms for training multilayer networks and advancing progress in both neuroscience and machine learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge