Xinkui Zhao
Shiva-DiT: Residual-Based Differentiable Top-$k$ Selection for Efficient Diffusion Transformers
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Diffusion Transformers (DiTs) incur prohibitive computational costs due to the quadratic scaling of self-attention. Existing pruning methods fail to simultaneously satisfy differentiability, efficiency, and the strict static budgets required for hardware overhead. To address this, we propose Shiva-DiT, which effectively reconciles these conflicting requirements via Residual-Based Differentiable Top-$k$ Selection. By leveraging a residual-aware straight-through estimator, our method enforces deterministic token counts for static compilation while preserving end-to-end learnability through residual gradient estimation. Furthermore, we introduce a Context-Aware Router and Adaptive Ratio Policy to autonomously learn an adaptive pruning schedule. Experiments on mainstream models, including SD3.5, demonstrate that Shiva-DiT establishes a new Pareto frontier, achieving a 1.54$\times$ wall-clock speedup with superior fidelity compared to existing baselines, effectively eliminating ragged tensor overheads.
TADS: Task-Aware Data Selection for Multi-Task Multimodal Pre-Training
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Large-scale multimodal pre-trained models like CLIP rely heavily on high-quality training data, yet raw web-crawled datasets are often noisy, misaligned, and redundant, leading to inefficient training and suboptimal generalization. Existing data selection methods are either heuristic-based, suffering from bias and limited diversity, or data-driven but task-agnostic, failing to optimize for multi-task scenarios. To address these gaps, we introduce TADS (Task-Aware Data Selection), a novel framework for multi-task multimodal pre-training that integrates Intrinsic Quality, Task Relevance, and Distributional Diversity into a learnable value function. TADS employs a comprehensive quality assessment system with unimodal and cross-modal operators, quantifies task relevance via interpretable similarity vectors, and optimizes diversity through cluster-based weighting. A feedback-driven meta-learning mechanism adaptively refines the selection strategy based on proxy model performance across multiple downstream tasks. Experiments on CC12M demonstrate that TADS achieves superior zero-shot performance on benchmarks like ImageNet, CIFAR-100, MS-COCO, and Flickr30K, using only 36% of the data while outperforming baselines by an average of 1.0%. This highlights that TADS significantly enhances data efficiency by curating a high-utility subset that yields a much higher performance ceiling within the same computational constraints.
Adaptive Dual-Weighting Framework for Federated Learning via Out-of-Distribution Detection
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) enables collaborative model training across large-scale distributed service nodes while preserving data privacy, making it a cornerstone of intelligent service systems in edge-cloud environments. However, in real-world service-oriented deployments, data generated by heterogeneous users, devices, and application scenarios are inherently non-IID. This severe data heterogeneity critically undermines the convergence stability, generalization ability, and ultimately the quality of service delivered by the global model. To address this challenge, we propose FLood, a novel FL framework inspired by out-of-distribution (OOD) detection. FLood dynamically counteracts the adverse effects of heterogeneity through a dual-weighting mechanism that jointly governs local training and global aggregation. At the client level, it adaptively reweights the supervised loss by upweighting pseudo-OOD samples, thereby encouraging more robust learning from distributionally misaligned or challenging data. At the server level, it refines model aggregation by weighting client contributions according to their OOD confidence scores, prioritizing updates from clients with higher in-distribution consistency and enhancing the global model's robustness and convergence stability. Extensive experiments across multiple benchmarks under diverse non-IID settings demonstrate that FLood consistently outperforms state-of-the-art FL methods in both accuracy and generalization. Furthermore, FLood functions as an orthogonal plug-in module: it seamlessly integrates with existing FL algorithms to boost their performance under heterogeneity without modifying their core optimization logic. These properties make FLood a practical and scalable solution for deploying reliable intelligent services in real-world federated environments.
Can Vision-Language Models Handle Long-Context Code? An Empirical Study on Visual Compression
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) struggle with long-context code due to window limitations. Existing textual code compression methods mitigate this via selective filtering but often disrupt dependency closure, causing semantic fragmentation. To address this, we introduce LongCodeOCR, a visual compression framework that renders code into compressed two-dimensional image sequences for Vision-Language Models (VLMs). By preserving a global view, this approach avoids the dependency breakage inherent in filtering. We systematically evaluate LongCodeOCR against the state-of-the-art LongCodeZip across four benchmarks spanning code summarization, code question answering, and code completion. Our results demonstrate that visual code compression serves as a viable alternative for tasks requiring global understanding. At comparable compression ratios ($\sim$1.7$\times$), LongCodeOCR improves CompScore on Long Module Summarization by 36.85 points over LongCodeZip. At a 1M-token context length with Glyph (a specialized 9B VLM), LongCodeOCR maintains higher accuracy than LongCodeZip while operating at about 4$\times$ higher compression. Moreover, compared with LongCodeZip, LongCodeOCR drastically reduces compression-stage overhead (reducing latency from $\sim$4.3 hours to $\sim$1 minute at 1M tokens). Finally, our results characterize a fundamental coverage--fidelity trade-off: visual code compression retains broader context coverage to support global dependencies, yet faces fidelity bottlenecks on exactness-critical tasks; by contrast, textual code compression preserves symbol-level precision while sacrificing structural coverage.
Role-Based Fault Tolerance System for LLM RL Post-Training
Dec 27, 2025Abstract:RL post-training for LLMs has been widely scaled to enhance reasoning and tool-using capabilities. However, RL post-training interleaves training and inference workloads, exposing the system to faults from both sides. Existing fault tolerance frameworks for LLMs target either training or inference, leaving the optimization potential in the asynchronous execution unexplored for RL. Our key insight is role-based fault isolation so the failure in one machine does not affect the others. We treat trainer, rollout, and other management roles in RL training as distinct distributed sub-tasks. Instead of restarting the entire RL task in ByteRobust, we recover only the failed role and reconnect it to living ones, thereby eliminating the full-restart overhead including rollout replay and initialization delay. We present RobustRL, the first comprehensive robust system to handle GPU machine errors for RL post-training Effective Training Time Ratio improvement. (1) \textit{Detect}. We implement role-aware monitoring to distinguish actual failures from role-specific behaviors to avoid the false positive and delayed detection. (2) \textit{Restart}. For trainers, we implement a non-disruptive recovery where rollouts persist state and continue trajectory generation, while the trainer is rapidly restored via rollout warm standbys. For rollout, we perform isolated machine replacement without interrupting the RL task. (3) \textit{Reconnect}. We replace static collective communication with dynamic, UCX-based (Unified Communication X) point-to-point communication, enabling immediate weight synchronization between recovered roles. In an RL training task on a 256-GPU cluster with Qwen3-8B-Math workload under 10\% failure injection frequency, RobustRL can achieve an ETTR of over 80\% compared with the 60\% in ByteRobust and achieves 8.4\%-17.4\% faster in end-to-end training time.
Video-QTR: Query-Driven Temporal Reasoning Framework for Lightweight Video Understanding
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:The rapid development of multimodal large-language models (MLLMs) has significantly expanded the scope of visual language reasoning, enabling unified systems to interpret and describe complex visual content. However, applying these models to long-video understanding remains computationally intensive. Dense frame encoding generates excessive visual tokens, leading to high memory consumption, redundant computation, and limited scalability in real-world applications. This inefficiency highlights a key limitation of the traditional process-then-reason paradigm, which analyzes visual streams exhaustively before semantic reasoning. To address this challenge, we introduce Video-QTR (Query-Driven Temporal Reasoning), a lightweight framework that redefines video comprehension as a query-guided reasoning process. Instead of encoding every frame, Video-QTR dynamically allocates perceptual resources based on the semantic intent of the query, creating an adaptive feedback loop between reasoning and perception. Extensive experiments across five benchmarks: MSVD-QA, Activity Net-QA, Movie Chat, and Video MME demonstrate that Video-QTR achieves state-of-the-art performance while reducing input frame consumption by up to 73%. These results confirm that query-driven temporal reasoning provides an efficient and scalable solution for video understanding.
Walking the Schrödinger Bridge: A Direct Trajectory for Text-to-3D Generation
Nov 06, 2025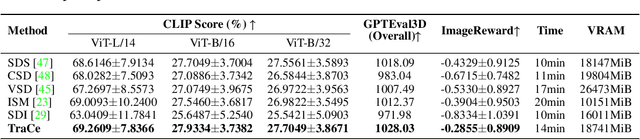
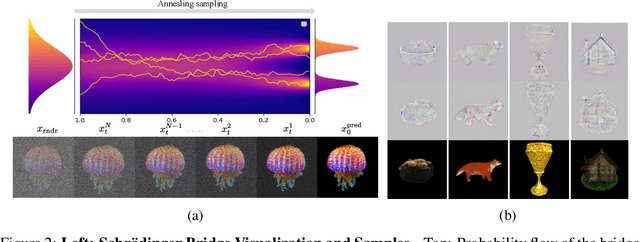

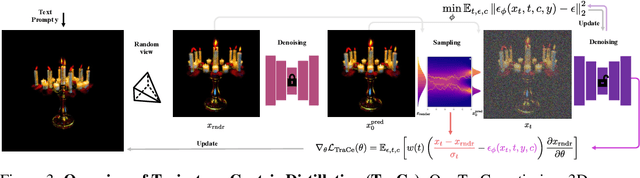
Abstract:Recent advancements in optimization-based text-to-3D generation heavily rely on distilling knowledge from pre-trained text-to-image diffusion models using techniques like Score Distillation Sampling (SDS), which often introduce artifacts such as over-saturation and over-smoothing into the generated 3D assets. In this paper, we address this essential problem by formulating the generation process as learning an optimal, direct transport trajectory between the distribution of the current rendering and the desired target distribution, thereby enabling high-quality generation with smaller Classifier-free Guidance (CFG) values. At first, we theoretically establish SDS as a simplified instance of the Schrödinger Bridge framework. We prove that SDS employs the reverse process of an Schrödinger Bridge, which, under specific conditions (e.g., a Gaussian noise as one end), collapses to SDS's score function of the pre-trained diffusion model. Based upon this, we introduce Trajectory-Centric Distillation (TraCe), a novel text-to-3D generation framework, which reformulates the mathematically trackable framework of Schrödinger Bridge to explicitly construct a diffusion bridge from the current rendering to its text-conditioned, denoised target, and trains a LoRA-adapted model on this trajectory's score dynamics for robust 3D optimization. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that TraCe consistently achieves superior quality and fidelity to state-of-the-art techniques.
LightRouter: Towards Efficient LLM Collaboration with Minimal Overhead
May 22, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of large language models has unlocked remarkable capabilities across a diverse array of natural language processing tasks. However, the considerable differences among available LLMs-in terms of cost, performance, and computational demands-pose significant challenges for users aiming to identify the most suitable model for specific tasks. In this work, we present LightRouter, a novel framework designed to systematically select and integrate a small subset of LLMs from a larger pool, with the objective of jointly optimizing both task performance and cost efficiency. LightRouter leverages an adaptive selection mechanism to identify models that require only a minimal number of boot tokens, thereby reducing costs, and further employs an effective integration strategy to combine their outputs. Extensive experiments across multiple benchmarks demonstrate that LightRouter matches or outperforms widely-used ensemble baselines, achieving up to a 25% improvement in accuracy. Compared with leading high-performing models, LightRouter achieves comparable performance while reducing inference costs by up to 27%. Importantly, our framework operates without any prior knowledge of individual models and relies exclusively on inexpensive, lightweight models. This work introduces a practical approach for efficient LLM selection and provides valuable insights into optimal strategies for model combination.
Scalable Multi-Stage Influence Function for Large Language Models via Eigenvalue-Corrected Kronecker-Factored Parameterization
May 08, 2025Abstract:Pre-trained large language models (LLMs) are commonly fine-tuned to adapt to downstream tasks. Since the majority of knowledge is acquired during pre-training, attributing the predictions of fine-tuned LLMs to their pre-training data may provide valuable insights. Influence functions have been proposed as a means to explain model predictions based on training data. However, existing approaches fail to compute ``multi-stage'' influence and lack scalability to billion-scale LLMs. In this paper, we propose the multi-stage influence function to attribute the downstream predictions of fine-tuned LLMs to pre-training data under the full-parameter fine-tuning paradigm. To enhance the efficiency and practicality of our multi-stage influence function, we leverage Eigenvalue-corrected Kronecker-Factored (EK-FAC) parameterization for efficient approximation. Empirical results validate the superior scalability of EK-FAC approximation and the effectiveness of our multi-stage influence function. Additionally, case studies on a real-world LLM, dolly-v2-3b, demonstrate its interpretive power, with exemplars illustrating insights provided by multi-stage influence estimates. Our code is public at https://github.com/colored-dye/multi_stage_influence_function.
Lossless Privacy-Preserving Aggregation for Decentralized Federated Learning
Jan 08, 2025



Abstract:Privacy concerns arise as sensitive data proliferate. Despite decentralized federated learning (DFL) aggregating gradients from neighbors to avoid direct data transmission, it still poses indirect data leaks from the transmitted gradients. Existing privacy-preserving methods for DFL add noise to gradients. They either diminish the model predictive accuracy or suffer from ineffective gradient protection. In this paper, we propose a novel lossless privacy-preserving aggregation rule named LPPA to enhance gradient protection as much as possible but without loss of DFL model predictive accuracy. LPPA subtly injects the noise difference between the sent and received noise into transmitted gradients for gradient protection. The noise difference incorporates neighbors' randomness for each client, effectively safeguarding against data leaks. LPPA employs the noise flow conservation theory to ensure that the noise impact can be globally eliminated. The global sum of all noise differences remains zero, ensuring that accurate gradient aggregation is unaffected and the model accuracy remains intact. We theoretically prove that the privacy-preserving capacity of LPPA is \sqrt{2} times greater than that of noise addition, while maintaining comparable model accuracy to the standard DFL aggregation without noise injection. Experimental results verify the theoretical findings and show that LPPA achieves a 13% mean improvement in accuracy over noise addition. We also demonstrate the effectiveness of LPPA in protecting raw data and guaranteeing lossless model accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge