Jianwei Yin
Faithful Bi-Directional Model Steering via Distribution Matching and Distributed Interchange Interventions
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Intervention-based model steering offers a lightweight and interpretable alternative to prompting and fine-tuning. However, by adapting strong optimization objectives from fine-tuning, current methods are susceptible to overfitting and often underperform, sometimes generating unnatural outputs. We hypothesize that this is because effective steering requires the faithful identification of internal model mechanisms, not the enforcement of external preferences. To this end, we build on the principles of distributed alignment search (DAS), the standard for causal variable localization, to propose a new steering method: Concept DAS (CDAS). While we adopt the core mechanism of DAS, distributed interchange intervention (DII), we introduce a novel distribution matching objective tailored for the steering task by aligning intervened output distributions with counterfactual distributions. CDAS differs from prior work in two main ways: first, it learns interventions via weak-supervised distribution matching rather than probability maximization; second, it uses DIIs that naturally enable bi-directional steering and allow steering factors to be derived from data, reducing the effort required for hyperparameter tuning and resulting in more faithful and stable control. On AxBench, a large-scale model steering benchmark, we show that CDAS does not always outperform preference-optimization methods but may benefit more from increased model scale. In two safety-related case studies, overriding refusal behaviors of safety-aligned models and neutralizing a chain-of-thought backdoor, CDAS achieves systematic steering while maintaining general model utility. These results indicate that CDAS is complementary to preference-optimization approaches and conditionally constitutes a robust approach to intervention-based model steering. Our code is available at https://github.com/colored-dye/concept_das.
Can Vision-Language Models Handle Long-Context Code? An Empirical Study on Visual Compression
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) struggle with long-context code due to window limitations. Existing textual code compression methods mitigate this via selective filtering but often disrupt dependency closure, causing semantic fragmentation. To address this, we introduce LongCodeOCR, a visual compression framework that renders code into compressed two-dimensional image sequences for Vision-Language Models (VLMs). By preserving a global view, this approach avoids the dependency breakage inherent in filtering. We systematically evaluate LongCodeOCR against the state-of-the-art LongCodeZip across four benchmarks spanning code summarization, code question answering, and code completion. Our results demonstrate that visual code compression serves as a viable alternative for tasks requiring global understanding. At comparable compression ratios ($\sim$1.7$\times$), LongCodeOCR improves CompScore on Long Module Summarization by 36.85 points over LongCodeZip. At a 1M-token context length with Glyph (a specialized 9B VLM), LongCodeOCR maintains higher accuracy than LongCodeZip while operating at about 4$\times$ higher compression. Moreover, compared with LongCodeZip, LongCodeOCR drastically reduces compression-stage overhead (reducing latency from $\sim$4.3 hours to $\sim$1 minute at 1M tokens). Finally, our results characterize a fundamental coverage--fidelity trade-off: visual code compression retains broader context coverage to support global dependencies, yet faces fidelity bottlenecks on exactness-critical tasks; by contrast, textual code compression preserves symbol-level precision while sacrificing structural coverage.
Dep-Search: Learning Dependency-Aware Reasoning Traces with Persistent Memory
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in complex reasoning tasks, particularly when augmented with search mechanisms that enable systematic exploration of external knowledge bases. The field has evolved from traditional retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) frameworks to more sophisticated search-based frameworks that orchestrate multi-step reasoning through explicit search strategies. However, existing search frameworks still rely heavily on implicit natural language reasoning to determine search strategies and how to leverage retrieved information across reasoning steps. This reliance on implicit reasoning creates fundamental challenges for managing dependencies between sub-questions, efficiently reusing previously retrieved knowledge, and learning optimal search strategies through reinforcement learning. To address these limitations, we propose Dep-Search, a dependency-aware search framework that advances beyond existing search frameworks by integrating structured reasoning, retrieval, and persistent memory through GRPO. Dep-Search introduces explicit control mechanisms that enable the model to decompose questions with dependency relationships, retrieve information when needed, access previously stored knowledge from memory, and summarize long reasoning contexts into reusable memory entries. Through extensive experiments on seven diverse question answering datasets, we demonstrate that Dep-Search significantly enhances LLMs' ability to tackle complex multi-hop reasoning tasks, achieving substantial improvements over strong baselines across different model scales.
Adaptive Fidelity Estimation for Quantum Programs with Graph-Guided Noise Awareness
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Fidelity estimation is a critical yet resource-intensive step in testing quantum programs on noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) devices, where the required number of measurements is difficult to predefine due to hardware noise, device heterogeneity, and transpilation-induced circuit transformations. We present QuFid, an adaptive and noise-aware framework that determines measurement budgets online by leveraging circuit structure and runtime statistical feedback. QuFid models a quantum program as a directed acyclic graph (DAG) and employs a control-flow-aware random walk to characterize noise propagation along gate dependencies. Backend-specific effects are captured via transpilation-induced structural deformation metrics, which are integrated into the random-walk formulation to induce a noise-propagation operator. Circuit complexity is then quantified through the spectral characteristics of this operator, providing a principled and lightweight basis for adaptive measurement planning. Experiments on 18 quantum benchmarks executed on IBM Quantum backends show that QuFid significantly reduces measurement cost compared to fixed-shot and learning-based baselines, while consistently maintaining acceptable fidelity bias.
Ground What You See: Hallucination-Resistant MLLMs via Caption Feedback, Diversity-Aware Sampling, and Conflict Regularization
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:While Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have achieved remarkable success across diverse tasks, their practical deployment is severely hindered by hallucination issues, which become particularly acute during Reinforcement Learning (RL) optimization. This paper systematically analyzes the root causes of hallucinations in MLLMs under RL training, identifying three critical factors: (1) an over-reliance on chained visual reasoning, where inaccurate initial descriptions or redundant information anchor subsequent inferences to incorrect premises; (2) insufficient exploration diversity during policy optimization, leading the model to generate overly confident but erroneous outputs; and (3) destructive conflicts between training samples, where Neural Tangent Kernel (NTK) similarity causes false associations and unstable parameter updates. To address these challenges, we propose a comprehensive framework comprising three core modules. First, we enhance visual localization by introducing dedicated planning and captioning stages before the reasoning phase, employing a quality-based caption reward to ensure accurate initial anchoring. Second, to improve exploration, we categorize samples based on the mean and variance of their reward distributions, prioritizing samples with high variance to focus the model on diverse and informative data. Finally, to mitigate sample interference, we regulate NTK similarity by grouping sample pairs and applying an InfoNCE loss to push overly similar pairs apart and pull dissimilar ones closer, thereby guiding gradient interactions toward a balanced range. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method significantly reduces hallucination rates and effectively enhances the inference accuracy of MLLMs.
ToolGate: Contract-Grounded and Verified Tool Execution for LLMs
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) augmented with external tools have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in complex reasoning tasks. However, existing frameworks rely heavily on natural language reasoning to determine when tools can be invoked and whether their results should be committed, lacking formal guarantees for logical safety and verifiability. We present \textbf{ToolGate}, a forward execution framework that provides logical safety guarantees and verifiable state evolution for LLM tool calling. ToolGate maintains an explicit symbolic state space as a typed key-value mapping representing trusted world information throughout the reasoning process. Each tool is formalized as a Hoare-style contract consisting of a precondition and a postcondition, where the precondition gates tool invocation by checking whether the current state satisfies the required conditions, and the postcondition determines whether the tool's result can be committed to update the state through runtime verification. Our approach guarantees that the symbolic state evolves only through verified tool executions, preventing invalid or hallucinated results from corrupting the world representation. Experimental validation demonstrates that ToolGate significantly improves the reliability and verifiability of tool-augmented LLM systems while maintaining competitive performance on complex multi-step reasoning tasks. This work establishes a foundation for building more trustworthy and debuggable AI systems that integrate language models with external tools.
IBISAgent: Reinforcing Pixel-Level Visual Reasoning in MLLMs for Universal Biomedical Object Referring and Segmentation
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Recent research on medical MLLMs has gradually shifted its focus from image-level understanding to fine-grained, pixel-level comprehension. Although segmentation serves as the foundation for pixel-level understanding, existing approaches face two major challenges. First, they introduce implicit segmentation tokens and require simultaneous fine-tuning of both the MLLM and external pixel decoders, which increases the risk of catastrophic forgetting and limits generalization to out-of-domain scenarios. Second, most methods rely on single-pass reasoning and lack the capability to iteratively refine segmentation results, leading to suboptimal performance. To overcome these limitations, we propose a novel agentic MLLM, named IBISAgent, that reformulates segmentation as a vision-centric, multi-step decision-making process. IBISAgent enables MLLMs to generate interleaved reasoning and text-based click actions, invoke segmentation tools, and produce high-quality masks without architectural modifications. By iteratively performing multi-step visual reasoning on masked image features, IBISAgent naturally supports mask refinement and promotes the development of pixel-level visual reasoning capabilities. We further design a two-stage training framework consisting of cold-start supervised fine-tuning and agentic reinforcement learning with tailored, fine-grained rewards, enhancing the model's robustness in complex medical referring and reasoning segmentation tasks. Extensive experiments demonstrate that IBISAgent consistently outperforms both closed-source and open-source SOTA methods. All datasets, code, and trained models will be released publicly.
Role-Based Fault Tolerance System for LLM RL Post-Training
Dec 27, 2025Abstract:RL post-training for LLMs has been widely scaled to enhance reasoning and tool-using capabilities. However, RL post-training interleaves training and inference workloads, exposing the system to faults from both sides. Existing fault tolerance frameworks for LLMs target either training or inference, leaving the optimization potential in the asynchronous execution unexplored for RL. Our key insight is role-based fault isolation so the failure in one machine does not affect the others. We treat trainer, rollout, and other management roles in RL training as distinct distributed sub-tasks. Instead of restarting the entire RL task in ByteRobust, we recover only the failed role and reconnect it to living ones, thereby eliminating the full-restart overhead including rollout replay and initialization delay. We present RobustRL, the first comprehensive robust system to handle GPU machine errors for RL post-training Effective Training Time Ratio improvement. (1) \textit{Detect}. We implement role-aware monitoring to distinguish actual failures from role-specific behaviors to avoid the false positive and delayed detection. (2) \textit{Restart}. For trainers, we implement a non-disruptive recovery where rollouts persist state and continue trajectory generation, while the trainer is rapidly restored via rollout warm standbys. For rollout, we perform isolated machine replacement without interrupting the RL task. (3) \textit{Reconnect}. We replace static collective communication with dynamic, UCX-based (Unified Communication X) point-to-point communication, enabling immediate weight synchronization between recovered roles. In an RL training task on a 256-GPU cluster with Qwen3-8B-Math workload under 10\% failure injection frequency, RobustRL can achieve an ETTR of over 80\% compared with the 60\% in ByteRobust and achieves 8.4\%-17.4\% faster in end-to-end training time.
Video-QTR: Query-Driven Temporal Reasoning Framework for Lightweight Video Understanding
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:The rapid development of multimodal large-language models (MLLMs) has significantly expanded the scope of visual language reasoning, enabling unified systems to interpret and describe complex visual content. However, applying these models to long-video understanding remains computationally intensive. Dense frame encoding generates excessive visual tokens, leading to high memory consumption, redundant computation, and limited scalability in real-world applications. This inefficiency highlights a key limitation of the traditional process-then-reason paradigm, which analyzes visual streams exhaustively before semantic reasoning. To address this challenge, we introduce Video-QTR (Query-Driven Temporal Reasoning), a lightweight framework that redefines video comprehension as a query-guided reasoning process. Instead of encoding every frame, Video-QTR dynamically allocates perceptual resources based on the semantic intent of the query, creating an adaptive feedback loop between reasoning and perception. Extensive experiments across five benchmarks: MSVD-QA, Activity Net-QA, Movie Chat, and Video MME demonstrate that Video-QTR achieves state-of-the-art performance while reducing input frame consumption by up to 73%. These results confirm that query-driven temporal reasoning provides an efficient and scalable solution for video understanding.
Walking the Schrödinger Bridge: A Direct Trajectory for Text-to-3D Generation
Nov 06, 2025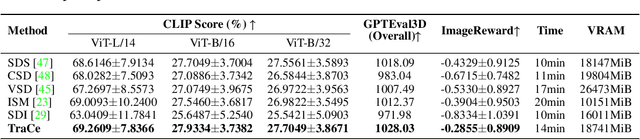
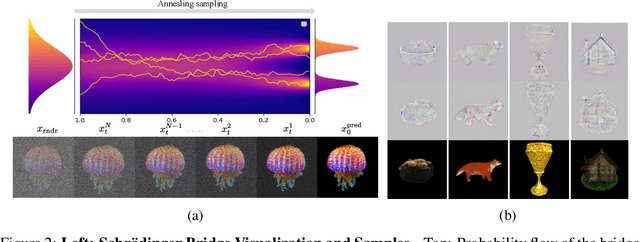

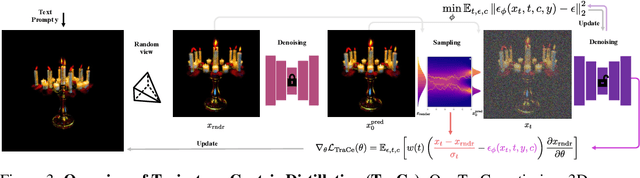
Abstract:Recent advancements in optimization-based text-to-3D generation heavily rely on distilling knowledge from pre-trained text-to-image diffusion models using techniques like Score Distillation Sampling (SDS), which often introduce artifacts such as over-saturation and over-smoothing into the generated 3D assets. In this paper, we address this essential problem by formulating the generation process as learning an optimal, direct transport trajectory between the distribution of the current rendering and the desired target distribution, thereby enabling high-quality generation with smaller Classifier-free Guidance (CFG) values. At first, we theoretically establish SDS as a simplified instance of the Schrödinger Bridge framework. We prove that SDS employs the reverse process of an Schrödinger Bridge, which, under specific conditions (e.g., a Gaussian noise as one end), collapses to SDS's score function of the pre-trained diffusion model. Based upon this, we introduce Trajectory-Centric Distillation (TraCe), a novel text-to-3D generation framework, which reformulates the mathematically trackable framework of Schrödinger Bridge to explicitly construct a diffusion bridge from the current rendering to its text-conditioned, denoised target, and trains a LoRA-adapted model on this trajectory's score dynamics for robust 3D optimization. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that TraCe consistently achieves superior quality and fidelity to state-of-the-art techniques.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge