Haozhan Shen
Geo-R1: Improving Few-Shot Geospatial Referring Expression Understanding with Reinforcement Fine-Tuning
Sep 26, 2025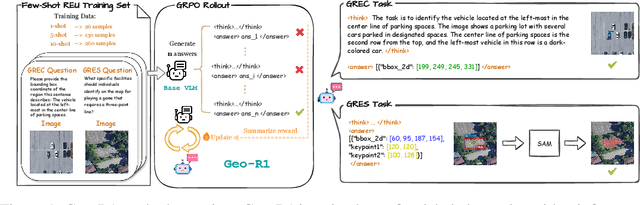


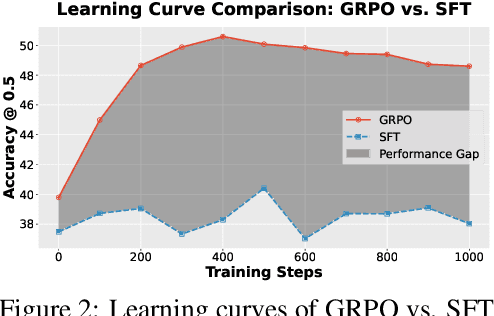
Abstract:Referring expression understanding in remote sensing poses unique challenges, as it requires reasoning over complex object-context relationships. While supervised fine-tuning (SFT) on multimodal large language models achieves strong performance with massive labeled datasets, they struggle in data-scarce scenarios, leading to poor generalization. To address this limitation, we propose Geo-R1, a reasoning-centric reinforcement fine-tuning (RFT) paradigm for few-shot geospatial referring. Geo-R1 enforces the model to first generate explicit, interpretable reasoning chains that decompose referring expressions, and then leverage these rationales to localize target objects. This "reason first, then act" process enables the model to make more effective use of limited annotations, enhances generalization, and provides interpretability. We validate Geo-R1 on three carefully designed few-shot geospatial referring benchmarks, where our model consistently and substantially outperforms SFT baselines. It also demonstrates strong cross-dataset generalization, highlighting its robustness. Code and data will be released at http://geo-r1.github.io.
Unifying Language Agent Algorithms with Graph-based Orchestration Engine for Reproducible Agent Research
May 30, 2025


Abstract:Language agents powered by large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in understanding, reasoning, and executing complex tasks. However, developing robust agents presents significant challenges: substantial engineering overhead, lack of standardized components, and insufficient evaluation frameworks for fair comparison. We introduce Agent Graph-based Orchestration for Reasoning and Assessment (AGORA), a flexible and extensible framework that addresses these challenges through three key contributions: (1) a modular architecture with a graph-based workflow engine, efficient memory management, and clean component abstraction; (2) a comprehensive suite of reusable agent algorithms implementing state-of-the-art reasoning approaches; and (3) a rigorous evaluation framework enabling systematic comparison across multiple dimensions. Through extensive experiments on mathematical reasoning and multimodal tasks, we evaluate various agent algorithms across different LLMs, revealing important insights about their relative strengths and applicability. Our results demonstrate that while sophisticated reasoning approaches can enhance agent capabilities, simpler methods like Chain-of-Thought often exhibit robust performance with significantly lower computational overhead. AGORA not only simplifies language agent development but also establishes a foundation for reproducible agent research through standardized evaluation protocols.
VLM-R1: A Stable and Generalizable R1-style Large Vision-Language Model
Apr 10, 2025
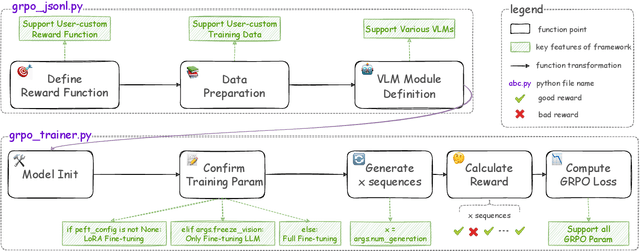
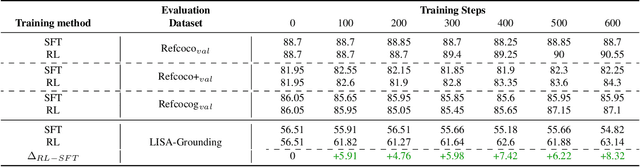
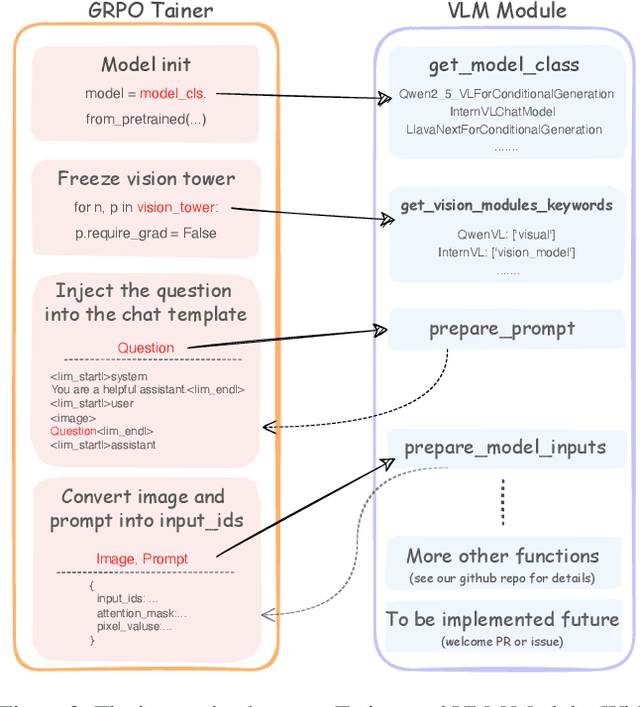
Abstract:Recently DeepSeek R1 has shown that reinforcement learning (RL) can substantially improve the reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) through a simple yet effective design. The core of R1 lies in its rule-based reward formulation, which leverages tasks with deterministic ground-truth answers to enable precise and stable reward computation. In the visual domain, we similarly observe that a wide range of visual understanding tasks are inherently equipped with well-defined ground-truth annotations. This property makes them naturally compatible with rule-based reward mechanisms. Motivated by this observation, we investigate the extension of R1-style reinforcement learning to Vision-Language Models (VLMs), aiming to enhance their visual reasoning capabilities. To this end, we develop VLM-R1, a dedicated framework designed to harness RL for improving VLMs' performance on general vision-language tasks. Using this framework, we further explore the feasibility of applying RL to visual domain. Experimental results indicate that the RL-based model not only delivers competitive performance on visual understanding tasks but also surpasses Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) in generalization ability. Furthermore, we conduct comprehensive ablation studies that uncover a series of noteworthy insights, including the presence of reward hacking in object detection, the emergence of the "OD aha moment", the impact of training data quality, and the scaling behavior of RL across different model sizes. Through these analyses, we aim to deepen the understanding of how reinforcement learning enhances the capabilities of vision-language models, and we hope our findings and open-source contributions will support continued progress in the vision-language RL community. Our code and model are available at https://github.com/om-ai-lab/VLM-R1
GeoRSMLLM: A Multimodal Large Language Model for Vision-Language Tasks in Geoscience and Remote Sensing
Mar 16, 2025Abstract:The application of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) in remote sensing (RS) has demonstrated significant potential in traditional tasks such as scene classification, object detection, and image captioning. However, current models, which excel in Referring Expression Comprehension (REC), struggle with tasks involving complex instructions (e.g., exists multiple conditions) or pixel-level operations like segmentation and change detection. In this white paper, we provide a comprehensive hierarchical summary of vision-language tasks in RS, categorized by the varying levels of cognitive capability required. We introduce the Remote Sensing Vision-Language Task Set (RSVLTS), which includes Open-Vocabulary Tasks (OVT), Referring Expression Tasks (RET), and Described Object Tasks (DOT) with increased difficulty, and Visual Question Answering (VQA) aloneside. Moreover, we propose a novel unified data representation using a set-of-points approach for RSVLTS, along with a condition parser and a self-augmentation strategy based on cyclic referring. These features are integrated into the GeoRSMLLM model, and this enhanced model is designed to handle a broad range of tasks of RSVLTS, paving the way for a more generalized solution for vision-language tasks in geoscience and remote sensing.
GUI Testing Arena: A Unified Benchmark for Advancing Autonomous GUI Testing Agent
Dec 24, 2024



Abstract:Nowadays, research on GUI agents is a hot topic in the AI community. However, current research focuses on GUI task automation, limiting the scope of applications in various GUI scenarios. In this paper, we propose a formalized and comprehensive environment to evaluate the entire process of automated GUI Testing (GTArena), offering a fair, standardized environment for consistent operation of diverse multimodal large language models. We divide the testing process into three key subtasks: test intention generation, test task execution, and GUI defect detection, and construct a benchmark dataset based on these to conduct a comprehensive evaluation. It evaluates the performance of different models using three data types: real mobile applications, mobile applications with artificially injected defects, and synthetic data, thoroughly assessing their capabilities in this relevant task. Additionally, we propose a method that helps researchers explore the correlation between the performance of multimodal language large models in specific scenarios and their general capabilities in standard benchmark tests. Experimental results indicate that even the most advanced models struggle to perform well across all sub-tasks of automated GUI Testing, highlighting a significant gap between the current capabilities of Autonomous GUI Testing and its practical, real-world applicability. This gap provides guidance for the future direction of GUI Agent development. Our code is available at https://github.com/ZJU-ACES-ISE/ChatUITest.
ZoomEye: Enhancing Multimodal LLMs with Human-Like Zooming Capabilities through Tree-Based Image Exploration
Nov 25, 2024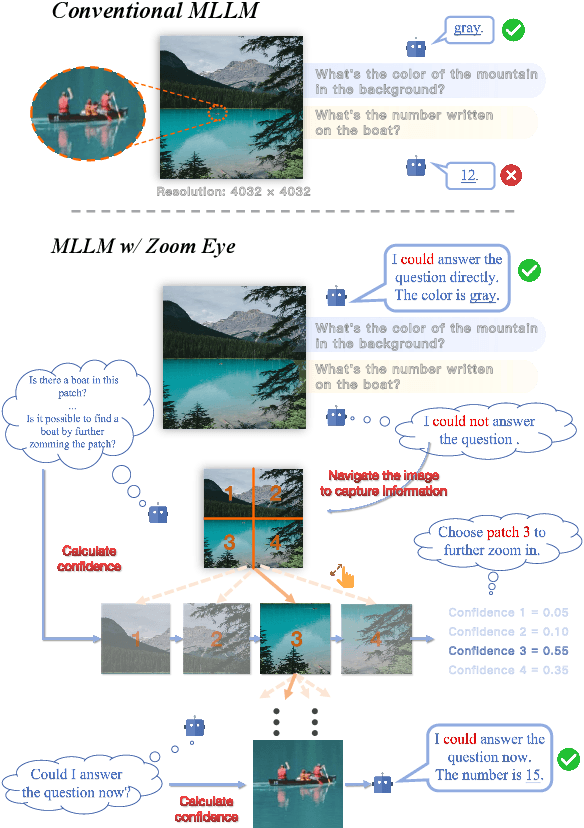
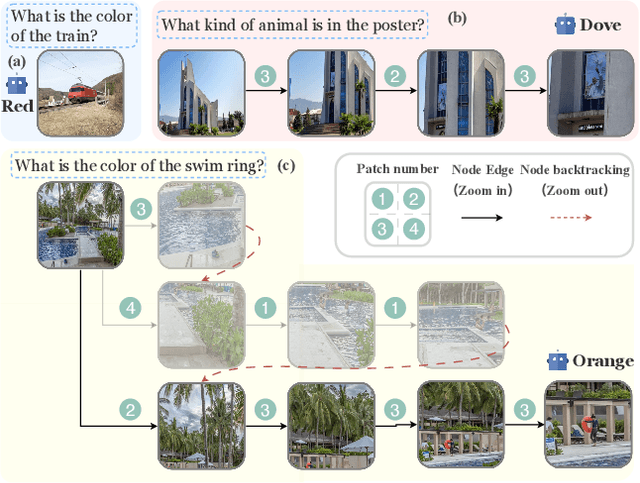
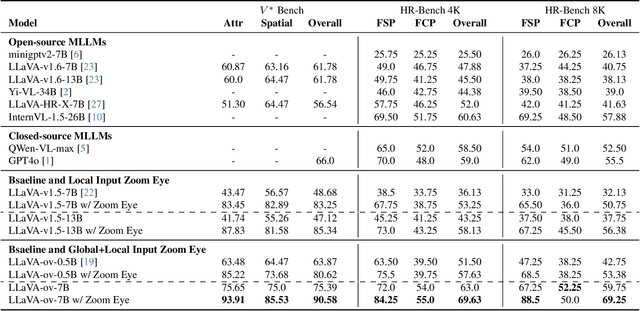
Abstract:An image, especially with high-resolution, typically consists of numerous visual elements, ranging from dominant large objects to fine-grained detailed objects. When perceiving such images, multimodal large language models~(MLLMs) face limitations due to the restricted input resolution of the pretrained vision encoder and the cluttered, dense context of the image, resulting in a focus on primary objects while easily overlooking detailed ones. In this paper, we propose Zoom Eye, a tree search algorithm designed to navigate the hierarchical and visual nature of images to capture relevant information. Zoom Eye conceptualizes an image as a tree, with each children node representing a zoomed sub-patch of the parent node and the root represents the overall image. Moreover, Zoom Eye is model-agnostic and training-free, so it enables any MLLMs to simulate human zooming actions by searching along the image tree from root to leaf nodes, seeking out pertinent information, and accurately responding to related queries. We experiment on a series of elaborate high-resolution benchmarks and the results demonstrate that Zoom Eye not only consistently improves the performance of a series base MLLMs with large margin~(e.g., LLaVA-v1.5-7B increases by 34.57\% on $V^*$ Bench and 17.88\% on HR-Bench), but also enables small 7B MLLMs to outperform strong large models such as GPT-4o. Our code is available at \href{https://github.com/om-ai-lab/ZoomEye}{https://github.com/om-ai-lab/ZoomEye}.
Enhancing Ultra High Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery Analysis with ImageRAG
Nov 12, 2024


Abstract:Ultra High Resolution (UHR) remote sensing imagery (RSI) (e.g. 100,000 $\times$ 100,000 pixels or more) poses a significant challenge for current Remote Sensing Multimodal Large Language Models (RSMLLMs). If choose to resize the UHR image to standard input image size, the extensive spatial and contextual information that UHR images contain will be neglected. Otherwise, the original size of these images often exceeds the token limits of standard RSMLLMs, making it difficult to process the entire image and capture long-range dependencies to answer the query based on the abundant visual context. In this paper, we introduce ImageRAG for RS, a training-free framework to address the complexities of analyzing UHR remote sensing imagery. By transforming UHR remote sensing image analysis task to image's long context selection task, we design an innovative image contextual retrieval mechanism based on the Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) technique, denoted as ImageRAG. ImageRAG's core innovation lies in its ability to selectively retrieve and focus on the most relevant portions of the UHR image as visual contexts that pertain to a given query. Fast path and slow path are proposed in this framework to handle this task efficiently and effectively. ImageRAG allows RSMLLMs to manage extensive context and spatial information from UHR RSI, ensuring the analysis is both accurate and efficient.
GroundVLP: Harnessing Zero-shot Visual Grounding from Vision-Language Pre-training and Open-Vocabulary Object Detection
Dec 22, 2023



Abstract:Visual grounding, a crucial vision-language task involving the understanding of the visual context based on the query expression, necessitates the model to capture the interactions between objects, as well as various spatial and attribute information. However, the annotation data of visual grounding task is limited due to its time-consuming and labor-intensive annotation process, resulting in the trained models being constrained from generalizing its capability to a broader domain. To address this challenge, we propose GroundVLP, a simple yet effective zero-shot method that harnesses visual grounding ability from the existing models trained from image-text pairs and pure object detection data, both of which are more conveniently obtainable and offer a broader domain compared to visual grounding annotation data. GroundVLP proposes a fusion mechanism that combines the heatmap from GradCAM and the object proposals of open-vocabulary detectors. We demonstrate that the proposed method significantly outperforms other zero-shot methods on RefCOCO/+/g datasets, surpassing prior zero-shot state-of-the-art by approximately 28\% on the test split of RefCOCO and RefCOCO+. Furthermore, GroundVLP performs comparably to or even better than some non-VLP-based supervised models on the Flickr30k entities dataset. Our code is available at https://github.com/om-ai-lab/GroundVLP.
VL-CheckList: Evaluating Pre-trained Vision-Language Models with Objects, Attributes and Relations
Jul 01, 2022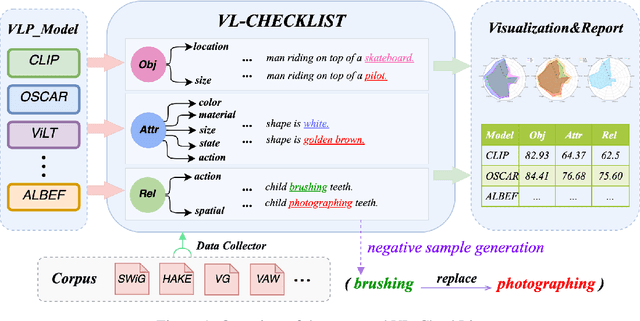
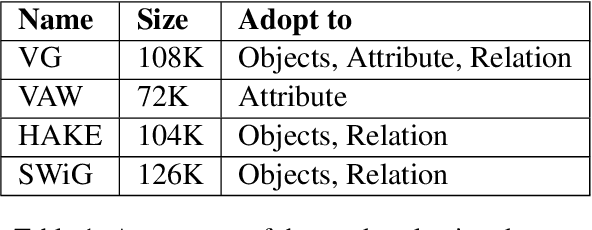
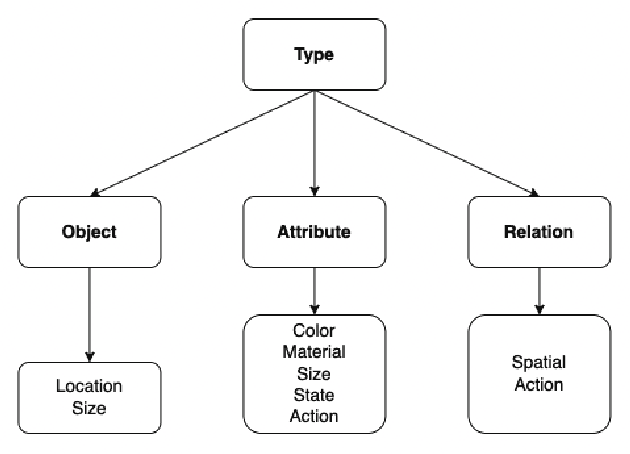
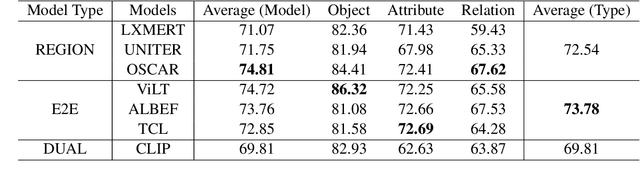
Abstract:Vision-Language Pretraining (VLP) models have recently successfully facilitated many cross-modal downstream tasks. Most existing works evaluated their systems by comparing the fine-tuned downstream task performance. However, only average downstream task accuracy provides little information about the pros and cons of each VLP method, let alone provides insights on how the community can improve the systems in the future. Inspired by the CheckList for testing natural language processing, we introduce VL-CheckList, a novel framework to understand the capabilities of VLP models. The proposed method divides the image-texting ability of a VLP model into three categories: objects, attributes, and relations, and uses a novel taxonomy to further break down these three aspects. We conduct comprehensive studies to analyze seven recently popular VLP models via the proposed framework. Results confirm the effectiveness of the proposed method by revealing fine-grained differences among the compared models that were not visible from downstream task-only evaluation. Further results show promising research direction in building better VLP models. Data and Code: https://github.com/om-ai-lab/VL-CheckList
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge