Yuxiang Cai
Faithful Bi-Directional Model Steering via Distribution Matching and Distributed Interchange Interventions
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Intervention-based model steering offers a lightweight and interpretable alternative to prompting and fine-tuning. However, by adapting strong optimization objectives from fine-tuning, current methods are susceptible to overfitting and often underperform, sometimes generating unnatural outputs. We hypothesize that this is because effective steering requires the faithful identification of internal model mechanisms, not the enforcement of external preferences. To this end, we build on the principles of distributed alignment search (DAS), the standard for causal variable localization, to propose a new steering method: Concept DAS (CDAS). While we adopt the core mechanism of DAS, distributed interchange intervention (DII), we introduce a novel distribution matching objective tailored for the steering task by aligning intervened output distributions with counterfactual distributions. CDAS differs from prior work in two main ways: first, it learns interventions via weak-supervised distribution matching rather than probability maximization; second, it uses DIIs that naturally enable bi-directional steering and allow steering factors to be derived from data, reducing the effort required for hyperparameter tuning and resulting in more faithful and stable control. On AxBench, a large-scale model steering benchmark, we show that CDAS does not always outperform preference-optimization methods but may benefit more from increased model scale. In two safety-related case studies, overriding refusal behaviors of safety-aligned models and neutralizing a chain-of-thought backdoor, CDAS achieves systematic steering while maintaining general model utility. These results indicate that CDAS is complementary to preference-optimization approaches and conditionally constitutes a robust approach to intervention-based model steering. Our code is available at https://github.com/colored-dye/concept_das.
IBISAgent: Reinforcing Pixel-Level Visual Reasoning in MLLMs for Universal Biomedical Object Referring and Segmentation
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Recent research on medical MLLMs has gradually shifted its focus from image-level understanding to fine-grained, pixel-level comprehension. Although segmentation serves as the foundation for pixel-level understanding, existing approaches face two major challenges. First, they introduce implicit segmentation tokens and require simultaneous fine-tuning of both the MLLM and external pixel decoders, which increases the risk of catastrophic forgetting and limits generalization to out-of-domain scenarios. Second, most methods rely on single-pass reasoning and lack the capability to iteratively refine segmentation results, leading to suboptimal performance. To overcome these limitations, we propose a novel agentic MLLM, named IBISAgent, that reformulates segmentation as a vision-centric, multi-step decision-making process. IBISAgent enables MLLMs to generate interleaved reasoning and text-based click actions, invoke segmentation tools, and produce high-quality masks without architectural modifications. By iteratively performing multi-step visual reasoning on masked image features, IBISAgent naturally supports mask refinement and promotes the development of pixel-level visual reasoning capabilities. We further design a two-stage training framework consisting of cold-start supervised fine-tuning and agentic reinforcement learning with tailored, fine-grained rewards, enhancing the model's robustness in complex medical referring and reasoning segmentation tasks. Extensive experiments demonstrate that IBISAgent consistently outperforms both closed-source and open-source SOTA methods. All datasets, code, and trained models will be released publicly.
Fine-Grained Zero-Shot Learning with Attribute-Centric Representations
Dec 13, 2025Abstract:Recognizing unseen fine-grained categories demands a model that can distinguish subtle visual differences. This is typically achieved by transferring visual-attribute relationships from seen classes to unseen classes. The core challenge is attribute entanglement, where conventional models collapse distinct attributes like color, shape, and texture into a single visual embedding. This causes interference that masks these critical distinctions. The post-hoc solutions of previous work are insufficient, as they operate on representations that are already mixed. We propose a zero-shot learning framework that learns AttributeCentric Representations (ACR) to tackle this problem by imposing attribute disentanglement during representation learning. ACR is achieved with two mixture-of-experts components, including Mixture of Patch Experts (MoPE) and Mixture of Attribute Experts (MoAE). First, MoPE is inserted into the transformer using a dual-level routing mechanism to conditionally dispatch image patches to specialized experts. This ensures coherent attribute families are processed by dedicated experts. Finally, the MoAE head projects these expert-refined features into sparse, partaware attribute maps for robust zero-shot classification. On zero-shot learning benchmark datasets CUB, AwA2, and SUN, our ACR achieves consistent state-of-the-art results.
Geo-R1: Improving Few-Shot Geospatial Referring Expression Understanding with Reinforcement Fine-Tuning
Sep 26, 2025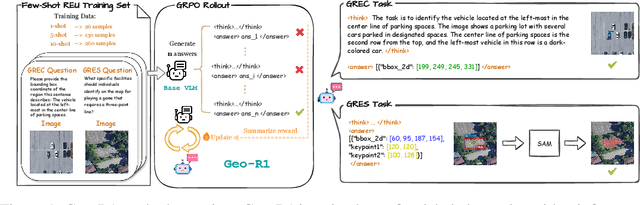


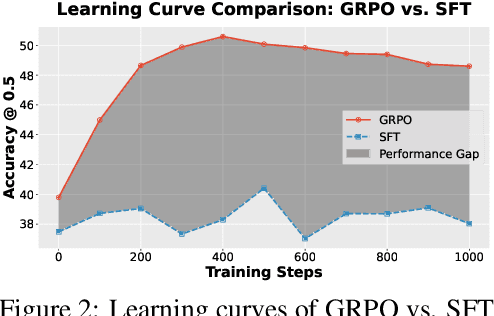
Abstract:Referring expression understanding in remote sensing poses unique challenges, as it requires reasoning over complex object-context relationships. While supervised fine-tuning (SFT) on multimodal large language models achieves strong performance with massive labeled datasets, they struggle in data-scarce scenarios, leading to poor generalization. To address this limitation, we propose Geo-R1, a reasoning-centric reinforcement fine-tuning (RFT) paradigm for few-shot geospatial referring. Geo-R1 enforces the model to first generate explicit, interpretable reasoning chains that decompose referring expressions, and then leverage these rationales to localize target objects. This "reason first, then act" process enables the model to make more effective use of limited annotations, enhances generalization, and provides interpretability. We validate Geo-R1 on three carefully designed few-shot geospatial referring benchmarks, where our model consistently and substantially outperforms SFT baselines. It also demonstrates strong cross-dataset generalization, highlighting its robustness. Code and data will be released at http://geo-r1.github.io.
TK-Mamba: Marrying KAN with Mamba for Text-Driven 3D Medical Image Segmentation
May 24, 2025



Abstract:3D medical image segmentation is vital for clinical diagnosis and treatment but is challenged by high-dimensional data and complex spatial dependencies. Traditional single-modality networks, such as CNNs and Transformers, are often limited by computational inefficiency and constrained contextual modeling in 3D settings. We introduce a novel multimodal framework that leverages Mamba and Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KAN) as an efficient backbone for long-sequence modeling. Our approach features three key innovations: First, an EGSC (Enhanced Gated Spatial Convolution) module captures spatial information when unfolding 3D images into 1D sequences. Second, we extend Group-Rational KAN (GR-KAN), a Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks variant with rational basis functions, into 3D-Group-Rational KAN (3D-GR-KAN) for 3D medical imaging - its first application in this domain - enabling superior feature representation tailored to volumetric data. Third, a dual-branch text-driven strategy leverages CLIP's text embeddings: one branch swaps one-hot labels for semantic vectors to preserve inter-organ semantic relationships, while the other aligns images with detailed organ descriptions to enhance semantic alignment. Experiments on the Medical Segmentation Decathlon (MSD) and KiTS23 datasets show our method achieving state-of-the-art performance, surpassing existing approaches in accuracy and efficiency. This work highlights the power of combining advanced sequence modeling, extended network architectures, and vision-language synergy to push forward 3D medical image segmentation, delivering a scalable solution for clinical use. The source code is openly available at https://github.com/yhy-whu/TK-Mamba.
GeoRSMLLM: A Multimodal Large Language Model for Vision-Language Tasks in Geoscience and Remote Sensing
Mar 16, 2025Abstract:The application of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) in remote sensing (RS) has demonstrated significant potential in traditional tasks such as scene classification, object detection, and image captioning. However, current models, which excel in Referring Expression Comprehension (REC), struggle with tasks involving complex instructions (e.g., exists multiple conditions) or pixel-level operations like segmentation and change detection. In this white paper, we provide a comprehensive hierarchical summary of vision-language tasks in RS, categorized by the varying levels of cognitive capability required. We introduce the Remote Sensing Vision-Language Task Set (RSVLTS), which includes Open-Vocabulary Tasks (OVT), Referring Expression Tasks (RET), and Described Object Tasks (DOT) with increased difficulty, and Visual Question Answering (VQA) aloneside. Moreover, we propose a novel unified data representation using a set-of-points approach for RSVLTS, along with a condition parser and a self-augmentation strategy based on cyclic referring. These features are integrated into the GeoRSMLLM model, and this enhanced model is designed to handle a broad range of tasks of RSVLTS, paving the way for a more generalized solution for vision-language tasks in geoscience and remote sensing.
Enhancing Ultra High Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery Analysis with ImageRAG
Nov 12, 2024


Abstract:Ultra High Resolution (UHR) remote sensing imagery (RSI) (e.g. 100,000 $\times$ 100,000 pixels or more) poses a significant challenge for current Remote Sensing Multimodal Large Language Models (RSMLLMs). If choose to resize the UHR image to standard input image size, the extensive spatial and contextual information that UHR images contain will be neglected. Otherwise, the original size of these images often exceeds the token limits of standard RSMLLMs, making it difficult to process the entire image and capture long-range dependencies to answer the query based on the abundant visual context. In this paper, we introduce ImageRAG for RS, a training-free framework to address the complexities of analyzing UHR remote sensing imagery. By transforming UHR remote sensing image analysis task to image's long context selection task, we design an innovative image contextual retrieval mechanism based on the Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) technique, denoted as ImageRAG. ImageRAG's core innovation lies in its ability to selectively retrieve and focus on the most relevant portions of the UHR image as visual contexts that pertain to a given query. Fast path and slow path are proposed in this framework to handle this task efficiently and effectively. ImageRAG allows RSMLLMs to manage extensive context and spatial information from UHR RSI, ensuring the analysis is both accurate and efficient.
DiffuTraj: A Stochastic Vessel Trajectory Prediction Approach via Guided Diffusion Process
Oct 12, 2024Abstract:Maritime vessel maneuvers, characterized by their inherent complexity and indeterminacy, requires vessel trajectory prediction system capable of modeling the multi-modality nature of future motion states. Conventional stochastic trajectory prediction methods utilize latent variables to represent the multi-modality of vessel motion, however, tends to overlook the complexity and dynamics inherent in maritime behavior. In contrast, we explicitly simulate the transition of vessel motion from uncertainty towards a state of certainty, effectively handling future indeterminacy in dynamic scenes. In this paper, we present a novel framework (\textit{DiffuTraj}) to conceptualize the trajectory prediction task as a guided reverse process of motion pattern uncertainty diffusion, in which we progressively remove uncertainty from maritime regions to delineate the intended trajectory. Specifically, we encode the previous states of the target vessel, vessel-vessel interactions, and the environment context as guiding factors for trajectory generation. Subsequently, we devise a transformer-based conditional denoiser to capture spatio-temporal dependencies, enabling the generation of trajectories better aligned for particular maritime environment. Comprehensive experiments on vessel trajectory prediction benchmarks demonstrate the superiority of our method.
Synergistic Anchored Contrastive Pre-training for Few-Shot Relation Extraction
Dec 24, 2023



Abstract:Few-shot Relation Extraction (FSRE) aims to extract relational facts from a sparse set of labeled corpora. Recent studies have shown promising results in FSRE by employing Pre-trained Language Models (PLMs) within the framework of supervised contrastive learning, which considers both instances and label facts. However, how to effectively harness massive instance-label pairs to encompass the learned representation with semantic richness in this learning paradigm is not fully explored. To address this gap, we introduce a novel synergistic anchored contrastive pre-training framework. This framework is motivated by the insight that the diverse viewpoints conveyed through instance-label pairs capture incomplete yet complementary intrinsic textual semantics. Specifically, our framework involves a symmetrical contrastive objective that encompasses both sentence-anchored and label-anchored contrastive losses. By combining these two losses, the model establishes a robust and uniform representation space. This space effectively captures the reciprocal alignment of feature distributions among instances and relational facts, simultaneously enhancing the maximization of mutual information across diverse perspectives within the same relation. Experimental results demonstrate that our framework achieves significant performance enhancements compared to baseline models in downstream FSRE tasks. Furthermore, our approach exhibits superior adaptability to handle the challenges of domain shift and zero-shot relation extraction. Our code is available online at https://github.com/AONE-NLP/FSRE-SaCon.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge