Mingshuai Chen
The Self-Improvement Paradox: Can Language Models Bootstrap Reasoning Capabilities without External Scaffolding?
Feb 19, 2025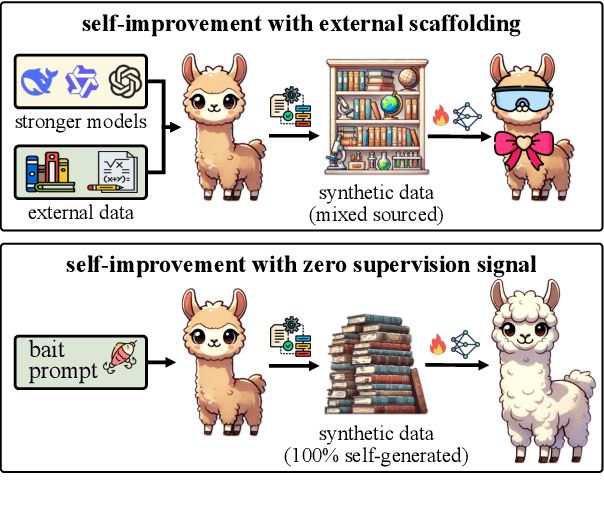
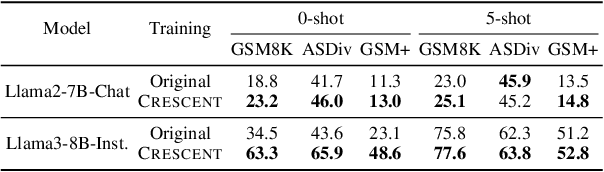
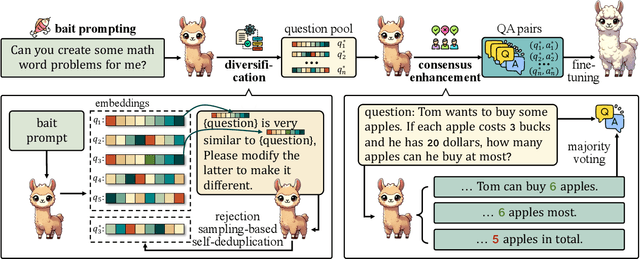
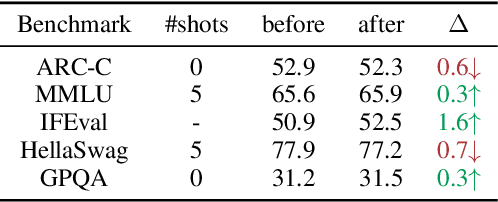
Abstract:Self-improving large language models (LLMs) -- i.e., to improve the performance of an LLM by fine-tuning it with synthetic data generated by itself -- is a promising way to advance the capabilities of LLMs while avoiding extensive supervision. Existing approaches to self-improvement often rely on external supervision signals in the form of seed data and/or assistance from third-party models. This paper presents Crescent -- a simple yet effective framework for generating high-quality synthetic question-answer data in a fully autonomous manner. Crescent first elicits the LLM to generate raw questions via a bait prompt, then diversifies these questions leveraging a rejection sampling-based self-deduplication, and finally feeds the questions to the LLM and collects the corresponding answers by means of majority voting. We show that Crescent sheds light on the potential of true self-improvement with zero external supervision signals for math reasoning; in particular, Crescent-generated question-answer pairs suffice to (i) improve the reasoning capabilities of an LLM while preserving its general performance (especially in the 0-shot setting); and (ii) distil LLM knowledge to weaker models more effectively than existing methods based on seed-dataset augmentation.
HORAE: A Domain-Agnostic Modeling Language for Automating Multimodal Service Regulation
Jun 06, 2024



Abstract:Artificial intelligence is rapidly encroaching on the field of service regulation. This work presents the design principles behind HORAE, a unified specification language to model multimodal regulation rules across a diverse set of domains. We show how HORAE facilitates an intelligent service regulation pipeline by further exploiting a fine-tuned large language model named HORAE that automates the HORAE modeling process, thereby yielding an end-to-end framework for fully automated intelligent service regulation.
NIL: Learning Nonlinear Interpolants
May 28, 2019

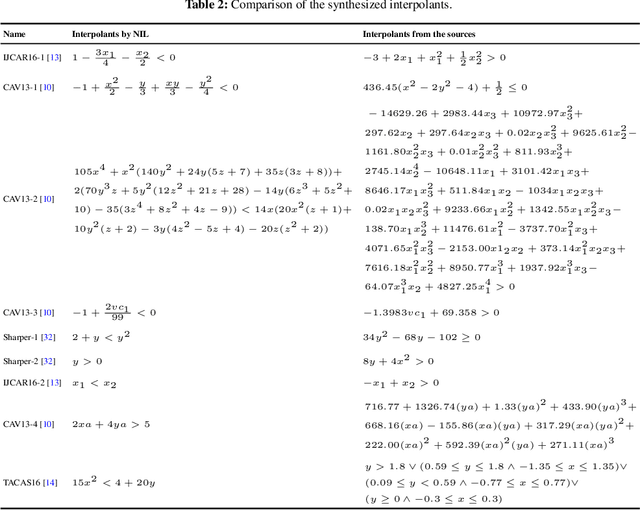

Abstract:Nonlinear interpolants have been shown useful for the verification of programs and hybrid systems in contexts of theorem proving, model checking, abstract interpretation, etc. The underlying synthesis problem, however, is challenging and existing methods have limitations on the form of formulae to be interpolated. We leverage classification techniques with space transformations and kernel tricks as established in the realm of machine learning, and present a counterexample-guided method named NIL for synthesizing polynomial interpolants, thereby yielding a unified framework tackling the interpolation problem for the general quantifier-free theory of nonlinear arithmetic, possibly involving transcendental functions. We prove the soundness of NIL and propose sufficient conditions under which NIL is guaranteed to converge, i.e., the derived sequence of candidate interpolants converges to an actual interpolant, and is complete, namely the algorithm terminates by producing an interpolant if there exists one. The applicability and effectiveness of our technique are demonstrated experimentally on a collection of representative benchmarks from the literature, where in particular, our method suffices to address more interpolation tasks, including those with perturbations in parameters, and in many cases synthesizes simpler interpolants compared with existing approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge