Qiyong Zhong
A Remarkably Efficient Paradigm to Multimodal Large Language Models for Sequential Recommendation
Nov 11, 2025
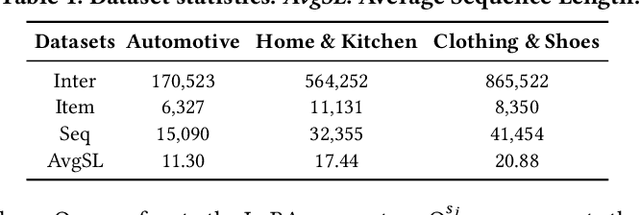
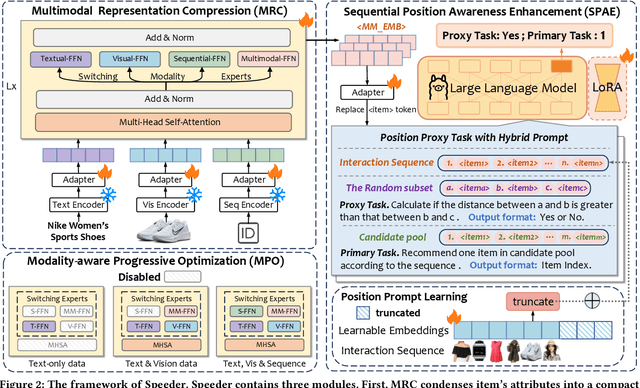
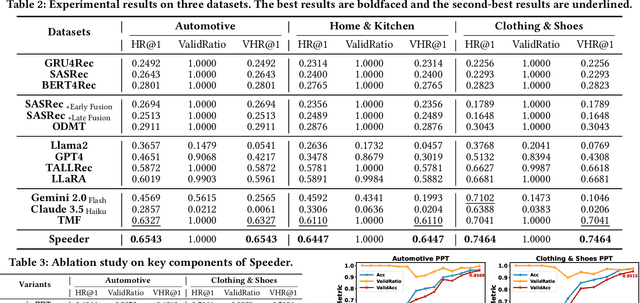
Abstract:Sequential recommendations (SR) predict users' future interactions based on their historical behavior. The rise of Large Language Models (LLMs) has brought powerful generative and reasoning capabilities, significantly enhancing SR performance, while Multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) further extend this by introducing data like images and interactive relationships. However, critical issues remain, i.e., (a) Suboptimal item representations caused by lengthy and redundant descriptions, leading to inefficiencies in both training and inference; (b) Modality-related cognitive bias, as LLMs are predominantly pretrained on textual data, limiting their ability to effectively integrate and utilize non-textual modalities; (c) Weakening sequential perception in long interaction sequences, where attention mechanisms struggle to capture earlier interactions, hindering the modeling of long-range dependencies. To address these issues, we propose Speeder, an efficient MLLM-based paradigm for SR featuring three key innovations: 1) Multimodal Representation Compression (MRC), which condenses item attributes into concise yet informative tokens, reducing redundancy and computational cost; 2) Modality-aware Progressive Optimization (MPO), enabling gradual learning of multimodal representations; 3) Sequential Position Awareness Enhancement (SPAE), improving the LLM's capability to capture both relative and absolute sequential dependencies in long interaction sequences. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of Speeder. Speeder increases training speed to 250% of the original while reducing inference time to 25% on the Amazon dataset.
Distilling Transitional Pattern to Large Language Models for Multimodal Session-based Recommendation
Apr 13, 2025Abstract:Session-based recommendation (SBR) predicts the next item based on anonymous sessions. Traditional SBR explores user intents based on ID collaborations or auxiliary content. To further alleviate data sparsity and cold-start issues, recent Multimodal SBR (MSBR) methods utilize simplistic pre-trained models for modality learning but have limitations in semantic richness. Considering semantic reasoning abilities of Large Language Models (LLM), we focus on the LLM-enhanced MSBR scenario in this paper, which leverages LLM cognition for comprehensive multimodal representation generation, to enhance downstream MSBR. Tackling this problem faces two challenges: i) how to obtain LLM cognition on both transitional patterns and inherent multimodal knowledge, ii) how to align both features into one unified LLM, minimize discrepancy while maximizing representation utility. To this end, we propose a multimodal LLM-enhanced framework TPAD, which extends a distillation paradigm to decouple and align transitional patterns for promoting MSBR. TPAD establishes parallel Knowledge-MLLM and Transfer-MLLM, where the former interprets item knowledge-reflected features and the latter extracts transition-aware features underneath sessions. A transitional pattern alignment module harnessing mutual information estimation theory unites two MLLMs, alleviating distribution discrepancy and distilling transitional patterns into modal representations. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework.
LoGoFair: Post-Processing for Local and Global Fairness in Federated Learning
Mar 21, 2025Abstract:Federated learning (FL) has garnered considerable interest for its capability to learn from decentralized data sources. Given the increasing application of FL in decision-making scenarios, addressing fairness issues across different sensitive groups (e.g., female, male) in FL is crucial. Current research often focuses on facilitating fairness at each client's data (local fairness) or within the entire dataset across all clients (global fairness). However, existing approaches that focus exclusively on either local or global fairness fail to address two key challenges: (\textbf{CH1}) Under statistical heterogeneity, global fairness does not imply local fairness, and vice versa. (\textbf{CH2}) Achieving fairness under model-agnostic setting. To tackle the aforementioned challenges, this paper proposes a novel post-processing framework for achieving both Local and Global Fairness in the FL context, namely LoGoFair. To address CH1, LoGoFair endeavors to seek the Bayes optimal classifier under local and global fairness constraints, which strikes the optimal accuracy-fairness balance in the probabilistic sense. To address CH2, LoGoFair employs a model-agnostic federated post-processing procedure that enables clients to collaboratively optimize global fairness while ensuring local fairness, thereby achieving the optimal fair classifier within FL. Experimental results on three real-world datasets further illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed LoGoFair framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge