Xiaolin Zheng
Generalizable Multimodal Large Language Model Editing via Invariant Trajectory Learning
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Knowledge editing emerges as a crucial technique for efficiently correcting incorrect or outdated knowledge in large language models (LLM). Existing editing methods rely on a rigid mapping from parameter or module modifications to output, which causes the generalization limitation in Multimodal LLM (MLLM). In this paper, we reformulate MLLM editing as an out-of-distribution (OOD) generalization problem, where the goal is to discern semantic shift with factual shift and thus achieve robust editing among diverse cross-modal prompting. The key challenge of this OOD problem lies in identifying invariant causal trajectories that generalize accurately while suppressing spurious correlations. To address it, we propose ODEdit, a plug-and-play invariant learning based framework that optimizes the tripartite OOD risk objective to simultaneously enhance editing reliability, locality, and generality.We further introduce an edit trajectory invariant learning method, which integrates a total variation penalty into the risk minimization objective to stabilize edit trajectories against environmental variations. Theoretical analysis and extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of ODEdit.
Potent but Stealthy: Rethink Profile Pollution against Sequential Recommendation via Bi-level Constrained Reinforcement Paradigm
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Sequential Recommenders, which exploit dynamic user intents through interaction sequences, is vulnerable to adversarial attacks. While existing attacks primarily rely on data poisoning, they require large-scale user access or fake profiles thus lacking practicality. In this paper, we focus on the Profile Pollution Attack that subtly contaminates partial user interactions to induce targeted mispredictions. Previous PPA methods suffer from two limitations, i.e., i) over-reliance on sequence horizon impact restricts fine-grained perturbations on item transitions, and ii) holistic modifications cause detectable distribution shifts. To address these challenges, we propose a constrained reinforcement driven attack CREAT that synergizes a bi-level optimization framework with multi-reward reinforcement learning to balance adversarial efficacy and stealthiness. We first develop a Pattern Balanced Rewarding Policy, which integrates pattern inversion rewards to invert critical patterns and distribution consistency rewards to minimize detectable shifts via unbalanced co-optimal transport. Then we employ a Constrained Group Relative Reinforcement Learning paradigm, enabling step-wise perturbations through dynamic barrier constraints and group-shared experience replay, achieving targeted pollution with minimal detectability. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of CREAT.
TermGPT: Multi-Level Contrastive Fine-Tuning for Terminology Adaptation in Legal and Financial Domain
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive performance in text generation tasks; however, their embedding spaces often suffer from the isotropy problem, resulting in poor discrimination of domain-specific terminology, particularly in legal and financial contexts. This weakness in terminology-level representation can severely hinder downstream tasks such as legal judgment prediction or financial risk analysis, where subtle semantic distinctions are critical. To address this problem, we propose TermGPT, a multi-level contrastive fine-tuning framework designed for terminology adaptation. We first construct a sentence graph to capture semantic and structural relations, and generate semantically consistent yet discriminative positive and negative samples based on contextual and topological cues. We then devise a multi-level contrastive learning approach at both the sentence and token levels, enhancing global contextual understanding and fine-grained terminology discrimination. To support robust evaluation, we construct the first financial terminology dataset derived from official regulatory documents. Experiments show that TermGPT outperforms existing baselines in term discrimination tasks within the finance and legal domains.
A Remarkably Efficient Paradigm to Multimodal Large Language Models for Sequential Recommendation
Nov 11, 2025
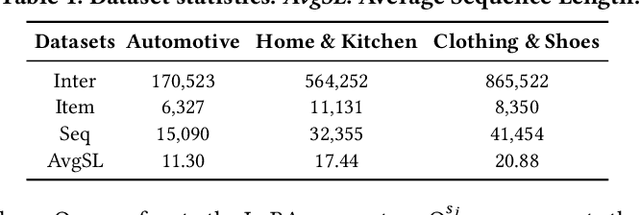
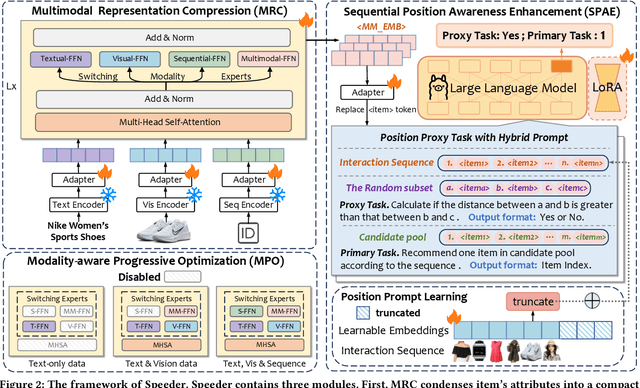
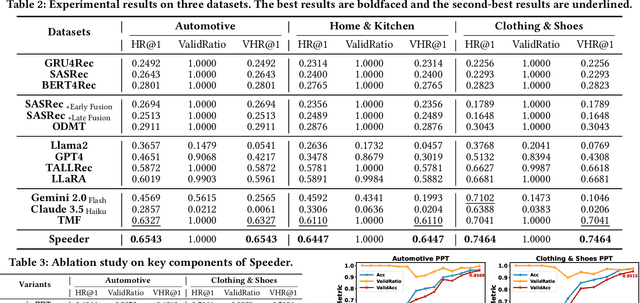
Abstract:Sequential recommendations (SR) predict users' future interactions based on their historical behavior. The rise of Large Language Models (LLMs) has brought powerful generative and reasoning capabilities, significantly enhancing SR performance, while Multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) further extend this by introducing data like images and interactive relationships. However, critical issues remain, i.e., (a) Suboptimal item representations caused by lengthy and redundant descriptions, leading to inefficiencies in both training and inference; (b) Modality-related cognitive bias, as LLMs are predominantly pretrained on textual data, limiting their ability to effectively integrate and utilize non-textual modalities; (c) Weakening sequential perception in long interaction sequences, where attention mechanisms struggle to capture earlier interactions, hindering the modeling of long-range dependencies. To address these issues, we propose Speeder, an efficient MLLM-based paradigm for SR featuring three key innovations: 1) Multimodal Representation Compression (MRC), which condenses item attributes into concise yet informative tokens, reducing redundancy and computational cost; 2) Modality-aware Progressive Optimization (MPO), enabling gradual learning of multimodal representations; 3) Sequential Position Awareness Enhancement (SPAE), improving the LLM's capability to capture both relative and absolute sequential dependencies in long interaction sequences. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of Speeder. Speeder increases training speed to 250% of the original while reducing inference time to 25% on the Amazon dataset.
Distilling Transitional Pattern to Large Language Models for Multimodal Session-based Recommendation
Apr 13, 2025Abstract:Session-based recommendation (SBR) predicts the next item based on anonymous sessions. Traditional SBR explores user intents based on ID collaborations or auxiliary content. To further alleviate data sparsity and cold-start issues, recent Multimodal SBR (MSBR) methods utilize simplistic pre-trained models for modality learning but have limitations in semantic richness. Considering semantic reasoning abilities of Large Language Models (LLM), we focus on the LLM-enhanced MSBR scenario in this paper, which leverages LLM cognition for comprehensive multimodal representation generation, to enhance downstream MSBR. Tackling this problem faces two challenges: i) how to obtain LLM cognition on both transitional patterns and inherent multimodal knowledge, ii) how to align both features into one unified LLM, minimize discrepancy while maximizing representation utility. To this end, we propose a multimodal LLM-enhanced framework TPAD, which extends a distillation paradigm to decouple and align transitional patterns for promoting MSBR. TPAD establishes parallel Knowledge-MLLM and Transfer-MLLM, where the former interprets item knowledge-reflected features and the latter extracts transition-aware features underneath sessions. A transitional pattern alignment module harnessing mutual information estimation theory unites two MLLMs, alleviating distribution discrepancy and distilling transitional patterns into modal representations. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework.
Reproducibility Companion Paper:In-processing User Constrained Dominant Sets for User-Oriented Fairness in Recommender Systems
Mar 29, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we reproduce experimental results presented in our earlier work titled "In-processing User Constrained Dominant Sets for User-Oriented Fairness in Recommender Systems" that was presented in the proceeding of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia.This work aims to verify the effectiveness of our previously proposed method and provide guidance for reproducibility. We present detailed descriptions of our preprocessed datasets, the structure of our source code, configuration file settings, experimental environment, and the reproduced experimental results.
Reproducibility Companion Paper: Making Users Indistinguishable: Attribute-wise Unlearning in Recommender Systems
Mar 29, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we reproduce the experimental results presented in our previous work titled "Making Users Indistinguishable: Attribute-wise Unlearning in Recommender Systems," which was published in the proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia. This paper aims to validate the effectiveness of our proposed method and help others reproduce our experimental results. We provide detailed descriptions of our preprocessed datasets, source code structure, configuration file settings, experimental environment, and reproduced experimental results.
LoGoFair: Post-Processing for Local and Global Fairness in Federated Learning
Mar 21, 2025Abstract:Federated learning (FL) has garnered considerable interest for its capability to learn from decentralized data sources. Given the increasing application of FL in decision-making scenarios, addressing fairness issues across different sensitive groups (e.g., female, male) in FL is crucial. Current research often focuses on facilitating fairness at each client's data (local fairness) or within the entire dataset across all clients (global fairness). However, existing approaches that focus exclusively on either local or global fairness fail to address two key challenges: (\textbf{CH1}) Under statistical heterogeneity, global fairness does not imply local fairness, and vice versa. (\textbf{CH2}) Achieving fairness under model-agnostic setting. To tackle the aforementioned challenges, this paper proposes a novel post-processing framework for achieving both Local and Global Fairness in the FL context, namely LoGoFair. To address CH1, LoGoFair endeavors to seek the Bayes optimal classifier under local and global fairness constraints, which strikes the optimal accuracy-fairness balance in the probabilistic sense. To address CH2, LoGoFair employs a model-agnostic federated post-processing procedure that enables clients to collaboratively optimize global fairness while ensuring local fairness, thereby achieving the optimal fair classifier within FL. Experimental results on three real-world datasets further illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed LoGoFair framework.
Joint Similarity Item Exploration and Overlapped User Guidance for Multi-Modal Cross-Domain Recommendation
Feb 22, 2025Abstract:Cross-Domain Recommendation (CDR) has been widely investigated for solving long-standing data sparsity problem via knowledge sharing across domains. In this paper, we focus on the Multi-Modal Cross-Domain Recommendation (MMCDR) problem where different items have multi-modal information while few users are overlapped across domains. MMCDR is particularly challenging in two aspects: fully exploiting diverse multi-modal information within each domain and leveraging useful knowledge transfer across domains. However, previous methods fail to cluster items with similar characteristics while filtering out inherit noises within different modalities, hurdling the model performance. What is worse, conventional CDR models primarily rely on overlapped users for domain adaptation, making them ill-equipped to handle scenarios where the majority of users are non-overlapped. To fill this gap, we propose Joint Similarity Item Exploration and Overlapped User Guidance (SIEOUG) for solving the MMCDR problem. SIEOUG first proposes similarity item exploration module, which not only obtains pair-wise and group-wise item-item graph knowledge, but also reduces irrelevant noise for multi-modal modeling. Then SIEOUG proposes user-item collaborative filtering module to aggregate user/item embeddings with the attention mechanism for collaborative filtering. Finally SIEOUG proposes overlapped user guidance module with optimal user matching for knowledge sharing across domains. Our empirical study on Amazon dataset with several different tasks demonstrates that SIEOUG significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art models under the MMCDR setting.
WassFFed: Wasserstein Fair Federated Learning
Nov 11, 2024



Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) employs a training approach to address scenarios where users' data cannot be shared across clients. Achieving fairness in FL is imperative since training data in FL is inherently geographically distributed among diverse user groups. Existing research on fairness predominantly assumes access to the entire training data, making direct transfer to FL challenging. However, the limited existing research on fairness in FL does not effectively address two key challenges, i.e., (CH1) Current methods fail to deal with the inconsistency between fair optimization results obtained with surrogate functions and fair classification results. (CH2) Directly aggregating local fair models does not always yield a globally fair model due to non Identical and Independent data Distributions (non-IID) among clients. To address these challenges, we propose a Wasserstein Fair Federated Learning framework, namely WassFFed. To tackle CH1, we ensure that the outputs of local models, rather than the loss calculated with surrogate functions or classification results with a threshold, remain independent of various user groups. To resolve CH2, we employ a Wasserstein barycenter calculation of all local models' outputs for each user group, bringing local model outputs closer to the global output distribution to ensure consistency between the global model and local models. We conduct extensive experiments on three real-world datasets, demonstrating that WassFFed outperforms existing approaches in striking a balance between accuracy and fairness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge