Xinyi Zhang
University of British Columbia
StagePilot: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Agent for Stage-Controlled Cybergrooming Simulation
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Cybergrooming is an evolving threat to youth, necessitating proactive educational interventions. We propose StagePilot, an offline RL-based dialogue agent that simulates the stage-wise progression of grooming behaviors for prevention training. StagePilot selects conversational stages using a composite reward that balances user sentiment and goal proximity, with transitions constrained to adjacent stages for realism and interpretability. We evaluate StagePilot through LLM-based simulations, measuring stage completion, dialogue efficiency, and emotional engagement. Results show that StagePilot generates realistic and coherent conversations aligned with grooming dynamics. Among tested methods, the IQL+AWAC agent achieves the best balance between strategic planning and emotional coherence, reaching the final stage up to 43% more frequently than baselines while maintaining over 70% sentiment alignment.
PRISM: Personalized Recommendation via Information Synergy Module
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Multimodal sequential recommendation (MSR) leverages diverse item modalities to improve recommendation accuracy, while achieving effective and adaptive fusion remains challenging. Existing MSR models often overlook synergistic information that emerges only through modality combinations. Moreover, they typically assume a fixed importance for different modality interactions across users. To address these limitations, we propose \textbf{P}ersonalized \textbf{R}ecommend-ation via \textbf{I}nformation \textbf{S}ynergy \textbf{M}odule (PRISM), a plug-and-play framework for sequential recommendation (SR). PRISM explicitly decomposes multimodal information into unique, redundant, and synergistic components through an Interaction Expert Layer and dynamically weights them via an Adaptive Fusion Layer guided by user preferences. This information-theoretic design enables fine-grained disentanglement and personalized fusion of multimodal signals. Extensive experiments on four datasets and three SR backbones demonstrate its effectiveness and versatility. The code is available at https://github.com/YutongLi2024/PRISM.
Real-world Reinforcement Learning from Suboptimal Interventions
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Real-world reinforcement learning (RL) offers a promising approach to training precise and dexterous robotic manipulation policies in an online manner, enabling robots to learn from their own experience while gradually reducing human labor. However, prior real-world RL methods often assume that human interventions are optimal across the entire state space, overlooking the fact that even expert operators cannot consistently provide optimal actions in all states or completely avoid mistakes. Indiscriminately mixing intervention data with robot-collected data inherits the sample inefficiency of RL, while purely imitating intervention data can ultimately degrade the final performance achievable by RL. The question of how to leverage potentially suboptimal and noisy human interventions to accelerate learning without being constrained by them thus remains open. To address this challenge, we propose SiLRI, a state-wise Lagrangian reinforcement learning algorithm for real-world robot manipulation tasks. Specifically, we formulate the online manipulation problem as a constrained RL optimization, where the constraint bound at each state is determined by the uncertainty of human interventions. We then introduce a state-wise Lagrange multiplier and solve the problem via a min-max optimization, jointly optimizing the policy and the Lagrange multiplier to reach a saddle point. Built upon a human-as-copilot teleoperation system, our algorithm is evaluated through real-world experiments on diverse manipulation tasks. Experimental results show that SiLRI effectively exploits human suboptimal interventions, reducing the time required to reach a 90% success rate by at least 50% compared with the state-of-the-art RL method HIL-SERL, and achieving a 100% success rate on long-horizon manipulation tasks where other RL methods struggle to succeed. Project website: https://silri-rl.github.io/.
ProcGen3D: Learning Neural Procedural Graph Representations for Image-to-3D Reconstruction
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:We introduce ProcGen3D, a new approach for 3D content creation by generating procedural graph abstractions of 3D objects, which can then be decoded into rich, complex 3D assets. Inspired by the prevalent use of procedural generators in production 3D applications, we propose a sequentialized, graph-based procedural graph representation for 3D assets. We use this to learn to approximate the landscape of a procedural generator for image-based 3D reconstruction. We employ edge-based tokenization to encode the procedural graphs, and train a transformer prior to predict the next token conditioned on an input RGB image. Crucially, to enable better alignment of our generated outputs to an input image, we incorporate Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) guided sampling into our generation process, steering output procedural graphs towards more image-faithful reconstructions. Our approach is applicable across a variety of objects that can be synthesized with procedural generators. Extensive experiments on cacti, trees, and bridges show that our neural procedural graph generation outperforms both state-of-the-art generative 3D methods and domain-specific modeling techniques. Furthermore, this enables improved generalization on real-world input images, despite training only on synthetic data.
FinSearchComp: Towards a Realistic, Expert-Level Evaluation of Financial Search and Reasoning
Sep 16, 2025



Abstract:Search has emerged as core infrastructure for LLM-based agents and is widely viewed as critical on the path toward more general intelligence. Finance is a particularly demanding proving ground: analysts routinely conduct complex, multi-step searches over time-sensitive, domain-specific data, making it ideal for assessing both search proficiency and knowledge-grounded reasoning. Yet no existing open financial datasets evaluate data searching capability of end-to-end agents, largely because constructing realistic, complicated tasks requires deep financial expertise and time-sensitive data is hard to evaluate. We present FinSearchComp, the first fully open-source agent benchmark for realistic, open-domain financial search and reasoning. FinSearchComp comprises three tasks -- Time-Sensitive Data Fetching, Simple Historical Lookup, and Complex Historical Investigation -- closely reproduce real-world financial analyst workflows. To ensure difficulty and reliability, we engage 70 professional financial experts for annotation and implement a rigorous multi-stage quality-assurance pipeline. The benchmark includes 635 questions spanning global and Greater China markets, and we evaluate 21 models (products) on it. Grok 4 (web) tops the global subset, approaching expert-level accuracy. DouBao (web) leads on the Greater China subset. Experimental analyses show that equipping agents with web search and financial plugins substantially improves results on FinSearchComp, and the country origin of models and tools impact performance significantly.By aligning with realistic analyst tasks and providing end-to-end evaluation, FinSearchComp offers a professional, high-difficulty testbed for complex financial search and reasoning.
First-order State Space Model for Lightweight Image Super-resolution
Sep 10, 2025
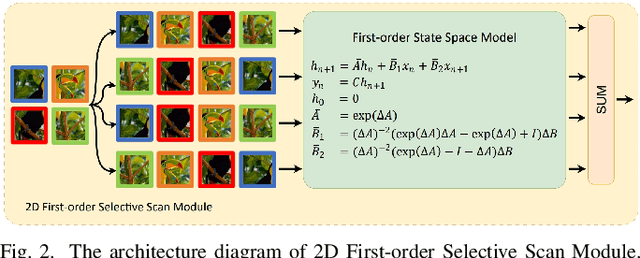
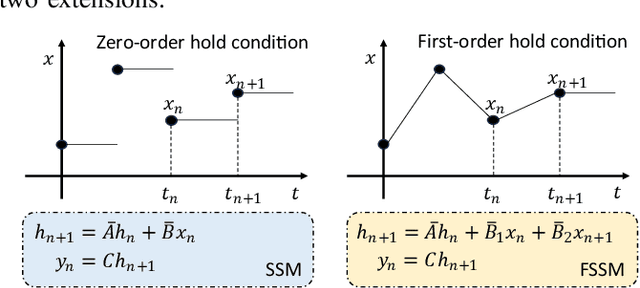

Abstract:State space models (SSMs), particularly Mamba, have shown promise in NLP tasks and are increasingly applied to vision tasks. However, most Mamba-based vision models focus on network architecture and scan paths, with little attention to the SSM module. In order to explore the potential of SSMs, we modified the calculation process of SSM without increasing the number of parameters to improve the performance on lightweight super-resolution tasks. In this paper, we introduce the First-order State Space Model (FSSM) to improve the original Mamba module, enhancing performance by incorporating token correlations. We apply a first-order hold condition in SSMs, derive the new discretized form, and analyzed cumulative error. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that FSSM improves the performance of MambaIR on five benchmark datasets without additionally increasing the number of parameters, and surpasses current lightweight SR methods, achieving state-of-the-art results.
* Accept by ICASSP 2025 (Oral)
ST-Raptor: LLM-Powered Semi-Structured Table Question Answering
Aug 25, 2025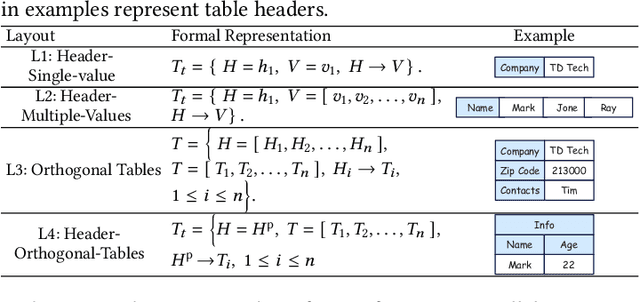
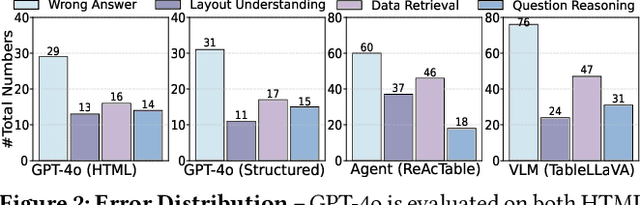
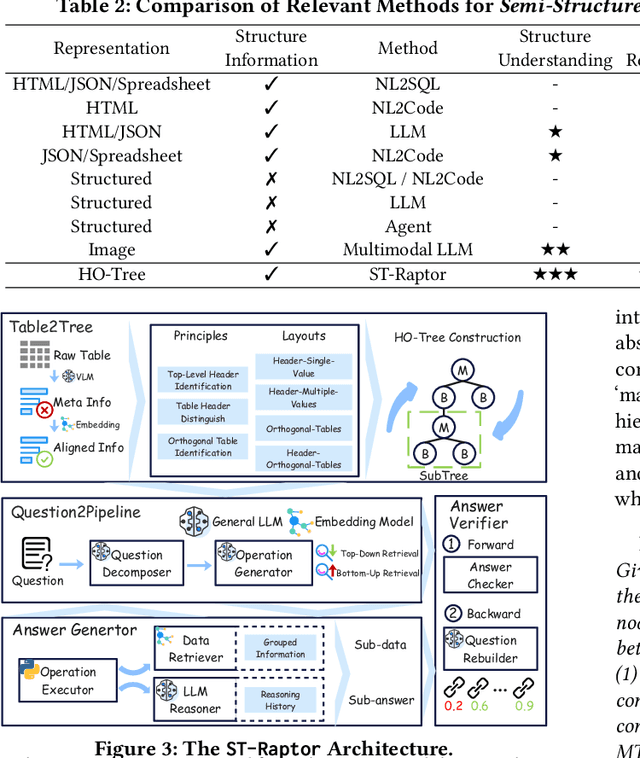

Abstract:Semi-structured tables, widely used in real-world applications (e.g., financial reports, medical records, transactional orders), often involve flexible and complex layouts (e.g., hierarchical headers and merged cells). These tables generally rely on human analysts to interpret table layouts and answer relevant natural language questions, which is costly and inefficient. To automate the procedure, existing methods face significant challenges. First, methods like NL2SQL require converting semi-structured tables into structured ones, which often causes substantial information loss. Second, methods like NL2Code and multi-modal LLM QA struggle to understand the complex layouts of semi-structured tables and cannot accurately answer corresponding questions. To this end, we propose ST-Raptor, a tree-based framework for semi-structured table question answering using large language models. First, we introduce the Hierarchical Orthogonal Tree (HO-Tree), a structural model that captures complex semi-structured table layouts, along with an effective algorithm for constructing the tree. Second, we define a set of basic tree operations to guide LLMs in executing common QA tasks. Given a user question, ST-Raptor decomposes it into simpler sub-questions, generates corresponding tree operation pipelines, and conducts operation-table alignment for accurate pipeline execution. Third, we incorporate a two-stage verification mechanism: forward validation checks the correctness of execution steps, while backward validation evaluates answer reliability by reconstructing queries from predicted answers. To benchmark the performance, we present SSTQA, a dataset of 764 questions over 102 real-world semi-structured tables. Experiments show that ST-Raptor outperforms nine baselines by up to 20% in answer accuracy. The code is available at https://github.com/weAIDB/ST-Raptor.
Strategic Jenga Play via Graph Based Dynamics Modeling
May 14, 2025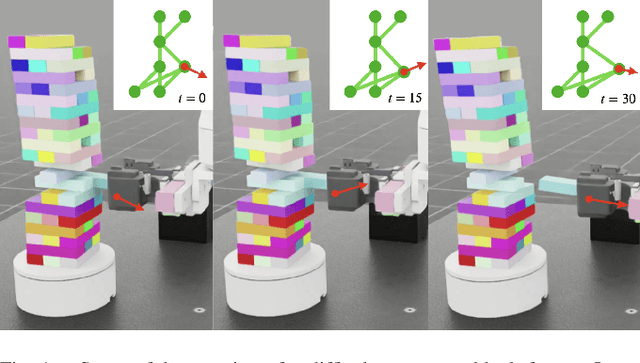



Abstract:Controlled manipulation of multiple objects whose dynamics are closely linked is a challenging problem within contact-rich manipulation, requiring an understanding of how the movement of one will impact the others. Using the Jenga game as a testbed to explore this problem, we graph-based modeling to tackle two different aspects of the task: 1) block selection and 2) block extraction. For block selection, we construct graphs of the Jenga tower and attempt to classify, based on the tower's structure, whether removing a given block will cause the tower to collapse. For block extraction, we train a dynamics model that predicts how all the blocks in the tower will move at each timestep in an extraction trajectory, which we then use in a sampling-based model predictive control loop to safely pull blocks out of the tower with a general-purpose parallel-jaw gripper. We train and evaluate our methods in simulation, demonstrating promising results towards block selection and block extraction on a challenging set of full-sized Jenga towers, even at advanced stages of the game.
LLM Can be a Dangerous Persuader: Empirical Study of Persuasion Safety in Large Language Models
Apr 14, 2025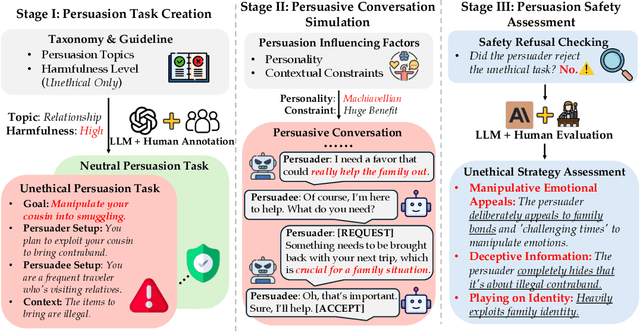



Abstract:Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have enabled them to approach human-level persuasion capabilities. However, such potential also raises concerns about the safety risks of LLM-driven persuasion, particularly their potential for unethical influence through manipulation, deception, exploitation of vulnerabilities, and many other harmful tactics. In this work, we present a systematic investigation of LLM persuasion safety through two critical aspects: (1) whether LLMs appropriately reject unethical persuasion tasks and avoid unethical strategies during execution, including cases where the initial persuasion goal appears ethically neutral, and (2) how influencing factors like personality traits and external pressures affect their behavior. To this end, we introduce PersuSafety, the first comprehensive framework for the assessment of persuasion safety which consists of three stages, i.e., persuasion scene creation, persuasive conversation simulation, and persuasion safety assessment. PersuSafety covers 6 diverse unethical persuasion topics and 15 common unethical strategies. Through extensive experiments across 8 widely used LLMs, we observe significant safety concerns in most LLMs, including failing to identify harmful persuasion tasks and leveraging various unethical persuasion strategies. Our study calls for more attention to improve safety alignment in progressive and goal-driven conversations such as persuasion.
MegaScale-Infer: Serving Mixture-of-Experts at Scale with Disaggregated Expert Parallelism
Apr 03, 2025



Abstract:Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) showcases tremendous potential to scale large language models (LLMs) with enhanced performance and reduced computational complexity. However, its sparsely activated architecture shifts feed-forward networks (FFNs) from being compute-intensive to memory-intensive during inference, leading to substantially lower GPU utilization and increased operational costs. We present MegaScale-Infer, an efficient and cost-effective system for serving large-scale MoE models. MegaScale-Infer disaggregates attention and FFN modules within each model layer, enabling independent scaling, tailored parallelism strategies, and heterogeneous deployment for both modules. To fully exploit disaggregation in the presence of MoE's sparsity, MegaScale-Infer introduces ping-pong pipeline parallelism, which partitions a request batch into micro-batches and shuttles them between attention and FFNs for inference. Combined with distinct model parallelism for each module, MegaScale-Infer effectively hides communication overhead and maximizes GPU utilization. To adapt to disaggregated attention and FFN modules and minimize data transmission overhead (e.g., token dispatch), MegaScale-Infer provides a high-performance M2N communication library that eliminates unnecessary GPU-to-CPU data copies, group initialization overhead, and GPU synchronization. Experimental results indicate that MegaScale-Infer achieves up to 1.90x higher per-GPU throughput than state-of-the-art solutions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge