Pengyang Zhou
FOOGD: Federated Collaboration for Both Out-of-distribution Generalization and Detection
Oct 15, 2024



Abstract:Federated learning (FL) is a promising machine learning paradigm that collaborates with client models to capture global knowledge. However, deploying FL models in real-world scenarios remains unreliable due to the coexistence of in-distribution data and unexpected out-of-distribution (OOD) data, such as covariate-shift and semantic-shift data. Current FL researches typically address either covariate-shift data through OOD generalization or semantic-shift data via OOD detection, overlooking the simultaneous occurrence of various OOD shifts. In this work, we propose FOOGD, a method that estimates the probability density of each client and obtains reliable global distribution as guidance for the subsequent FL process. Firstly, SM3D in FOOGD estimates score model for arbitrary distributions without prior constraints, and detects semantic-shift data powerfully. Then SAG in FOOGD provides invariant yet diverse knowledge for both local covariate-shift generalization and client performance generalization. In empirical validations, FOOGD significantly enjoys three main advantages: (1) reliably estimating non-normalized decentralized distributions, (2) detecting semantic shift data via score values, and (3) generalizing to covariate-shift data by regularizing feature extractor. The prejoct is open in https://github.com/XeniaLLL/FOOGD-main.git.
Rethinking the Representation in Federated Unsupervised Learning with Non-IID Data
Mar 25, 2024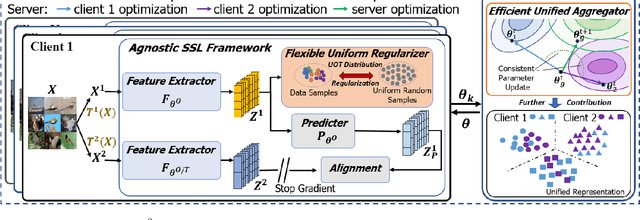
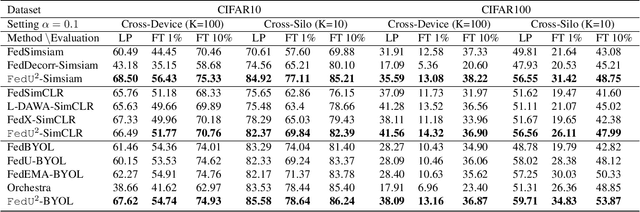
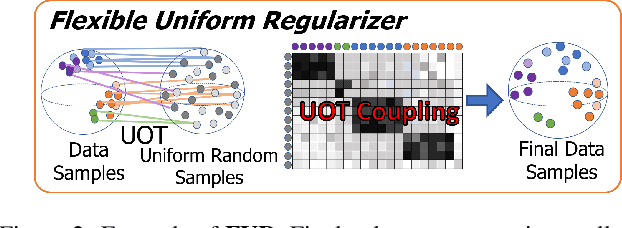
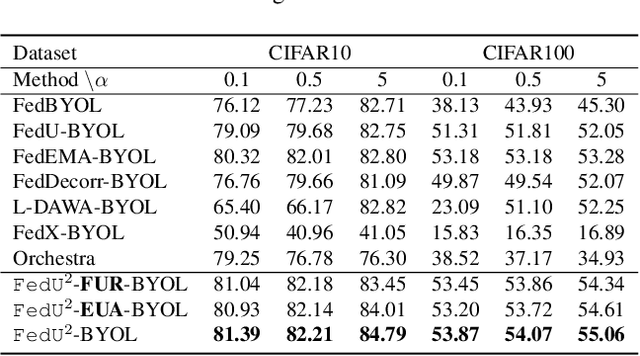
Abstract:Federated learning achieves effective performance in modeling decentralized data. In practice, client data are not well-labeled, which makes it potential for federated unsupervised learning (FUSL) with non-IID data. However, the performance of existing FUSL methods suffers from insufficient representations, i.e., (1) representation collapse entanglement among local and global models, and (2) inconsistent representation spaces among local models. The former indicates that representation collapse in local model will subsequently impact the global model and other local models. The latter means that clients model data representation with inconsistent parameters due to the deficiency of supervision signals. In this work, we propose FedU2 which enhances generating uniform and unified representation in FUSL with non-IID data. Specifically, FedU2 consists of flexible uniform regularizer (FUR) and efficient unified aggregator (EUA). FUR in each client avoids representation collapse via dispersing samples uniformly, and EUA in server promotes unified representation by constraining consistent client model updating. To extensively validate the performance of FedU2, we conduct both cross-device and cross-silo evaluation experiments on two benchmark datasets, i.e., CIFAR10 and CIFAR100.
Joint Local Relational Augmentation and Global Nash Equilibrium for Federated Learning with Non-IID Data
Aug 17, 2023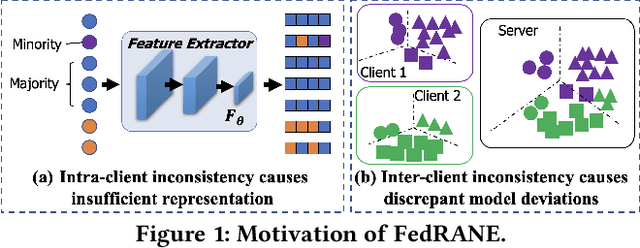
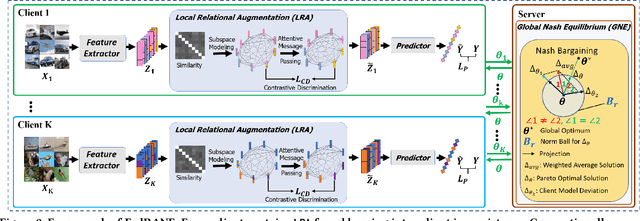
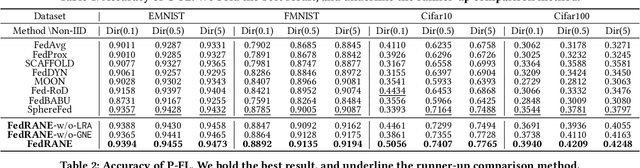
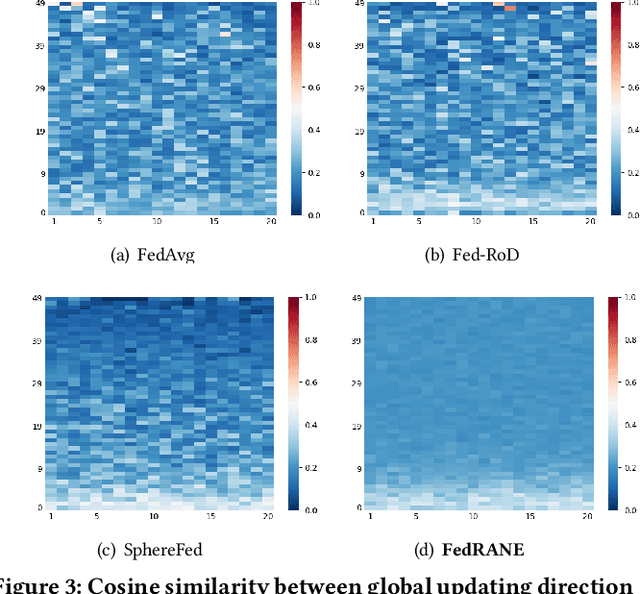
Abstract:Federated learning (FL) is a distributed machine learning paradigm that needs collaboration between a server and a series of clients with decentralized data. To make FL effective in real-world applications, existing work devotes to improving the modeling of decentralized data with non-independent and identical distributions (non-IID). In non-IID settings, there are intra-client inconsistency that comes from the imbalanced data modeling, and inter-client inconsistency among heterogeneous client distributions, which not only hinders sufficient representation of the minority data, but also brings discrepant model deviations. However, previous work overlooks to tackle the above two coupling inconsistencies together. In this work, we propose FedRANE, which consists of two main modules, i.e., local relational augmentation (LRA) and global Nash equilibrium (GNE), to resolve intra- and inter-client inconsistency simultaneously. Specifically, in each client, LRA mines the similarity relations among different data samples and enhances the minority sample representations with their neighbors using attentive message passing. In server, GNE reaches an agreement among inconsistent and discrepant model deviations from clients to server, which encourages the global model to update in the direction of global optimum without breaking down the clients optimization toward their local optimums. We conduct extensive experiments on four benchmark datasets to show the superiority of FedRANE in enhancing the performance of FL with non-IID data.
HyperFed: Hyperbolic Prototypes Exploration with Consistent Aggregation for Non-IID Data in Federated Learning
Jul 26, 2023



Abstract:Federated learning (FL) collaboratively models user data in a decentralized way. However, in the real world, non-identical and independent data distributions (non-IID) among clients hinder the performance of FL due to three issues, i.e., (1) the class statistics shifting, (2) the insufficient hierarchical information utilization, and (3) the inconsistency in aggregating clients. To address the above issues, we propose HyperFed which contains three main modules, i.e., hyperbolic prototype Tammes initialization (HPTI), hyperbolic prototype learning (HPL), and consistent aggregation (CA). Firstly, HPTI in the server constructs uniformly distributed and fixed class prototypes, and shares them with clients to match class statistics, further guiding consistent feature representation for local clients. Secondly, HPL in each client captures the hierarchical information in local data with the supervision of shared class prototypes in the hyperbolic model space. Additionally, CA in the server mitigates the impact of the inconsistent deviations from clients to server. Extensive studies of four datasets prove that HyperFed is effective in enhancing the performance of FL under the non-IID set.
Attention-based Neural Load Forecasting: A Dynamic Feature Selection Approach
Aug 25, 2021



Abstract:Encoder-decoder-based recurrent neural network (RNN) has made significant progress in sequence-to-sequence learning tasks such as machine translation and conversational models. Recent works have shown the advantage of this type of network in dealing with various time series forecasting tasks. The present paper focuses on the problem of multi-horizon short-term load forecasting, which plays a key role in the power system's planning and operation. Leveraging the encoder-decoder RNN, we develop an attention model to select the relevant features and similar temporal information adaptively. First, input features are assigned with different weights by a feature selection attention layer, while the updated historical features are encoded by a bi-directional long short-term memory (BiLSTM) layer. Then, a decoder with hierarchical temporal attention enables a similar day selection, which re-evaluates the importance of historical information at each time step. Numerical results tested on the dataset of the global energy forecasting competition 2014 show that our proposed model significantly outperforms some existing forecasting schemes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge