Ankit Shah
Department of Industrial and Management Systems Engineering, University of South Florida, Tampa, Florida, USA
Deciphering GunType Hierarchy through Acoustic Analysis of Gunshot Recordings
Jun 25, 2025Abstract:The escalating rates of gun-related violence and mass shootings represent a significant threat to public safety. Timely and accurate information for law enforcement agencies is crucial in mitigating these incidents. Current commercial gunshot detection systems, while effective, often come with prohibitive costs. This research explores a cost-effective alternative by leveraging acoustic analysis of gunshot recordings, potentially obtainable from ubiquitous devices like cell phones, to not only detect gunshots but also classify the type of firearm used. This paper details a study on deciphering gun type hierarchies using a curated dataset of 3459 recordings. We investigate the fundamental acoustic characteristics of gunshots, including muzzle blasts and shockwaves, which vary based on firearm type, ammunition, and shooting direction. We propose and evaluate machine learning frameworks, including Support Vector Machines (SVMs) as a baseline and a more advanced Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architecture for joint gunshot detection and gun type classification. Results indicate that our deep learning approach achieves a mean average precision (mAP) of 0.58 on clean labeled data, outperforming the SVM baseline (mAP 0.39). Challenges related to data quality, environmental noise, and the generalization capabilities when using noisy web-sourced data (mAP 0.35) are also discussed. The long-term vision is to develop a highly accurate, real-time system deployable on common recording devices, significantly reducing detection costs and providing critical intelligence to first responders.
Did You Hear That? Introducing AADG: A Framework for Generating Benchmark Data in Audio Anomaly Detection
Oct 04, 2024



Abstract:We introduce a novel, general-purpose audio generation framework specifically designed for anomaly detection and localization. Unlike existing datasets that predominantly focus on industrial and machine-related sounds, our framework focuses a broader range of environments, particularly useful in real-world scenarios where only audio data are available, such as in video-derived or telephonic audio. To generate such data, we propose a new method inspired by the LLM-Modulo framework, which leverages large language models(LLMs) as world models to simulate such real-world scenarios. This tool is modular allowing a plug-and-play approach. It operates by first using LLMs to predict plausible real-world scenarios. An LLM further extracts the constituent sounds, the order and the way in which these should be merged to create coherent wholes. Much like the LLM-Modulo framework, we include rigorous verification of each output stage, ensuring the reliability of the generated data. The data produced using the framework serves as a benchmark for anomaly detection applications, potentially enhancing the performance of models trained on audio data, particularly in handling out-of-distribution cases. Our contributions thus fill a critical void in audio anomaly detection resources and provide a scalable tool for generating diverse, realistic audio data.
Automatic Dataset Construction (ADC): Sample Collection, Data Curation, and Beyond
Aug 21, 2024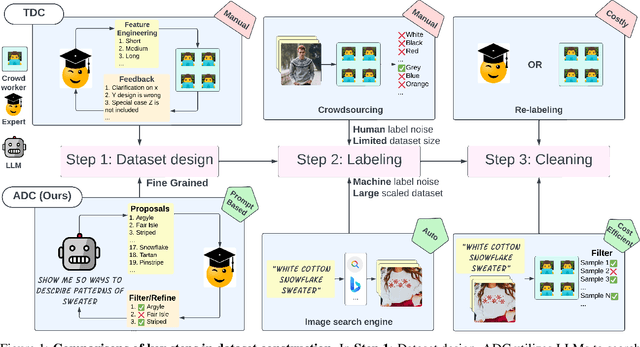
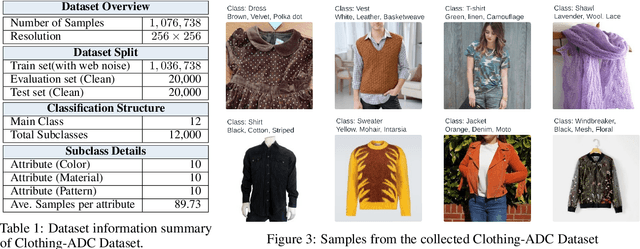
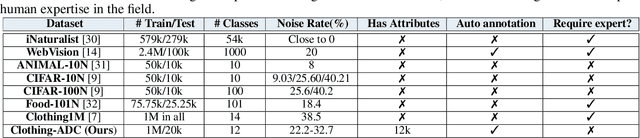
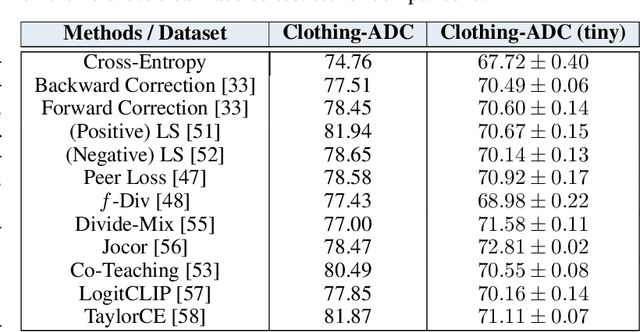
Abstract:Large-scale data collection is essential for developing personalized training data, mitigating the shortage of training data, and fine-tuning specialized models. However, creating high-quality datasets quickly and accurately remains a challenge due to annotation errors, the substantial time and costs associated with human labor. To address these issues, we propose Automatic Dataset Construction (ADC), an innovative methodology that automates dataset creation with negligible cost and high efficiency. Taking the image classification task as a starting point, ADC leverages LLMs for the detailed class design and code generation to collect relevant samples via search engines, significantly reducing the need for manual annotation and speeding up the data generation process. Despite these advantages, ADC also encounters real-world challenges such as label errors (label noise) and imbalanced data distributions (label bias). We provide open-source software that incorporates existing methods for label error detection, robust learning under noisy and biased data, ensuring a higher-quality training data and more robust model training procedure. Furthermore, we design three benchmark datasets focused on label noise detection, label noise learning, and class-imbalanced learning. These datasets are vital because there are few existing datasets specifically for label noise detection, despite its importance. Finally, we evaluate the performance of existing popular methods on these datasets, thereby facilitating further research in the field.
A Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Framework for Evaluating the U.S. Ending the HIV Epidemic Plan
Nov 06, 2023Abstract:Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a major public health concern in the United States, with about 1.2 million people living with HIV and 35,000 newly infected each year. There are considerable geographical disparities in HIV burden and care access across the U.S. The 2019 Ending the HIV Epidemic (EHE) initiative aims to reduce new infections by 90% by 2030, by improving coverage of diagnoses, treatment, and prevention interventions and prioritizing jurisdictions with high HIV prevalence. Identifying optimal scale-up of intervention combinations will help inform resource allocation. Existing HIV decision analytic models either evaluate specific cities or the overall national population, thus overlooking jurisdictional interactions or differences. In this paper, we propose a multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) model, that enables jurisdiction-specific decision analyses but in an environment with cross-jurisdictional epidemiological interactions. In experimental analyses, conducted on jurisdictions within California and Florida, optimal policies from MARL were significantly different than those generated from single-agent RL, highlighting the influence of jurisdictional variations and interactions. By using comprehensive modeling of HIV and formulations of state space, action space, and reward functions, this work helps demonstrate the strengths and applicability of MARL for informing public health policies, and provides a framework for expanding to the national-level to inform the EHE.
Psychoacoustic Challenges Of Speech Enhancement On VoIP Platforms
Oct 11, 2023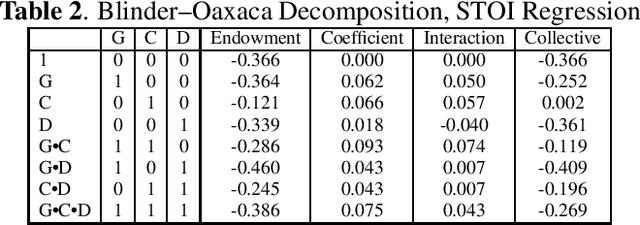
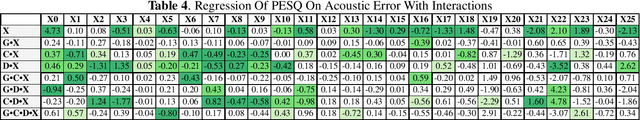
Abstract:Within the ambit of VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) telecommunications, the complexities introduced by acoustic transformations merit rigorous analysis. This research, rooted in the exploration of proprietary sender-side denoising effects, meticulously evaluates platforms such as Google Meets and Zoom. The study draws upon the Deep Noise Suppression (DNS) 2020 dataset, ensuring a structured examination tailored to various denoising settings and receiver interfaces. A methodological novelty is introduced via the Oaxaca decomposition, traditionally an econometric tool, repurposed herein to analyze acoustic-phonetic perturbations within VoIP systems. To further ground the implications of these transformations, psychoacoustic metrics, specifically PESQ and STOI, were harnessed to furnish a comprehensive understanding of speech alterations. Cumulatively, the insights garnered underscore the intricate landscape of VoIP-influenced acoustic dynamics. In addition to the primary findings, a multitude of metrics are reported, extending the research purview. Moreover, out-of-domain benchmarking for both time and time-frequency domain speech enhancement models is included, thereby enhancing the depth and applicability of this inquiry.
LoFT: Local Proxy Fine-tuning For Improving Transferability Of Adversarial Attacks Against Large Language Model
Oct 02, 2023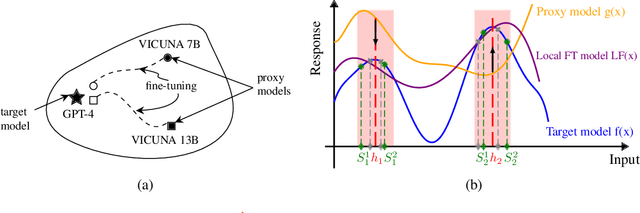

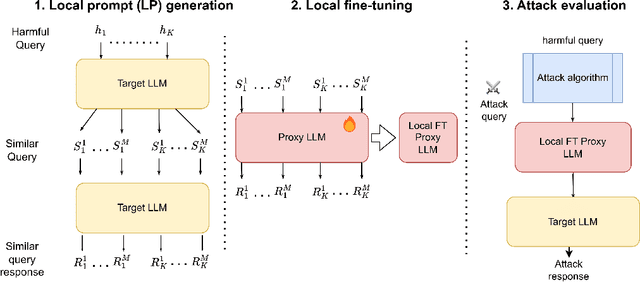
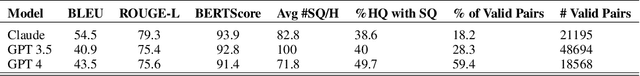
Abstract:It has been shown that Large Language Model (LLM) alignments can be circumvented by appending specially crafted attack suffixes with harmful queries to elicit harmful responses. To conduct attacks against private target models whose characterization is unknown, public models can be used as proxies to fashion the attack, with successful attacks being transferred from public proxies to private target models. The success rate of attack depends on how closely the proxy model approximates the private model. We hypothesize that for attacks to be transferrable, it is sufficient if the proxy can approximate the target model in the neighborhood of the harmful query. Therefore, in this paper, we propose \emph{Local Fine-Tuning (LoFT)}, \textit{i.e.}, fine-tuning proxy models on similar queries that lie in the lexico-semantic neighborhood of harmful queries to decrease the divergence between the proxy and target models. First, we demonstrate three approaches to prompt private target models to obtain similar queries given harmful queries. Next, we obtain data for local fine-tuning by eliciting responses from target models for the generated similar queries. Then, we optimize attack suffixes to generate attack prompts and evaluate the impact of our local fine-tuning on the attack's success rate. Experiments show that local fine-tuning of proxy models improves attack transferability and increases attack success rate by $39\%$, $7\%$, and $0.5\%$ (absolute) on target models ChatGPT, GPT-4, and Claude respectively.
Understanding and Mitigating the Label Noise in Pre-training on Downstream Tasks
Sep 29, 2023



Abstract:Pre-training on large-scale datasets and then fine-tuning on downstream tasks have become a standard practice in deep learning. However, pre-training data often contain label noise that may adversely affect the generalization of the model. This paper aims to understand the nature of noise in pre-training datasets and to mitigate its impact on downstream tasks. More specifically, through extensive experiments of supervised pre-training models on synthetic noisy ImageNet-1K and YFCC15M datasets, we demonstrate that while slight noise in pre-training can benefit in-domain (ID) transfer performance, where the training and testing data share the same distribution, it always deteriorates out-of-domain (OOD) performance, where training and testing data distribution are different. We empirically verify that the reason behind is noise in pre-training shapes the feature space differently. We then propose a lightweight black-box tuning method (NMTune) to affine the feature space to mitigate the malignant effect of noise and improve generalization on both ID and OOD tasks, considering one may not be able to fully fine-tune or even access the pre-trained models. We conduct practical experiments on popular vision and language models that are pre-trained on noisy data for evaluation of our approach. Our analysis and results show the importance of this interesting and novel research direction, which we term Noisy Model Learning.
Online Active Learning For Sound Event Detection
Sep 25, 2023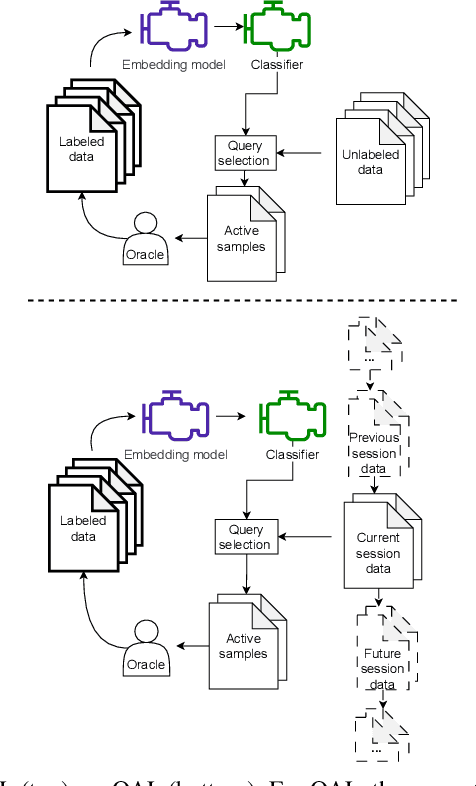
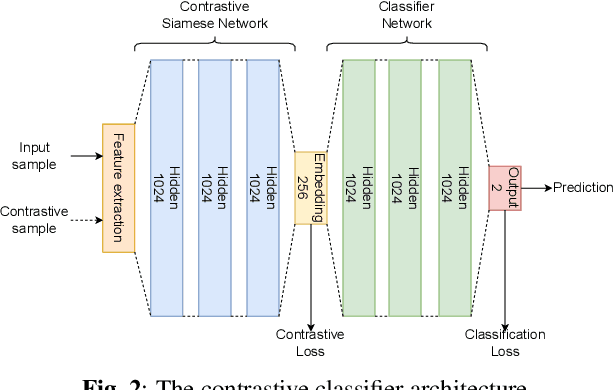
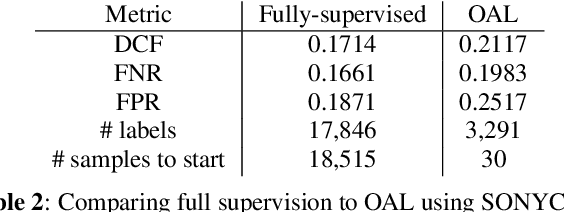
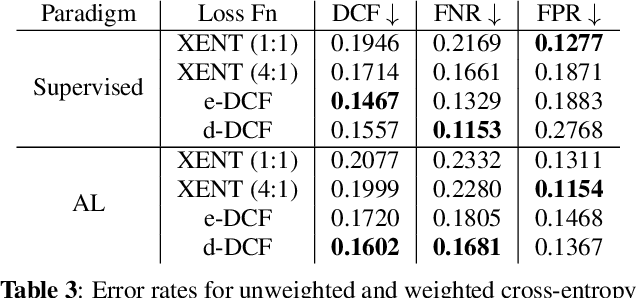
Abstract:Data collection and annotation is a laborious, time-consuming prerequisite for supervised machine learning tasks. Online Active Learning (OAL) is a paradigm that addresses this issue by simultaneously minimizing the amount of annotation required to train a classifier and adapting to changes in the data over the duration of the data collection process. Prior work has indicated that fluctuating class distributions and data drift are still common problems for OAL. This work presents new loss functions that address these challenges when OAL is applied to Sound Event Detection (SED). Experimental results from the SONYC dataset and two Voice-Type Discrimination (VTD) corpora indicate that OAL can reduce the time and effort required to train SED classifiers by a factor of 5 for SONYC, and that the new methods presented here successfully resolve issues present in existing OAL methods.
Importance of negative sampling in weak label learning
Sep 23, 2023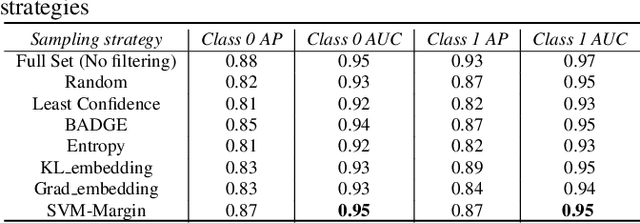
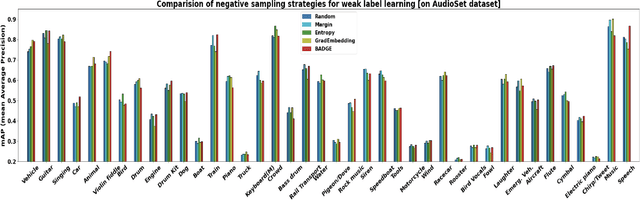
Abstract:Weak-label learning is a challenging task that requires learning from data "bags" containing positive and negative instances, but only the bag labels are known. The pool of negative instances is usually larger than positive instances, thus making selecting the most informative negative instance critical for performance. Such a selection strategy for negative instances from each bag is an open problem that has not been well studied for weak-label learning. In this paper, we study several sampling strategies that can measure the usefulness of negative instances for weak-label learning and select them accordingly. We test our method on CIFAR-10 and AudioSet datasets and show that it improves the weak-label classification performance and reduces the computational cost compared to random sampling methods. Our work reveals that negative instances are not all equally irrelevant, and selecting them wisely can benefit weak-label learning.
Plug in the Safety Chip: Enforcing Constraints for LLM-driven Robot Agents
Sep 18, 2023



Abstract:Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have enabled a new research domain, LLM agents, for solving robotics and planning tasks by leveraging the world knowledge and general reasoning abilities of LLMs obtained during pretraining. However, while considerable effort has been made to teach the robot the "dos," the "don'ts" received relatively less attention. We argue that, for any practical usage, it is as crucial to teach the robot the "don'ts": conveying explicit instructions about prohibited actions, assessing the robot's comprehension of these restrictions, and, most importantly, ensuring compliance. Moreover, verifiable safe operation is essential for deployments that satisfy worldwide standards such as ISO 61508, which defines standards for safely deploying robots in industrial factory environments worldwide. Aiming at deploying the LLM agents in a collaborative environment, we propose a queryable safety constraint module based on linear temporal logic (LTL) that simultaneously enables natural language (NL) to temporal constraints encoding, safety violation reasoning and explaining, and unsafe action pruning. To demonstrate the effectiveness of our system, we conducted experiments in VirtualHome environment and on a real robot. The experimental results show that our system strictly adheres to the safety constraints and scales well with complex safety constraints, highlighting its potential for practical utility.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge