Yixin Fei
GenAI-Bench: Evaluating and Improving Compositional Text-to-Visual Generation
Jun 19, 2024



Abstract:While text-to-visual models now produce photo-realistic images and videos, they struggle with compositional text prompts involving attributes, relationships, and higher-order reasoning such as logic and comparison. In this work, we conduct an extensive human study on GenAI-Bench to evaluate the performance of leading image and video generation models in various aspects of compositional text-to-visual generation. We also compare automated evaluation metrics against our collected human ratings and find that VQAScore -- a metric measuring the likelihood that a VQA model views an image as accurately depicting the prompt -- significantly outperforms previous metrics such as CLIPScore. In addition, VQAScore can improve generation in a black-box manner (without finetuning) via simply ranking a few (3 to 9) candidate images. Ranking by VQAScore is 2x to 3x more effective than other scoring methods like PickScore, HPSv2, and ImageReward at improving human alignment ratings for DALL-E 3 and Stable Diffusion, especially on compositional prompts that require advanced visio-linguistic reasoning. We will release a new GenAI-Rank benchmark with over 40,000 human ratings to evaluate scoring metrics on ranking images generated from the same prompt. Lastly, we discuss promising areas for improvement in VQAScore, such as addressing fine-grained visual details. We will release all human ratings (over 80,000) to facilitate scientific benchmarking of both generative models and automated metrics.
SIM2E: Benchmarking the Group Equivariant Capability of Correspondence Matching Algorithms
Aug 21, 2022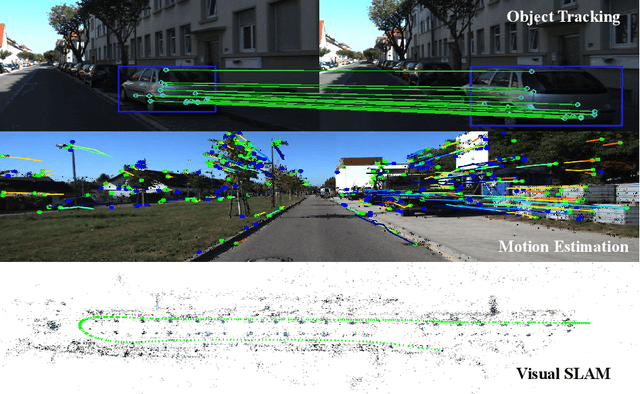
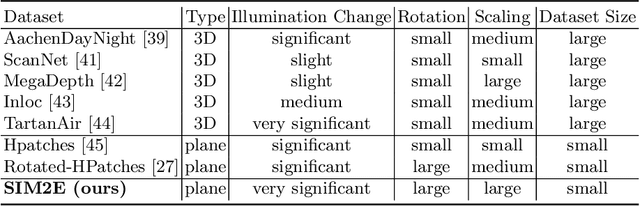
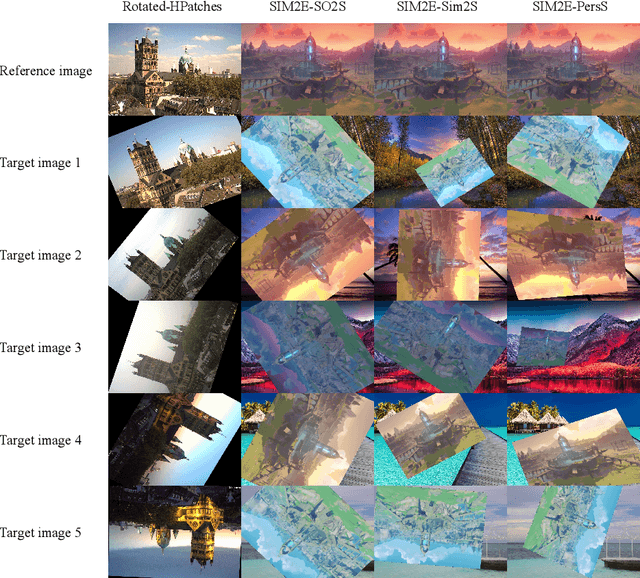
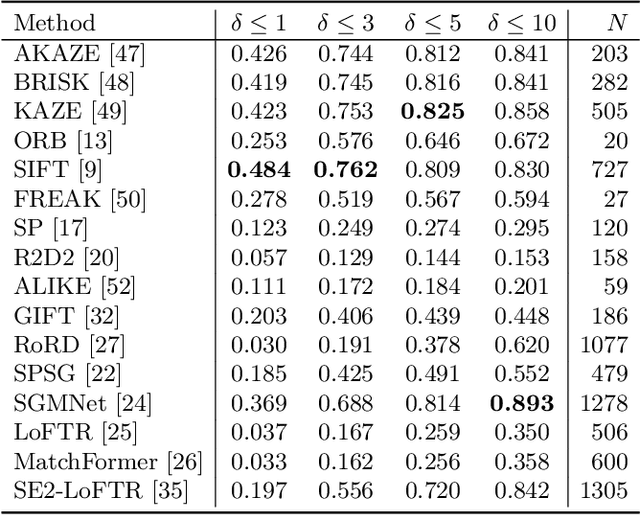
Abstract:Correspondence matching is a fundamental problem in computer vision and robotics applications. Solving correspondence matching problems using neural networks has been on the rise recently. Rotation-equivariance and scale-equivariance are both critical in correspondence matching applications. Classical correspondence matching approaches are designed to withstand scaling and rotation transformations. However, the features extracted using convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are only translation-equivariant to a certain extent. Recently, researchers have strived to improve the rotation-equivariance of CNNs based on group theories. Sim(2) is the group of similarity transformations in the 2D plane. This paper presents a specialized dataset dedicated to evaluating sim(2)-equivariant correspondence matching algorithms. We compare the performance of 16 state-of-the-art (SoTA) correspondence matching approaches. The experimental results demonstrate the importance of group equivariant algorithms for correspondence matching on various sim(2) transformation conditions. Since the subpixel accuracy achieved by CNN-based correspondence matching approaches is unsatisfactory, this specific area requires more attention in future works. Our dataset is publicly available at: mias.group/SIM2E.
XCon: Learning with Experts for Fine-grained Category Discovery
Aug 03, 2022
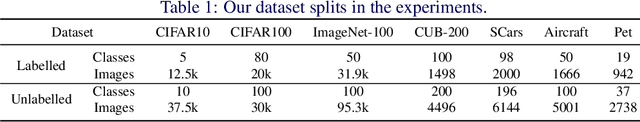
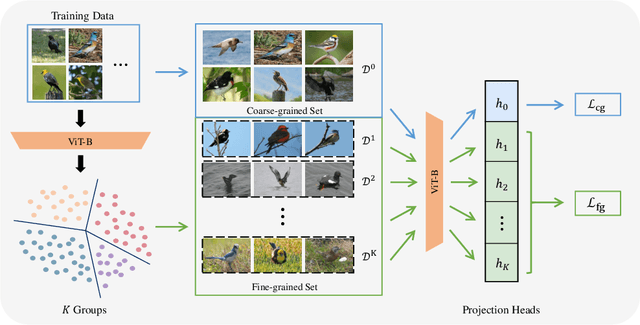
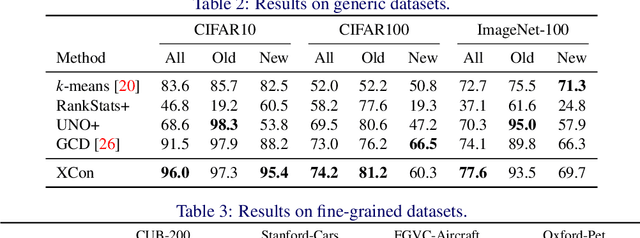
Abstract:We address the problem of generalized category discovery (GCD) in this paper, i.e. clustering the unlabeled images leveraging the information from a set of seen classes, where the unlabeled images could contain both seen classes and unseen classes. The seen classes can be seen as an implicit criterion of classes, which makes this setting different from unsupervised clustering where the cluster criteria may be ambiguous. We mainly concern the problem of discovering categories within a fine-grained dataset since it is one of the most direct applications of category discovery, i.e. helping experts discover novel concepts within an unlabeled dataset using the implicit criterion set forth by the seen classes. State-of-the-art methods for generalized category discovery leverage contrastive learning to learn the representations, but the large inter-class similarity and intra-class variance pose a challenge for the methods because the negative examples may contain irrelevant cues for recognizing a category so the algorithms may converge to a local-minima. We present a novel method called Expert-Contrastive Learning (XCon) to help the model to mine useful information from the images by first partitioning the dataset into sub-datasets using k-means clustering and then performing contrastive learning on each of the sub-datasets to learn fine-grained discriminative features. Experiments on fine-grained datasets show a clear improved performance over the previous best methods, indicating the effectiveness of our method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge