Qijun Chen
DST-Calib: A Dual-Path, Self-Supervised, Target-Free LiDAR-Camera Extrinsic Calibration Network
Jan 03, 2026Abstract:LiDAR-camera extrinsic calibration is essential for multi-modal data fusion in robotic perception systems. However, existing approaches typically rely on handcrafted calibration targets (e.g., checkerboards) or specific, static scene types, limiting their adaptability and deployment in real-world autonomous and robotic applications. This article presents the first self-supervised LiDAR-camera extrinsic calibration network that operates in an online fashion and eliminates the need for specific calibration targets. We first identify a significant generalization degradation problem in prior methods, caused by the conventional single-sided data augmentation strategy. To overcome this limitation, we propose a novel double-sided data augmentation technique that generates multi-perspective camera views using estimated depth maps, thereby enhancing robustness and diversity during training. Built upon this augmentation strategy, we design a dual-path, self-supervised calibration framework that reduces the dependence on high-precision ground truth labels and supports fully adaptive online calibration. Furthermore, to improve cross-modal feature association, we replace the traditional dual-branch feature extraction design with a difference map construction process that explicitly correlates LiDAR and camera features. This not only enhances calibration accuracy but also reduces model complexity. Extensive experiments conducted on five public benchmark datasets, as well as our own recorded dataset, demonstrate that the proposed method significantly outperforms existing approaches in terms of generalizability.
CLASH: Collaborative Large-Small Hierarchical Framework for Continuous Vision-and-Language Navigation
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) requires robots to follow natural language instructions and navigate complex environments without prior maps. While recent vision-language large models demonstrate strong reasoning abilities, they often underperform task-specific panoramic small models in VLN tasks. To address this, we propose CLASH (Collaborative Large-Small Hierarchy), a VLN-CE framework that integrates a reactive small-model planner (RSMP) with a reflective large-model reasoner (RLMR). RSMP adopts a causal-learning-based dual-branch architecture to enhance generalization, while RLMR leverages panoramic visual prompting with chain-of-thought reasoning to support interpretable spatial understanding and navigation. We further introduce an uncertainty-aware collaboration mechanism (UCM) that adaptively fuses decisions from both models. For obstacle avoidance, in simulation, we replace the rule-based controller with a fully learnable point-goal policy, and in real-world deployment, we design a LiDAR-based clustering module for generating navigable waypoints and pair it with an online SLAM-based local controller. CLASH achieves state-of-the-art (SoTA) results (ranking 1-st) on the VLN-CE leaderboard, significantly improving SR and SPL on the test-unseen set over the previous SoTA methods. Real-world experiments demonstrate CLASH's strong robustness, validating its effectiveness in both simulation and deployment scenarios.
Rethinking the Embodied Gap in Vision-and-Language Navigation: A Holistic Study of Physical and Visual Disparities
Jul 17, 2025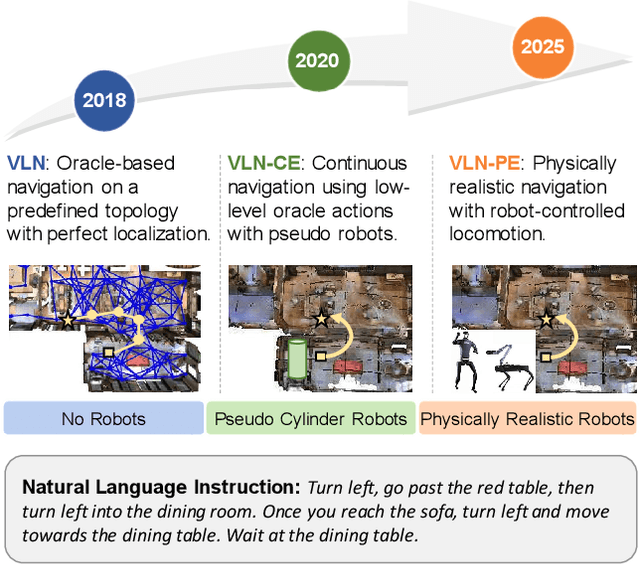
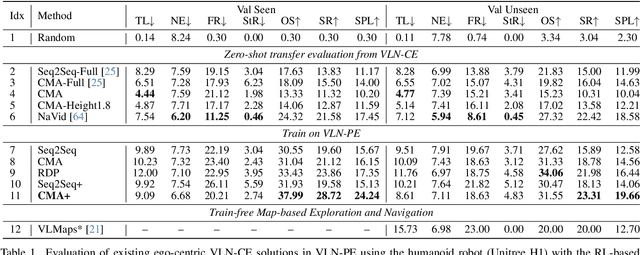
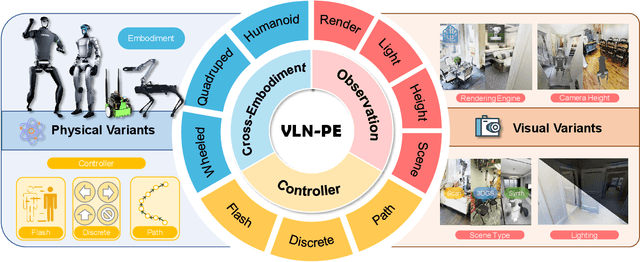
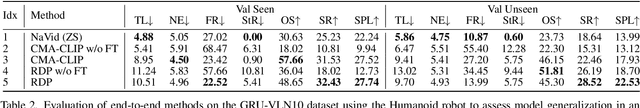
Abstract:Recent Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) advancements are promising, but their idealized assumptions about robot movement and control fail to reflect physically embodied deployment challenges. To bridge this gap, we introduce VLN-PE, a physically realistic VLN platform supporting humanoid, quadruped, and wheeled robots. For the first time, we systematically evaluate several ego-centric VLN methods in physical robotic settings across different technical pipelines, including classification models for single-step discrete action prediction, a diffusion model for dense waypoint prediction, and a train-free, map-based large language model (LLM) integrated with path planning. Our results reveal significant performance degradation due to limited robot observation space, environmental lighting variations, and physical challenges like collisions and falls. This also exposes locomotion constraints for legged robots in complex environments. VLN-PE is highly extensible, allowing seamless integration of new scenes beyond MP3D, thereby enabling more comprehensive VLN evaluation. Despite the weak generalization of current models in physical deployment, VLN-PE provides a new pathway for improving cross-embodiment's overall adaptability. We hope our findings and tools inspire the community to rethink VLN limitations and advance robust, practical VLN models. The code is available at https://crystalsixone.github.io/vln_pe.github.io/.
Realizing Text-Driven Motion Generation on NAO Robot: A Reinforcement Learning-Optimized Control Pipeline
Jun 05, 2025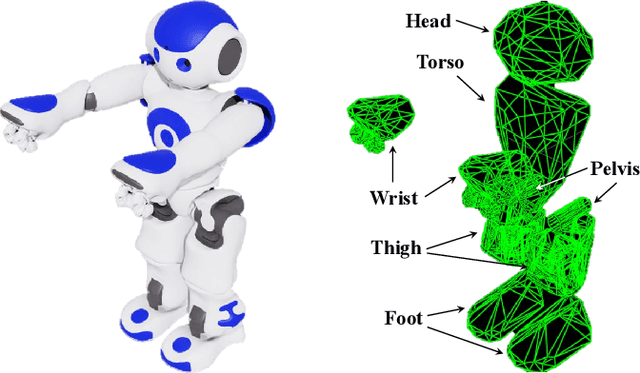
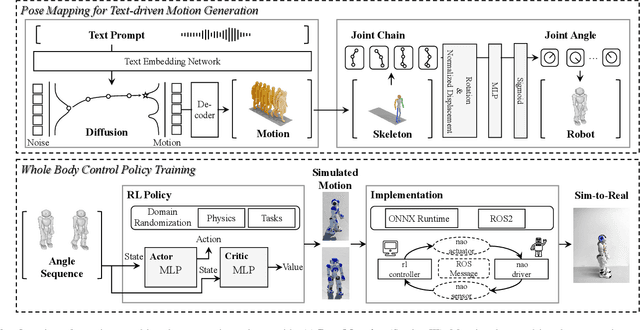
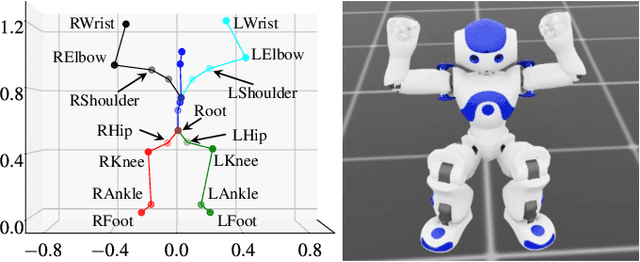
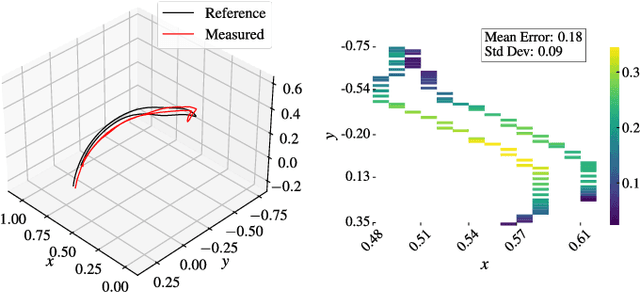
Abstract:Human motion retargeting for humanoid robots, transferring human motion data to robots for imitation, presents significant challenges but offers considerable potential for real-world applications. Traditionally, this process relies on human demonstrations captured through pose estimation or motion capture systems. In this paper, we explore a text-driven approach to mapping human motion to humanoids. To address the inherent discrepancies between the generated motion representations and the kinematic constraints of humanoid robots, we propose an angle signal network based on norm-position and rotation loss (NPR Loss). It generates joint angles, which serve as inputs to a reinforcement learning-based whole-body joint motion control policy. The policy ensures tracking of the generated motions while maintaining the robot's stability during execution. Our experimental results demonstrate the efficacy of this approach, successfully transferring text-driven human motion to a real humanoid robot NAO.
A Birotation Solution for Relative Pose Problems
May 04, 2025Abstract:Relative pose estimation, a fundamental computer vision problem, has been extensively studied for decades. Existing methods either estimate and decompose the essential matrix or directly estimate the rotation and translation to obtain the solution. In this article, we break the mold by tackling this traditional problem with a novel birotation solution. We first introduce three basis transformations, each associated with a geometric metric to quantify the distance between the relative pose to be estimated and its corresponding basis transformation. Three energy functions, designed based on these metrics, are then minimized on the Riemannian manifold $\mathrm{SO(3)}$ by iteratively updating the two rotation matrices. The two rotation matrices and the basis transformation corresponding to the minimum energy are ultimately utilized to recover the relative pose. Extensive quantitative and qualitative evaluations across diverse relative pose estimation tasks demonstrate the superior performance of our proposed birotation solution. Source code, demo video, and datasets will be available at \href{https://mias.group/birotation-solution}{mias.group/birotation-solution} upon publication.
A Real-time Multimodal Transformer Neural Network-powered Wildfire Forecasting System
Mar 07, 2025Abstract:Due to climate change, the extreme wildfire has become one of the most dangerous natural hazards to human civilization. Even though, some wildfires may be initially caused by human activity, but the spread of wildfires is mainly determined by environmental factors, for examples, (1) weather conditions such as temperature, wind direction and intensity, and moisture levels; (2) the amount and types of dry vegetation in a local area, and (3) topographic or local terrian conditions, which affects how much rain an area gets and how fire dynamics will be constrained or faciliated. Thus, to accurately forecast wildfire occurrence has become one of most urgent and taunting environmental challenges in global scale. In this work, we developed a real-time Multimodal Transformer Neural Network Machine Learning model that combines several advanced artificial intelligence techniques and statistical methods to practically forecast the occurrence of wildfire at the precise location in real time, which not only utilizes large scale data information such as hourly weather forecasting data, but also takes into account small scale topographical data such as local terrain condition and local vegetation conditions collecting from Google Earth images to determine the probabilities of wildfire occurrence location at small scale as well as their timing synchronized with weather forecast information. By using the wildfire data in the United States from 1992 to 2015 to train the multimodal transformer neural network, it can predict the probabilities of wildfire occurrence according to the real-time weather forecast and the synchronized Google Earth image data to provide the wildfire occurrence probability in any small location ($100m^2$) within 24 hours ahead.
Fully Exploiting Vision Foundation Model's Profound Prior Knowledge for Generalizable RGB-Depth Driving Scene Parsing
Feb 10, 2025



Abstract:Recent vision foundation models (VFMs), typically based on Vision Transformer (ViT), have significantly advanced numerous computer vision tasks. Despite their success in tasks focused solely on RGB images, the potential of VFMs in RGB-depth driving scene parsing remains largely under-explored. In this article, we take one step toward this emerging research area by investigating a feasible technique to fully exploit VFMs for generalizable RGB-depth driving scene parsing. Specifically, we explore the inherent characteristics of RGB and depth data, thereby presenting a Heterogeneous Feature Integration Transformer (HFIT). This network enables the efficient extraction and integration of comprehensive heterogeneous features without re-training ViTs. Relative depth prediction results from VFMs, used as inputs to the HFIT side adapter, overcome the limitations of the dependence on depth maps. Our proposed HFIT demonstrates superior performance compared to all other traditional single-modal and data-fusion scene parsing networks, pre-trained VFMs, and ViT adapters on the Cityscapes and KITTI Semantics datasets. We believe this novel strategy paves the way for future innovations in VFM-based data-fusion techniques for driving scene parsing. Our source code is publicly available at https://mias.group/HFIT.
CleanPose: Category-Level Object Pose Estimation via Causal Learning and Knowledge Distillation
Feb 03, 2025



Abstract:Category-level object pose estimation aims to recover the rotation, translation and size of unseen instances within predefined categories. In this task, deep neural network-based methods have demonstrated remarkable performance. However, previous studies show they suffer from spurious correlations raised by "unclean" confounders in models, hindering their performance on novel instances with significant variations. To address this issue, we propose CleanPose, a novel approach integrating causal learning and knowledge distillation to enhance category-level pose estimation. To mitigate the negative effect of unobserved confounders, we develop a causal inference module based on front-door adjustment, which promotes unbiased estimation by reducing potential spurious correlations. Additionally, to further improve generalization ability, we devise a residual-based knowledge distillation method that has proven effective in providing comprehensive category information guidance. Extensive experiments across multiple benchmarks (REAL275, CAMERA25 and HouseCat6D) hightlight the superiority of proposed CleanPose over state-of-the-art methods. Code will be released.
These Maps Are Made by Propagation: Adapting Deep Stereo Networks to Road Scenarios with Decisive Disparity Diffusion
Nov 06, 2024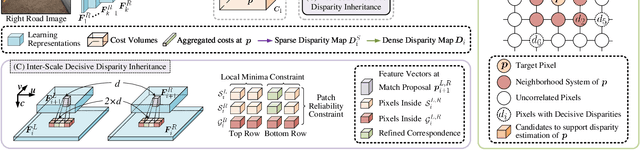
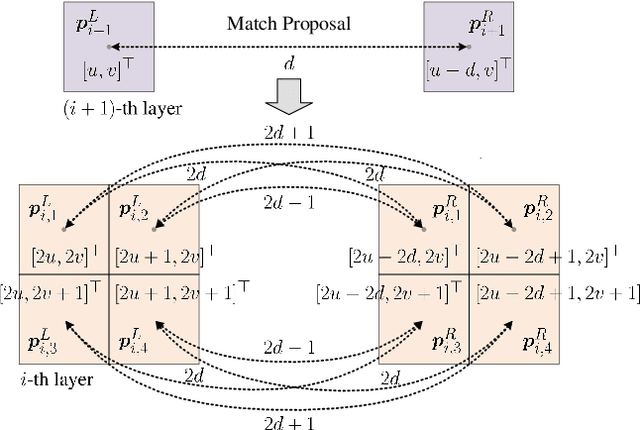
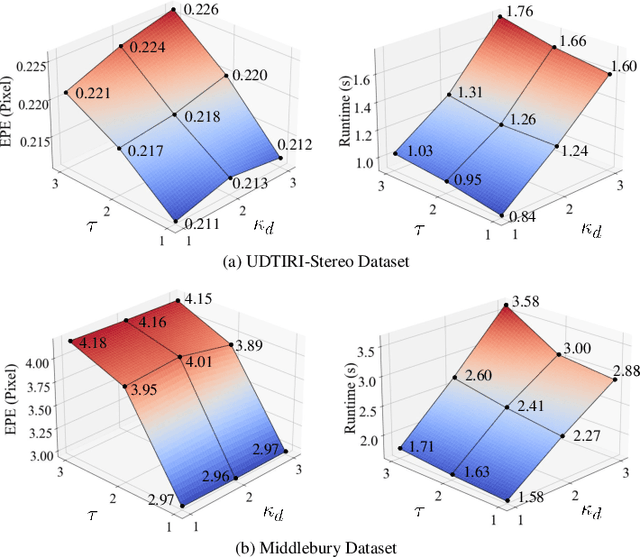
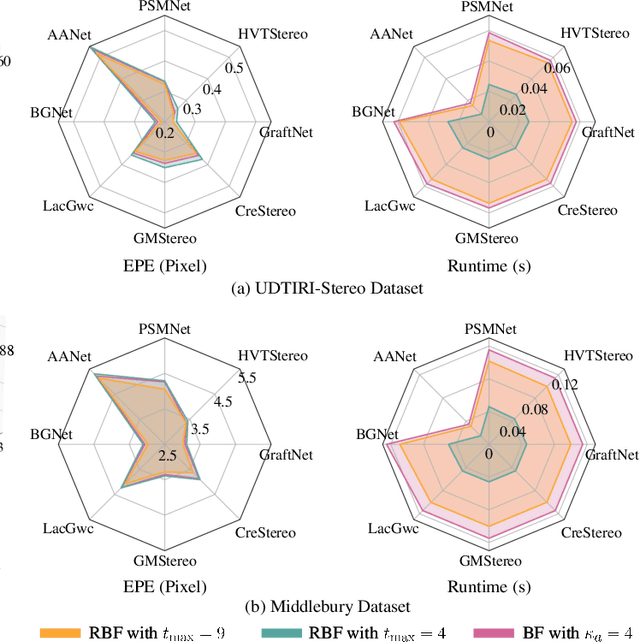
Abstract:Stereo matching has emerged as a cost-effective solution for road surface 3D reconstruction, garnering significant attention towards improving both computational efficiency and accuracy. This article introduces decisive disparity diffusion (D3Stereo), marking the first exploration of dense deep feature matching that adapts pre-trained deep convolutional neural networks (DCNNs) to previously unseen road scenarios. A pyramid of cost volumes is initially created using various levels of learned representations. Subsequently, a novel recursive bilateral filtering algorithm is employed to aggregate these costs. A key innovation of D3Stereo lies in its alternating decisive disparity diffusion strategy, wherein intra-scale diffusion is employed to complete sparse disparity images, while inter-scale inheritance provides valuable prior information for higher resolutions. Extensive experiments conducted on our created UDTIRI-Stereo and Stereo-Road datasets underscore the effectiveness of D3Stereo strategy in adapting pre-trained DCNNs and its superior performance compared to all other explicit programming-based algorithms designed specifically for road surface 3D reconstruction. Additional experiments conducted on the Middlebury dataset with backbone DCNNs pre-trained on the ImageNet database further validate the versatility of D3Stereo strategy in tackling general stereo matching problems.
MoTE: Reconciling Generalization with Specialization for Visual-Language to Video Knowledge Transfer
Oct 14, 2024Abstract:Transferring visual-language knowledge from large-scale foundation models for video recognition has proved to be effective. To bridge the domain gap, additional parametric modules are added to capture the temporal information. However, zero-shot generalization diminishes with the increase in the number of specialized parameters, making existing works a trade-off between zero-shot and close-set performance. In this paper, we present MoTE, a novel framework that enables generalization and specialization to be balanced in one unified model. Our approach tunes a mixture of temporal experts to learn multiple task views with various degrees of data fitting. To maximally preserve the knowledge of each expert, we propose \emph{Weight Merging Regularization}, which regularizes the merging process of experts in weight space. Additionally with temporal feature modulation to regularize the contribution of temporal feature during test. We achieve a sound balance between zero-shot and close-set video recognition tasks and obtain state-of-the-art or competitive results on various datasets, including Kinetics-400 \& 600, UCF, and HMDB. Code is available at \url{https://github.com/ZMHH-H/MoTE}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge