Mengxian Hu
CLASH: Collaborative Large-Small Hierarchical Framework for Continuous Vision-and-Language Navigation
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) requires robots to follow natural language instructions and navigate complex environments without prior maps. While recent vision-language large models demonstrate strong reasoning abilities, they often underperform task-specific panoramic small models in VLN tasks. To address this, we propose CLASH (Collaborative Large-Small Hierarchy), a VLN-CE framework that integrates a reactive small-model planner (RSMP) with a reflective large-model reasoner (RLMR). RSMP adopts a causal-learning-based dual-branch architecture to enhance generalization, while RLMR leverages panoramic visual prompting with chain-of-thought reasoning to support interpretable spatial understanding and navigation. We further introduce an uncertainty-aware collaboration mechanism (UCM) that adaptively fuses decisions from both models. For obstacle avoidance, in simulation, we replace the rule-based controller with a fully learnable point-goal policy, and in real-world deployment, we design a LiDAR-based clustering module for generating navigable waypoints and pair it with an online SLAM-based local controller. CLASH achieves state-of-the-art (SoTA) results (ranking 1-st) on the VLN-CE leaderboard, significantly improving SR and SPL on the test-unseen set over the previous SoTA methods. Real-world experiments demonstrate CLASH's strong robustness, validating its effectiveness in both simulation and deployment scenarios.
Realizing Text-Driven Motion Generation on NAO Robot: A Reinforcement Learning-Optimized Control Pipeline
Jun 05, 2025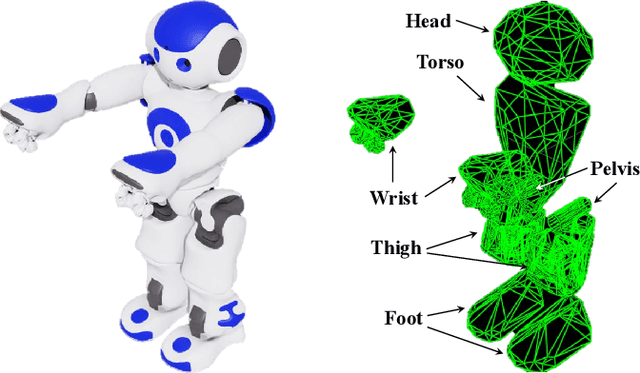
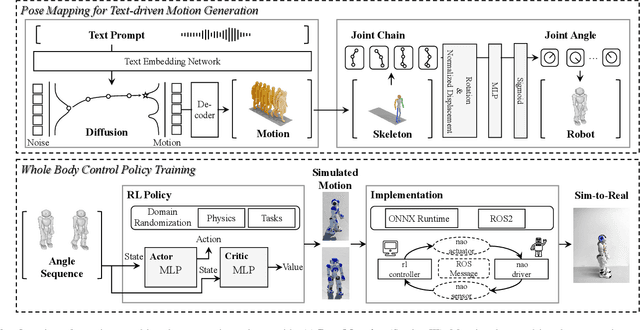
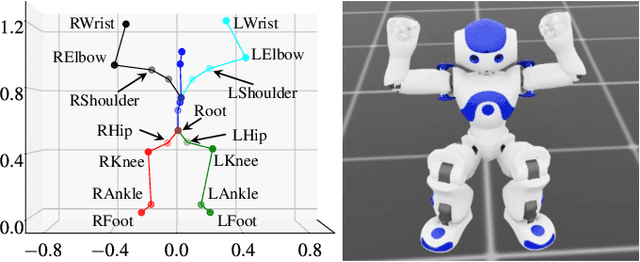
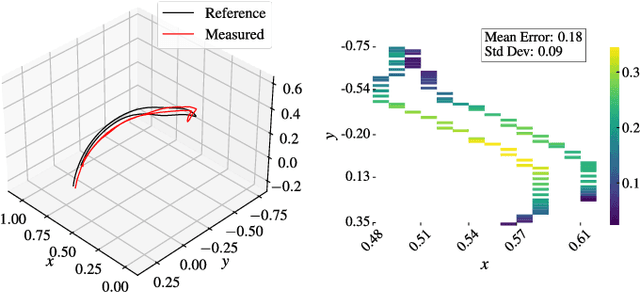
Abstract:Human motion retargeting for humanoid robots, transferring human motion data to robots for imitation, presents significant challenges but offers considerable potential for real-world applications. Traditionally, this process relies on human demonstrations captured through pose estimation or motion capture systems. In this paper, we explore a text-driven approach to mapping human motion to humanoids. To address the inherent discrepancies between the generated motion representations and the kinematic constraints of humanoid robots, we propose an angle signal network based on norm-position and rotation loss (NPR Loss). It generates joint angles, which serve as inputs to a reinforcement learning-based whole-body joint motion control policy. The policy ensures tracking of the generated motions while maintaining the robot's stability during execution. Our experimental results demonstrate the efficacy of this approach, successfully transferring text-driven human motion to a real humanoid robot NAO.
MoTE: Reconciling Generalization with Specialization for Visual-Language to Video Knowledge Transfer
Oct 14, 2024Abstract:Transferring visual-language knowledge from large-scale foundation models for video recognition has proved to be effective. To bridge the domain gap, additional parametric modules are added to capture the temporal information. However, zero-shot generalization diminishes with the increase in the number of specialized parameters, making existing works a trade-off between zero-shot and close-set performance. In this paper, we present MoTE, a novel framework that enables generalization and specialization to be balanced in one unified model. Our approach tunes a mixture of temporal experts to learn multiple task views with various degrees of data fitting. To maximally preserve the knowledge of each expert, we propose \emph{Weight Merging Regularization}, which regularizes the merging process of experts in weight space. Additionally with temporal feature modulation to regularize the contribution of temporal feature during test. We achieve a sound balance between zero-shot and close-set video recognition tasks and obtain state-of-the-art or competitive results on various datasets, including Kinetics-400 \& 600, UCF, and HMDB. Code is available at \url{https://github.com/ZMHH-H/MoTE}.
Efficient Text-driven Motion Generation via Latent Consistency Training
May 05, 2024Abstract:Motion diffusion models have recently proven successful for text-driven human motion generation. Despite their excellent generation performance, they are challenging to infer in real time due to the multi-step sampling mechanism that involves tens or hundreds of repeat function evaluation iterations. To this end, we investigate a motion latent consistency Training (MLCT) for motion generation to alleviate the computation and time consumption during iteration inference. It applies diffusion pipelines to low-dimensional motion latent spaces to mitigate the computational burden of each function evaluation. Explaining the diffusion process with probabilistic flow ordinary differential equation (PF-ODE) theory, the MLCT allows extremely few steps infer between the prior distribution to the motion latent representation distribution via maintaining consistency of the outputs over the trajectory of PF-ODE. Especially, we introduce a quantization constraint to optimize motion latent representations that are bounded, regular, and well-reconstructed compared to traditional variational constraints. Furthermore, we propose a conditional PF-ODE trajectory simulation method, which improves the conditional generation performance with minimal additional training costs. Extensive experiments on two human motion generation benchmarks show that the proposed model achieves state-of-the-art performance with less than 10\% time cost.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge