Yaoyao Liu
FreeOrbit4D: Training-Free Arbitrary Camera Redirection for Monocular Videos via Geometry-Complete 4D Reconstruction
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Camera redirection aims to replay a dynamic scene from a single monocular video under a user-specified camera trajectory. However, large-angle redirection is inherently ill-posed: a monocular video captures only a narrow spatio-temporal view of a dynamic 3D scene, providing highly partial observations of the underlying 4D world. The key challenge is therefore to recover a complete and coherent representation from this limited input, with consistent geometry and motion. While recent diffusion-based methods achieve impressive results, they often break down under large-angle viewpoint changes far from the original trajectory, where missing visual grounding leads to severe geometric ambiguity and temporal inconsistency. To address this, we present FreeOrbit4D, an effective training-free framework that tackles this geometric ambiguity by recovering a geometry-complete 4D proxy as structural grounding for video generation. We obtain this proxy by decoupling foreground and background reconstructions: we unproject the monocular video into a static background and geometry-incomplete foreground point clouds in a unified global space, then leverage an object-centric multi-view diffusion model to synthesize multi-view images and reconstruct geometry-complete foreground point clouds in canonical object space. By aligning the canonical foreground point cloud to the global scene space via dense pixel-synchronized 3D--3D correspondences and projecting the geometry-complete 4D proxy onto target camera viewpoints, we provide geometric scaffolds that guide a conditional video diffusion model. Extensive experiments show that FreeOrbit4D produces more faithful redirected videos under challenging large-angle trajectories, and our geometry-complete 4D proxy further opens a potential avenue for practical applications such as edit propagation and 4D data generation. Project page and code will be released soon.
Towards Generalized Routing: Model and Agent Orchestration for Adaptive and Efficient Inference
Sep 09, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) and domain-specific AI agents has greatly expanded the ecosystem of AI-powered services. User queries, however, are highly diverse and often span multiple domains and task types, resulting in a complex and heterogeneous landscape. This diversity presents a fundamental routing challenge: how to accurately direct each query to an appropriate execution unit while optimizing both performance and efficiency. To address this, we propose MoMA (Mixture of Models and Agents), a generalized routing framework that integrates both LLM and agent-based routing. Built upon a deep understanding of model and agent capabilities, MoMA effectively handles diverse queries through precise intent recognition and adaptive routing strategies, achieving an optimal balance between efficiency and cost. Specifically, we construct a detailed training dataset to profile the capabilities of various LLMs under different routing model structures, identifying the most suitable tasks for each LLM. During inference, queries are dynamically routed to the LLM with the best cost-performance efficiency. We also introduce an efficient agent selection strategy based on a context-aware state machine and dynamic masking. Experimental results demonstrate that the MoMA router offers superior cost-efficiency and scalability compared to existing approaches.
iNeMo: Incremental Neural Mesh Models for Robust Class-Incremental Learning
Jul 12, 2024Abstract:Different from human nature, it is still common practice today for vision tasks to train deep learning models only initially and on fixed datasets. A variety of approaches have recently addressed handling continual data streams. However, extending these methods to manage out-of-distribution (OOD) scenarios has not effectively been investigated. On the other hand, it has recently been shown that non-continual neural mesh models exhibit strong performance in generalizing to such OOD scenarios. To leverage this decisive property in a continual learning setting, we propose incremental neural mesh models that can be extended with new meshes over time. In addition, we present a latent space initialization strategy that enables us to allocate feature space for future unseen classes in advance and a positional regularization term that forces the features of the different classes to consistently stay in respective latent space regions. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method through extensive experiments on the Pascal3D and ObjectNet3D datasets and show that our approach outperforms the baselines for classification by $2-6\%$ in the in-domain and by $6-50\%$ in the OOD setting. Our work also presents the first incremental learning approach for pose estimation. Our code and model can be found at https://github.com/Fischer-Tom/iNeMo.
ImageNet3D: Towards General-Purpose Object-Level 3D Understanding
Jun 13, 2024
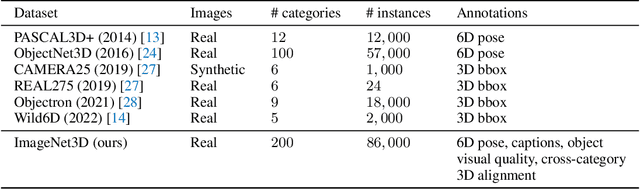

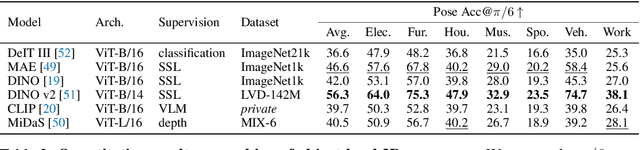
Abstract:A vision model with general-purpose object-level 3D understanding should be capable of inferring both 2D (e.g., class name and bounding box) and 3D information (e.g., 3D location and 3D viewpoint) for arbitrary rigid objects in natural images. This is a challenging task, as it involves inferring 3D information from 2D signals and most importantly, generalizing to rigid objects from unseen categories. However, existing datasets with object-level 3D annotations are often limited by the number of categories or the quality of annotations. Models developed on these datasets become specialists for certain categories or domains, and fail to generalize. In this work, we present ImageNet3D, a large dataset for general-purpose object-level 3D understanding. ImageNet3D augments 200 categories from the ImageNet dataset with 2D bounding box, 3D pose, 3D location annotations, and image captions interleaved with 3D information. With the new annotations available in ImageNet3D, we could (i) analyze the object-level 3D awareness of visual foundation models, and (ii) study and develop general-purpose models that infer both 2D and 3D information for arbitrary rigid objects in natural images, and (iii) integrate unified 3D models with large language models for 3D-related reasoning.. We consider two new tasks, probing of object-level 3D awareness and open vocabulary pose estimation, besides standard classification and pose estimation. Experimental results on ImageNet3D demonstrate the potential of our dataset in building vision models with stronger general-purpose object-level 3D understanding.
HDR-GS: Efficient High Dynamic Range Novel View Synthesis at 1000x Speed via Gaussian Splatting
May 27, 2024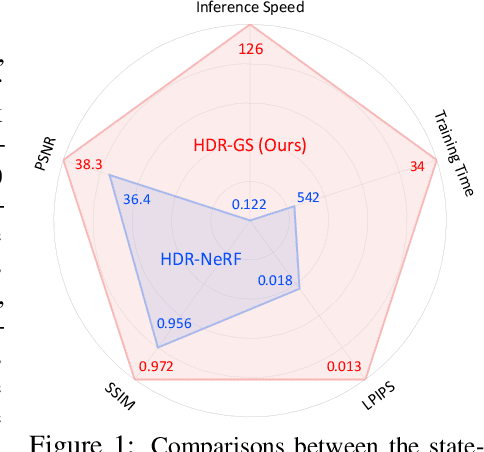
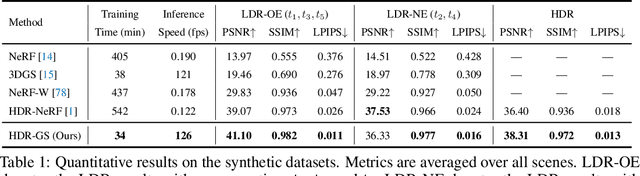

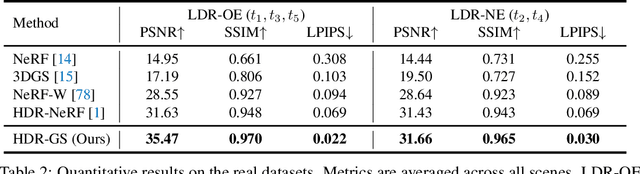
Abstract:High dynamic range (HDR) novel view synthesis (NVS) aims to create photorealistic images from novel viewpoints using HDR imaging techniques. The rendered HDR images capture a wider range of brightness levels containing more details of the scene than normal low dynamic range (LDR) images. Existing HDR NVS methods are mainly based on NeRF. They suffer from long training time and slow inference speed. In this paper, we propose a new framework, High Dynamic Range Gaussian Splatting (HDR-GS), which can efficiently render novel HDR views and reconstruct LDR images with a user input exposure time. Specifically, we design a Dual Dynamic Range (DDR) Gaussian point cloud model that uses spherical harmonics to fit HDR color and employs an MLP-based tone-mapper to render LDR color. The HDR and LDR colors are then fed into two Parallel Differentiable Rasterization (PDR) processes to reconstruct HDR and LDR views. To establish the data foundation for the research of 3D Gaussian splatting-based methods in HDR NVS, we recalibrate the camera parameters and compute the initial positions for Gaussian point clouds. Experiments demonstrate that our HDR-GS surpasses the state-of-the-art NeRF-based method by 3.84 and 1.91 dB on LDR and HDR NVS while enjoying 1000x inference speed and only requiring 6.3% training time. Code, models, and recalibrated data will be publicly available at https://github.com/caiyuanhao1998/HDR-GS
Learning a Category-level Object Pose Estimator without Pose Annotations
Apr 08, 2024



Abstract:3D object pose estimation is a challenging task. Previous works always require thousands of object images with annotated poses for learning the 3D pose correspondence, which is laborious and time-consuming for labeling. In this paper, we propose to learn a category-level 3D object pose estimator without pose annotations. Instead of using manually annotated images, we leverage diffusion models (e.g., Zero-1-to-3) to generate a set of images under controlled pose differences and propose to learn our object pose estimator with those images. Directly using the original diffusion model leads to images with noisy poses and artifacts. To tackle this issue, firstly, we exploit an image encoder, which is learned from a specially designed contrastive pose learning, to filter the unreasonable details and extract image feature maps. Additionally, we propose a novel learning strategy that allows the model to learn object poses from those generated image sets without knowing the alignment of their canonical poses. Experimental results show that our method has the capability of category-level object pose estimation from a single shot setting (as pose definition), while significantly outperforming other state-of-the-art methods on the few-shot category-level object pose estimation benchmarks.
Continual Adversarial Defense
Dec 15, 2023



Abstract:In response to the rapidly evolving nature of adversarial attacks on a monthly basis, numerous defenses have been proposed to generalize against as many known attacks as possible. However, designing a defense method that can generalize to all types of attacks, including unseen ones, is not realistic because the environment in which defense systems operate is dynamic and comprises various unique attacks used by many attackers. The defense system needs to upgrade itself by utilizing few-shot defense feedback and efficient memory. Therefore, we propose the first continual adversarial defense (CAD) framework that adapts to any attacks in a dynamic scenario, where various attacks emerge stage by stage. In practice, CAD is modeled under four principles: (1) continual adaptation to new attacks without catastrophic forgetting, (2) few-shot adaptation, (3) memory-efficient adaptation, and (4) high accuracy on both clean and adversarial images. We leverage cutting-edge continual learning, few-shot learning, and ensemble learning techniques to qualify the principles. Experiments conducted on CIFAR-10 and ImageNet-100 validate the effectiveness of our approach against multiple stages of 10 modern adversarial attacks and significant improvements over 10 baseline methods. In particular, CAD is capable of quickly adapting with minimal feedback and a low cost of defense failure, while maintaining good performance against old attacks. Our research sheds light on a brand-new paradigm for continual defense adaptation against dynamic and evolving attacks.
Prompt-Based Exemplar Super-Compression and Regeneration for Class-Incremental Learning
Nov 30, 2023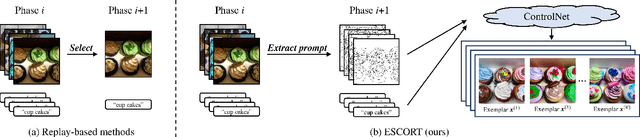
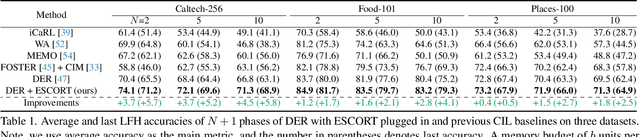
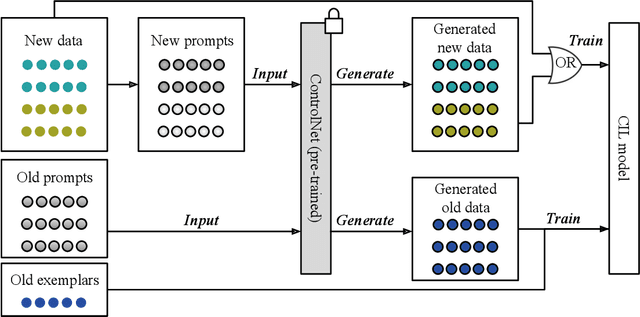
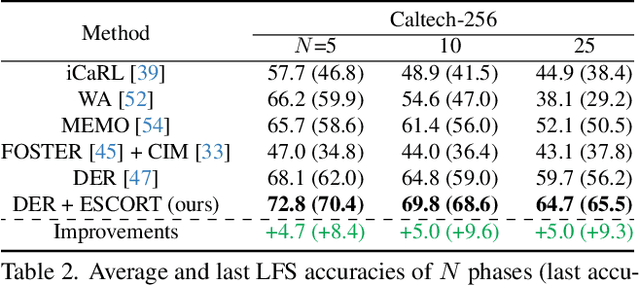
Abstract:Replay-based methods in class-incremental learning (CIL) have attained remarkable success, as replaying the exemplars of old classes can significantly mitigate catastrophic forgetting. Despite their effectiveness, the inherent memory restrictions of CIL result in saving a limited number of exemplars with poor diversity, leading to data imbalance and overfitting issues. In this paper, we introduce a novel exemplar super-compression and regeneration method, ESCORT, which substantially increases the quantity and enhances the diversity of exemplars. Rather than storing past images, we compress images into visual and textual prompts, e.g., edge maps and class tags, and save the prompts instead, reducing the memory usage of each exemplar to 1/24 of the original size. In subsequent learning phases, diverse high-resolution exemplars are generated from the prompts by a pre-trained diffusion model, e.g., ControlNet. To minimize the domain gap between generated exemplars and real images, we propose partial compression and diffusion-based data augmentation, allowing us to utilize an off-the-shelf diffusion model without fine-tuning it on the target dataset. Therefore, the same diffusion model can be downloaded whenever it is needed, incurring no memory consumption. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our method significantly improves model performance across multiple CIL benchmarks, e.g., 5.0 percentage points higher than the previous state-of-the-art on 10-phase Caltech-256 dataset.
Wakening Past Concepts without Past Data: Class-Incremental Learning from Online Placebos
Oct 24, 2023Abstract:Not forgetting old class knowledge is a key challenge for class-incremental learning (CIL) when the model continuously adapts to new classes. A common technique to address this is knowledge distillation (KD), which penalizes prediction inconsistencies between old and new models. Such prediction is made with almost new class data, as old class data is extremely scarce due to the strict memory limitation in CIL. In this paper, we take a deep dive into KD losses and find that "using new class data for KD" not only hinders the model adaption (for learning new classes) but also results in low efficiency for preserving old class knowledge. We address this by "using the placebos of old classes for KD", where the placebos are chosen from a free image stream, such as Google Images, in an automatical and economical fashion. To this end, we train an online placebo selection policy to quickly evaluate the quality of streaming images (good or bad placebos) and use only good ones for one-time feed-forward computation of KD. We formulate the policy training process as an online Markov Decision Process (MDP), and introduce an online learning algorithm to solve this MDP problem without causing much computation costs. In experiments, we show that our method 1) is surprisingly effective even when there is no class overlap between placebos and original old class data, 2) does not require any additional supervision or memory budget, and 3) significantly outperforms a number of top-performing CIL methods, in particular when using lower memory budgets for old class exemplars, e.g., five exemplars per class.
Adding 3D Geometry Control to Diffusion Models
Jun 13, 2023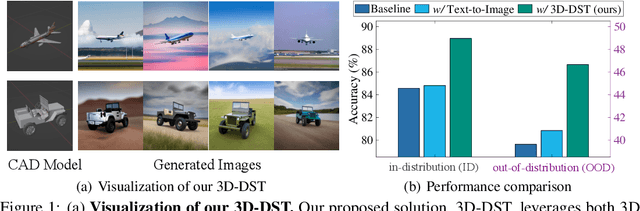
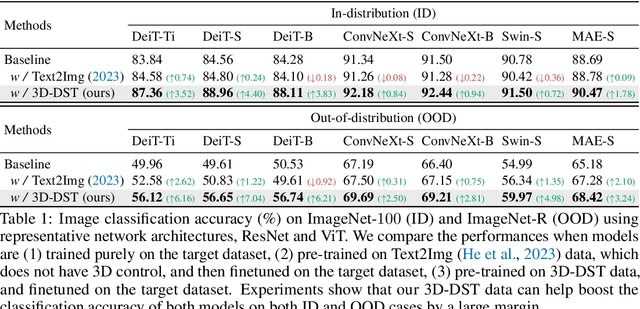
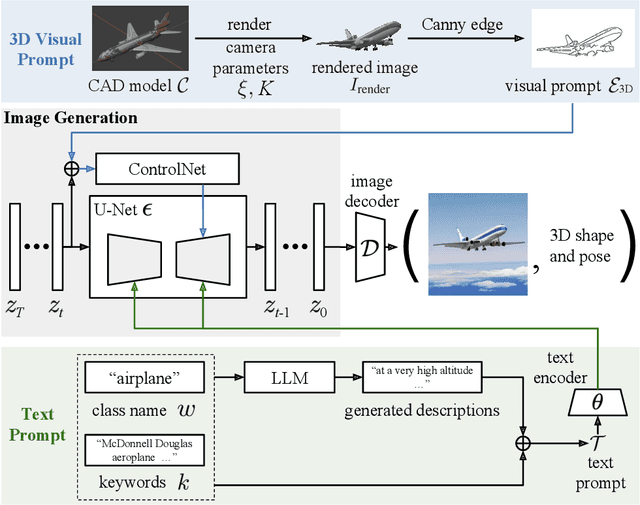
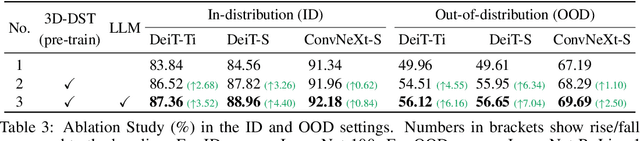
Abstract:Diffusion models have emerged as a powerful method of generative modeling across a range of fields, capable of producing stunning photo-realistic images from natural language descriptions. However, these models lack explicit control over the 3D structure of the objects in the generated images. In this paper, we propose a novel method that incorporates 3D geometry control into diffusion models, making them generate even more realistic and diverse images. To achieve this, our method exploits ControlNet, which extends diffusion models by using visual prompts in addition to text prompts. We generate images of 3D objects taken from a 3D shape repository (e.g., ShapeNet and Objaverse), render them from a variety of poses and viewing directions, compute the edge maps of the rendered images, and use these edge maps as visual prompts to generate realistic images. With explicit 3D geometry control, we can easily change the 3D structures of the objects in the generated images and obtain ground-truth 3D annotations automatically. This allows us to use the generated images to improve a lot of vision tasks, e.g., classification and 3D pose estimation, in both in-distribution (ID) and out-of-distribution (OOD) settings. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method through extensive experiments on ImageNet-50, ImageNet-R, PASCAL3D+, ObjectNet3D, and OOD-CV datasets. The results show that our method significantly outperforms existing methods across multiple benchmarks (e.g., 4.6 percentage points on ImageNet-50 using ViT and 3.5 percentage points on PASCAL3D+ and ObjectNet3D using NeMo).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge