Yueqi Duan
Revisiting 3D Reconstruction Kernels as Low-Pass Filters
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:3D reconstruction is to recover 3D signals from the sampled discrete 2D pixels, with the goal to converge continuous 3D spaces. In this paper, we revisit 3D reconstruction from the perspective of signal processing, identifying the periodic spectral extension induced by discrete sampling as the fundamental challenge. Previous 3D reconstruction kernels, such as Gaussians, Exponential functions, and Student's t distributions, serve as the low pass filters to isolate the baseband spectrum. However, their unideal low-pass property results in the overlap of high-frequency components with low-frequency components in the discrete-time signal's spectrum. To this end, we introduce Jinc kernel with an instantaneous drop to zero magnitude exactly at the cutoff frequency, which is corresponding to the ideal low pass filters. As Jinc kernel suffers from low decay speed in the spatial domain, we further propose modulated kernels to strick an effective balance, and achieves superior rendering performance by reconciling spatial efficiency and frequency-domain fidelity. Experimental results have demonstrated the effectiveness of our Jinc and modulated kernels.
E-GRPO: High Entropy Steps Drive Effective Reinforcement Learning for Flow Models
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:Recent reinforcement learning has enhanced the flow matching models on human preference alignment. While stochastic sampling enables the exploration of denoising directions, existing methods which optimize over multiple denoising steps suffer from sparse and ambiguous reward signals. We observe that the high entropy steps enable more efficient and effective exploration while the low entropy steps result in undistinguished roll-outs. To this end, we propose E-GRPO, an entropy aware Group Relative Policy Optimization to increase the entropy of SDE sampling steps. Since the integration of stochastic differential equations suffer from ambiguous reward signals due to stochasticity from multiple steps, we specifically merge consecutive low entropy steps to formulate one high entropy step for SDE sampling, while applying ODE sampling on other steps. Building upon this, we introduce multi-step group normalized advantage, which computes group-relative advantages within samples sharing the same consolidated SDE denoising step. Experimental results on different reward settings have demonstrated the effectiveness of our methods.
Geometry Forcing: Marrying Video Diffusion and 3D Representation for Consistent World Modeling
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:Videos inherently represent 2D projections of a dynamic 3D world. However, our analysis suggests that video diffusion models trained solely on raw video data often fail to capture meaningful geometric-aware structure in their learned representations. To bridge this gap between video diffusion models and the underlying 3D nature of the physical world, we propose Geometry Forcing, a simple yet effective method that encourages video diffusion models to internalize latent 3D representations. Our key insight is to guide the model's intermediate representations toward geometry-aware structure by aligning them with features from a pretrained geometric foundation model. To this end, we introduce two complementary alignment objectives: Angular Alignment, which enforces directional consistency via cosine similarity, and Scale Alignment, which preserves scale-related information by regressing unnormalized geometric features from normalized diffusion representation. We evaluate Geometry Forcing on both camera view-conditioned and action-conditioned video generation tasks. Experimental results demonstrate that our method substantially improves visual quality and 3D consistency over the baseline methods. Project page: https://GeometryForcing.github.io.
Ambiguity-aware Point Cloud Segmentation by Adaptive Margin Contrastive Learning
Jul 09, 2025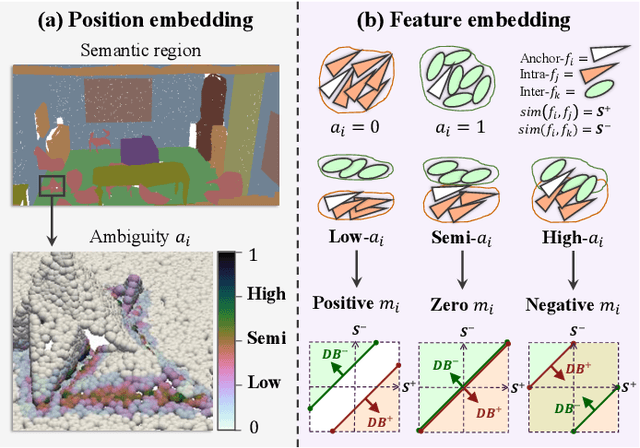
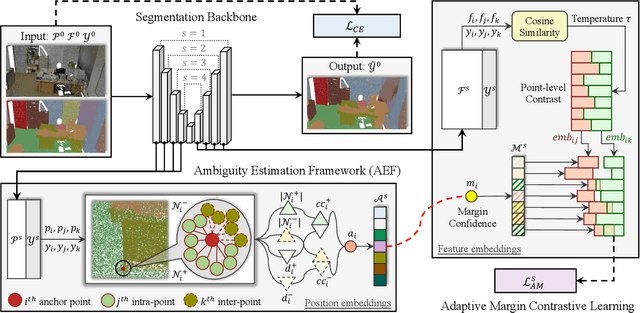
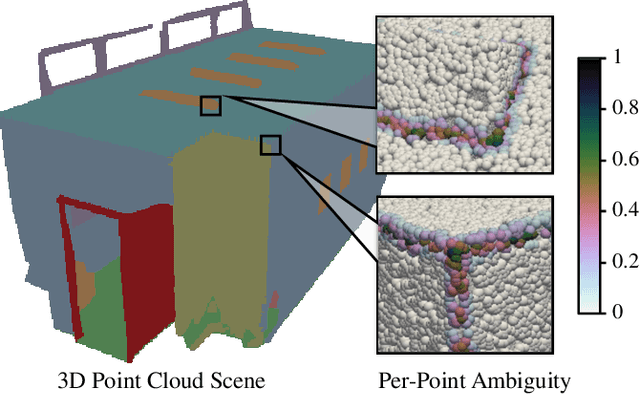
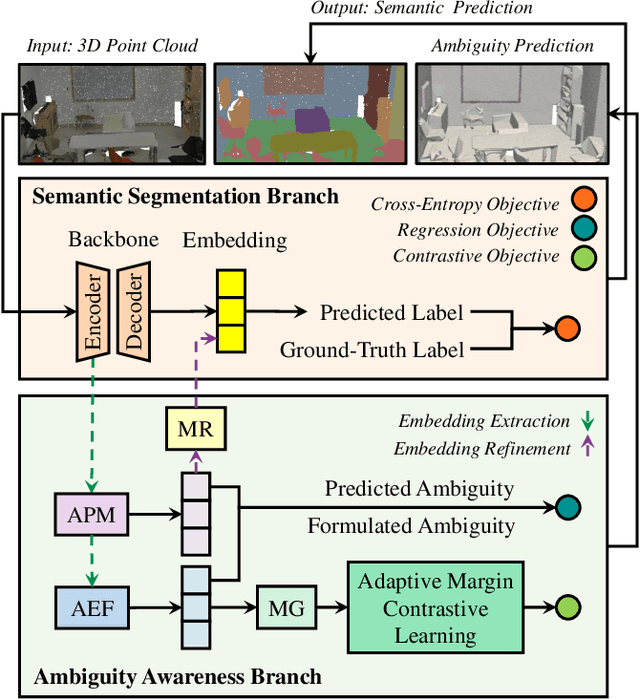
Abstract:This paper proposes an adaptive margin contrastive learning method for 3D semantic segmentation on point clouds. Most existing methods use equally penalized objectives, which ignore the per-point ambiguities and less discriminated features stemming from transition regions. However, as highly ambiguous points may be indistinguishable even for humans, their manually annotated labels are less reliable, and hard constraints over these points would lead to sub-optimal models. To address this, we first design AMContrast3D, a method comprising contrastive learning into an ambiguity estimation framework, tailored to adaptive objectives for individual points based on ambiguity levels. As a result, our method promotes model training, which ensures the correctness of low-ambiguity points while allowing mistakes for high-ambiguity points. As ambiguities are formulated based on position discrepancies across labels, optimization during inference is constrained by the assumption that all unlabeled points are uniformly unambiguous, lacking ambiguity awareness. Inspired by the insight of joint training, we further propose AMContrast3D++ integrating with two branches trained in parallel, where a novel ambiguity prediction module concurrently learns point ambiguities from generated embeddings. To this end, we design a masked refinement mechanism that leverages predicted ambiguities to enable the ambiguous embeddings to be more reliable, thereby boosting segmentation performance and enhancing robustness. Experimental results on 3D indoor scene datasets, S3DIS and ScanNet, demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method. Code is available at https://github.com/YangChenApril/AMContrast3D.
PointVDP: Learning View-Dependent Projection by Fireworks Rays for 3D Point Cloud Segmentation
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we propose view-dependent projection (VDP) to facilitate point cloud segmentation, designing efficient 3D-to-2D mapping that dynamically adapts to the spatial geometry from view variations. Existing projection-based methods leverage view-independent projection in complex scenes, relying on straight lines to generate direct rays or upward curves to reduce occlusions. However, their view independence provides projection rays that are limited to pre-defined parameters by human settings, restricting point awareness and failing to capture sufficient projection diversity across different view planes. Although multiple projections per view plane are commonly used to enhance spatial variety, the projected redundancy leads to excessive computational overhead and inefficiency in image processing. To address these limitations, we design a framework of VDP to generate data-driven projections from 3D point distributions, producing highly informative single-image inputs by predicting rays inspired by the adaptive behavior of fireworks. In addition, we construct color regularization to optimize the framework, which emphasizes essential features within semantic pixels and suppresses the non-semantic features within black pixels, thereby maximizing 2D space utilization in a projected image. As a result, our approach, PointVDP, develops lightweight projections in marginal computation costs. Experiments on S3DIS and ScanNet benchmarks show that our approach achieves competitive results, offering a resource-efficient solution for semantic understanding.
LangScene-X: Reconstruct Generalizable 3D Language-Embedded Scenes with TriMap Video Diffusion
Jul 03, 2025


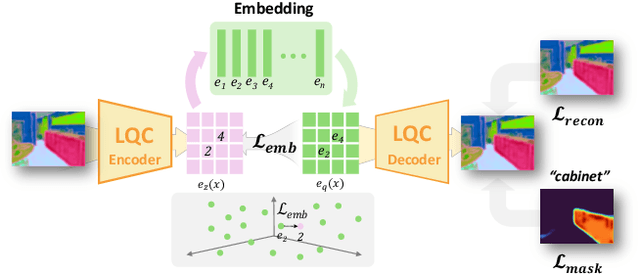
Abstract:Recovering 3D structures with open-vocabulary scene understanding from 2D images is a fundamental but daunting task. Recent developments have achieved this by performing per-scene optimization with embedded language information. However, they heavily rely on the calibrated dense-view reconstruction paradigm, thereby suffering from severe rendering artifacts and implausible semantic synthesis when limited views are available. In this paper, we introduce a novel generative framework, coined LangScene-X, to unify and generate 3D consistent multi-modality information for reconstruction and understanding. Powered by the generative capability of creating more consistent novel observations, we can build generalizable 3D language-embedded scenes from only sparse views. Specifically, we first train a TriMap video diffusion model that can generate appearance (RGBs), geometry (normals), and semantics (segmentation maps) from sparse inputs through progressive knowledge integration. Furthermore, we propose a Language Quantized Compressor (LQC), trained on large-scale image datasets, to efficiently encode language embeddings, enabling cross-scene generalization without per-scene retraining. Finally, we reconstruct the language surface fields by aligning language information onto the surface of 3D scenes, enabling open-ended language queries. Extensive experiments on real-world data demonstrate the superiority of our LangScene-X over state-of-the-art methods in terms of quality and generalizability. Project Page: https://liuff19.github.io/LangScene-X.
GenWorld: Towards Detecting AI-generated Real-world Simulation Videos
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:The flourishing of video generation technologies has endangered the credibility of real-world information and intensified the demand for AI-generated video detectors. Despite some progress, the lack of high-quality real-world datasets hinders the development of trustworthy detectors. In this paper, we propose GenWorld, a large-scale, high-quality, and real-world simulation dataset for AI-generated video detection. GenWorld features the following characteristics: (1) Real-world Simulation: GenWorld focuses on videos that replicate real-world scenarios, which have a significant impact due to their realism and potential influence; (2) High Quality: GenWorld employs multiple state-of-the-art video generation models to provide realistic and high-quality forged videos; (3) Cross-prompt Diversity: GenWorld includes videos generated from diverse generators and various prompt modalities (e.g., text, image, video), offering the potential to learn more generalizable forensic features. We analyze existing methods and find they fail to detect high-quality videos generated by world models (i.e., Cosmos), revealing potential drawbacks of ignoring real-world clues. To address this, we propose a simple yet effective model, SpannDetector, to leverage multi-view consistency as a strong criterion for real-world AI-generated video detection. Experiments show that our method achieves superior results, highlighting a promising direction for explainable AI-generated video detection based on physical plausibility. We believe that GenWorld will advance the field of AI-generated video detection. Project Page: https://chen-wl20.github.io/GenWorld
SceneCompleter: Dense 3D Scene Completion for Generative Novel View Synthesis
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Generative models have gained significant attention in novel view synthesis (NVS) by alleviating the reliance on dense multi-view captures. However, existing methods typically fall into a conventional paradigm, where generative models first complete missing areas in 2D, followed by 3D recovery techniques to reconstruct the scene, which often results in overly smooth surfaces and distorted geometry, as generative models struggle to infer 3D structure solely from RGB data. In this paper, we propose SceneCompleter, a novel framework that achieves 3D-consistent generative novel view synthesis through dense 3D scene completion. SceneCompleter achieves both visual coherence and 3D-consistent generative scene completion through two key components: (1) a geometry-appearance dual-stream diffusion model that jointly synthesizes novel views in RGBD space; (2) a scene embedder that encodes a more holistic scene understanding from the reference image. By effectively fusing structural and textural information, our method demonstrates superior coherence and plausibility in generative novel view synthesis across diverse datasets. Project Page: https://chen-wl20.github.io/SceneCompleter
SpectralAR: Spectral Autoregressive Visual Generation
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Autoregressive visual generation has garnered increasing attention due to its scalability and compatibility with other modalities compared with diffusion models. Most existing methods construct visual sequences as spatial patches for autoregressive generation. However, image patches are inherently parallel, contradicting the causal nature of autoregressive modeling. To address this, we propose a Spectral AutoRegressive (SpectralAR) visual generation framework, which realizes causality for visual sequences from the spectral perspective. Specifically, we first transform an image into ordered spectral tokens with Nested Spectral Tokenization, representing lower to higher frequency components. We then perform autoregressive generation in a coarse-to-fine manner with the sequences of spectral tokens. By considering different levels of detail in images, our SpectralAR achieves both sequence causality and token efficiency without bells and whistles. We conduct extensive experiments on ImageNet-1K for image reconstruction and autoregressive generation, and SpectralAR achieves 3.02 gFID with only 64 tokens and 310M parameters. Project page: https://huang-yh.github.io/spectralar/.
Spatial-MLLM: Boosting MLLM Capabilities in Visual-based Spatial Intelligence
May 29, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have significantly enhanced performance on 2D visual tasks. However, improving their spatial intelligence remains a challenge. Existing 3D MLLMs always rely on additional 3D or 2.5D data to incorporate spatial awareness, restricting their utility in scenarios with only 2D inputs, such as images or videos. In this paper, we present Spatial-MLLM, a novel framework for visual-based spatial reasoning from purely 2D observations. Unlike conventional video MLLMs which rely on CLIP-based visual encoders optimized for semantic understanding, our key insight is to unleash the strong structure prior from the feed-forward visual geometry foundation model. Specifically, we propose a dual-encoder architecture: a pretrained 2D visual encoder to extract semantic features, and a spatial encoder-initialized from the backbone of the visual geometry model-to extract 3D structure features. A connector then integrates both features into unified visual tokens for enhanced spatial understanding. Furthermore, we propose a space-aware frame sampling strategy at inference time, which selects the spatially informative frames of a video sequence, ensuring that even under limited token length, the model focuses on frames critical for spatial reasoning. Beyond architecture improvements, we construct the Spatial-MLLM-120k dataset and train the model on it using supervised fine-tuning and GRPO. Extensive experiments on various real-world datasets demonstrate that our spatial-MLLM achieves state-of-the-art performance in a wide range of visual-based spatial understanding and reasoning tasks. Project page: https://diankun-wu.github.io/Spatial-MLLM/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge