Yap-Peng Tan
E.M.Ground: A Temporal Grounding Vid-LLM with Holistic Event Perception and Matching
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Despite recent advances in Video Large Language Models (Vid-LLMs), Temporal Video Grounding (TVG), which aims to precisely localize time segments corresponding to query events, remains a significant challenge. Existing methods often match start and end frames by comparing frame features with two separate tokens, relying heavily on exact timestamps. However, this approach fails to capture the event's semantic continuity and integrity, leading to ambiguities. To address this, we propose E.M.Ground, a novel Vid-LLM for TVG that focuses on holistic and coherent event perception. E.M.Ground introduces three key innovations: (i) a special <event> token that aggregates information from all frames of a query event, preserving semantic continuity for accurate event matching; (ii) Savitzky-Golay smoothing to reduce noise in token-to-frame similarities across timestamps, improving prediction accuracy; (iii) multi-grained frame feature aggregation to enhance matching reliability and temporal understanding, compensating for compression-induced information loss. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets show that E.M.Ground consistently outperforms state-of-the-art Vid-LLMs by significant margins.
Cross-Domain Few-Shot Segmentation via Multi-view Progressive Adaptation
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Cross-Domain Few-Shot Segmentation aims to segment categories in data-scarce domains conditioned on a few exemplars. Typical methods first establish few-shot capability in a large-scale source domain and then adapt it to target domains. However, due to the limited quantity and diversity of target samples, existing methods still exhibit constrained performance. Moreover, the source-trained model's initially weak few-shot capability in target domains, coupled with substantial domain gaps, severely hinders the effective utilization of target samples and further impedes adaptation. To this end, we propose Multi-view Progressive Adaptation, which progressively adapts few-shot capability to target domains from both data and strategy perspectives. (i) From the data perspective, we introduce Hybrid Progressive Augmentation, which progressively generates more diverse and complex views through cumulative strong augmentations, thereby creating increasingly challenging learning scenarios. (ii) From the strategy perspective, we design Dual-chain Multi-view Prediction, which fully leverages these progressively complex views through sequential and parallel learning paths under extensive supervision. By jointly enforcing prediction consistency across diverse and complex views, MPA achieves both robust and accurate adaptation to target domains. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MPA effectively adapts few-shot capability to target domains, outperforming state-of-the-art methods by a large margin (+7.0%).
Boosting SAM for Cross-Domain Few-Shot Segmentation via Conditional Point Sparsification
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Motivated by the success of the Segment Anything Model (SAM) in promptable segmentation, recent studies leverage SAM to develop training-free solutions for few-shot segmentation, which aims to predict object masks in the target image based on a few reference exemplars. These SAM-based methods typically rely on point matching between reference and target images and use the matched dense points as prompts for mask prediction. However, we observe that dense points perform poorly in Cross-Domain Few-Shot Segmentation (CD-FSS), where target images are from medical or satellite domains. We attribute this issue to large domain shifts that disrupt the point-image interactions learned by SAM, and find that point density plays a crucial role under such conditions. To address this challenge, we propose Conditional Point Sparsification (CPS), a training-free approach that adaptively guides SAM interactions for cross-domain images based on reference exemplars. Leveraging ground-truth masks, the reference images provide reliable guidance for adaptively sparsifying dense matched points, enabling more accurate segmentation results. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CPS outperforms existing training-free SAM-based methods across diverse CD-FSS datasets.
CyIN: Cyclic Informative Latent Space for Bridging Complete and Incomplete Multimodal Learning
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Multimodal machine learning, mimicking the human brain's ability to integrate various modalities has seen rapid growth. Most previous multimodal models are trained on perfectly paired multimodal input to reach optimal performance. In real-world deployments, however, the presence of modality is highly variable and unpredictable, causing the pre-trained models in suffering significant performance drops and fail to remain robust with dynamic missing modalities circumstances. In this paper, we present a novel Cyclic INformative Learning framework (CyIN) to bridge the gap between complete and incomplete multimodal learning. Specifically, we firstly build an informative latent space by adopting token- and label-level Information Bottleneck (IB) cyclically among various modalities. Capturing task-related features with variational approximation, the informative bottleneck latents are purified for more efficient cross-modal interaction and multimodal fusion. Moreover, to supplement the missing information caused by incomplete multimodal input, we propose cross-modal cyclic translation by reconstruct the missing modalities with the remained ones through forward and reverse propagation process. With the help of the extracted and reconstructed informative latents, CyIN succeeds in jointly optimizing complete and incomplete multimodal learning in one unified model. Extensive experiments on 4 multimodal datasets demonstrate the superior performance of our method in both complete and diverse incomplete scenarios.
MAP-VLA: Memory-Augmented Prompting for Vision-Language-Action Model in Robotic Manipulation
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Pre-trained Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have achieved remarkable success in improving robustness and generalization for end-to-end robotic manipulation. However, these models struggle with long-horizon tasks due to their lack of memory and reliance solely on immediate sensory inputs. To address this limitation, we propose Memory-Augmented Prompting for Vision-Language-Action model (MAP-VLA), a novel framework that empowers pre-trained VLA models with demonstration-derived memory prompts to augment action generation for long-horizon robotic manipulation tasks. To achieve this, MAP-VLA first constructs a memory library from historical demonstrations, where each memory unit captures information about a specific stage of a task. These memory units are implemented as learnable soft prompts optimized through prompt tuning. Then, during real-time task execution, MAP-VLA retrieves relevant memory through trajectory similarity matching and dynamically integrates it into the VLA model for augmented action generation. Importantly, this prompt tuning and retrieval augmentation approach operates as a plug-and-play module for a frozen VLA model, offering a lightweight and flexible solution to improve task performance. Experimental results show that MAP-VLA delivers up to 7.0% absolute performance gains in the simulation benchmark and 25.0% on real robot evaluations for long-horizon tasks, surpassing the current state-of-the-art methods.
Ambiguity-aware Point Cloud Segmentation by Adaptive Margin Contrastive Learning
Jul 09, 2025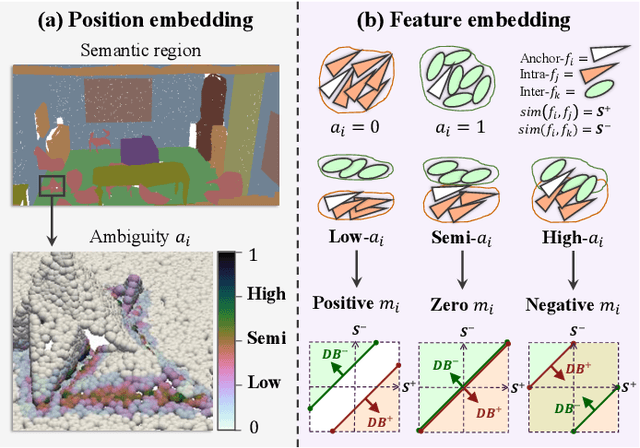
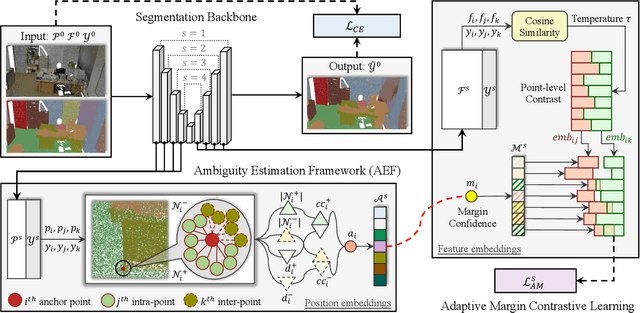
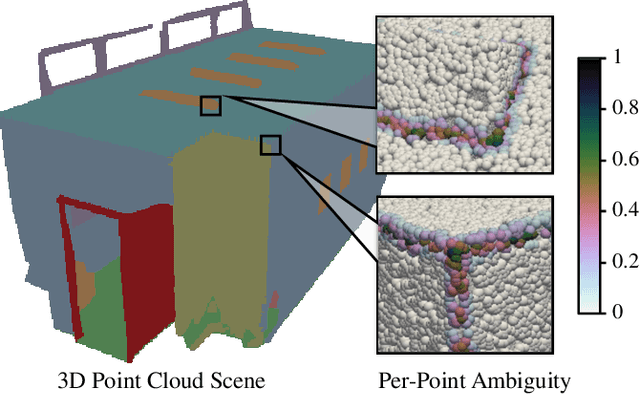
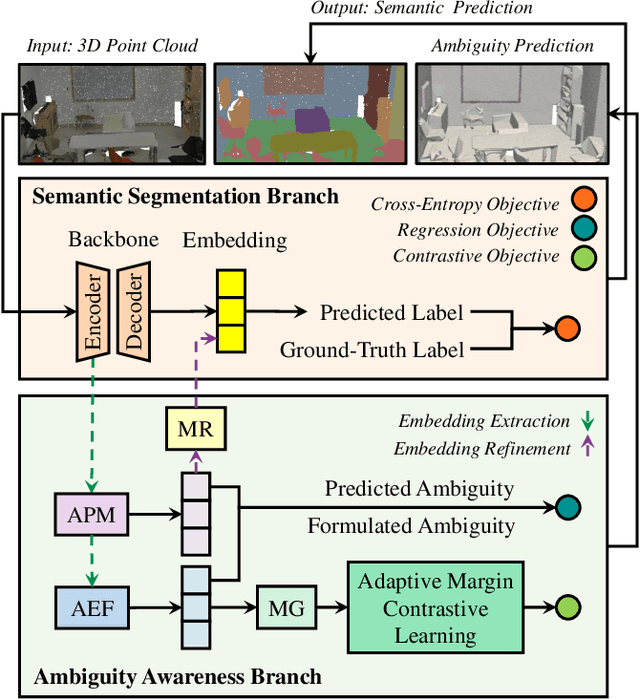
Abstract:This paper proposes an adaptive margin contrastive learning method for 3D semantic segmentation on point clouds. Most existing methods use equally penalized objectives, which ignore the per-point ambiguities and less discriminated features stemming from transition regions. However, as highly ambiguous points may be indistinguishable even for humans, their manually annotated labels are less reliable, and hard constraints over these points would lead to sub-optimal models. To address this, we first design AMContrast3D, a method comprising contrastive learning into an ambiguity estimation framework, tailored to adaptive objectives for individual points based on ambiguity levels. As a result, our method promotes model training, which ensures the correctness of low-ambiguity points while allowing mistakes for high-ambiguity points. As ambiguities are formulated based on position discrepancies across labels, optimization during inference is constrained by the assumption that all unlabeled points are uniformly unambiguous, lacking ambiguity awareness. Inspired by the insight of joint training, we further propose AMContrast3D++ integrating with two branches trained in parallel, where a novel ambiguity prediction module concurrently learns point ambiguities from generated embeddings. To this end, we design a masked refinement mechanism that leverages predicted ambiguities to enable the ambiguous embeddings to be more reliable, thereby boosting segmentation performance and enhancing robustness. Experimental results on 3D indoor scene datasets, S3DIS and ScanNet, demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method. Code is available at https://github.com/YangChenApril/AMContrast3D.
PointVDP: Learning View-Dependent Projection by Fireworks Rays for 3D Point Cloud Segmentation
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we propose view-dependent projection (VDP) to facilitate point cloud segmentation, designing efficient 3D-to-2D mapping that dynamically adapts to the spatial geometry from view variations. Existing projection-based methods leverage view-independent projection in complex scenes, relying on straight lines to generate direct rays or upward curves to reduce occlusions. However, their view independence provides projection rays that are limited to pre-defined parameters by human settings, restricting point awareness and failing to capture sufficient projection diversity across different view planes. Although multiple projections per view plane are commonly used to enhance spatial variety, the projected redundancy leads to excessive computational overhead and inefficiency in image processing. To address these limitations, we design a framework of VDP to generate data-driven projections from 3D point distributions, producing highly informative single-image inputs by predicting rays inspired by the adaptive behavior of fireworks. In addition, we construct color regularization to optimize the framework, which emphasizes essential features within semantic pixels and suppresses the non-semantic features within black pixels, thereby maximizing 2D space utilization in a projected image. As a result, our approach, PointVDP, develops lightweight projections in marginal computation costs. Experiments on S3DIS and ScanNet benchmarks show that our approach achieves competitive results, offering a resource-efficient solution for semantic understanding.
Rethinking Range-View LiDAR Segmentation in Adverse Weather
Jun 10, 2025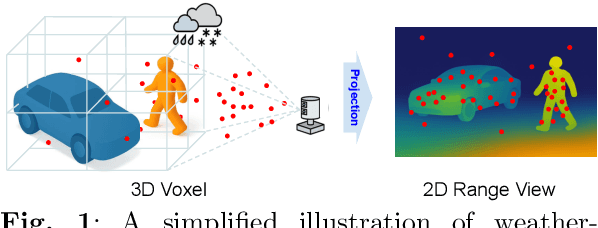
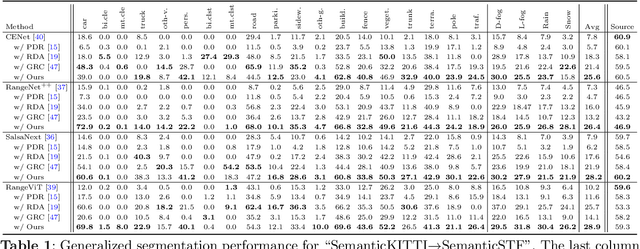
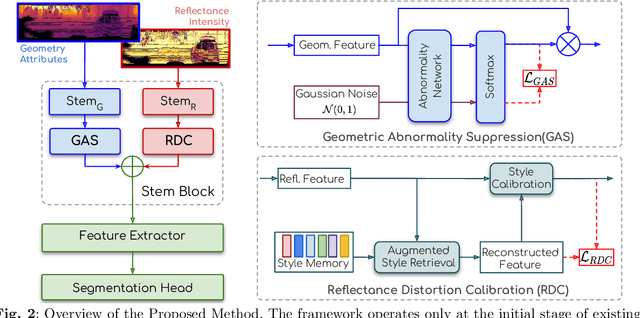
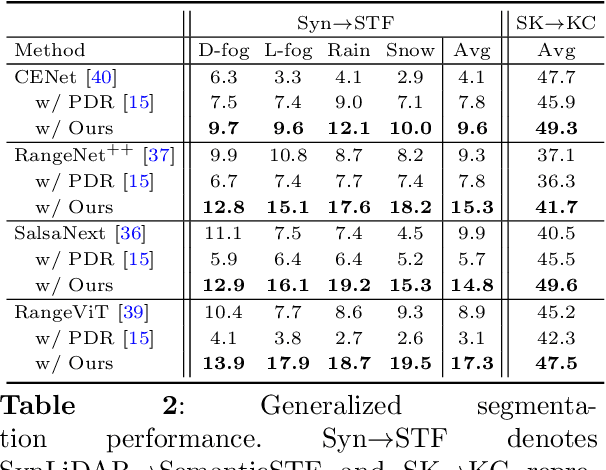
Abstract:LiDAR segmentation has emerged as an important task to enrich multimedia experiences and analysis. Range-view-based methods have gained popularity due to their high computational efficiency and compatibility with real-time deployment. However, their generalized performance under adverse weather conditions remains underexplored, limiting their reliability in real-world environments. In this work, we identify and analyze the unique challenges that affect the generalization of range-view LiDAR segmentation in severe weather. To address these challenges, we propose a modular and lightweight framework that enhances robustness without altering the core architecture of existing models. Our method reformulates the initial stem block of standard range-view networks into two branches to process geometric attributes and reflectance intensity separately. Specifically, a Geometric Abnormality Suppression (GAS) module reduces the influence of weather-induced spatial noise, and a Reflectance Distortion Calibration (RDC) module corrects reflectance distortions through memory-guided adaptive instance normalization. The processed features are then fused and passed to the original segmentation pipeline. Extensive experiments on different benchmarks and baseline models demonstrate that our approach significantly improves generalization to adverse weather with minimal inference overhead, offering a practical and effective solution for real-world LiDAR segmentation.
MTL-UE: Learning to Learn Nothing for Multi-Task Learning
May 08, 2025Abstract:Most existing unlearnable strategies focus on preventing unauthorized users from training single-task learning (STL) models with personal data. Nevertheless, the paradigm has recently shifted towards multi-task data and multi-task learning (MTL), targeting generalist and foundation models that can handle multiple tasks simultaneously. Despite their growing importance, MTL data and models have been largely neglected while pursuing unlearnable strategies. This paper presents MTL-UE, the first unified framework for generating unlearnable examples for multi-task data and MTL models. Instead of optimizing perturbations for each sample, we design a generator-based structure that introduces label priors and class-wise feature embeddings which leads to much better attacking performance. In addition, MTL-UE incorporates intra-task and inter-task embedding regularization to increase inter-class separation and suppress intra-class variance which enhances the attack robustness greatly. Furthermore, MTL-UE is versatile with good supports for dense prediction tasks in MTL. It is also plug-and-play allowing integrating existing surrogate-dependent unlearnable methods with little adaptation. Extensive experiments show that MTL-UE achieves superior attacking performance consistently across 4 MTL datasets, 3 base UE methods, 5 model backbones, and 5 MTL task-weighting strategies.
Towards Model Resistant to Transferable Adversarial Examples via Trigger Activation
Apr 20, 2025Abstract:Adversarial examples, characterized by imperceptible perturbations, pose significant threats to deep neural networks by misleading their predictions. A critical aspect of these examples is their transferability, allowing them to deceive {unseen} models in black-box scenarios. Despite the widespread exploration of defense methods, including those on transferability, they show limitations: inefficient deployment, ineffective defense, and degraded performance on clean images. In this work, we introduce a novel training paradigm aimed at enhancing robustness against transferable adversarial examples (TAEs) in a more efficient and effective way. We propose a model that exhibits random guessing behavior when presented with clean data $\boldsymbol{x}$ as input, and generates accurate predictions when with triggered data $\boldsymbol{x}+\boldsymbol{\tau}$. Importantly, the trigger $\boldsymbol{\tau}$ remains constant for all data instances. We refer to these models as \textbf{models with trigger activation}. We are surprised to find that these models exhibit certain robustness against TAEs. Through the consideration of first-order gradients, we provide a theoretical analysis of this robustness. Moreover, through the joint optimization of the learnable trigger and the model, we achieve improved robustness to transferable attacks. Extensive experiments conducted across diverse datasets, evaluating a variety of attacking methods, underscore the effectiveness and superiority of our approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge