Fangsheng Weng
Unveiling the Impact of Multi-Modal Interactions on User Engagement: A Comprehensive Evaluation in AI-driven Conversations
Jun 21, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have significantly advanced user-bot interactions, enabling more complex and coherent dialogues. However, the prevalent text-only modality might not fully exploit the potential for effective user engagement. This paper explores the impact of multi-modal interactions, which incorporate images and audio alongside text, on user engagement in chatbot conversations. We conduct a comprehensive analysis using a diverse set of chatbots and real-user interaction data, employing metrics such as retention rate and conversation length to evaluate user engagement. Our findings reveal a significant enhancement in user engagement with multi-modal interactions compared to text-only dialogues. Notably, the incorporation of a third modality significantly amplifies engagement beyond the benefits observed with just two modalities. These results suggest that multi-modal interactions optimize cognitive processing and facilitate richer information comprehension. This study underscores the importance of multi-modality in chatbot design, offering valuable insights for creating more engaging and immersive AI communication experiences and informing the broader AI community about the benefits of multi-modal interactions in enhancing user engagement.
Quality and Quantity: Unveiling a Million High-Quality Images for Text-to-Image Synthesis in Fashion Design
Nov 29, 2023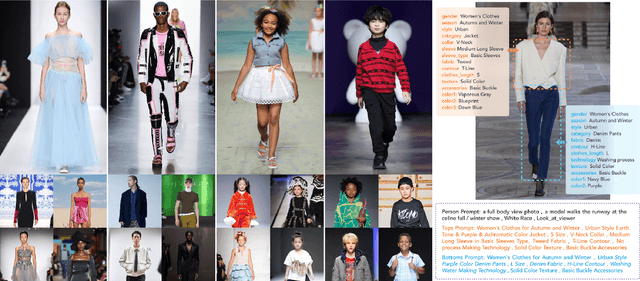

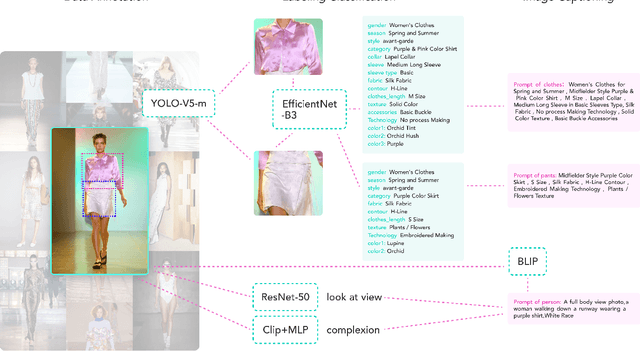

Abstract:The fusion of AI and fashion design has emerged as a promising research area. However, the lack of extensive, interrelated data on clothing and try-on stages has hindered the full potential of AI in this domain. Addressing this, we present the Fashion-Diffusion dataset, a product of multiple years' rigorous effort. This dataset, the first of its kind, comprises over a million high-quality fashion images, paired with detailed text descriptions. Sourced from a diverse range of geographical locations and cultural backgrounds, the dataset encapsulates global fashion trends. The images have been meticulously annotated with fine-grained attributes related to clothing and humans, simplifying the fashion design process into a Text-to-Image (T2I) task. The Fashion-Diffusion dataset not only provides high-quality text-image pairs and diverse human-garment pairs but also serves as a large-scale resource about humans, thereby facilitating research in T2I generation. Moreover, to foster standardization in the T2I-based fashion design field, we propose a new benchmark comprising multiple datasets for evaluating the performance of fashion design models. This work represents a significant leap forward in the realm of AI-driven fashion design, setting a new standard for future research in this field.
Tailored Visions: Enhancing Text-to-Image Generation with Personalized Prompt Rewriting
Oct 12, 2023Abstract:We propose a novel perspective of viewing large pretrained models as search engines, thereby enabling the repurposing of techniques previously used to enhance search engine performance. As an illustration, we employ a personalized query rewriting technique in the realm of text-to-image generation. Despite significant progress in the field, it is still challenging to create personalized visual representations that align closely with the desires and preferences of individual users. This process requires users to articulate their ideas in words that are both comprehensible to the models and accurately capture their vision, posing difficulties for many users. In this paper, we tackle this challenge by leveraging historical user interactions with the system to enhance user prompts. We propose a novel approach that involves rewriting user prompts based a new large-scale text-to-image dataset with over 300k prompts from 3115 users. Our rewriting model enhances the expressiveness and alignment of user prompts with their intended visual outputs. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our methods over baseline approaches, as evidenced in our new offline evaluation method and online tests. Our approach opens up exciting possibilities of applying more search engine techniques to build truly personalized large pretrained models.
RpBERT: A Text-image Relation Propagation-based BERT Model for Multimodal NER
Feb 05, 2021



Abstract:Recently multimodal named entity recognition (MNER) has utilized images to improve the accuracy of NER in tweets. However, most of the multimodal methods use attention mechanisms to extract visual clues regardless of whether the text and image are relevant. Practically, the irrelevant text-image pairs account for a large proportion in tweets. The visual clues that are unrelated to the texts will exert uncertain or even negative effects on multimodal model learning. In this paper, we introduce a method of text-image relation propagation into the multimodal BERT model. We integrate soft or hard gates to select visual clues and propose a multitask algorithm to train on the MNER datasets. In the experiments, we deeply analyze the changes in visual attention before and after the use of text-image relation propagation. Our model achieves state-of-the-art performance on the MNER datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge