Yuming Yan
Accelerating Autoregressive Speech Synthesis Inference With Speech Speculative Decoding
May 21, 2025Abstract:Modern autoregressive speech synthesis models leveraging language models have demonstrated remarkable performance. However, the sequential nature of next token prediction in these models leads to significant latency, hindering their deployment in scenarios where inference speed is critical. In this work, we propose Speech Speculative Decoding (SSD), a novel framework for autoregressive speech synthesis acceleration. Specifically, our method employs a lightweight draft model to generate candidate token sequences, which are subsequently verified in parallel by the target model using the proposed SSD framework. Experimental results demonstrate that SSD achieves a significant speedup of 1.4x compared with conventional autoregressive decoding, while maintaining high fidelity and naturalness. Subjective evaluations further validate the effectiveness of SSD in preserving the perceptual quality of the target model while accelerating inference.
Unveiling the Impact of Multi-Modal Interactions on User Engagement: A Comprehensive Evaluation in AI-driven Conversations
Jun 21, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have significantly advanced user-bot interactions, enabling more complex and coherent dialogues. However, the prevalent text-only modality might not fully exploit the potential for effective user engagement. This paper explores the impact of multi-modal interactions, which incorporate images and audio alongside text, on user engagement in chatbot conversations. We conduct a comprehensive analysis using a diverse set of chatbots and real-user interaction data, employing metrics such as retention rate and conversation length to evaluate user engagement. Our findings reveal a significant enhancement in user engagement with multi-modal interactions compared to text-only dialogues. Notably, the incorporation of a third modality significantly amplifies engagement beyond the benefits observed with just two modalities. These results suggest that multi-modal interactions optimize cognitive processing and facilitate richer information comprehension. This study underscores the importance of multi-modality in chatbot design, offering valuable insights for creating more engaging and immersive AI communication experiences and informing the broader AI community about the benefits of multi-modal interactions in enhancing user engagement.
Unveiling the Secrets of Engaging Conversations: Factors that Keep Users Hooked on Role-Playing Dialog Agents
Feb 18, 2024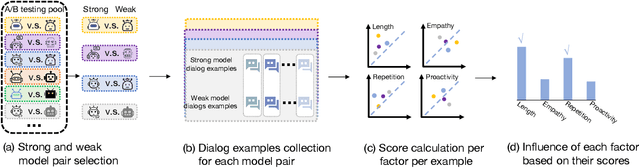



Abstract:With the growing humanlike nature of dialog agents, people are now engaging in extended conversations that can stretch from brief moments to substantial periods of time. Understanding the factors that contribute to sustaining these interactions is crucial, yet existing studies primarily focusing on short-term simulations that rarely explore such prolonged and real conversations. In this paper, we investigate the factors influencing retention rates in real interactions with roleplaying models. By analyzing a large dataset of interactions between real users and thousands of characters, we systematically examine multiple factors and assess their impact on user retention rate. Surprisingly, we find that the degree to which the bot embodies the roles it plays has limited influence on retention rates, while the length of each turn it speaks significantly affects retention rates. This study sheds light on the critical aspects of user engagement with role-playing models and provides valuable insights for future improvements in the development of large language models for role-playing purposes.
Quality and Quantity: Unveiling a Million High-Quality Images for Text-to-Image Synthesis in Fashion Design
Nov 29, 2023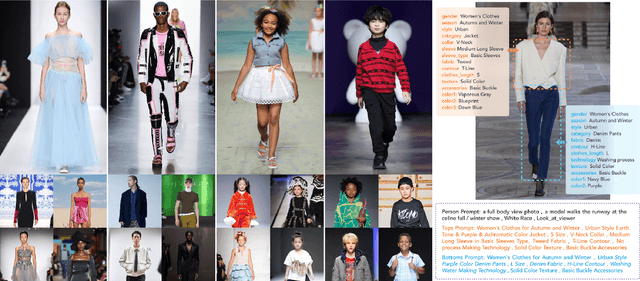

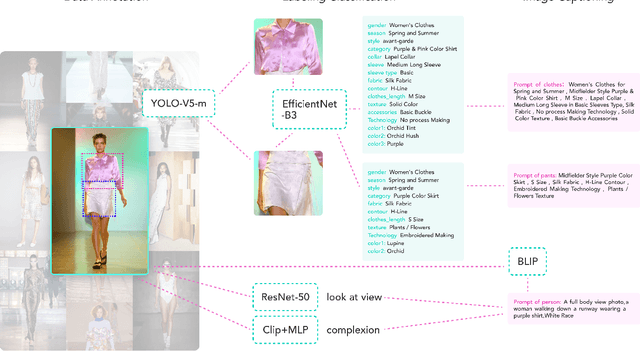

Abstract:The fusion of AI and fashion design has emerged as a promising research area. However, the lack of extensive, interrelated data on clothing and try-on stages has hindered the full potential of AI in this domain. Addressing this, we present the Fashion-Diffusion dataset, a product of multiple years' rigorous effort. This dataset, the first of its kind, comprises over a million high-quality fashion images, paired with detailed text descriptions. Sourced from a diverse range of geographical locations and cultural backgrounds, the dataset encapsulates global fashion trends. The images have been meticulously annotated with fine-grained attributes related to clothing and humans, simplifying the fashion design process into a Text-to-Image (T2I) task. The Fashion-Diffusion dataset not only provides high-quality text-image pairs and diverse human-garment pairs but also serves as a large-scale resource about humans, thereby facilitating research in T2I generation. Moreover, to foster standardization in the T2I-based fashion design field, we propose a new benchmark comprising multiple datasets for evaluating the performance of fashion design models. This work represents a significant leap forward in the realm of AI-driven fashion design, setting a new standard for future research in this field.
Exploring Shape Embedding for Cloth-Changing Person Re-Identification via 2D-3D Correspondences
Oct 27, 2023



Abstract:Cloth-Changing Person Re-Identification (CC-ReID) is a common and realistic problem since fashion constantly changes over time and people's aesthetic preferences are not set in stone. While most existing cloth-changing ReID methods focus on learning cloth-agnostic identity representations from coarse semantic cues (e.g. silhouettes and part segmentation maps), they neglect the continuous shape distributions at the pixel level. In this paper, we propose Continuous Surface Correspondence Learning (CSCL), a new shape embedding paradigm for cloth-changing ReID. CSCL establishes continuous correspondences between a 2D image plane and a canonical 3D body surface via pixel-to-vertex classification, which naturally aligns a person image to the surface of a 3D human model and simultaneously obtains pixel-wise surface embeddings. We further extract fine-grained shape features from the learned surface embeddings and then integrate them with global RGB features via a carefully designed cross-modality fusion module. The shape embedding paradigm based on 2D-3D correspondences remarkably enhances the model's global understanding of human body shape. To promote the study of ReID under clothing change, we construct 3D Dense Persons (DP3D), which is the first large-scale cloth-changing ReID dataset that provides densely annotated 2D-3D correspondences and a precise 3D mesh for each person image, while containing diverse cloth-changing cases over all four seasons. Experiments on both cloth-changing and cloth-consistent ReID benchmarks validate the effectiveness of our method.
Gated Domain-Invariant Feature Disentanglement for Domain Generalizable Object Detection
Mar 22, 2022



Abstract:For Domain Generalizable Object Detection (DGOD), Disentangled Representation Learning (DRL) helps a lot by explicitly disentangling Domain-Invariant Representations (DIR) from Domain-Specific Representations (DSR). Considering the domain category is an attribute of input data, it should be feasible for networks to fit a specific mapping which projects DSR into feature channels exclusive to domain-specific information, and thus much cleaner disentanglement of DIR from DSR can be achieved simply on channel dimension. Inspired by this idea, we propose a novel DRL method for DGOD, which is termed Gated Domain-Invariant Feature Disentanglement (GDIFD). In GDIFD, a Channel Gate Module (CGM) learns to output channel gate signals close to either 0 or 1, which can mask out the channels exclusive to domain-specific information helpful for domain recognition. With the proposed GDIFD, the backbone in our framework can fit the desired mapping easily, which enables the channel-wise disentanglement. In experiments, we demonstrate that our approach is highly effective and achieves state-of-the-art DGOD performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge