Yichong Lu
Orientation Matters: Making 3D Generative Models Orientation-Aligned
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Humans intuitively perceive object shape and orientation from a single image, guided by strong priors about canonical poses. However, existing 3D generative models often produce misaligned results due to inconsistent training data, limiting their usability in downstream tasks. To address this gap, we introduce the task of orientation-aligned 3D object generation: producing 3D objects from single images with consistent orientations across categories. To facilitate this, we construct Objaverse-OA, a dataset of 14,832 orientation-aligned 3D models spanning 1,008 categories. Leveraging Objaverse-OA, we fine-tune two representative 3D generative models based on multi-view diffusion and 3D variational autoencoder frameworks to produce aligned objects that generalize well to unseen objects across various categories. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our method over post-hoc alignment approaches. Furthermore, we showcase downstream applications enabled by our aligned object generation, including zero-shot object orientation estimation via analysis-by-synthesis and efficient arrow-based object rotation manipulation.
HUGSIM: A Real-Time, Photo-Realistic and Closed-Loop Simulator for Autonomous Driving
Dec 02, 2024
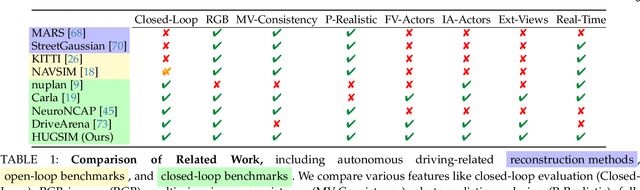
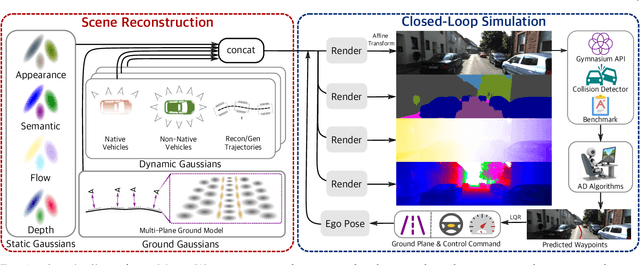
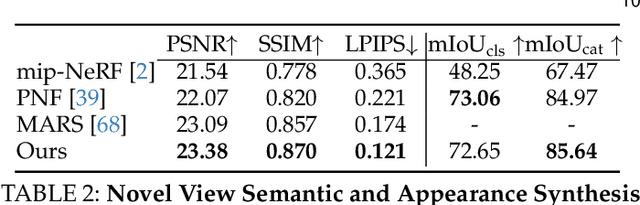
Abstract:In the past few decades, autonomous driving algorithms have made significant progress in perception, planning, and control. However, evaluating individual components does not fully reflect the performance of entire systems, highlighting the need for more holistic assessment methods. This motivates the development of HUGSIM, a closed-loop, photo-realistic, and real-time simulator for evaluating autonomous driving algorithms. We achieve this by lifting captured 2D RGB images into the 3D space via 3D Gaussian Splatting, improving the rendering quality for closed-loop scenarios, and building the closed-loop environment. In terms of rendering, We tackle challenges of novel view synthesis in closed-loop scenarios, including viewpoint extrapolation and 360-degree vehicle rendering. Beyond novel view synthesis, HUGSIM further enables the full closed simulation loop, dynamically updating the ego and actor states and observations based on control commands. Moreover, HUGSIM offers a comprehensive benchmark across more than 70 sequences from KITTI-360, Waymo, nuScenes, and PandaSet, along with over 400 varying scenarios, providing a fair and realistic evaluation platform for existing autonomous driving algorithms. HUGSIM not only serves as an intuitive evaluation benchmark but also unlocks the potential for fine-tuning autonomous driving algorithms in a photorealistic closed-loop setting.
UrbanCAD: Towards Highly Controllable and Photorealistic 3D Vehicles for Urban Scene Simulation
Nov 28, 2024Abstract:Photorealistic 3D vehicle models with high controllability are essential for autonomous driving simulation and data augmentation. While handcrafted CAD models provide flexible controllability, free CAD libraries often lack the high-quality materials necessary for photorealistic rendering. Conversely, reconstructed 3D models offer high-fidelity rendering but lack controllability. In this work, we introduce UrbanCAD, a framework that pushes the frontier of the photorealism-controllability trade-off by generating highly controllable and photorealistic 3D vehicle digital twins from a single urban image and a collection of free 3D CAD models and handcrafted materials. These digital twins enable realistic 360-degree rendering, vehicle insertion, material transfer, relighting, and component manipulation such as opening doors and rolling down windows, supporting the construction of long-tail scenarios. To achieve this, we propose a novel pipeline that operates in a retrieval-optimization manner, adapting to observational data while preserving flexible controllability and fine-grained handcrafted details. Furthermore, given multi-view background perspective and fisheye images, we approximate environment lighting using fisheye images and reconstruct the background with 3DGS, enabling the photorealistic insertion of optimized CAD models into rendered novel view backgrounds. Experimental results demonstrate that UrbanCAD outperforms baselines based on reconstruction and retrieval in terms of photorealism. Additionally, we show that various perception models maintain their accuracy when evaluated on UrbanCAD with in-distribution configurations but degrade when applied to realistic out-of-distribution data generated by our method. This suggests that UrbanCAD is a significant advancement in creating photorealistic, safety-critical driving scenarios for downstream applications.
Exploring Shape Embedding for Cloth-Changing Person Re-Identification via 2D-3D Correspondences
Oct 27, 2023



Abstract:Cloth-Changing Person Re-Identification (CC-ReID) is a common and realistic problem since fashion constantly changes over time and people's aesthetic preferences are not set in stone. While most existing cloth-changing ReID methods focus on learning cloth-agnostic identity representations from coarse semantic cues (e.g. silhouettes and part segmentation maps), they neglect the continuous shape distributions at the pixel level. In this paper, we propose Continuous Surface Correspondence Learning (CSCL), a new shape embedding paradigm for cloth-changing ReID. CSCL establishes continuous correspondences between a 2D image plane and a canonical 3D body surface via pixel-to-vertex classification, which naturally aligns a person image to the surface of a 3D human model and simultaneously obtains pixel-wise surface embeddings. We further extract fine-grained shape features from the learned surface embeddings and then integrate them with global RGB features via a carefully designed cross-modality fusion module. The shape embedding paradigm based on 2D-3D correspondences remarkably enhances the model's global understanding of human body shape. To promote the study of ReID under clothing change, we construct 3D Dense Persons (DP3D), which is the first large-scale cloth-changing ReID dataset that provides densely annotated 2D-3D correspondences and a precise 3D mesh for each person image, while containing diverse cloth-changing cases over all four seasons. Experiments on both cloth-changing and cloth-consistent ReID benchmarks validate the effectiveness of our method.
PanopticNeRF-360: Panoramic 3D-to-2D Label Transfer in Urban Scenes
Sep 19, 2023Abstract:Training perception systems for self-driving cars requires substantial annotations. However, manual labeling in 2D images is highly labor-intensive. While existing datasets provide rich annotations for pre-recorded sequences, they fall short in labeling rarely encountered viewpoints, potentially hampering the generalization ability for perception models. In this paper, we present PanopticNeRF-360, a novel approach that combines coarse 3D annotations with noisy 2D semantic cues to generate consistent panoptic labels and high-quality images from any viewpoint. Our key insight lies in exploiting the complementarity of 3D and 2D priors to mutually enhance geometry and semantics. Specifically, we propose to leverage noisy semantic and instance labels in both 3D and 2D spaces to guide geometry optimization. Simultaneously, the improved geometry assists in filtering noise present in the 3D and 2D annotations by merging them in 3D space via a learned semantic field. To further enhance appearance, we combine MLP and hash grids to yield hybrid scene features, striking a balance between high-frequency appearance and predominantly contiguous semantics. Our experiments demonstrate PanopticNeRF-360's state-of-the-art performance over existing label transfer methods on the challenging urban scenes of the KITTI-360 dataset. Moreover, PanopticNeRF-360 enables omnidirectional rendering of high-fidelity, multi-view and spatiotemporally consistent appearance, semantic and instance labels. We make our code and data available at https://github.com/fuxiao0719/PanopticNeRF
Panoptic NeRF: 3D-to-2D Label Transfer for Panoptic Urban Scene Segmentation
Mar 29, 2022



Abstract:Large-scale training data with high-quality annotations is critical for training semantic and instance segmentation models. Unfortunately, pixel-wise annotation is labor-intensive and costly, raising the demand for more efficient labeling strategies. In this work, we present a novel 3D-to-2D label transfer method, Panoptic NeRF, which aims for obtaining per-pixel 2D semantic and instance labels from easy-to-obtain coarse 3D bounding primitives. Our method utilizes NeRF as a differentiable tool to unify coarse 3D annotations and 2D semantic cues transferred from existing datasets. We demonstrate that this combination allows for improved geometry guided by semantic information, enabling rendering of accurate semantic maps across multiple views. Furthermore, this fusion process resolves label ambiguity of the coarse 3D annotations and filters noise in the 2D predictions. By inferring in 3D space and rendering to 2D labels, our 2D semantic and instance labels are multi-view consistent by design. Experimental results show that Panoptic NeRF outperforms existing semantic and instance label transfer methods in terms of accuracy and multi-view consistency on challenging urban scenes of the KITTI-360 dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge