Xiao Fu
DuoGen: Towards General Purpose Interleaved Multimodal Generation
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Interleaved multimodal generation enables capabilities beyond unimodal generation models, such as step-by-step instructional guides, visual planning, and generating visual drafts for reasoning. However, the quality of existing interleaved generation models under general instructions remains limited by insufficient training data and base model capacity. We present DuoGen, a general-purpose interleaved generation framework that systematically addresses data curation, architecture design, and evaluation. On the data side, we build a large-scale, high-quality instruction-tuning dataset by combining multimodal conversations rewritten from curated raw websites, and diverse synthetic examples covering everyday scenarios. Architecturally, DuoGen leverages the strong visual understanding of a pretrained multimodal LLM and the visual generation capabilities of a diffusion transformer (DiT) pretrained on video generation, avoiding costly unimodal pretraining and enabling flexible base model selection. A two-stage decoupled strategy first instruction-tunes the MLLM, then aligns DiT with it using curated interleaved image-text sequences. Across public and newly proposed benchmarks, DuoGen outperforms prior open-source models in text quality, image fidelity, and image-context alignment, and also achieves state-of-the-art performance on text-to-image and image editing among unified generation models. Data and code will be released at https://research.nvidia.com/labs/dir/duogen/.
SemanticGen: Video Generation in Semantic Space
Dec 24, 2025

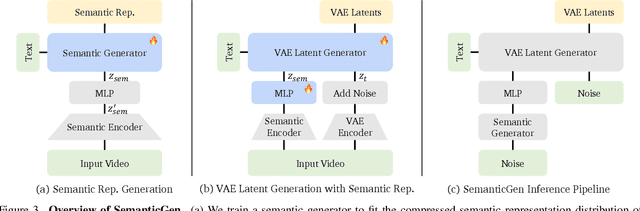

Abstract:State-of-the-art video generative models typically learn the distribution of video latents in the VAE space and map them to pixels using a VAE decoder. While this approach can generate high-quality videos, it suffers from slow convergence and is computationally expensive when generating long videos. In this paper, we introduce SemanticGen, a novel solution to address these limitations by generating videos in the semantic space. Our main insight is that, due to the inherent redundancy in videos, the generation process should begin in a compact, high-level semantic space for global planning, followed by the addition of high-frequency details, rather than directly modeling a vast set of low-level video tokens using bi-directional attention. SemanticGen adopts a two-stage generation process. In the first stage, a diffusion model generates compact semantic video features, which define the global layout of the video. In the second stage, another diffusion model generates VAE latents conditioned on these semantic features to produce the final output. We observe that generation in the semantic space leads to faster convergence compared to the VAE latent space. Our method is also effective and computationally efficient when extended to long video generation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SemanticGen produces high-quality videos and outperforms state-of-the-art approaches and strong baselines.
Rethinking Coupled Tensor Analysis for Hyperspectral Super-Resolution: Recoverable Modeling Under Endmember Variability
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:This work revisits the hyperspectral super-resolution (HSR) problem, i.e., fusing a pair of spatially co-registered hyperspectral (HSI) and multispectral (MSI) images to recover a super-resolution image (SRI) that enhances the spatial resolution of the HSI. Coupled tensor decomposition (CTD)-based methods have gained traction in this domain, offering recoverability guarantees under various assumptions. Existing models such as canonical polyadic decomposition (CPD) and Tucker decomposition provide strong expressive power but lack physical interpretability. The block-term decomposition model with rank-$(L_r, L_r, 1)$ terms (the LL1 model) yields interpretable factors under the linear mixture model (LMM) of spectral images, but LMM assumptions are often violated in practice -- primarily due to nonlinear effects such as endmember variability (EV). To address this, we propose modeling spectral images using a more flexible block-term tensor decomposition with rank-$(L_r, M_r, N_r)$ terms (the LMN model). This modeling choice retains interpretability, subsumes CPD, Tucker, and LL1 as special cases, and robustly accounts for non-ideal effects such as EV, offering a balanced tradeoff between expressiveness and interpretability for HSR. Importantly, under the LMN model for HSI and MSI, recoverability of the SRI can still be established under proper conditions -- providing strong theoretical support. Extensive experiments on synthetic and real datasets further validate the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed method compared with existing CTD-based approaches.
SEE4D: Pose-Free 4D Generation via Auto-Regressive Video Inpainting
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:Immersive applications call for synthesizing spatiotemporal 4D content from casual videos without costly 3D supervision. Existing video-to-4D methods typically rely on manually annotated camera poses, which are labor-intensive and brittle for in-the-wild footage. Recent warp-then-inpaint approaches mitigate the need for pose labels by warping input frames along a novel camera trajectory and using an inpainting model to fill missing regions, thereby depicting the 4D scene from diverse viewpoints. However, this trajectory-to-trajectory formulation often entangles camera motion with scene dynamics and complicates both modeling and inference. We introduce SEE4D, a pose-free, trajectory-to-camera framework that replaces explicit trajectory prediction with rendering to a bank of fixed virtual cameras, thereby separating camera control from scene modeling. A view-conditional video inpainting model is trained to learn a robust geometry prior by denoising realistically synthesized warped images and to inpaint occluded or missing regions across virtual viewpoints, eliminating the need for explicit 3D annotations. Building on this inpainting core, we design a spatiotemporal autoregressive inference pipeline that traverses virtual-camera splines and extends videos with overlapping windows, enabling coherent generation at bounded per-step complexity. We validate See4D on cross-view video generation and sparse reconstruction benchmarks. Across quantitative metrics and qualitative assessments, our method achieves superior generalization and improved performance relative to pose- or trajectory-conditioned baselines, advancing practical 4D world modeling from casual videos.
FieldFormer: Self-supervised Reconstruction of Physical Fields via Tensor Attention Prior
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Reconstructing physical field tensors from \textit{in situ} observations, such as radio maps and ocean sound speed fields, is crucial for enabling environment-aware decision making in various applications, e.g., wireless communications and underwater acoustics. Field data reconstruction is often challenging, due to the limited and noisy nature of the observations, necessitating the incorporation of prior information to aid the reconstruction process. Deep neural network-based data-driven structural constraints (e.g., ``deeply learned priors'') have showed promising performance. However, this family of techniques faces challenges such as model mismatches between training and testing phases. This work introduces FieldFormer, a self-supervised neural prior learned solely from the limited {\it in situ} observations without the need of offline training. Specifically, the proposed framework starts with modeling the fields of interest using the tensor Tucker model of a high multilinear rank, which ensures a universal approximation property for all fields. In the sequel, an attention mechanism is incorporated to learn the sparsity pattern that underlies the core tensor in order to reduce the solution space. In this way, a ``complexity-adaptive'' neural representation, grounded in the Tucker decomposition, is obtained that can flexibly represent various types of fields. A theoretical analysis is provided to support the recoverability of the proposed design. Moreover, extensive experiments, using various physical field tensors, demonstrate the superiority of the proposed approach compared to state-of-the-art baselines.
ReCamMaster: Camera-Controlled Generative Rendering from A Single Video
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:Camera control has been actively studied in text or image conditioned video generation tasks. However, altering camera trajectories of a given video remains under-explored, despite its importance in the field of video creation. It is non-trivial due to the extra constraints of maintaining multiple-frame appearance and dynamic synchronization. To address this, we present ReCamMaster, a camera-controlled generative video re-rendering framework that reproduces the dynamic scene of an input video at novel camera trajectories. The core innovation lies in harnessing the generative capabilities of pre-trained text-to-video models through a simple yet powerful video conditioning mechanism -- its capability often overlooked in current research. To overcome the scarcity of qualified training data, we construct a comprehensive multi-camera synchronized video dataset using Unreal Engine 5, which is carefully curated to follow real-world filming characteristics, covering diverse scenes and camera movements. It helps the model generalize to in-the-wild videos. Lastly, we further improve the robustness to diverse inputs through a meticulously designed training strategy. Extensive experiments tell that our method substantially outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches and strong baselines. Our method also finds promising applications in video stabilization, super-resolution, and outpainting. Project page: https://jianhongbai.github.io/ReCamMaster/
Domain-Factored Untrained Deep Prior for Spectrum Cartography
Jan 23, 2025Abstract:Spectrum cartography (SC) focuses on estimating the radio power propagation map of multiple emitters across space and frequency using limited sensor measurements. Recent advances in SC have shown that leveraging learned deep generative models (DGMs) as structural constraints yields state-of-the-art performance. By harnessing the expressive power of neural networks, these structural "priors" capture intricate patterns in radio maps. However, training DGMs requires substantial data, which is not always available, and distribution shifts between training and testing data can further degrade performance. To address these challenges, this work proposes using untrained neural networks (UNNs) for SC. UNNs, commonly applied in vision tasks to represent complex data without training, encode structural information of data in neural architectures. In our approach, a custom-designed UNN represents radio maps under a spatio-spectral domain factorization model, leveraging physical characteristics to reduce sample complexity of SC. Experiments show that the method achieves performance comparable to learned DGM-based SC, without requiring training data.
3DTrajMaster: Mastering 3D Trajectory for Multi-Entity Motion in Video Generation
Dec 10, 2024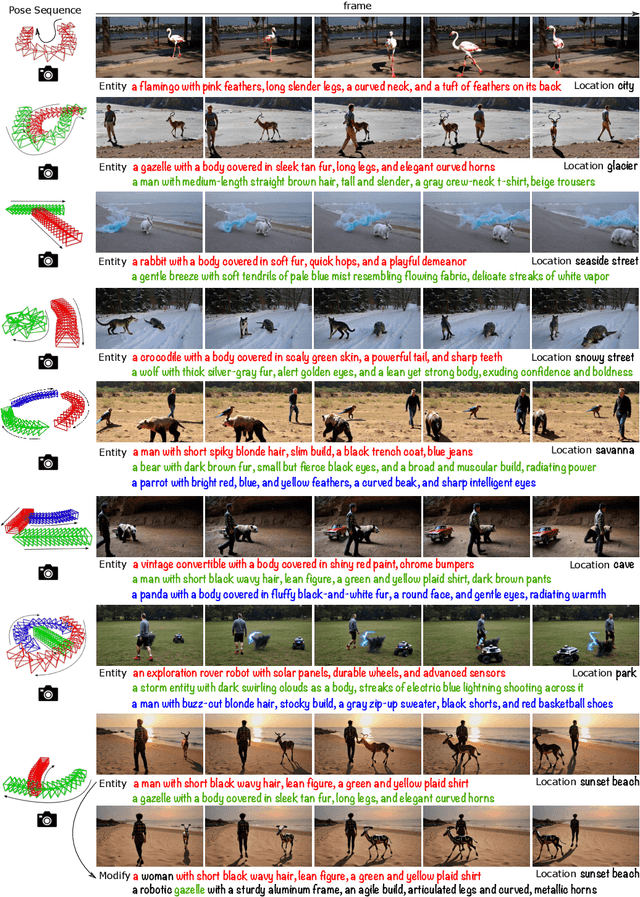
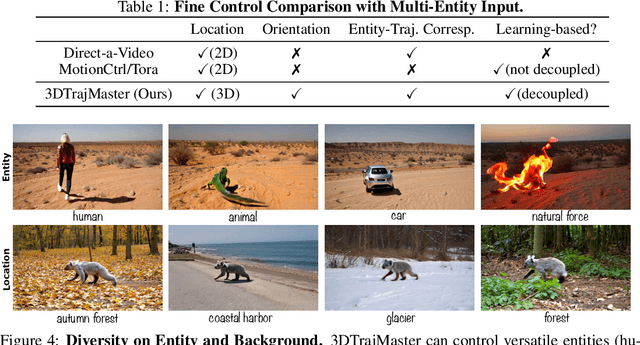
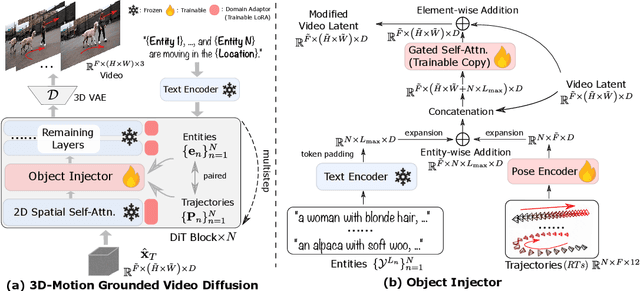
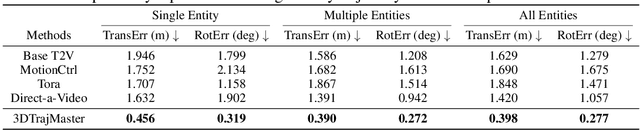
Abstract:This paper aims to manipulate multi-entity 3D motions in video generation. Previous methods on controllable video generation primarily leverage 2D control signals to manipulate object motions and have achieved remarkable synthesis results. However, 2D control signals are inherently limited in expressing the 3D nature of object motions. To overcome this problem, we introduce 3DTrajMaster, a robust controller that regulates multi-entity dynamics in 3D space, given user-desired 6DoF pose (location and rotation) sequences of entities. At the core of our approach is a plug-and-play 3D-motion grounded object injector that fuses multiple input entities with their respective 3D trajectories through a gated self-attention mechanism. In addition, we exploit an injector architecture to preserve the video diffusion prior, which is crucial for generalization ability. To mitigate video quality degradation, we introduce a domain adaptor during training and employ an annealed sampling strategy during inference. To address the lack of suitable training data, we construct a 360-Motion Dataset, which first correlates collected 3D human and animal assets with GPT-generated trajectory and then captures their motion with 12 evenly-surround cameras on diverse 3D UE platforms. Extensive experiments show that 3DTrajMaster sets a new state-of-the-art in both accuracy and generalization for controlling multi-entity 3D motions. Project page: http://fuxiao0719.github.io/projects/3dtrajmaster
SynCamMaster: Synchronizing Multi-Camera Video Generation from Diverse Viewpoints
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in video diffusion models have shown exceptional abilities in simulating real-world dynamics and maintaining 3D consistency. This progress inspires us to investigate the potential of these models to ensure dynamic consistency across various viewpoints, a highly desirable feature for applications such as virtual filming. Unlike existing methods focused on multi-view generation of single objects for 4D reconstruction, our interest lies in generating open-world videos from arbitrary viewpoints, incorporating 6 DoF camera poses. To achieve this, we propose a plug-and-play module that enhances a pre-trained text-to-video model for multi-camera video generation, ensuring consistent content across different viewpoints. Specifically, we introduce a multi-view synchronization module to maintain appearance and geometry consistency across these viewpoints. Given the scarcity of high-quality training data, we design a hybrid training scheme that leverages multi-camera images and monocular videos to supplement Unreal Engine-rendered multi-camera videos. Furthermore, our method enables intriguing extensions, such as re-rendering a video from novel viewpoints. We also release a multi-view synchronized video dataset, named SynCamVideo-Dataset. Project page: https://jianhongbai.github.io/SynCamMaster/.
Downlink MIMO Channel Estimation from Bits: Recoverability and Algorithm
Nov 25, 2024



Abstract:In frequency division duplex (FDD) massive MIMO systems, a major challenge lies in acquiring the downlink channel state information}\ (CSI) at the base station (BS) from limited feedback sent by the user equipment (UE). To tackle this fundamental task, our contribution is twofold: First, a simple feedback framework is proposed, where a compression and Gaussian dithering-based quantization strategy is adopted at the UE side, and then a maximum likelihood estimator (MLE) is formulated at the BS side. Recoverability of the MIMO channel under the widely used double directional model is established. Specifically, analyses are presented for two compression schemes -- showing one being more overhead-economical and the other computationally lighter at the UE side. Second, to realize the MLE, an alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) algorithm is proposed. The algorithm is carefully designed to integrate a sophisticated harmonic retrieval (HR) solver as subroutine, which turns out to be the key of effectively tackling this hard MLE problem.Extensive numerical experiments are conducted to validate the efficacy of our approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge