Jianhong Bai
CineScene: Implicit 3D as Effective Scene Representation for Cinematic Video Generation
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:Cinematic video production requires control over scene-subject composition and camera movement, but live-action shooting remains costly due to the need for constructing physical sets. To address this, we introduce the task of cinematic video generation with decoupled scene context: given multiple images of a static environment, the goal is to synthesize high-quality videos featuring dynamic subject while preserving the underlying scene consistency and following a user-specified camera trajectory. We present CineScene, a framework that leverages implicit 3D-aware scene representation for cinematic video generation. Our key innovation is a novel context conditioning mechanism that injects 3D-aware features in an implicit way: By encoding scene images into visual representations through VGGT, CineScene injects spatial priors into a pretrained text-to-video generation model by additional context concatenation, enabling camera-controlled video synthesis with consistent scenes and dynamic subjects. To further enhance the model's robustness, we introduce a simple yet effective random-shuffling strategy for the input scene images during training. To address the lack of training data, we construct a scene-decoupled dataset with Unreal Engine 5, containing paired videos of scenes with and without dynamic subjects, panoramic images representing the underlying static scene, along with their camera trajectories. Experiments show that CineScene achieves state-of-the-art performance in scene-consistent cinematic video generation, handling large camera movements and demonstrating generalization across diverse environments.
SemanticGen: Video Generation in Semantic Space
Dec 24, 2025

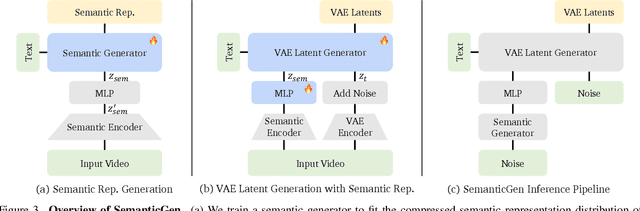

Abstract:State-of-the-art video generative models typically learn the distribution of video latents in the VAE space and map them to pixels using a VAE decoder. While this approach can generate high-quality videos, it suffers from slow convergence and is computationally expensive when generating long videos. In this paper, we introduce SemanticGen, a novel solution to address these limitations by generating videos in the semantic space. Our main insight is that, due to the inherent redundancy in videos, the generation process should begin in a compact, high-level semantic space for global planning, followed by the addition of high-frequency details, rather than directly modeling a vast set of low-level video tokens using bi-directional attention. SemanticGen adopts a two-stage generation process. In the first stage, a diffusion model generates compact semantic video features, which define the global layout of the video. In the second stage, another diffusion model generates VAE latents conditioned on these semantic features to produce the final output. We observe that generation in the semantic space leads to faster convergence compared to the VAE latent space. Our method is also effective and computationally efficient when extended to long video generation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SemanticGen produces high-quality videos and outperforms state-of-the-art approaches and strong baselines.
RelightMaster: Precise Video Relighting with Multi-plane Light Images
Nov 09, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in diffusion models enable high-quality video generation and editing, but precise relighting with consistent video contents, which is critical for shaping scene atmosphere and viewer attention, remains unexplored. Mainstream text-to-video (T2V) models lack fine-grained lighting control due to text's inherent limitation in describing lighting details and insufficient pre-training on lighting-related prompts. Additionally, constructing high-quality relighting training data is challenging, as real-world controllable lighting data is scarce. To address these issues, we propose RelightMaster, a novel framework for accurate and controllable video relighting. First, we build RelightVideo, the first dataset with identical dynamic content under varying precise lighting conditions based on the Unreal Engine. Then, we introduce Multi-plane Light Image (MPLI), a novel visual prompt inspired by Multi-Plane Image (MPI). MPLI models lighting via K depth-aligned planes, representing 3D light source positions, intensities, and colors while supporting multi-source scenarios and generalizing to unseen light setups. Third, we design a Light Image Adapter that seamlessly injects MPLI into pre-trained Video Diffusion Transformers (DiT): it compresses MPLI via a pre-trained Video VAE and injects latent light features into DiT blocks, leveraging the base model's generative prior without catastrophic forgetting. Experiments show that RelightMaster generates physically plausible lighting and shadows and preserves original scene content. Demos are available at https://wkbian.github.io/Projects/RelightMaster/.
No Pixel Left Behind: A Detail-Preserving Architecture for Robust High-Resolution AI-Generated Image Detection
Aug 24, 2025Abstract:The rapid growth of high-resolution, meticulously crafted AI-generated images poses a significant challenge to existing detection methods, which are often trained and evaluated on low-resolution, automatically generated datasets that do not align with the complexities of high-resolution scenarios. A common practice is to resize or center-crop high-resolution images to fit standard network inputs. However, without full coverage of all pixels, such strategies risk either obscuring subtle, high-frequency artifacts or discarding information from uncovered regions, leading to input information loss. In this paper, we introduce the High-Resolution Detail-Aggregation Network (HiDA-Net), a novel framework that ensures no pixel is left behind. We use the Feature Aggregation Module (FAM), which fuses features from multiple full-resolution local tiles with a down-sampled global view of the image. These local features are aggregated and fused with global representations for final prediction, ensuring that native-resolution details are preserved and utilized for detection. To enhance robustness against challenges such as localized AI manipulations and compression, we introduce Token-wise Forgery Localization (TFL) module for fine-grained spatial sensitivity and JPEG Quality Factor Estimation (QFE) module to disentangle generative artifacts from compression noise explicitly. Furthermore, to facilitate future research, we introduce HiRes-50K, a new challenging benchmark consisting of 50,568 images with up to 64 megapixels. Extensive experiments show that HiDA-Net achieves state-of-the-art, increasing accuracy by over 13% on the challenging Chameleon dataset and 10% on our HiRes-50K.
ReCamMaster: Camera-Controlled Generative Rendering from A Single Video
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:Camera control has been actively studied in text or image conditioned video generation tasks. However, altering camera trajectories of a given video remains under-explored, despite its importance in the field of video creation. It is non-trivial due to the extra constraints of maintaining multiple-frame appearance and dynamic synchronization. To address this, we present ReCamMaster, a camera-controlled generative video re-rendering framework that reproduces the dynamic scene of an input video at novel camera trajectories. The core innovation lies in harnessing the generative capabilities of pre-trained text-to-video models through a simple yet powerful video conditioning mechanism -- its capability often overlooked in current research. To overcome the scarcity of qualified training data, we construct a comprehensive multi-camera synchronized video dataset using Unreal Engine 5, which is carefully curated to follow real-world filming characteristics, covering diverse scenes and camera movements. It helps the model generalize to in-the-wild videos. Lastly, we further improve the robustness to diverse inputs through a meticulously designed training strategy. Extensive experiments tell that our method substantially outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches and strong baselines. Our method also finds promising applications in video stabilization, super-resolution, and outpainting. Project page: https://jianhongbai.github.io/ReCamMaster/
Enhancing Facial Consistency in Conditional Video Generation via Facial Landmark Transformation
Dec 12, 2024

Abstract:Landmark-guided character animation generation is an important field. Generating character animations with facial features consistent with a reference image remains a significant challenge in conditional video generation, especially involving complex motions like dancing. Existing methods often fail to maintain facial feature consistency due to mismatches between the facial landmarks extracted from source videos and the target facial features in the reference image. To address this problem, we propose a facial landmark transformation method based on the 3D Morphable Model (3DMM). We obtain transformed landmarks that align with the target facial features by reconstructing 3D faces from the source landmarks and adjusting the 3DMM parameters to match the reference image. Our method improves the facial consistency between the generated videos and the reference images, effectively improving the facial feature mismatch problem.
SynCamMaster: Synchronizing Multi-Camera Video Generation from Diverse Viewpoints
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in video diffusion models have shown exceptional abilities in simulating real-world dynamics and maintaining 3D consistency. This progress inspires us to investigate the potential of these models to ensure dynamic consistency across various viewpoints, a highly desirable feature for applications such as virtual filming. Unlike existing methods focused on multi-view generation of single objects for 4D reconstruction, our interest lies in generating open-world videos from arbitrary viewpoints, incorporating 6 DoF camera poses. To achieve this, we propose a plug-and-play module that enhances a pre-trained text-to-video model for multi-camera video generation, ensuring consistent content across different viewpoints. Specifically, we introduce a multi-view synchronization module to maintain appearance and geometry consistency across these viewpoints. Given the scarcity of high-quality training data, we design a hybrid training scheme that leverages multi-camera images and monocular videos to supplement Unreal Engine-rendered multi-camera videos. Furthermore, our method enables intriguing extensions, such as re-rendering a video from novel viewpoints. We also release a multi-view synchronized video dataset, named SynCamVideo-Dataset. Project page: https://jianhongbai.github.io/SynCamMaster/.
InstructAvatar: Text-Guided Emotion and Motion Control for Avatar Generation
May 24, 2024



Abstract:Recent talking avatar generation models have made strides in achieving realistic and accurate lip synchronization with the audio, but often fall short in controlling and conveying detailed expressions and emotions of the avatar, making the generated video less vivid and controllable. In this paper, we propose a novel text-guided approach for generating emotionally expressive 2D avatars, offering fine-grained control, improved interactivity, and generalizability to the resulting video. Our framework, named InstructAvatar, leverages a natural language interface to control the emotion as well as the facial motion of avatars. Technically, we design an automatic annotation pipeline to construct an instruction-video paired training dataset, equipped with a novel two-branch diffusion-based generator to predict avatars with audio and text instructions at the same time. Experimental results demonstrate that InstructAvatar produces results that align well with both conditions, and outperforms existing methods in fine-grained emotion control, lip-sync quality, and naturalness. Our project page is https://wangyuchi369.github.io/InstructAvatar/.
LaDiC: Are Diffusion Models Really Inferior to Autoregressive Counterparts for Image-to-Text Generation?
Apr 16, 2024



Abstract:Diffusion models have exhibited remarkable capabilities in text-to-image generation. However, their performance in image-to-text generation, specifically image captioning, has lagged behind Auto-Regressive (AR) models, casting doubt on their applicability for such tasks. In this work, we revisit diffusion models, highlighting their capacity for holistic context modeling and parallel decoding. With these benefits, diffusion models can alleviate the inherent limitations of AR methods, including their slow inference speed, error propagation, and unidirectional constraints. Furthermore, we identify the prior underperformance of diffusion models stemming from the absence of an effective latent space for image-text alignment, and the discrepancy between continuous diffusion processes and discrete textual data. In response, we introduce a novel architecture, LaDiC, which utilizes a split BERT to create a dedicated latent space for captions and integrates a regularization module to manage varying text lengths. Our framework also includes a diffuser for semantic image-to-text conversion and a Back&Refine technique to enhance token interactivity during inference. LaDiC achieves state-of-the-art performance for diffusion-based methods on the MS COCO dataset with 38.2 BLEU@4 and 126.2 CIDEr, demonstrating exceptional performance without pre-training or ancillary modules. This indicates strong competitiveness with AR models, revealing the previously untapped potential of diffusion models in image-to-text generation.
UniEdit: A Unified Tuning-Free Framework for Video Motion and Appearance Editing
Feb 24, 2024



Abstract:Recent advances in text-guided video editing have showcased promising results in appearance editing (e.g., stylization). However, video motion editing in the temporal dimension (e.g., from eating to waving), which distinguishes video editing from image editing, is underexplored. In this work, we present UniEdit, a tuning-free framework that supports both video motion and appearance editing by harnessing the power of a pre-trained text-to-video generator within an inversion-then-generation framework. To realize motion editing while preserving source video content, based on the insights that temporal and spatial self-attention layers encode inter-frame and intra-frame dependency respectively, we introduce auxiliary motion-reference and reconstruction branches to produce text-guided motion and source features respectively. The obtained features are then injected into the main editing path via temporal and spatial self-attention layers. Extensive experiments demonstrate that UniEdit covers video motion editing and various appearance editing scenarios, and surpasses the state-of-the-art methods. Our code will be publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge