Yang Feng
Alibaba Group
Towards Compositional Generalization of LLMs via Skill Taxonomy Guided Data Synthesis
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) and agent-based systems often struggle with compositional generalization due to a data bottleneck in which complex skill combinations follow a long-tailed, power-law distribution, limiting both instruction-following performance and generalization in agent-centric tasks. To address this challenge, we propose STEPS, a Skill Taxonomy guided Entropy-based Post-training data Synthesis framework for generating compositionally challenging data. STEPS explicitly targets compositional generalization by uncovering latent relationships among skills and organizing them into an interpretable, hierarchical skill taxonomy using structural information theory. Building on this taxonomy, we formulate data synthesis as a constrained information maximization problem, selecting skill combinations that maximize marginal structural information within the hierarchy while preserving semantic coherence. Experiments on challenging instruction-following benchmarks show that STEPS outperforms existing data synthesis baselines, while also yielding improved compositional generalization in downstream agent-based evaluations.
PSO-Merging: Merging Models Based on Particle Swarm Optimization
Aug 27, 2025Abstract:Model merging has emerged as an efficient strategy for constructing multitask models by integrating the strengths of multiple available expert models, thereby reducing the need to fine-tune a pre-trained model for all the tasks from scratch. Existing data-independent methods struggle with performance limitations due to the lack of data-driven guidance. Data-driven approaches also face key challenges: gradient-based methods are computationally expensive, limiting their practicality for merging large expert models, whereas existing gradient-free methods often fail to achieve satisfactory results within a limited number of optimization steps. To address these limitations, this paper introduces PSO-Merging, a novel data-driven merging method based on the Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO). In this approach, we initialize the particle swarm with a pre-trained model, expert models, and sparsified expert models. We then perform multiple iterations, with the final global best particle serving as the merged model. Experimental results on different language models show that PSO-Merging generally outperforms baseline merging methods, offering a more efficient and scalable solution for model merging.
Knowing or Guessing? Robust Medical Visual Question Answering via Joint Consistency and Contrastive Learning
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:In high-stakes medical applications, consistent answering across diverse question phrasings is essential for reliable diagnosis. However, we reveal that current Medical Vision-Language Models (Med-VLMs) exhibit concerning fragility in Medical Visual Question Answering, as their answers fluctuate significantly when faced with semantically equivalent rephrasings of medical questions. We attribute this to two limitations: (1) insufficient alignment of medical concepts, leading to divergent reasoning patterns, and (2) hidden biases in training data that prioritize syntactic shortcuts over semantic understanding. To address these challenges, we construct RoMed, a dataset built upon original VQA datasets containing 144k questions with variations spanning word-level, sentence-level, and semantic-level perturbations. When evaluating state-of-the-art (SOTA) models like LLaVA-Med on RoMed, we observe alarming performance drops (e.g., a 40\% decline in Recall) compared to original VQA benchmarks, exposing critical robustness gaps. To bridge this gap, we propose Consistency and Contrastive Learning (CCL), which integrates two key components: (1) knowledge-anchored consistency learning, aligning Med-VLMs with medical knowledge rather than shallow feature patterns, and (2) bias-aware contrastive learning, mitigating data-specific priors through discriminative representation refinement. CCL achieves SOTA performance on three popular VQA benchmarks and notably improves answer consistency by 50\% on the challenging RoMed test set, demonstrating significantly enhanced robustness. Code will be released.
StreamUni: Achieving Streaming Speech Translation with a Unified Large Speech-Language Model
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:Streaming speech translation (StreamST) requires determining appropriate timing, known as policy, to generate translations while continuously receiving source speech inputs, balancing low latency with high translation quality. However, existing StreamST methods typically operate on sentence-level speech segments, referred to as simultaneous speech translation (SimulST). In practice, they require collaboration with segmentation models to accomplish StreamST, where the truncated speech segments constrain SimulST models to make policy decisions and generate translations based on limited contextual information. Moreover, SimulST models struggle to learn effective policies due to the complexity of speech inputs and cross-lingual generation. To address these challenges, we propose StreamUni, which achieves StreamST through a unified Large Speech-Language Model (LSLM). Specifically, StreamUni incorporates speech Chain-of-Thought (CoT) in guiding the LSLM to generate multi-stage outputs. Leveraging these multi-stage outputs, StreamUni simultaneously accomplishes speech segmentation, policy decision, and translation generation, completing StreamST without requiring massive policy-specific training. Additionally, we propose a streaming CoT training method that enhances low-latency policy decisions and generation capabilities using limited CoT data. Experiments demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on StreamST tasks.
Stream-Omni: Simultaneous Multimodal Interactions with Large Language-Vision-Speech Model
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:The emergence of GPT-4o-like large multimodal models (LMMs) has raised the exploration of integrating text, vision, and speech modalities to support more flexible multimodal interaction. Existing LMMs typically concatenate representation of modalities along the sequence dimension and feed them into a large language model (LLM) backbone. While sequence-dimension concatenation is straightforward for modality integration, it often relies heavily on large-scale data to learn modality alignments. In this paper, we aim to model the relationships between modalities more purposefully, thereby achieving more efficient and flexible modality alignments. To this end, we propose Stream-Omni, a large language-vision-speech model with efficient modality alignments, which can simultaneously support interactions under various modality combinations. Stream-Omni employs LLM as the backbone and aligns the vision and speech to the text based on their relationships. For vision that is semantically complementary to text, Stream-Omni uses sequence-dimension concatenation to achieve vision-text alignment. For speech that is semantically consistent with text, Stream-Omni introduces a CTC-based layer-dimension mapping to achieve speech-text alignment. In this way, Stream-Omni can achieve modality alignments with less data (especially speech), enabling the transfer of text capabilities to other modalities. Experiments on various benchmarks demonstrate that Stream-Omni achieves strong performance on visual understanding, speech interaction, and vision-grounded speech interaction tasks. Owing to the layer-dimensional mapping, Stream-Omni can simultaneously provide intermediate text outputs (such as ASR transcriptions and model responses) during speech interaction, offering users a comprehensive multimodal experience.
CAPO: Reinforcing Consistent Reasoning in Medical Decision-Making
Jun 15, 2025
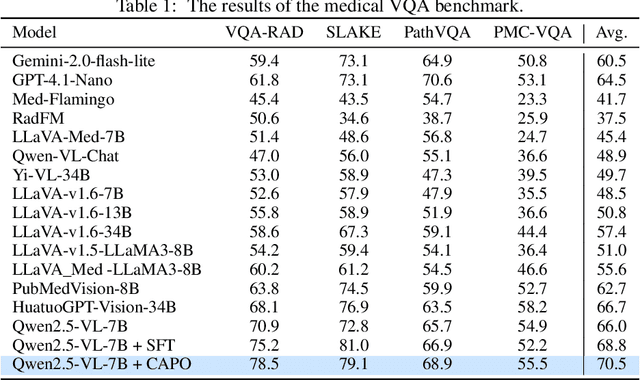
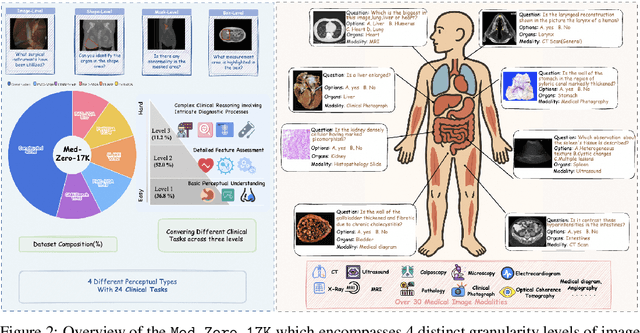
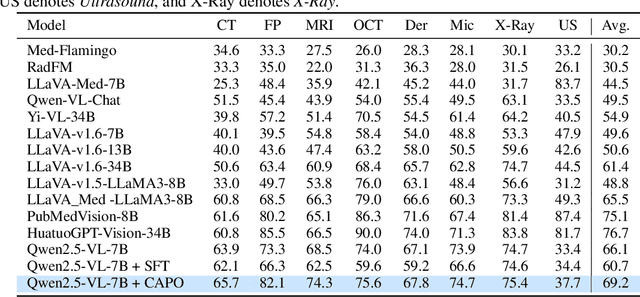
Abstract:In medical visual question answering (Med-VQA), achieving accurate responses relies on three critical steps: precise perception of medical imaging data, logical reasoning grounded in visual input and textual questions, and coherent answer derivation from the reasoning process. Recent advances in general vision-language models (VLMs) show that large-scale reinforcement learning (RL) could significantly enhance both reasoning capabilities and overall model performance. However, their application in medical domains is hindered by two fundamental challenges: 1) misalignment between perceptual understanding and reasoning stages, and 2) inconsistency between reasoning pathways and answer generation, both compounded by the scarcity of high-quality medical datasets for effective large-scale RL. In this paper, we first introduce Med-Zero-17K, a curated dataset for pure RL-based training, encompassing over 30 medical image modalities and 24 clinical tasks. Moreover, we propose a novel large-scale RL framework for Med-VLMs, Consistency-Aware Preference Optimization (CAPO), which integrates rewards to ensure fidelity between perception and reasoning, consistency in reasoning-to-answer derivation, and rule-based accuracy for final responses. Extensive experiments on both in-domain and out-of-domain scenarios demonstrate the superiority of our method over strong VLM baselines, showcasing strong generalization capability to 3D Med-VQA benchmarks and R1-like training paradigms.
FlexRAG: A Flexible and Comprehensive Framework for Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) plays a pivotal role in modern large language model applications, with numerous existing frameworks offering a wide range of functionalities to facilitate the development of RAG systems. However, we have identified several persistent challenges in these frameworks, including difficulties in algorithm reproduction and sharing, lack of new techniques, and high system overhead. To address these limitations, we introduce \textbf{FlexRAG}, an open-source framework specifically designed for research and prototyping. FlexRAG supports text-based, multimodal, and network-based RAG, providing comprehensive lifecycle support alongside efficient asynchronous processing and persistent caching capabilities. By offering a robust and flexible solution, FlexRAG enables researchers to rapidly develop, deploy, and share advanced RAG systems. Our toolkit and resources are available at \href{https://github.com/ictnlp/FlexRAG}{https://github.com/ictnlp/FlexRAG}.
Efficient Speech Language Modeling via Energy Distance in Continuous Latent Space
May 19, 2025Abstract:We introduce SLED, an alternative approach to speech language modeling by encoding speech waveforms into sequences of continuous latent representations and modeling them autoregressively using an energy distance objective. The energy distance offers an analytical measure of the distributional gap by contrasting simulated and target samples, enabling efficient training to capture the underlying continuous autoregressive distribution. By bypassing reliance on residual vector quantization, SLED avoids discretization errors and eliminates the need for the complicated hierarchical architectures common in existing speech language models. It simplifies the overall modeling pipeline while preserving the richness of speech information and maintaining inference efficiency. Empirical results demonstrate that SLED achieves strong performance in both zero-shot and streaming speech synthesis, showing its potential for broader applications in general-purpose speech language models.
LLaMA-Omni2: LLM-based Real-time Spoken Chatbot with Autoregressive Streaming Speech Synthesis
May 05, 2025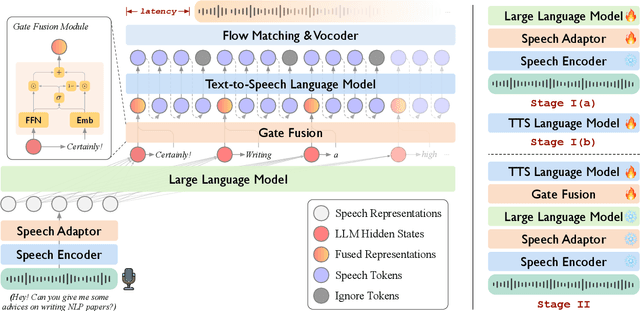
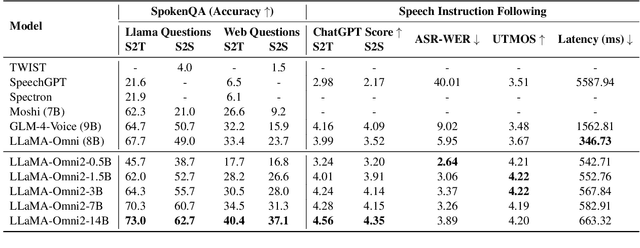
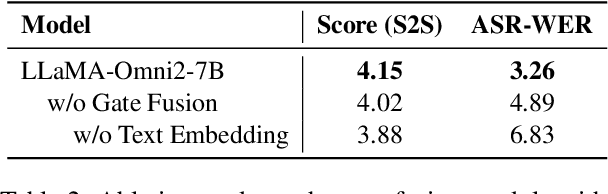
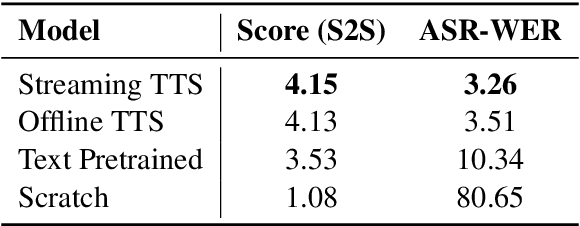
Abstract:Real-time, intelligent, and natural speech interaction is an essential part of the next-generation human-computer interaction. Recent advancements have showcased the potential of building intelligent spoken chatbots based on large language models (LLMs). In this paper, we introduce LLaMA-Omni 2, a series of speech language models (SpeechLMs) ranging from 0.5B to 14B parameters, capable of achieving high-quality real-time speech interaction. LLaMA-Omni 2 is built upon the Qwen2.5 series models, integrating a speech encoder and an autoregressive streaming speech decoder. Despite being trained on only 200K multi-turn speech dialogue samples, LLaMA-Omni 2 demonstrates strong performance on several spoken question answering and speech instruction following benchmarks, surpassing previous state-of-the-art SpeechLMs like GLM-4-Voice, which was trained on millions of hours of speech data.
GeoERM: Geometry-Aware Multi-Task Representation Learning on Riemannian Manifolds
May 05, 2025Abstract:Multi-Task Learning (MTL) seeks to boost statistical power and learning efficiency by discovering structure shared across related tasks. State-of-the-art MTL representation methods, however, usually treat the latent representation matrix as a point in ordinary Euclidean space, ignoring its often non-Euclidean geometry, thus sacrificing robustness when tasks are heterogeneous or even adversarial. We propose GeoERM, a geometry-aware MTL framework that embeds the shared representation on its natural Riemannian manifold and optimizes it via explicit manifold operations. Each training cycle performs (i) a Riemannian gradient step that respects the intrinsic curvature of the search space, followed by (ii) an efficient polar retraction to remain on the manifold, guaranteeing geometric fidelity at every iteration. The procedure applies to a broad class of matrix-factorized MTL models and retains the same per-iteration cost as Euclidean baselines. Across a set of synthetic experiments with task heterogeneity and on a wearable-sensor activity-recognition benchmark, GeoERM consistently improves estimation accuracy, reduces negative transfer, and remains stable under adversarial label noise, outperforming leading MTL and single-task alternatives.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge