Zhuocheng Zhang
SURE: Safe Uncertainty-Aware Robot-Environment Interaction using Trajectory Optimization
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:Robotic tasks involving contact interactions pose significant challenges for trajectory optimization due to discontinuous dynamics. Conventional formulations typically assume deterministic contact events, which limit robustness and adaptability in real-world settings. In this work, we propose SURE, a robust trajectory optimization framework that explicitly accounts for contact timing uncertainty. By allowing multiple trajectories to branch from possible pre-impact states and later rejoin a shared trajectory, SURE achieves both robustness and computational efficiency within a unified optimization framework. We evaluate SURE on two representative tasks with unknown impact times. In a cart-pole balancing task involving uncertain wall location, SURE achieves an average improvement of 21.6% in success rate when branch switching is enabled during control. In an egg-catching experiment using a robotic manipulator, SURE improves the success rate by 40%. These results demonstrate that SURE substantially enhances robustness compared to conventional nominal formulations.
Eliminating Hallucination in Diffusion-Augmented Interactive Text-to-Image Retrieval
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Diffusion-Augmented Interactive Text-to-Image Retrieval (DAI-TIR) is a promising paradigm that improves retrieval performance by generating query images via diffusion models and using them as additional ``views'' of the user's intent. However, these generative views can be incorrect because diffusion generation may introduce hallucinated visual cues that conflict with the original query text. Indeed, we empirically demonstrate that these hallucinated cues can substantially degrade DAI-TIR performance. To address this, we propose Diffusion-aware Multi-view Contrastive Learning (DMCL), a hallucination-robust training framework that casts DAI-TIR as joint optimization over representations of query intent and the target image. DMCL introduces semantic-consistency and diffusion-aware contrastive objectives to align textual and diffusion-generated query views while suppressing hallucinated query signals. This yields an encoder that acts as a semantic filter, effectively mapping hallucinated cues into a null space, improving robustness to spurious cues and better representing the user's intent. Attention visualization and geometric embedding-space analyses corroborate this filtering behavior. Across five standard benchmarks, DMCL delivers consistent improvements in multi-round Hits@10, reaching as high as 7.37\% over prior fine-tuned and zero-shot baselines, which indicates it is a general and robust training framework for DAI-TIR.
RoboEye: Enhancing 2D Robotic Object Identification with Selective 3D Geometric Keypoint Matching
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:The rapidly growing number of product categories in large-scale e-commerce makes accurate object identification for automated packing in warehouses substantially more difficult. As the catalog grows, intra-class variability and a long tail of rare or visually similar items increase, and when combined with diverse packaging, cluttered containers, frequent occlusion, and large viewpoint changes-these factors amplify discrepancies between query and reference images, causing sharp performance drops for methods that rely solely on 2D appearance features. Thus, we propose RoboEye, a two-stage identification framework that dynamically augments 2D semantic features with domain-adapted 3D reasoning and lightweight adapters to bridge training deployment gaps. In the first stage, we train a large vision model to extract 2D features for generating candidate rankings. A lightweight 3D-feature-awareness module then estimates 3D feature quality and predicts whether 3D re-ranking is necessary, preventing performance degradation and avoiding unnecessary computation. When invoked, the second stage uses our robot 3D retrieval transformer, comprising a 3D feature extractor that produces geometry-aware dense features and a keypoint-based matcher that computes keypoint-correspondence confidences between query and reference images instead of conventional cosine-similarity scoring. Experiments show that RoboEye improves Recall@1 by 7.1% over the prior state of the art (RoboLLM). Moreover, RoboEye operates using only RGB images, avoiding reliance on explicit 3D inputs and reducing deployment costs. The code used in this paper is publicly available at: https://github.com/longkukuhi/RoboEye.
FlexRAG: A Flexible and Comprehensive Framework for Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) plays a pivotal role in modern large language model applications, with numerous existing frameworks offering a wide range of functionalities to facilitate the development of RAG systems. However, we have identified several persistent challenges in these frameworks, including difficulties in algorithm reproduction and sharing, lack of new techniques, and high system overhead. To address these limitations, we introduce \textbf{FlexRAG}, an open-source framework specifically designed for research and prototyping. FlexRAG supports text-based, multimodal, and network-based RAG, providing comprehensive lifecycle support alongside efficient asynchronous processing and persistent caching capabilities. By offering a robust and flexible solution, FlexRAG enables researchers to rapidly develop, deploy, and share advanced RAG systems. Our toolkit and resources are available at \href{https://github.com/ictnlp/FlexRAG}{https://github.com/ictnlp/FlexRAG}.
LevelRAG: Enhancing Retrieval-Augmented Generation with Multi-hop Logic Planning over Rewriting Augmented Searchers
Feb 25, 2025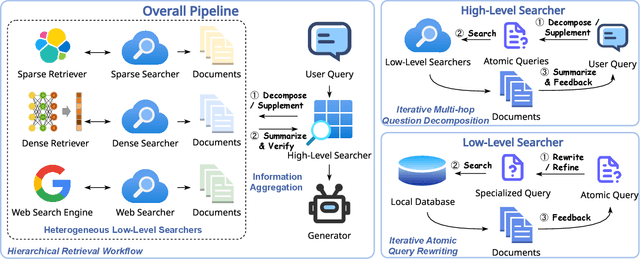
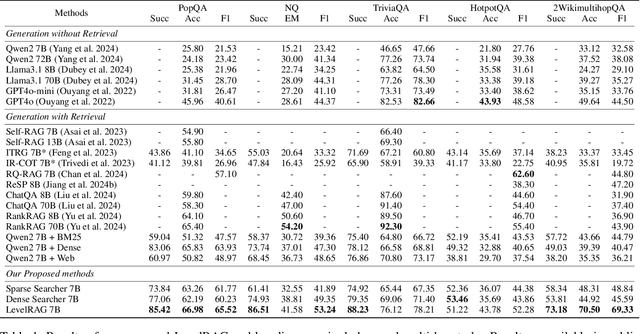

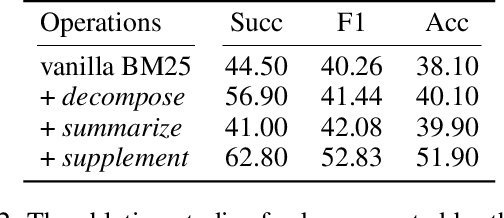
Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a crucial method for mitigating hallucinations in Large Language Models (LLMs) and integrating external knowledge into their responses. Existing RAG methods typically employ query rewriting to clarify the user intent and manage multi-hop logic, while using hybrid retrieval to expand search scope. However, the tight coupling of query rewriting to the dense retriever limits its compatibility with hybrid retrieval, impeding further RAG performance improvements. To address this challenge, we introduce a high-level searcher that decomposes complex queries into atomic queries, independent of any retriever-specific optimizations. Additionally, to harness the strengths of sparse retrievers for precise keyword retrieval, we have developed a new sparse searcher that employs Lucene syntax to enhance retrieval accuracy.Alongside web and dense searchers, these components seamlessly collaborate within our proposed method, \textbf{LevelRAG}. In LevelRAG, the high-level searcher orchestrates the retrieval logic, while the low-level searchers (sparse, web, and dense) refine the queries for optimal retrieval. This approach enhances both the completeness and accuracy of the retrieval process, overcoming challenges associated with current query rewriting techniques in hybrid retrieval scenarios. Empirical experiments conducted on five datasets, encompassing both single-hop and multi-hop question answering tasks, demonstrate the superior performance of LevelRAG compared to existing RAG methods. Notably, LevelRAG outperforms the state-of-the-art proprietary model, GPT4o, underscoring its effectiveness and potential impact on the RAG field.
Addressing the Length Bias Problem in Document-Level Neural Machine Translation
Nov 20, 2023Abstract:Document-level neural machine translation (DNMT) has shown promising results by incorporating more context information. However, this approach also introduces a length bias problem, whereby DNMT suffers from significant translation quality degradation when decoding documents that are much shorter or longer than the maximum sequence length during training. %i.e., the length bias problem. To solve the length bias problem, we propose to improve the DNMT model in training method, attention mechanism, and decoding strategy. Firstly, we propose to sample the training data dynamically to ensure a more uniform distribution across different sequence lengths. Then, we introduce a length-normalized attention mechanism to aid the model in focusing on target information, mitigating the issue of attention divergence when processing longer sequences. Lastly, we propose a sliding window strategy during decoding that integrates as much context information as possible without exceeding the maximum sequence length. The experimental results indicate that our method can bring significant improvements on several open datasets, and further analysis shows that our method can significantly alleviate the length bias problem.
Enhancing Neural Machine Translation with Semantic Units
Oct 17, 2023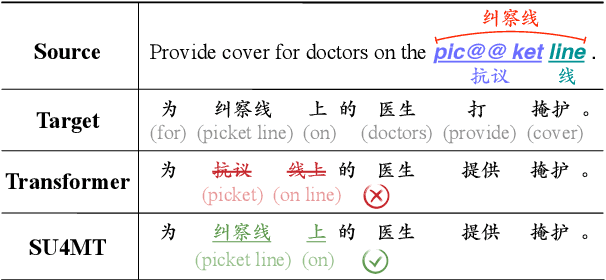
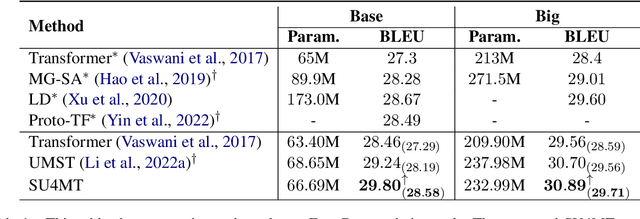
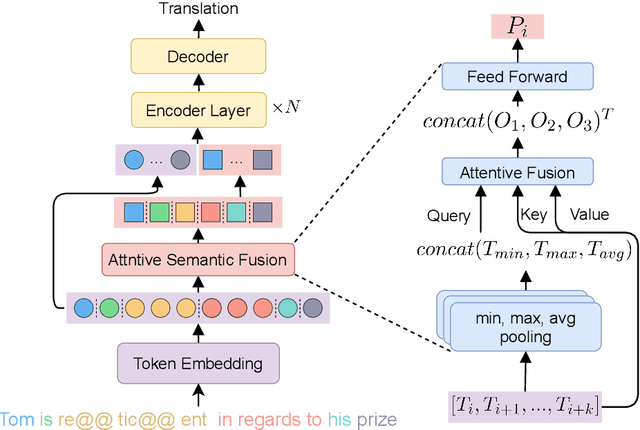
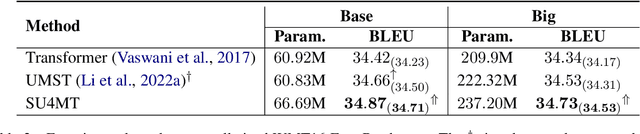
Abstract:Conventional neural machine translation (NMT) models typically use subwords and words as the basic units for model input and comprehension. However, complete words and phrases composed of several tokens are often the fundamental units for expressing semantics, referred to as semantic units. To address this issue, we propose a method Semantic Units for Machine Translation (SU4MT) which models the integral meanings of semantic units within a sentence, and then leverages them to provide a new perspective for understanding the sentence. Specifically, we first propose Word Pair Encoding (WPE), a phrase extraction method to help identify the boundaries of semantic units. Next, we design an Attentive Semantic Fusion (ASF) layer to integrate the semantics of multiple subwords into a single vector: the semantic unit representation. Lastly, the semantic-unit-level sentence representation is concatenated to the token-level one, and they are combined as the input of encoder. Experimental results demonstrate that our method effectively models and leverages semantic-unit-level information and outperforms the strong baselines. The code is available at https://github.com/ictnlp/SU4MT.
BayLing: Bridging Cross-lingual Alignment and Instruction Following through Interactive Translation for Large Language Models
Jun 21, 2023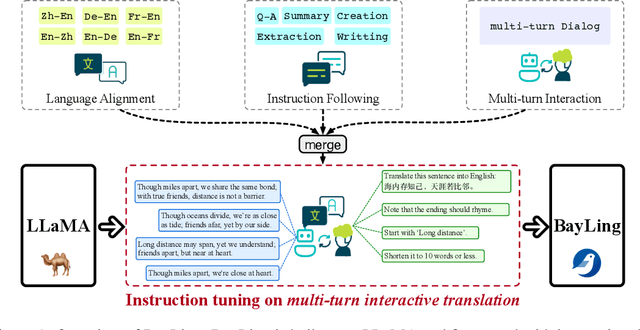
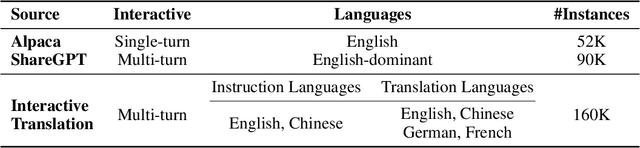

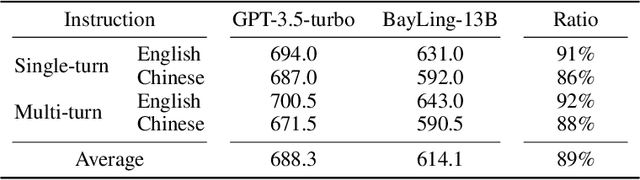
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable prowess in language understanding and generation. Advancing from foundation LLMs to instructionfollowing LLMs, instruction tuning plays a vital role in aligning LLMs to human preferences. However, the existing LLMs are usually focused on English, leading to inferior performance in non-English languages. In order to improve the performance for non-English languages, it is necessary to collect language-specific training data for foundation LLMs and construct language-specific instructions for instruction tuning, both of which are heavy loads. To minimize human workload, we propose to transfer the capabilities of language generation and instruction following from English to other languages through an interactive translation task. We have developed BayLing, an instruction-following LLM by utilizing LLaMA as the foundation LLM and automatically constructing interactive translation instructions for instructing tuning. Extensive assessments demonstrate that BayLing achieves comparable performance to GPT-3.5-turbo, despite utilizing a considerably smaller parameter size of only 13 billion. Experimental results on translation tasks show that BayLing achieves 95% of single-turn translation capability compared to GPT-4 with automatic evaluation and 96% of interactive translation capability compared to GPT-3.5-turbo with human evaluation. To estimate the performance on general tasks, we created a multi-turn instruction test set called BayLing-80. The experimental results on BayLing-80 indicate that BayLing achieves 89% of performance compared to GPT-3.5-turbo. BayLing also demonstrates outstanding performance on knowledge assessment of Chinese GaoKao and English SAT, second only to GPT-3.5-turbo among a multitude of instruction-following LLMs. Demo, homepage, code and models of BayLing are available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge