Shaolei Zhang
Controlled Self-Evolution for Algorithmic Code Optimization
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Self-evolution methods enhance code generation through iterative "generate-verify-refine" cycles, yet existing approaches suffer from low exploration efficiency, failing to discover solutions with superior complexity within limited budgets. This inefficiency stems from initialization bias trapping evolution in poor solution regions, uncontrolled stochastic operations lacking feedback guidance, and insufficient experience utilization across tasks. To address these bottlenecks, we propose Controlled Self-Evolution (CSE), which consists of three key components. Diversified Planning Initialization generates structurally distinct algorithmic strategies for broad solution space coverage. Genetic Evolution replaces stochastic operations with feedback-guided mechanisms, enabling targeted mutation and compositional crossover. Hierarchical Evolution Memory captures both successful and failed experiences at inter-task and intra-task levels. Experiments on EffiBench-X demonstrate that CSE consistently outperforms all baselines across various LLM backbones. Furthermore, CSE achieves higher efficiency from early generations and maintains continuous improvement throughout evolution. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/QuantaAlpha/EvoControl.
MemGovern: Enhancing Code Agents through Learning from Governed Human Experiences
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:While autonomous software engineering (SWE) agents are reshaping programming paradigms, they currently suffer from a "closed-world" limitation: they attempt to fix bugs from scratch or solely using local context, ignoring the immense historical human experience available on platforms like GitHub. Accessing this open-world experience is hindered by the unstructured and fragmented nature of real-world issue-tracking data. In this paper, we introduce MemGovern, a framework designed to govern and transform raw GitHub data into actionable experiential memory for agents. MemGovern employs experience governance to convert human experience into agent-friendly experience cards and introduces an agentic experience search strategy that enables logic-driven retrieval of human expertise. By producing 135K governed experience cards, MemGovern achieves a significant performance boost, improving resolution rates on the SWE-bench Verified by 4.65%. As a plug-in approach, MemGovern provides a solution for agent-friendly memory infrastructure.
RealMem: Benchmarking LLMs in Real-World Memory-Driven Interaction
Jan 11, 2026Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) evolve from static dialogue interfaces to autonomous general agents, effective memory is paramount to ensuring long-term consistency. However, existing benchmarks primarily focus on casual conversation or task-oriented dialogue, failing to capture **"long-term project-oriented"** interactions where agents must track evolving goals. To bridge this gap, we introduce **RealMem**, the first benchmark grounded in realistic project scenarios. RealMem comprises over 2,000 cross-session dialogues across eleven scenarios, utilizing natural user queries for evaluation. We propose a synthesis pipeline that integrates Project Foundation Construction, Multi-Agent Dialogue Generation, and Memory and Schedule Management to simulate the dynamic evolution of memory. Experiments reveal that current memory systems face significant challenges in managing the long-term project states and dynamic context dependencies inherent in real-world projects. Our code and datasets are available at [https://github.com/AvatarMemory/RealMemBench](https://github.com/AvatarMemory/RealMemBench).
MiMo-V2-Flash Technical Report
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:We present MiMo-V2-Flash, a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model with 309B total parameters and 15B active parameters, designed for fast, strong reasoning and agentic capabilities. MiMo-V2-Flash adopts a hybrid attention architecture that interleaves Sliding Window Attention (SWA) with global attention, with a 128-token sliding window under a 5:1 hybrid ratio. The model is pre-trained on 27 trillion tokens with Multi-Token Prediction (MTP), employing a native 32k context length and subsequently extended to 256k. To efficiently scale post-training compute, MiMo-V2-Flash introduces a novel Multi-Teacher On-Policy Distillation (MOPD) paradigm. In this framework, domain-specialized teachers (e.g., trained via large-scale reinforcement learning) provide dense and token-level reward, enabling the student model to perfectly master teacher expertise. MiMo-V2-Flash rivals top-tier open-weight models such as DeepSeek-V3.2 and Kimi-K2, despite using only 1/2 and 1/3 of their total parameters, respectively. During inference, by repurposing MTP as a draft model for speculative decoding, MiMo-V2-Flash achieves up to 3.6 acceptance length and 2.6x decoding speedup with three MTP layers. We open-source both the model weights and the three-layer MTP weights to foster open research and community collaboration.
PSO-Merging: Merging Models Based on Particle Swarm Optimization
Aug 27, 2025Abstract:Model merging has emerged as an efficient strategy for constructing multitask models by integrating the strengths of multiple available expert models, thereby reducing the need to fine-tune a pre-trained model for all the tasks from scratch. Existing data-independent methods struggle with performance limitations due to the lack of data-driven guidance. Data-driven approaches also face key challenges: gradient-based methods are computationally expensive, limiting their practicality for merging large expert models, whereas existing gradient-free methods often fail to achieve satisfactory results within a limited number of optimization steps. To address these limitations, this paper introduces PSO-Merging, a novel data-driven merging method based on the Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO). In this approach, we initialize the particle swarm with a pre-trained model, expert models, and sparsified expert models. We then perform multiple iterations, with the final global best particle serving as the merged model. Experimental results on different language models show that PSO-Merging generally outperforms baseline merging methods, offering a more efficient and scalable solution for model merging.
StreamUni: Achieving Streaming Speech Translation with a Unified Large Speech-Language Model
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:Streaming speech translation (StreamST) requires determining appropriate timing, known as policy, to generate translations while continuously receiving source speech inputs, balancing low latency with high translation quality. However, existing StreamST methods typically operate on sentence-level speech segments, referred to as simultaneous speech translation (SimulST). In practice, they require collaboration with segmentation models to accomplish StreamST, where the truncated speech segments constrain SimulST models to make policy decisions and generate translations based on limited contextual information. Moreover, SimulST models struggle to learn effective policies due to the complexity of speech inputs and cross-lingual generation. To address these challenges, we propose StreamUni, which achieves StreamST through a unified Large Speech-Language Model (LSLM). Specifically, StreamUni incorporates speech Chain-of-Thought (CoT) in guiding the LSLM to generate multi-stage outputs. Leveraging these multi-stage outputs, StreamUni simultaneously accomplishes speech segmentation, policy decision, and translation generation, completing StreamST without requiring massive policy-specific training. Additionally, we propose a streaming CoT training method that enhances low-latency policy decisions and generation capabilities using limited CoT data. Experiments demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on StreamST tasks.
Stream-Omni: Simultaneous Multimodal Interactions with Large Language-Vision-Speech Model
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:The emergence of GPT-4o-like large multimodal models (LMMs) has raised the exploration of integrating text, vision, and speech modalities to support more flexible multimodal interaction. Existing LMMs typically concatenate representation of modalities along the sequence dimension and feed them into a large language model (LLM) backbone. While sequence-dimension concatenation is straightforward for modality integration, it often relies heavily on large-scale data to learn modality alignments. In this paper, we aim to model the relationships between modalities more purposefully, thereby achieving more efficient and flexible modality alignments. To this end, we propose Stream-Omni, a large language-vision-speech model with efficient modality alignments, which can simultaneously support interactions under various modality combinations. Stream-Omni employs LLM as the backbone and aligns the vision and speech to the text based on their relationships. For vision that is semantically complementary to text, Stream-Omni uses sequence-dimension concatenation to achieve vision-text alignment. For speech that is semantically consistent with text, Stream-Omni introduces a CTC-based layer-dimension mapping to achieve speech-text alignment. In this way, Stream-Omni can achieve modality alignments with less data (especially speech), enabling the transfer of text capabilities to other modalities. Experiments on various benchmarks demonstrate that Stream-Omni achieves strong performance on visual understanding, speech interaction, and vision-grounded speech interaction tasks. Owing to the layer-dimensional mapping, Stream-Omni can simultaneously provide intermediate text outputs (such as ASR transcriptions and model responses) during speech interaction, offering users a comprehensive multimodal experience.
TAIJI: MCP-based Multi-Modal Data Analytics on Data Lakes
May 16, 2025Abstract:The variety of data in data lakes presents significant challenges for data analytics, as data scientists must simultaneously analyze multi-modal data, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. While Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated promising capabilities, they still remain inadequate for multi-modal data analytics in terms of accuracy, efficiency, and freshness. First, current natural language (NL) or SQL-like query languages may struggle to precisely and comprehensively capture users' analytical intent. Second, relying on a single unified LLM to process diverse data modalities often leads to substantial inference overhead. Third, data stored in data lakes may be incomplete or outdated, making it essential to integrate external open-domain knowledge to generate timely and relevant analytics results. In this paper, we envision a new multi-modal data analytics system. Specifically, we propose a novel architecture built upon the Model Context Protocol (MCP), an emerging paradigm that enables LLMs to collaborate with knowledgeable agents. First, we define a semantic operator hierarchy tailored for querying multi-modal data in data lakes and develop an AI-agent-powered NL2Operator translator to bridge user intent and analytical execution. Next, we introduce an MCP-based execution framework, in which each MCP server hosts specialized foundation models optimized for specific data modalities. This design enhances both accuracy and efficiency, while supporting high scalability through modular deployment. Finally, we propose a updating mechanism by harnessing the deep research and machine unlearning techniques to refresh the data lakes and LLM knowledges, with the goal of balancing the data freshness and inference efficiency.
LLaMA-Omni2: LLM-based Real-time Spoken Chatbot with Autoregressive Streaming Speech Synthesis
May 05, 2025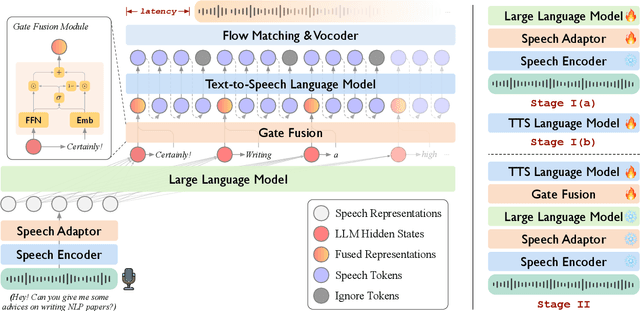
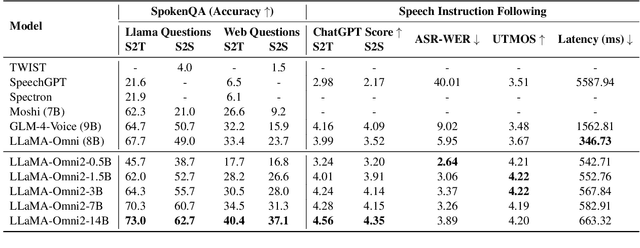
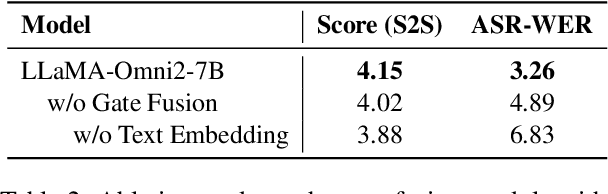
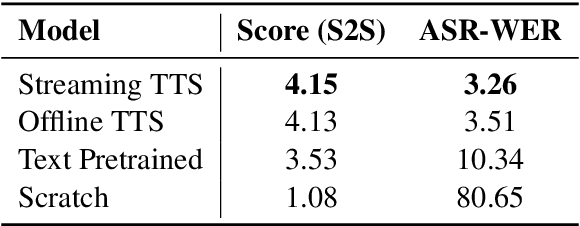
Abstract:Real-time, intelligent, and natural speech interaction is an essential part of the next-generation human-computer interaction. Recent advancements have showcased the potential of building intelligent spoken chatbots based on large language models (LLMs). In this paper, we introduce LLaMA-Omni 2, a series of speech language models (SpeechLMs) ranging from 0.5B to 14B parameters, capable of achieving high-quality real-time speech interaction. LLaMA-Omni 2 is built upon the Qwen2.5 series models, integrating a speech encoder and an autoregressive streaming speech decoder. Despite being trained on only 200K multi-turn speech dialogue samples, LLaMA-Omni 2 demonstrates strong performance on several spoken question answering and speech instruction following benchmarks, surpassing previous state-of-the-art SpeechLMs like GLM-4-Voice, which was trained on millions of hours of speech data.
Prompt Guiding Multi-Scale Adaptive Sparse Representation-driven Network for Low-Dose CT MAR
Apr 28, 2025Abstract:Low-dose CT (LDCT) is capable of reducing X-ray radiation exposure, but it will potentially degrade image quality, even yields metal artifacts at the case of metallic implants. For simultaneous LDCT reconstruction and metal artifact reduction (LDMAR), existing deep learning-based efforts face two main limitations: i) the network design neglects multi-scale and within-scale information; ii) training a distinct model for each dose necessitates significant storage space for multiple doses. To fill these gaps, we propose a prompt guiding multi-scale adaptive sparse representation-driven network, abbreviated as PMSRNet, for LDMAR task. Specifically, we construct PMSRNet inspired from multi-scale sparsifying frames, and it can simultaneously employ within-scale characteristics and cross-scale complementarity owing to an elaborated prompt guiding scale-adaptive threshold generator (PSATG) and a built multi-scale coefficient fusion module (MSFuM). The PSATG can adaptively capture multiple contextual information to generate more faithful thresholds, achieved by fusing features from local, regional, and global levels. Furthermore, we elaborate a model interpretable dual domain LDMAR framework called PDuMSRNet, and train single model with a prompt guiding strategy for multiple dose levels. We build a prompt guiding module, whose input contains dose level, metal mask and input instance, to provide various guiding information, allowing a single model to accommodate various CT dose settings. Extensive experiments at various dose levels demonstrate that the proposed methods outperform the state-of-the-art LDMAR methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge